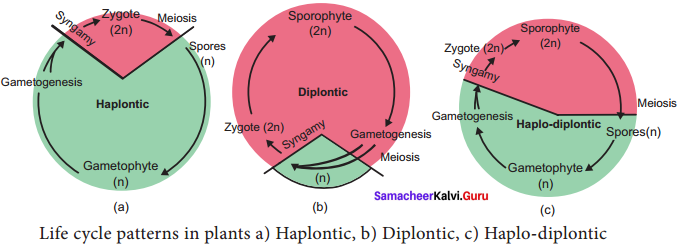
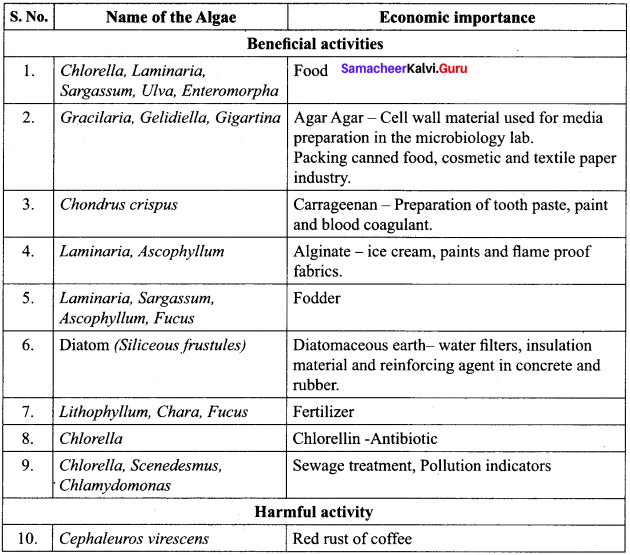
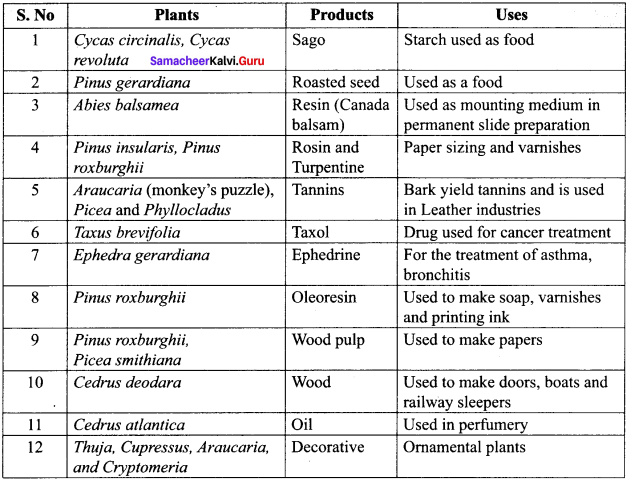
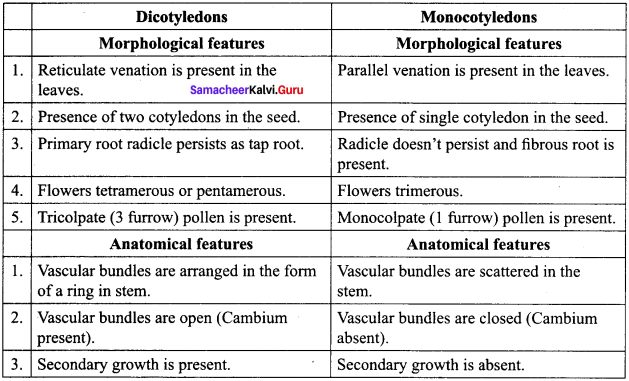
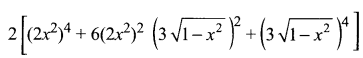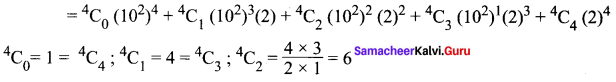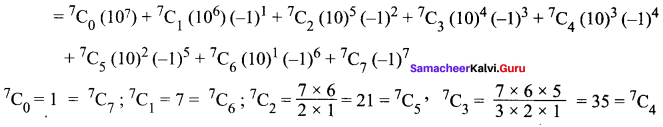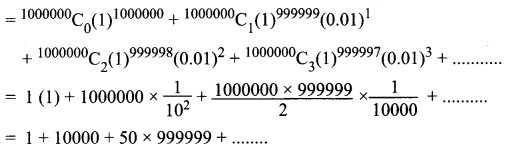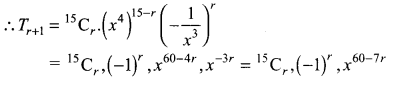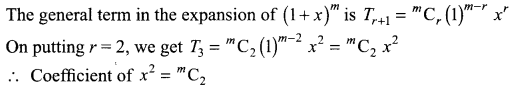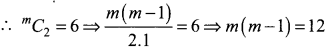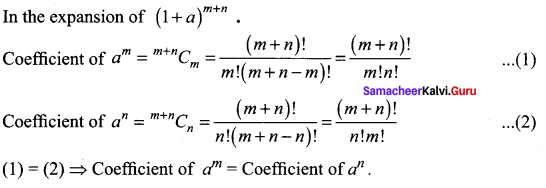Understand topics of 11th Chemistry that you never seemed to understand by utilizing the Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for 11th Chemistry prevailing. Practice using the Samacheer Kalvi 11th Physics Book Solutions Questions and Answers PDF regularly and get to know different questions that you might witness as a part of your exam. Just tap on the direct links available and score better grades in your exam and clear the exams with flying colors.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Book Solutions Answers Guide
Use the Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Book Solutions Questions and Answers to learn various chapters of the subject easily. All the Solutions are given by subject expertise keeping in mind the latest syllabus guidelines and test pattern. Stand out from the crowd with frequent practice using the Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Book Solutions Questions and Answers PDF so that you can attempt the exam with confidence.
Students can also read Tamil Nadu 11th Chemistry Model Question Papers 2019-2020 English & Tamil Medium.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Guide Book Back Answers
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Book Back Answers
Tamilnadu State Board Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Book Volume 1 Solutions
- Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations
- Chapter 2 Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
- Chapter 3 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 4 Hydrogen
- Chapter 5 Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals
- Chapter 6 Gaseous State
- Chapter 7 Thermodynamics
Tamilnadu State Board Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Book Volume 2 Solutions
- Chapter 8 Physical and Chemical Equilibrium
- Chapter 9 Solutions
- Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding
- Chapter 11 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
- Chapter 12 Basic Concepts of Organic Reactions
- Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- Chapter 14 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Chapter 15 Environmental Chemistry
Hope the information shared regarding the Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for 11th Chemistry has been beneficial to you. If you feel any information is missing or needs to be added feel free to reach us and we will revert back to you at the earliest. Keep in touch with our site to know the latest updates at your fingertips.