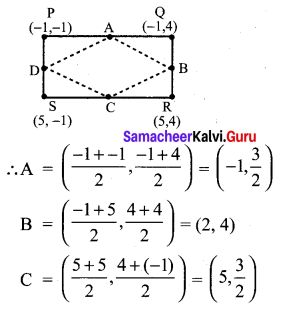
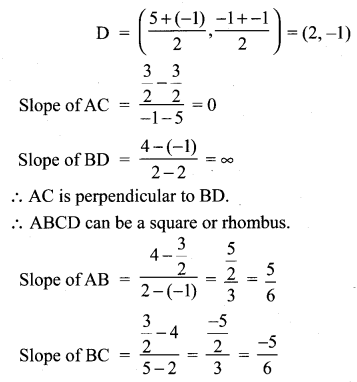
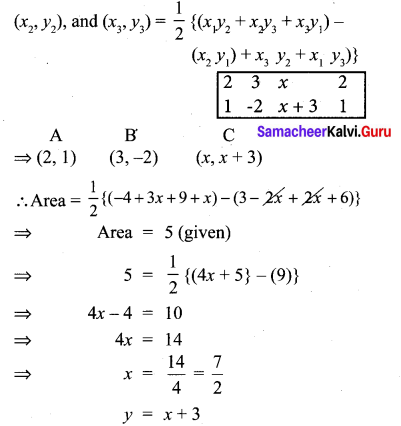
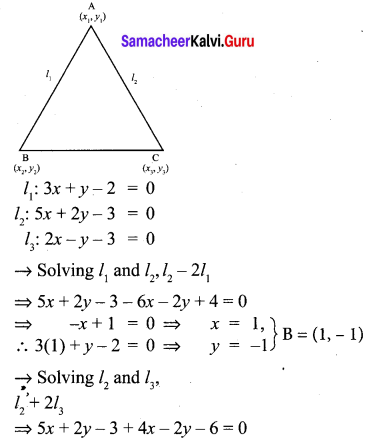
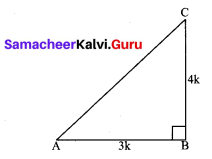
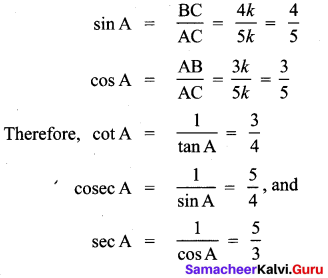
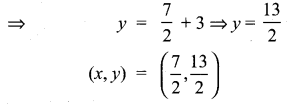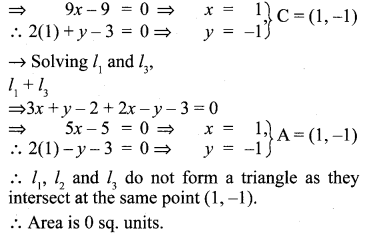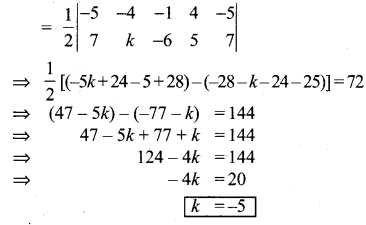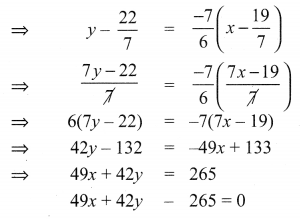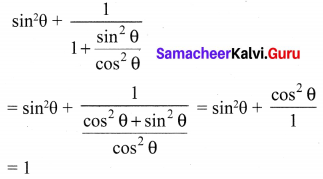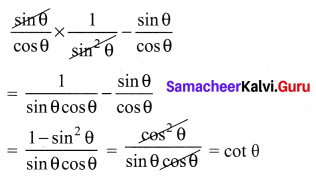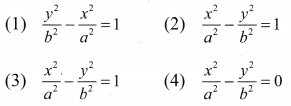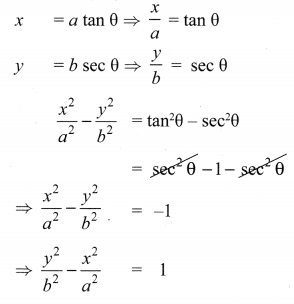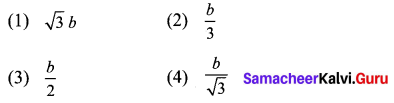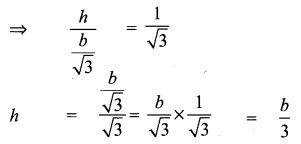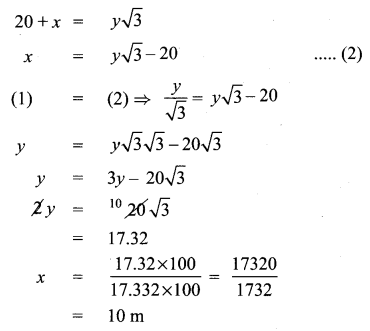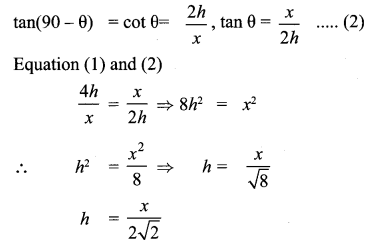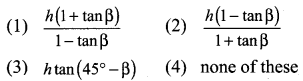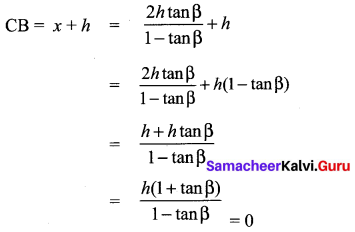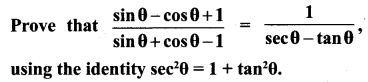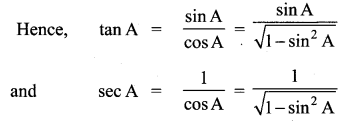You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 6 Trigonometry Unit Exercise 6
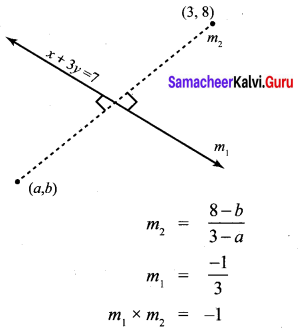
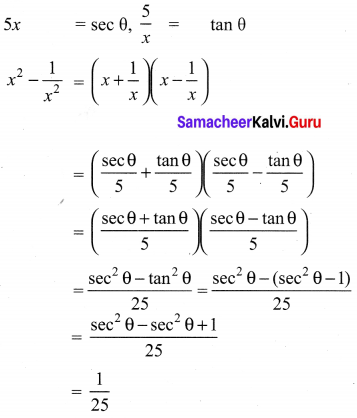
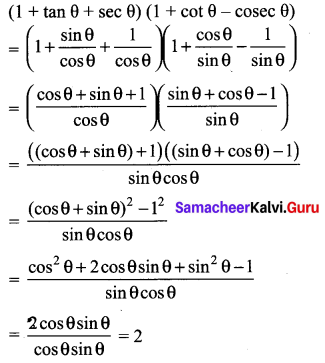
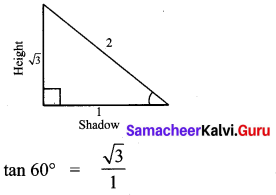
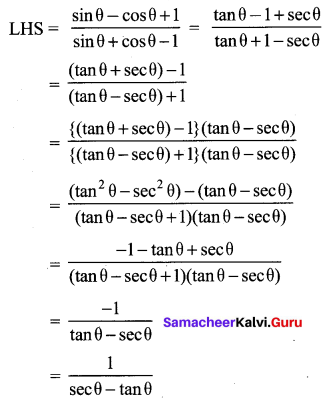
Question 1.
Prove that
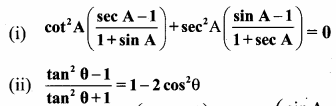
Solution:
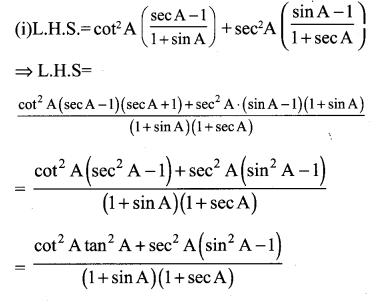
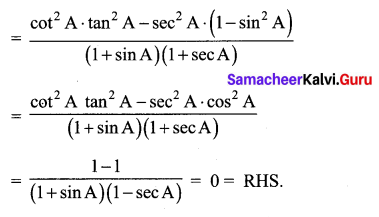
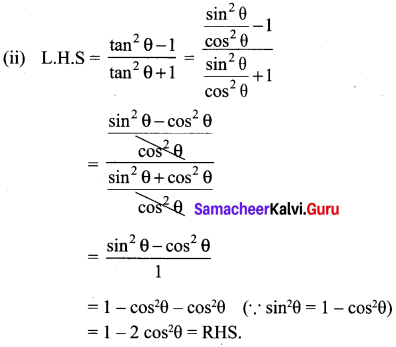
![]()
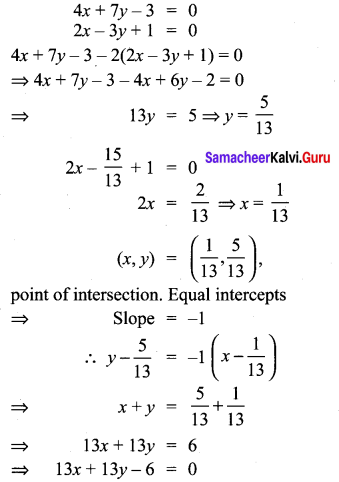
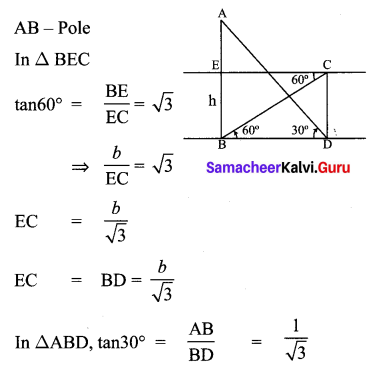
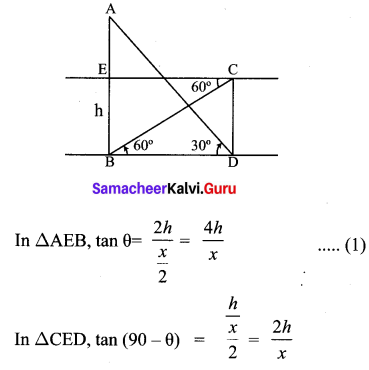
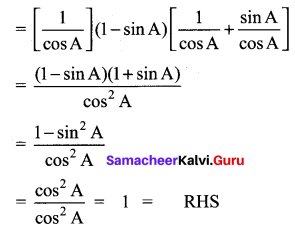
Question 2.
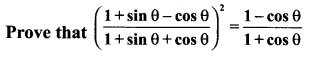
Solution:

Hence proved
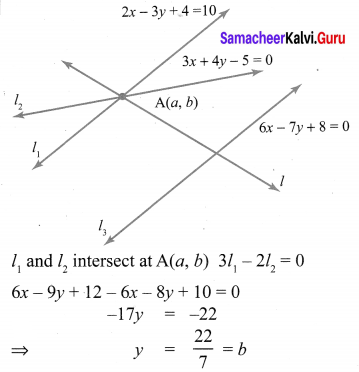
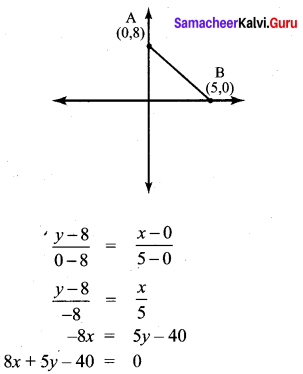
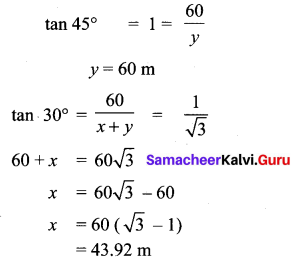
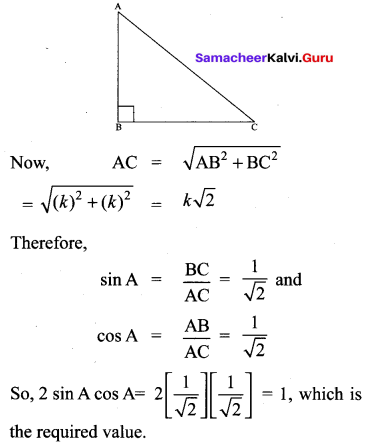
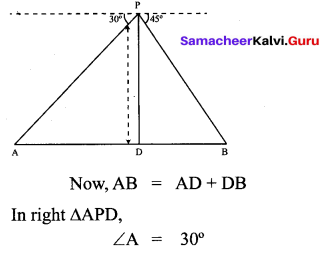
Question 3.
If x sin3θ + y cos3θ = sin θ cos θ and x sin θ =
y cos θ , then prove that x2 + y2 = 1.
Solution:
x sin3θ +y cos3θ= sinθ cosθ ; x sinθ y cosθ.
x (sinθ) [sin2θ + cos2θ] = sinθ cosθ
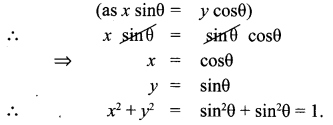
![]()
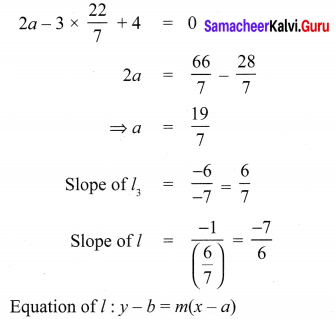
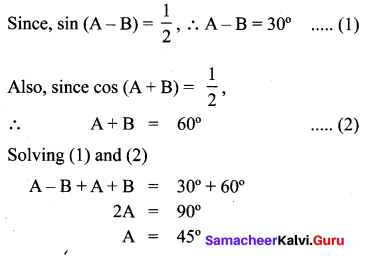
Question 4.
If a cos θ – b sin θ = c, then prove that (a sin θ + b cos θ) = \(\pm \sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}-c^{2}}\)
Solution:

Hence Proved.
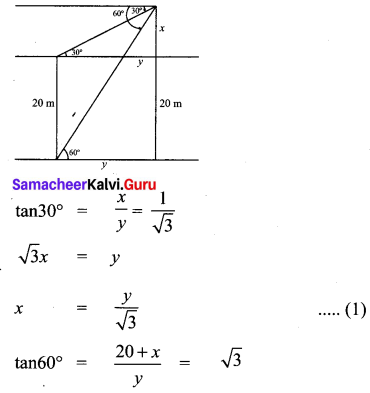
Question 5.
A bird is sitting on the top of a 80 m high tree. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the bird is 45°. The bird flies away horizontally in such away that it remained at a constant height from the ground. After 2 seconds, the angle of elevation of the bird from the same point is 30°. Determine the speed at which the bird flies. ( \(\sqrt{3}\) = 1.732).
Solution:
Let s be the speed of the bird. In 2 seconds, the bird goes from C to D, it covers a distance ‘d’
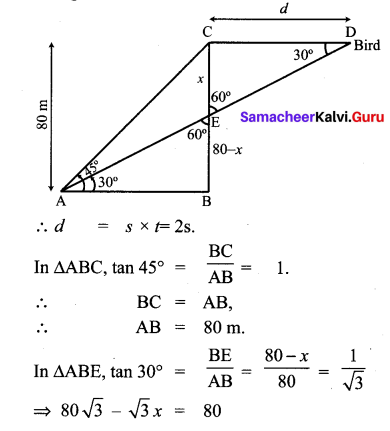
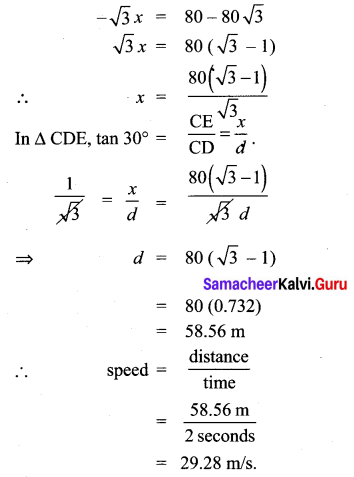
![]()
Question 6.
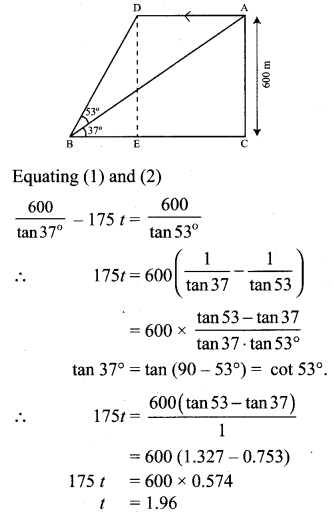
An aeroplane is flying parallel to the Earth’s surface at a speed of 175 m/sec and at a height of 600 m. The angle of elevation of the aeroplane from a point on the Earth’s surface is 37° at a given point. After what period of time does the angle of elevation increase to 53°? (tan 53° = 1.3270, tan 37° = 0.7536)
Solution:
Let Plane’s initial position be A. Plane’s final position = D Plane travels from A ➝ D.

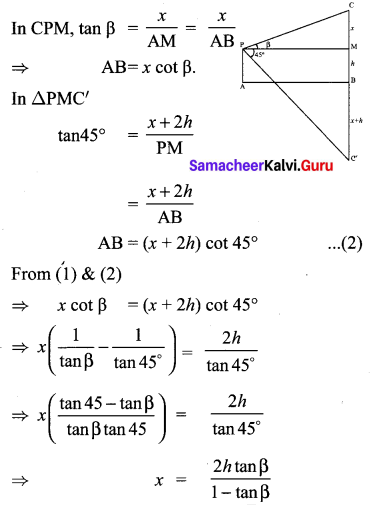
Question 7.
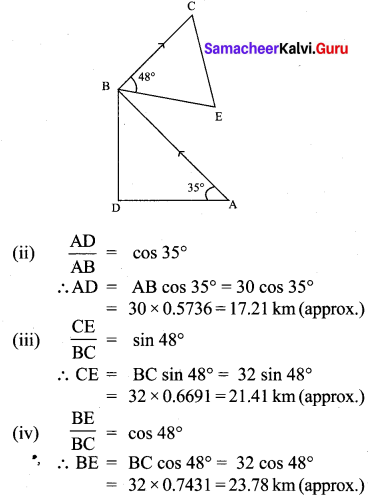
A bird is flying from A towards B at an angle of 35°, a point 30 km away from A. At B it changes its course of flight and heads towards C on a bearing of 48° and distance 32 km away.
(i) How far is B to the North of A?
(ii) How far is B to the West of A?
(iii) How far is C to the North of B?
(iv) How far is C to the East of B?
(sin 55° = 0.8192, cos 55° = 0.5736,
sin 42° = 0.6691, cos 42° = 0.7431)
Solution:

![]()
Question 8.
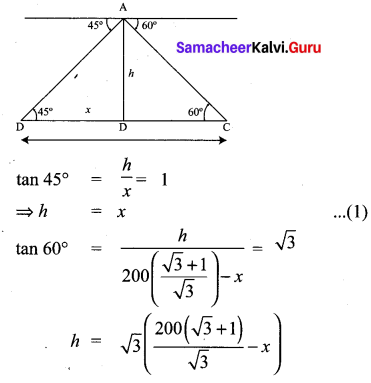
Two ships are sailing in the sea on either side of the lighthouse. The angles of depression of two ships as observed from the top of the lighthouse are 60° and 45° respectively. If the
distance between the ships is \(200\left(\frac{\sqrt{3}+1}{\sqrt{3}}\right)\) metres, find the height of the lighthouse.
Solution:
From the figure AB – height of the light house = h CD – Distance between the ships
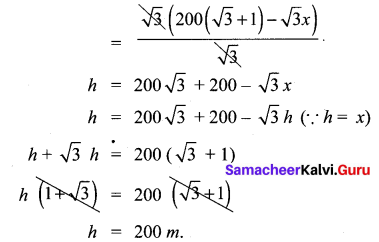
∴ The height of the light house is 200 metres.
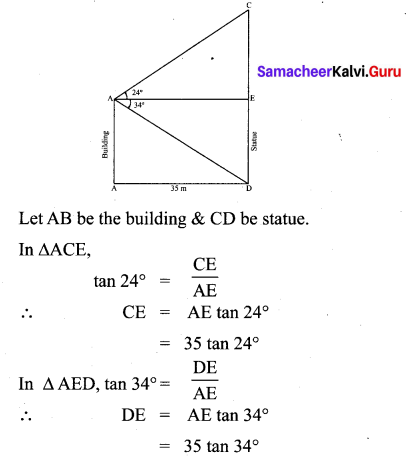
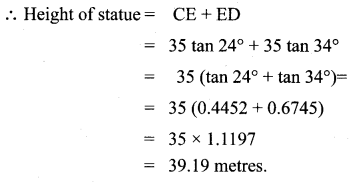
Question 9.
A building and a statue are in opposite side of a street from each other 35 m apart. From a point on the roof of building the angle of elevation of the top of statue is 24° and the angle of depression of base of the statue is 34°. Find the height of the statue.
(tan 24° = 0.4452, tan 34° = 0.6745)
Solution: