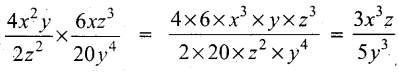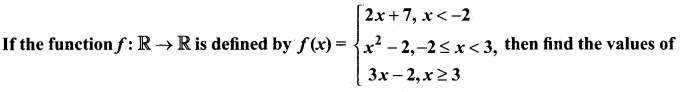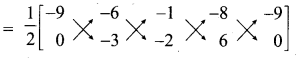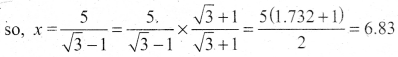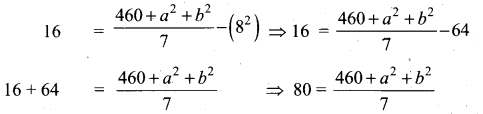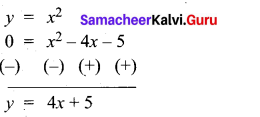Students can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Model Question Paper 2 English Medium Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Model Question Paper 2 English Medium
Instructions
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 14 in Part I are Multiple Choice Quèstions of one-mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and.writing the option code and the corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 15 to 28 in Part II àre two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 29 to 42 in Part III are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 43 to 44 in Part IV are eight-marks questions. These are to be answered in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Max Marks: 100
PART-I
I. Choose the correct answer. Answer all the questions. [14 × 1 = 14]
Question 1.
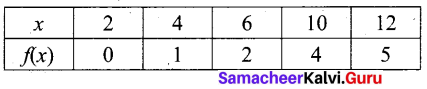
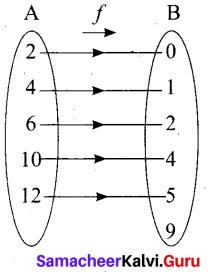
Let f and g be two functions given by f = {(0,1),(2,0),(3,-4),(4,2),(5,7)} g = {(0,2),(1, 0),(2,4),(-4,2),(7, 0)} then the range of fog is …………. .
(1) {0,2,3,4,5}
(2) {-4,1,0,2,7}
(3) {1,2,3,4,5}
(4) {0,1,2}
Answer:
(4) {0,1,2}
![]()
Question 2.
An A.P consists of 31 terms. If its 16th term is m, then the sum of all the terms of this A.P. is …………. .
(1) 16m
(2) 62 m
(3) 31m
(4) \(\frac{31}{2}\)m
Answer:
(3) 31m
Question 3.
The value of (13 + 23 + 33 +….+ 153) – (1 + 2 + 3 +….+ 15) is …………. .
(1) 14400
(2) 14200
(3) 14280
(4) 14520
Answer:
(3) 14280
Question 4.
Which of the following should be added to make x4 + 64 a perfect square …………. .
(1) 4x2
(2) 16x2
(3) 8x2
(4) -8x2
Answer:
(2) 16x2
Question 5.
The number of points of intersection of the quadratic polynomial x2 + 4x + 4 with the X axis is …………. .
(1) 0
(2) 1
(3) 0 or 1
(4) 2
Answer:
(2) 1
Question 6.
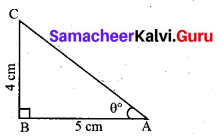
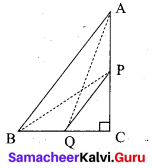
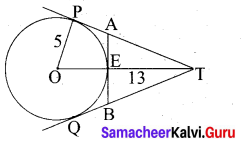
In the adjacent figure ∠BAC = 90° and AD ⊥BC then …………. .
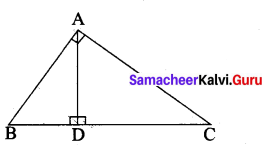
(1) BDCD = BC2
(2) AB.AC = BC2
(3) BD.CD = AD2
(4) AB.AC = AD2
Answer:
(3) BDCD = AD2
Question 7.
If (5, 7), (3, p) and (6, 6) are collinear, then the value of p is …………. .
(1) 3
(2) 6
(3) 9
(4) 12
Answer:
(3) 9
Question 8.
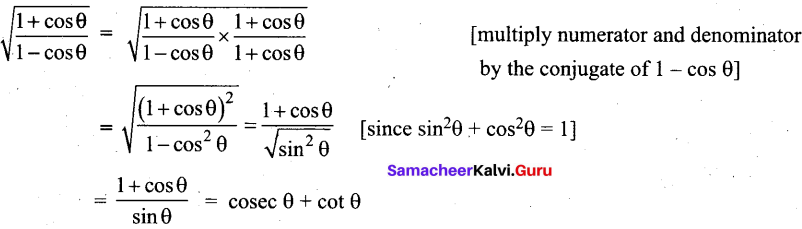
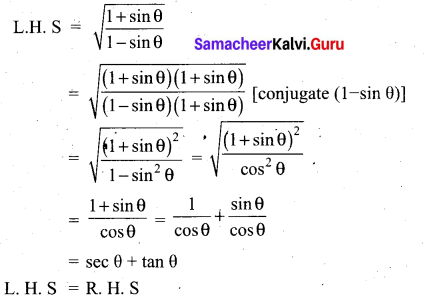
(1 + tan θ + sec θ) (1 + cot θ – cosec θ) is equal to …………. .
(1) 0
(2) 1
(3) 2
(4) -1
Answer:
(3) 2
![]()
Question 9.
The total surface area of a cylinder whose radius is \(\frac{1}{3}\) of its height is
(1) \(\frac{9 \pi h^{2}}{8}\) sq. units
(2) 24πh2 sq. units
(3) \(\frac{8 \pi h^{2}}{9}\) sq. units
(4) \(\frac{56 \pi h^{2}}{9}\) sq. units
Answer:
(3) \(\frac{8 \pi h^{2}}{9}\) sq. units
Question 10.
The mean of 100 observations is 40 and their standard deviation is 3. The sum of squares of all deviations is …………. .
(1) 40000
(2) 160900
(3) 160000
(4) 30000
Answer:
(2) 160900
Question 11.
The probability a red marble selected at random from a jar containing p red, q blue and r green marbles is …………. .
(1) \(\frac{q}{p+q+r}\)
(2) \(\frac{p}{p+q+r}\)
(3) \(\frac{p+q}{p+q+r}\)
(4) \(\frac{p+r}{p+q+r}\)
Answer:
(1) \(\frac{q}{p+q+r}\)
Question 12.
If there are 28 relation from a set A = {2,4, 6, 8} to a set B, then the number of elements in B is …………. .
(1) 7
(2) 14
(3) 5
(4) 4
Answer:
(1) 7
![]()
Question 13.
If a1 ,a2, a3 ……….. are in A.P. such that \(\frac{a_{4}}{a_{7}}=\frac{3}{2}\), then the 13th term of the AP is …………. .
(1) \(\frac{3}{2}\)
(2) 0
(3) 12a1
(4) 14a1
Answer:
(2) 0
Question 14.
The X-intercept of the line 2x – 3y + 5 = 0 is …………. .
(1) \(\frac{5}{2}\)
(2) \(\frac{-5}{2}\)
(3) \(\frac{2}{5}\)
(4) \(\frac{-2}{5}\)
Answer:
(2) \(\frac{-5}{2}\)
PART-II
II. Answer any ten questions. Question No. 28 is compulsory. [10 × 2 = 20]
Question 15.
A function f is defined by f(x) = 3 – 2x. Find x such that f(x2) = (f (x))2.
Answer:
f(x) = 3 – 2x
f(x2) = 3 – 2 (x2)
= 3 – 2x2
(f(x)2 = (3 – 2x)2
= 9 + 4x2 – 12x
But f(x2) = (f(x))2
3 – 2x2 = 9 + 4x2 – 12x
– 2x2 – 4x2 + 12x + 3 – 9 = 0
– 6x2 + 12x – 6 = 0
(÷ by – 6) ⇒ x2 – 2x + 1 = 0
(x – 1)(x – 1) = 0
x – 1 = 0 or x – 1 = 0
x = 1
The value of x = 1
![]()
Question 16.
If f(x) = x2 – 1, g(x) = x – 2 find a, if gof (a) = 1.
Answer:
f(x) = x2 – 1 ; g(x) = x – 2
gof = g [f(x)]
= g(x2 – 1)
= x2 – 1 – 2
= x2 – 3
given gof (a) = 1
a2 – 3 = 1 [But gof(x) = x2 – 3]
a2 = 4
a = √4 = ± 2
The value of a = ± 2
Question 17.
Find the number of integer solutions of = 1 (mod 15).
Answer:
3x ≡ 1 (mod 15) can be written as
3x – 1 = 15k for some integer k
3x = 15k + 1
x = \(\frac{15 k+1}{3}\) = 5k + \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Since 5k is an integer, 5k + \(\frac{1}{3}\) cannot be an integer. So there is no integer solution.
Question 18.
Find the rational form of the number \(0 . \overline{123}\)
Answer:
Let x = \(0 . \overline{123}\)
= 0.123123123 ….
= 0.123 + 0.000123 + 000000123 + ….
This is an infinite G.P
Here a = 0.123, r = \(\frac{0.000123}{0.123}\) = 0.001
Sn = \(\frac{a}{1-r}=\frac{0.123}{1-0.001}=\frac{0.123}{0.999}\)
Sn = \(\frac{41}{333}\)
![]()
Question 19.
Find the GCD of 12(x4 – x3), 8(x4 – 3x3 + 2x2) whose LCM is 24x3 (x – 1)(x – 2)
Answer:
p(x) = 12(x4 – x3)
= 12x3(x – 1)
g(x) = 8(x4 – 3x3 + 2x2)
= 8x2(x2 – 3x + 2)
= 8x2(x – 2) (x – 1)
L.C.M = 24x3(x – 1) (x – 2)
G.C.D = \(\frac{p(x) \times g(x)}{\text { L.C.M. }}\)
= \(\frac{12 x^{3}(x-1) \times 8 x^{2}(x-2)(x-1)}{24 x^{3}(x-1)(x-2)}\)
G.C.D = 4x2(x – 1)
Question 20.
Find the square root of the polynomial x4 – 12x3 + 42x2 – 36x + 9 by division method
Answer:
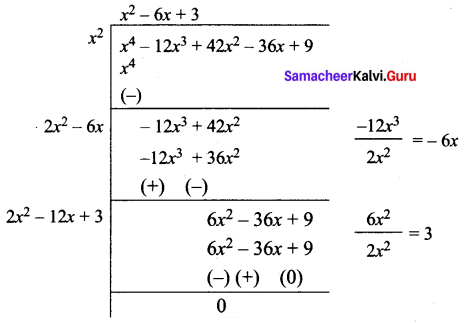
\(\sqrt{x^{4}-12 x^{3}+42 x^{2}-36 x+9}\) = |x2 – 6x + 3|
![]()
Question 21.
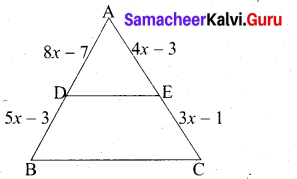
Write expression \(\frac{\alpha+3}{\beta}+\frac{\beta+3}{\alpha}\) interms of α + β and αβ.
Answer:
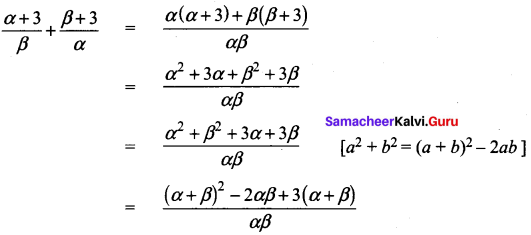
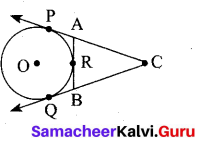
Question 22.
In the given diagram show that ∆PST ~ ∆PQR
Answer:
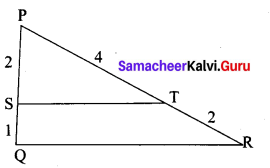
In ∆PST and ∆PQR,
\(\frac{P S}{P Q}=\frac{2}{2+1}=\frac{2}{3}\) , \(\frac{P T}{P R}=\frac{4}{4+2}=\frac{2}{3}\)
Thus, \(\frac{P S}{P Q}=\frac{P T}{P R}\) and ∠P is common
Therefore, by SAS similarity,
∆PST ~ ∆PQR
Question 23.
Find the value of for which the given points (2,3), (4, a) and (6, -3) are collinear.
Answer:
Let the points be A (2, 3), B(4, a) and C(6, -3).
Since the given points are collinear.
Area of a triangle =0
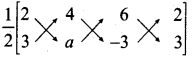
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [(x1y1 + x2y2 + x3y1) – (x2y1 + x3y2 + x1y3)] = 0
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [(2a – 12 + 18) – (12 + 6a – 6)] = 0
2a + 6 – (6 + 6a) = 0
2a + 6 – 6 – 6a = 0
-4 a = 0 ⇒ a = \(\frac { 0 }{ 4 }\) = 0
The value of a = 0
![]()
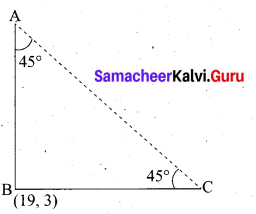
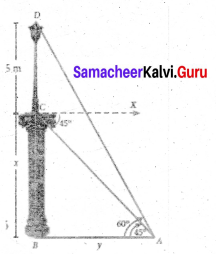
Question 24.
The horizontal distance between two buildings is 70 m. The angle of depression of the top of the first building when seen from the top of the second building is 45°. If the height of the second building is 120 m, find the height of the first building.
Answer:
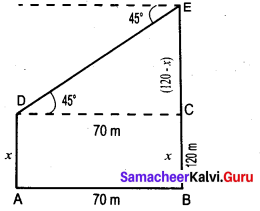
Let the height of the first building AD be “x” m
∴ EC = 120 – x
In the right ∆ CDE,
tan 45° = \(\frac{C E}{C D}\)
1 = \(\frac{120-x}{70}\) ⇒ 70 = 120 – x
x = 50m
∴ The height of the first building is 50 m
Question 25.
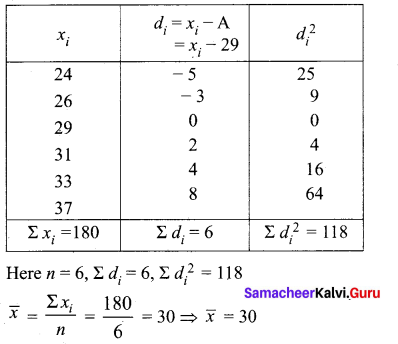
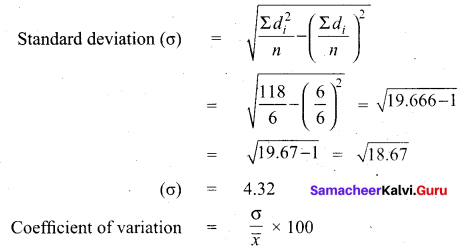
If the coefficient of variation of a collection of data is 57 and its standard deviation is 6,84, then find the mean.
Answer:
Given coefficient of variation =57
Standard deviation (σ) = 6.84
C.V = \(\frac{\sigma}{\bar{x}}\)
57 = \(\frac{6.84}{\bar{x}} \times 100\)
x̄ = \(\frac{6.84}{57} \times 100=\frac{684}{57}=12\)
∴ Arithmetic mean x̄ = 12
Question 26.
The radius and height of a cylinder are in the ratio 2:7. If the curved surface area of the cylinder is 352 sq.cm. Find its radius.
Answer:
Let the radius be “2x” and the height be “7x”
Curved surface area = 352cm2
2πrh = 352
2 × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 2x × 7x = 352
44 × 2x2 = 352
x2 = \(\frac{352}{44 \times 2}=\frac{176}{44}=4\)
x = √4 = 2
Radius of the cylinder (2 × 2) = 4 cm
![]()
Question 27.
A number is selected at random from integers 1 to 100. Find the probability that it is not a perfect cube.
Answer:
Sample space = {1, 2, 3,…. 100}
n(S) = 100
Let A be the event of getting a perfect cube.
A = (1, 8, 27, 64)
n(A) = 4
p(A) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{A})}{n(\mathrm{S})}\)
p(A) = \(\frac{4}{100}=\frac{1}{25}\)
The Probability that the selected number is not a perfect cube is
P(Ā) = 1 – P(A)
= 1 – \(\frac{1}{25}\)
= \(\frac{24}{25}\)
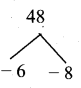
Question 28.
Find the value of k if 13 + 23 + 33 + ……… + k3 = 2025
Answer:
13 + 23 + 33 + ……… + k3 = 2025
\(\left[\frac{k(k+1)}{2}\right]^{2}\) = 2025
\(\frac{k(k+1)}{2}\) = \(\sqrt{2025}\) = 45
k2 + k = 90
K2 + k – 90 = 0
(k + 10) (k + 9) = 0
k = -10 or k = 9 k = 9 (k = -10) is not possible
∴ The value of k = 9
![]()
Part – III
III. Answer any ten questions. Question No. 42 is compulsory. [10 × 5 = 50]
Question 29.
Let A = The set of all natural numbers less than 8, B = The set of all prime numbers less than 8, C = The set of even prime number. Verify that A × (B – C) = (A × B) – (A × C)
Answer:
A= {1,2, 3, 4, 5,6, 7}; B = {2, 3, 5,7} and C= {2}
B – C = {2, 3, 5, 7} – {2}
= {3,5,7}
A × (B – C) = {1,2, 3,4, 5,6,7} × {3, 5,7}
= {(1,3) (1, 5) (1, 7) (2, 3) (2, 5) (2, 7) (3,3) (3, 5) (3, 7) (4, 3) (4, 5) (4, 7) (5,3) (5, 5) (5, 7) (6, 3) (6, 5) (6, 7) (7, 3) (7, 5) (7, 7)} …. (1)
A × B = {1,2, 3,4, 5,6,7} × {2, 3, 5,7}
= {(1,2) (1, 3) (1, 5) (1, 7) (2, 2) (2, 3) (2, 5) (2, 7) (3, 2) (3, 3) (3, 5) (3, 7) (4,2) . (4, 3) (4, 5) (4, 7) (5, 2) (5, 3) (5, 5) (5, 7) (6, 2) (6, 3) (6, 5) (6, 7) (7, 2) (7, 3) (7, 5) (7, 7)}
A × C = {1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} × {2}
= {(1, 2) (2, 2) (3, 2) (4, 2) (5, 2) (6, 2) (7, 2)}
(A × B) – (A × C) = {(1, 3) (1, 5) (1, 7) (2, 3) (2, 5) (2, 7) (3, 3) (3, 5) (3, 7) (4, 3) (4, 5) (4, 7) (5, 3) 5, 5) (5, 7) (6, 3) (6, 5) (6, 7) (7, 3) (7, 5) (7, 7)} ….(2)
From (1) and (2) we get
A × (B – C) = (A × B) – (A × C)
Question 30.
If f(x) = x – 4, g(x) = x2 and h(x) = 3x – 5 prove that fo(goh) = (fog)oh
Answer:
f(x) = x – 4; g(x) = x2; h(x) = 3x – 5
fog (x) = f[g(x)]
= f(x2)
= x2 – 4
(fog) oh(x) = fog[h(x)]
= fog (3x – 5)
= (3x – 5)2 – 4
= 9x2 – 30x + 25 – 4
= 9x2 – 30x + 21 …. (1)
goh(x) = g[h(x)]
= g(3x – 5)
= (3x – 5)2
= 9x2 + 25 – 30x
fo(goh) x = f[goh(x)]
= f [9x2 – 30x + 25]
= 9x2 – 30x + 25 – 4
= 9x2 – 30x + 21 ….(2)
Fróm (1) and (2) we get (fog)oh = fo(goh)
![]()
Question 31.
In an A.P., sum of four consecutive terms is 28 and their sum of their squares is 276. Find the four numbers.
Answer:
Let us take the four terms in the form (a – 3d), (a – d), (a + d) and (a + 3d).
Since sum of the four terms is 28,
a – 3d + a – d + a + d + a + 3d = 2%
4a = 28 gives a = 7
Similarly, since sum of their squares is 276,
(a – 3d)2 + (a – d)2 + (a + d)2+ (a + 3d)2 = 276.
a2 – 6ad + 9d2 + a2 – 2ad + d2 + a2 + 2ad + d2 + a2 + 6ad + 9d2 = 276
4a2 + 20d2 = 276 ⇒ 4(7)2 + 20d2 = 276.
d2 = 4 gives d = ± 2
If d = 2 then the four numbers are 7 – 3(2), 7 – 2, 7 + 2, 7 + 3(2)
That is the four numbers are 1, 5, 9 and 13.
If a = 7, d = -2 then the four numbers are 13, 9, 5 and 1
Therefore, the four consecutive terms of the A.P. are 1, 5, 9 and 13.
Question 32.
If a, b, c are three consecutive terms of an A.P. and x, y, z are three consecutive terms of a G.P. then prove that xb – c × yc – a × z a – b = 1.
Answer:
a, b, c are three consecutive terms of an A.P
∴ a = a, b = a + d and c = a + 2d respectively ……. (1)
x, y, z are three consecutive terms of a G.P
∴ x = x, y = xr, z = xr2 respectively ….(2)
L.H.S = xb – c × yc – a × z a – b
( Substitute the values from 1 and 2 we get)
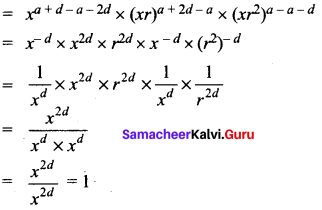
L.H.S = R.H.S
Hence it is proved
![]()
Question 33.
There are 12 pieces of five, ten and twenty rupee currencies whose total value is ₹105. But when first 2 sorts are interchanged in their numbers its value will be increased by ₹20. Find the number of currencies in each sort.
Answer:
Let the number of ₹5 currencies be “x”
Let the number of ₹10 currencies be “y”
and the number of ₹20 currencies be “z”
By the given first condition
x + y + z = 12 …….. (1)
By the given second condition
5x + 10y + 20z = 105
x + 2y + 4z = 21 (÷5) …….. (2)
By the given third condition
10x + 5y + 20z = 105 + 20
10x + 5y + 20z = 125
2x + y + 4z = 25 ………. (3)
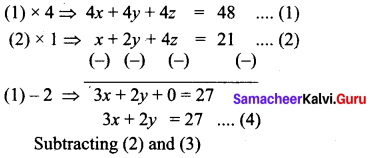
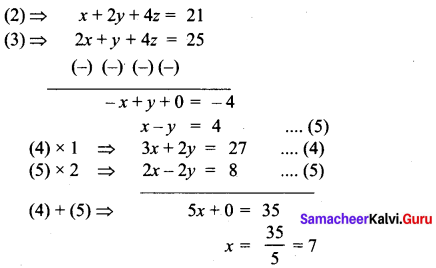
Substituting the value of x = 7 in (5)
7 – y = 4 ⇒ – y = 4 – 7
-y = -3 ⇒ y = 3
Substituting the value of x = 7, y = 3 in …. (1)
7 + 3 + z = 12
z = 12 – 10 = 2
x = 7,y = 3,z = 2
Number of currencies in ₹ 5 = 7
Number of currencies in ₹ 10 = 3
Number of currencies in ₹ 20 = 2
![]()
Question 34.
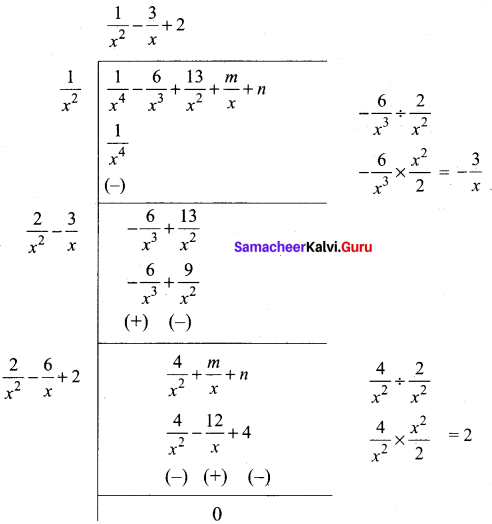
Find the square root of the expression \(\frac{4 x^{2}}{y^{2}}+\frac{20 x}{y}+13-\frac{30 y}{x}+\frac{9 y^{2}}{x^{2}}\)
Answer:
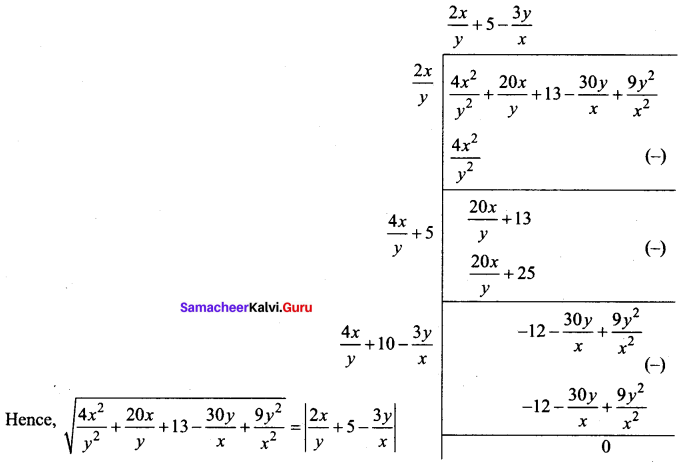
Question 35.
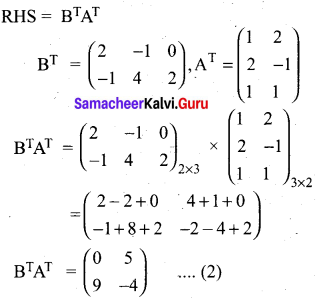
If A = \(\left[ \begin{matrix} 3 & 1 \\ -1 & 2 \end{matrix} \right]\) show that A2 – 5A + 7I2 = 0
Answer:
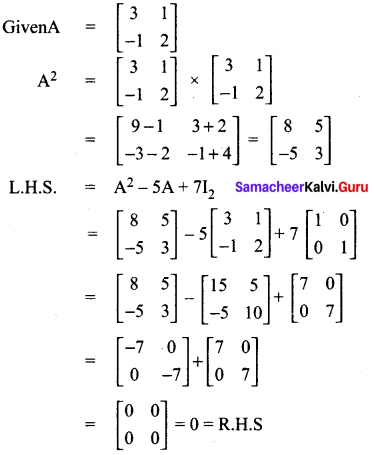
L.H.S = R.H.S
∴ A2 – 5A + 7I2 = 0
![]()
Question 36.
State and prove Thales theorem
Answer:
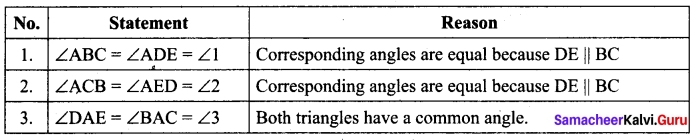
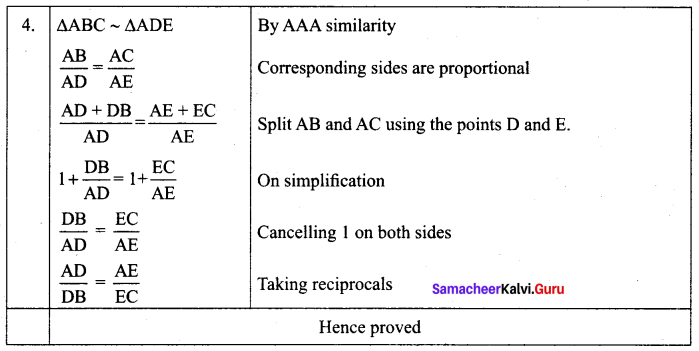
A straight line drawn parallel to a side of triangle intersecting the other two sides, divides the sides in the same ratio.
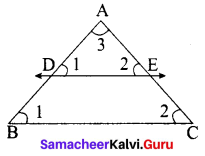
Proof
Given : In ∆ABC, D is a point on AB and E is a point on AC.
To prove : \(\frac{A D}{D B}=\frac{A E}{E C}\)
Construction : Draw a line DE || BC
Question 37.
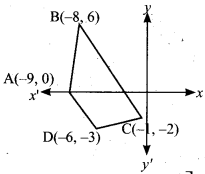
Find the value of k, if the area of a quadrilateral is 28 sq. units, whose vertices are (-4, -2), (-3, k), (3,-2) and (2,3)
Answer:
Let the vertices A (-4, -2), B (-3, k), C (3, -2) and D (2, 3)
Area of the Quadrilateral = 28 sq. units
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [(x1y2 + x2y3 + x3y4 + x4y1) – (x2y1 + x3y2 + x4y3 + x1y4)] = 28
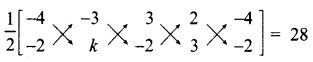
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [(-4k + 6 + 9 – 4)-(6 + 3k – 4 – 12)] = 28
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [(-4k + 11) – (3k – 10)] = 28
-4k + 11 – 3k + 10 = 56
-7k + 21 = 56
-7k = 56 – 21
-7k = 35 ⇒ 7k = -35
k = \(-\frac{35}{7}\) = -5
∴ The value of k = -5
![]()
Question 38.
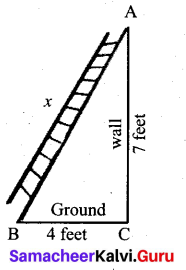
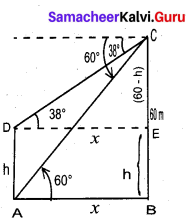
A bird is sitting on the top of a 80 m high tree. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the bird is 45° . The bird flies away horizontally in such away that it remained at a constant height from the ground. After 2 seconds, the angle of elevation of the bird from the same point is 30° . Determine the speed at which the bird flies. (√3 = 1.732)
Answer:
A is the initial position of the bird
B is the final position of the bird
Let the speed of the bird be “s”
Distance = speed × time
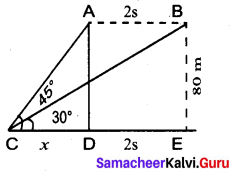
∴ AB = 2 s
Let CD be x
∴ CE = x + 2s
In the ∆ CDA, tan 45° = \(\frac{A D}{C D}\)
1 = \(\frac{80}{x}\)
x = 80 …(1)
In the ∆ BCE
tan 30° = \(\frac{\mathrm{BE}}{\mathrm{CE}}\)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{80}{x+2 s}\)
x + 2 s = 80 √3
x = 80 √3 – 2 s …(2)
From (1) and (2) we get
80 √3 – 2 s = 80
80 √3 – 80 = 2s ⇒ 80(√3 – 1) = 2 s
s = \(\frac{80(\sqrt{3}-1)}{2}\) = 40 (1.732 – 1) = 40 × 0. 732 = 29. 28
Speed of the flying bird = 29. 28 m / sec
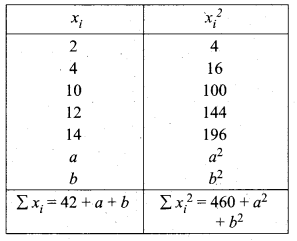
Question 39.
The total marks scored by two students Sathya and Vidhya in 5 subjects are 460 and 480 with standard deviation 4.6 and 2.4 respectively. Who is more consistent in performance?
Answer:
Total marks scored by Sathya = 460
Total marks scored by Vidhya = 480
Number of subjects = 5
x̄ = 92%
Mean marks of Sathya = \(\frac{460}{5}\)
Given standard deviation, (σ) = 4.6
Coefficient of variation = \(\frac{\sigma}{\bar{x}} \times 100 \%\)
= \(\frac{4.6}{92} \times 100 \%\)
= \(\frac{460}{92}=5 \%\)
Mean marks of vidhya = \(\frac{480}{5}\)
Given standard deviation (σ) = 2.4
Coefficient of variation = \(\frac{2.4}{96} \times 100=\frac{240}{96}=2.5 \%\)
CV1 > CV2
Vidhya coefficient of variation is less than Sathya
∴ Vidhya is more consistent.
![]()
Question 40.
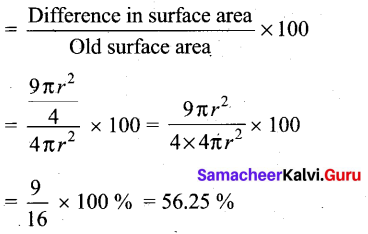
The perimeters of the ends of frustum of a cone are 207.24 cm and 169.56 cm. If the height of the frustum be 8 cm, find the whole surface area of the frustum. [Use π = 3.14]
Answer:
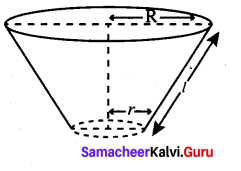
Let the radii of circular ends be R and r [R > r]
Perimeter of circular ends are 207.24 cm and 169.56 cm
∴ 2πR = 207.24 cm
⇒ R = \(\frac{207.24}{2 \pi}=\frac{207.24}{2 \times 3.14}=33\)
⇒ R = 33m and 2 πr = 169.56
⇒ r = \(\frac{169.56}{2 \pi}=\frac{169.56}{2 \times 3.14}=27\)
Slant-height of the frustum
l = \(\sqrt{h^{2}+(\mathrm{R}-r)^{2}}\)
\(=\sqrt{8^{2}+(33-27)^{2}}\)
\(=\sqrt{64+36}\) = 10 cm
The whole surface area of the frustum = π [(R2 + r22) + (R + r) l]
∴ Required whole surface area of the frustum
= 3.14 [332 + 272 + (33 + 27) × 10] cm2
= 3.14 [1089 + 729 + 600] cm2
= 3.14 [2418] cm2
= 7592.52 cm2
Question 41.
A jar contains 54 marbles each of which is blue, green or white. The probability of selecting a blue marbles at random from the jar is \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) and the probability of selecting a green marble at random is \(\frac { 4 }{ 9 }\) . How many white marbles does the jar contain?
Answer:
n(S) =54
Let the number of blue marble, be ‘x’
Let A be the event of getting blue marbles
n(A) = x
P(A) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{A})}{n(\mathrm{S})}\)
\(\frac{1}{3}=\frac{x}{54}\)
3x = 54
x = \(\frac{54}{3}\) = 18
Number of blue marble is 18. Let the number of green marble be “y”. Let B be the event of getting green marbles.
P(B) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{B})}{n(\mathrm{S})}\)
\(\frac{4}{9}=\frac{y}{54}\)
9y = 54 × 4
y = \(\frac{54 \times 4}{9}\) = 24
Blue marbles + green marbles + white marbles = 54
18 + 24 + white marbles = 54
∴ Number of white marbles = 54 – 42 = 12
The jar contain 12 white marbles.
![]()
Question 42.
One – fourth of a herd of camels was seen in the forest. Twice the square root of the herd had gone to mountain and the remaining 15 camels were seen on the bank of a river. Find the total number of camels.
Answer:
Le the total number of camels be ‘x’
Number of camels seen in the forest = \(\frac { x }{ 4 }\)
Number of camels gone to the mountain = 2√x
Number of camels on the bank of river = 15
Total number of camels = \(\frac { x }{ 4 }\) + 2√x + 15
x = \(\frac { x }{ 4 }\) + 2√x + 15
4x = x + 8√x + 60 (muliply by 4)
3x – 8√x – 60 = 0
Let x = a2
3a2 – 8√a2 – 60 = 0
3a2 – 8a – 6 = 0
3a (a – 6) + 10(a – 6) = 0
(3a + 10) (a – 6) = 0
3a + 10 = 0 or a – 6 = 0
a = \(\frac{-10}{3}\) or a = 6
x = \(\left(\frac{-10}{3}\right)^{2}\) or 62(x = a2)
x = \(\frac{100}{9}\) (or) 36
Number of camels can-not be a fraction
∴ Number of camels = 36
PART – IV
IV. Answer all the questions. [2 × 8 = 16]
Question 43.
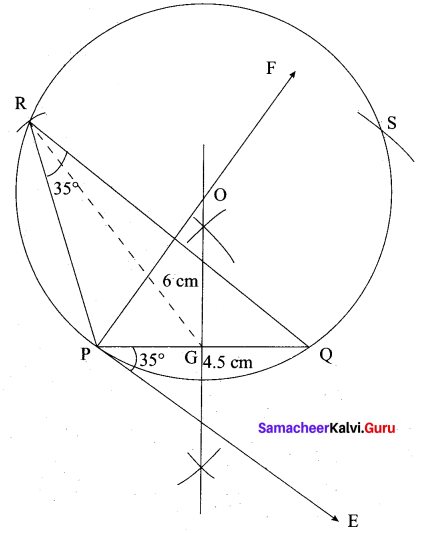
(a) Construct a triangle similar to a given triangle PQR with its sides equal to \(\frac { 7 }{ 4 }\) of the corresponding sides of the triangle PQR
Answer:
Given a triangle PQR, we are required to construct another triangle whose sides are \(\frac { 7 }{ 4 }\) of the corresponding sides of the triangle PQR.
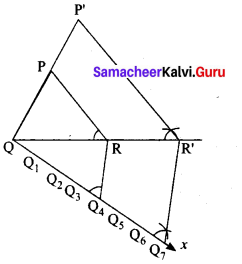
Steps of construction
1. Construct a ∆PQR with any measurement.
2. Draw a ray QX making an acute angle with QR on the side opposite to vertex P.
3. Locate 7 points (the greater of 7 and 4 in \(\frac { 7 }{ 4 }\))
Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4, Q5, Q6 and Q7 on QX so that
QQ1 = Q1Q2 = Q2Q3 = Q3Q4= Q4Q5 = Q5Q6 = Q6Q7
4. Join Q4 (the 4th point, 4 being smaller of 4 and 7 in \(\frac { 7 }{ 4 }\)) to R and draw a line through Q7 parallel to Q4 R, intersecting the extended line segment QR at R’.
5. Draw a line through R’ parallel to RP intersecting the extended line segment QP at P’ Then ∆P’QR’ is the required triangle each of whose sides is seven-fourths of the corresponding sides of ∆PQR.
[OR]
![]()
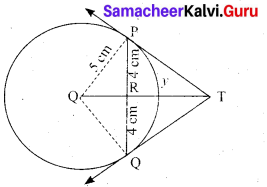
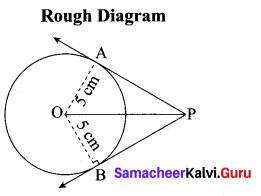
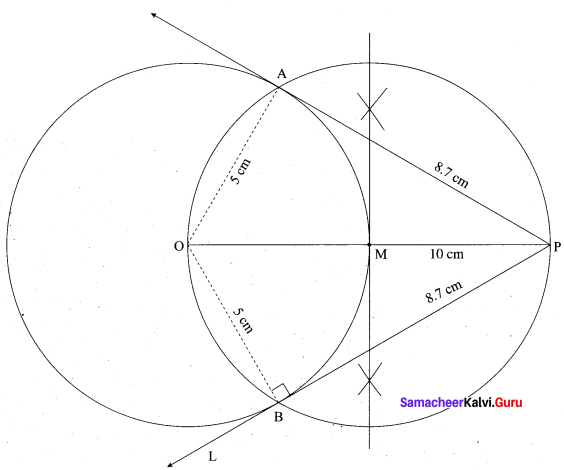
(b) Take a point which is 11 cm away from the centre of a circle of radius 4 cm and draw the two tangents to the circle from that point.
Answer:
Radius = 4 cm; Distance 11 cm
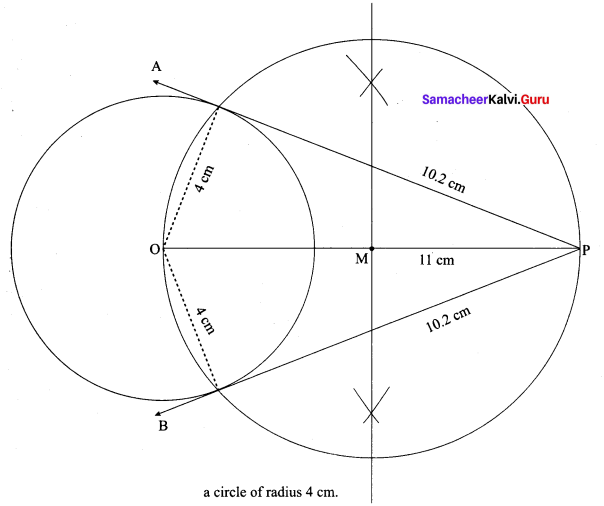
Steps of construction:
- With O as centre, draw a circle of radius 4 cm.
- Draw a line OP = 11 cm.
- Draw a perpendicular bisector of OP, which cuts OP at M.
- With M as centre and MO as radius, draw a circle which cuts previous circle A and B.
- Join AP and BP. AP and BP are the required tangents.
This the length of the tangents PA = PB = 10.2 cm
Verification: In the right angle triangle OAP
PA2 = OP2 – OA2
= 112 – 42 = 121 – 16= 105
PA = √105 = 10.2 cm
Length of the tangents = 10.2 cm
![]()
Question 44.
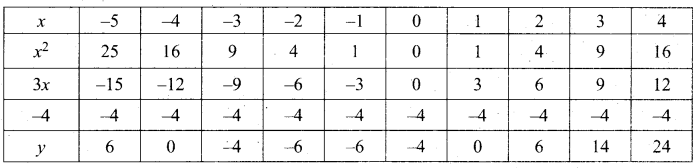
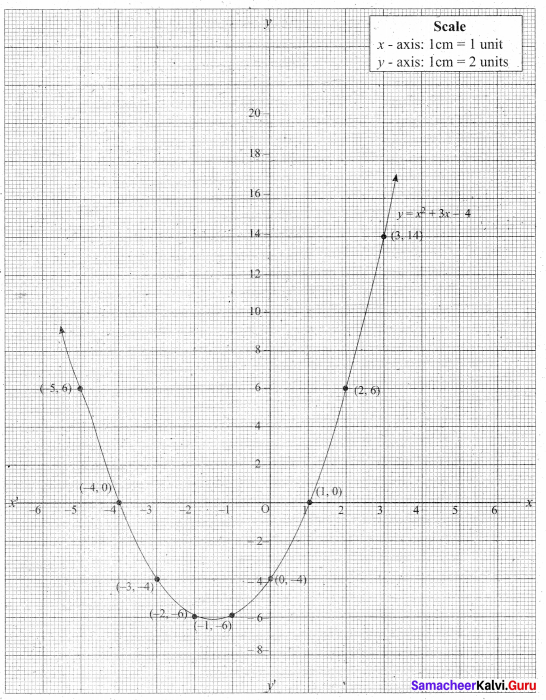
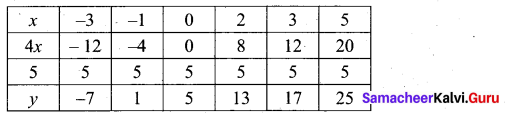
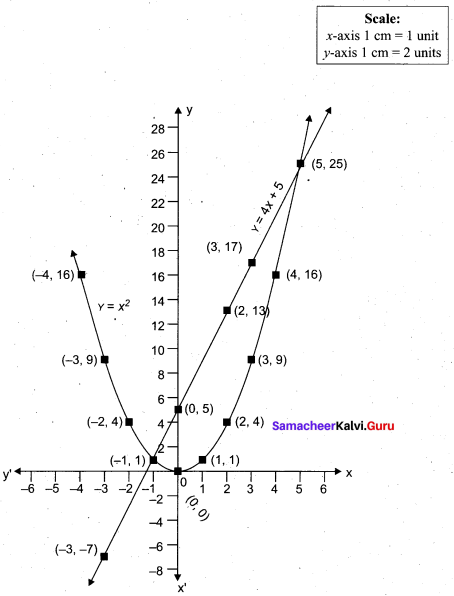
(a) Draw the graph of y = x2 + 3x + 2 and use it to solve x2 + 2x + 1 = 0.
Answer:
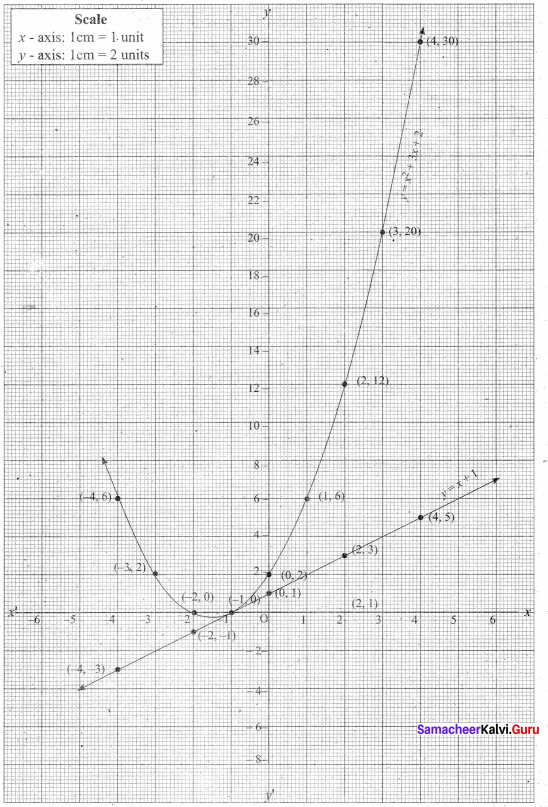
(i) Draw the graph of y = x2 + 3x + 2 preparing the table of values as below.
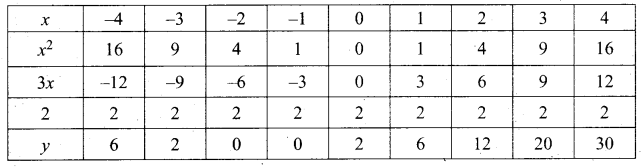
(ii) Plot the points (-4, 6), (-3, 2), (-2, 0), (-1, 0), (0, 2), (1, 6), (2, 12), (3, 20) (4, 30).
(iii) To solve x2 + 2x + 1 = 0 subtract x2 + 2x + 1 = 0 from y = x2 + 3x + 2

(iv) Draw the graph of y = x +1 from the table
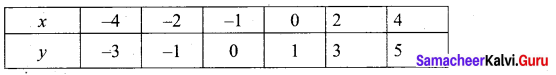
The equation y = x + 1 represents straight line.
This line intersect the curve at only one point (-1, 0). The solution set is (-1).
[OR]
![]()
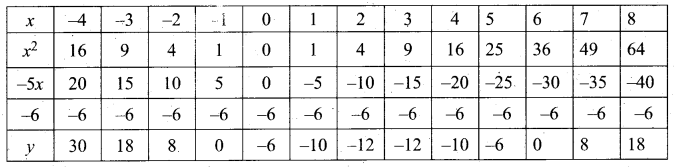
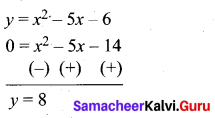
(b) (2x – 3) (x + 2) = 0
y = (2x – 3) (x + 2)
= 2x2 + 4x – 3x – 6
= 2x2 + x – 6
(i) Prepare a table of values for y from x – 4 to 4
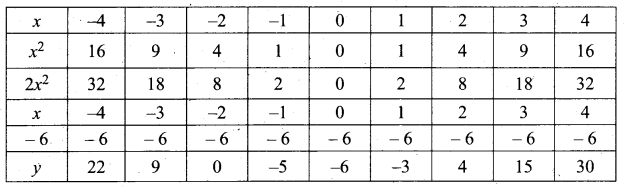
(ii) Plot the points (-4, 22) (-3, 9) (-2, 0) (-1, -5) (0, -6) (1,-3), (2, 4), (3, 15) and (4, 30).
(iii) Join the points by a free hand smooth curve.
The curve intersect the X – axis at (-2, 0) and \(\left(1 \frac{1}{2}, 0\right)\)
∴ The solution set is \(\left(-2,1 \frac{1}{2}\right)\)
(iv) Since there are two points of intersection with X – axis, the quadratic equation has real and un – equal roots.