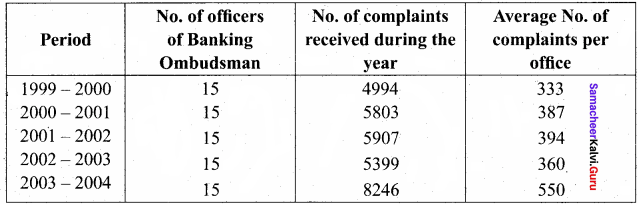
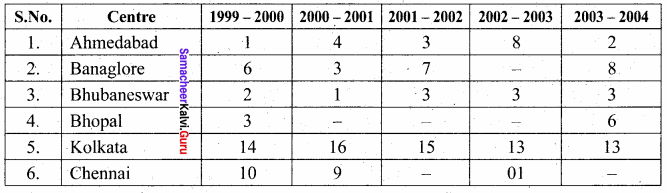
Students can find the most related topics which helps them to analyse the concepts if they practice according to the chapter-wise page. It is necessary for the students to practice more Questions and Answers for Tamilnadu State Board Solutions of 11th Commerce are given in the pdf format in chapter 13 Warehousing Questions and Answers so that students can prepare in both online and offline modes. So, Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Book Solutions Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, to score good marks.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Solutions Chapter 13 Warehousing
Get the Questions and Answers, in Tamilnadu State Board 11th Commerce Solutions for Chapter 13 Warehousing. Learn the concepts of 11th Commerce Chapter-Wise by referring to the Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Chapter 13 Warehousing Questions and Answers. Hence we suggest the students to Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Book Solutions Questions and Answers pdf to enhance your knowledge.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Warehousing Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
Warehouses removes the hindrance of ………………
(a) Person
(b) Time
(c) Risk
(d) Knowledge
Answer:
(b) Time
Question 2.
A warehouse holds goods as a ……………… center.
(a) Marketing
(b) Sorting
(c) Distribution
(d) Selling
Answer:
(c) Distribution
Question 3.
……………… can be given as a collateral security for getting financial assistance from bank.
(a) Dock warrant
(b) Warehouse receipt
(c) Dock receipt
(d) Warehouse warrant
Answer:
(d) Warehouse warrant
Question 4.
……………… warehouses are licensed by the government and are permitted to accept the goods on bond.
(a) Bonded
(b) Cold Storage
(c) Public
(d) None of these
Answer:
(d) None of these
Question 5.
……………… warehouses are used for storing perishable goods like fruits, vegetables etc.
(a) Bonded
(b) Private
(c) Cold storage
(d) Co – operative
Answer:
(c) Cold storage
Question 6.
The document which authorizes to deliver the goods either in part or full is called ………………
(a) Warehouse warrant
(b) Dock receipt
(c) Dock warrant
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Dock warrant
Question 7.
The Institutional warehouse started with the support of the government is ………………
(a) Bonded warehouse
(b) Public warehouse
(c) Food Corporation of India
(d) Custom bonded
Answer:
(c) Food Corporation of India
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is Warehouse?
Answer:
It is a place where goods are stored for future use and act as distribution centres. Warehouses are designed depending upon the nature of the products to be stored.
Question 2.
List the various types of Warehouses.
Answer:
- On the Basis of Ownership – Private, Public
- On the Basis of Commodities stored – General
Question 3.
Give any three functions of Warehouses.
Answer:
- Storage
- Price stabilization
- Equalization of demand and supply.
Question 4.
Tabulate the three differences between warehouse warrant and warehouse receipt.
Answer:
Warehouse Warrant:
- It is a document of title of goods.
- It is not only an acknowledgement for the
- receipt of goods but also gives an authority to get delivery of goods by the owner or by third party-
- It can be negotiated or transferred to others.
Warehouse Receipt:
- It is not a document of title of goods.
- It is only an acknowledgement for the
- receipt of goods.
- It cannot be transferred to others.
Question 5.
Give a note on FCI.
Answer:
FCI provides storage facilities for good grains. FCI also hires storage capacity from other sources such as CWC, SWC and private parties.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate the warehouse warrant from the warehouse receipt.
Answer:
Warehouse Warrant:
- It is a document of title of goods.
- It is not only an acknowledgement for the receipt of goods but also gives an authority to get delivery of goods by the
- owner or by third party.
- It can be negotiated or transferred to others.
Warehouse Receipt:
- It is not a document of title of goods.
- It is only an acknowledgement for the receipt of goods.
- It cannot be transferred to others.
Question 2.
Comment on cold storage warehouse.
Answer:
Goods are transferred in refrigerated containers and stored in refrigerated warehouse. These warehouses are used for storing perishable goods like fruits, vegetables, eggs, butter, fish, meat, etc. Goods stored in cold storages without deterioration in quality, can be made available throughout the year.
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the different types of warehouses A. On the Basis of Ownership
Answer:
1. Private Warehouses : Private warehouses are built and owned by private business enterprises in order to store the products produced by them.
2. Government Warehouses : They are created and operated by the Government to implement the programmes of the Government.
3. Public Warehouse : It is open for public at large. Most of the business organisations, especially small and medium scale units cannot afford to have their own warehouses.
4. Co – operative Warehouses : There are warehouses owned and managed by the marketing co-operative societies or agricultural co-operative societies. They are setup to provide warehousing facilities to their members.
5. Bonded Warehouses : Bonded warehouses are those warehouses, which are licensed by the government to accept storage of imported goods which are not cleared due to non – payment of customs duty by the importer.
Question 2.
Explain the advantages of warehousing functions.
Answer:
- It safeguards the stock for the merchants who do not have storage place.
- Warehouses reduces the distribution cost of the traders by storing the goods in bulk and allow the trader to take the goods in small lots to his shop.
- It helps in selection of channel of distribution. The producer will prefer whether to a wholesaler or retailer.
- It assists in maintaining the continuous sale and avoid the possibilities of “Out of Stock”.
- It creates employment opportunities for both skilled and unskilled workers to improve their standard of living.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Warehousing Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question 1.
NCDC is an example of ……………. warehouse.
(a) Private
(b) Government
(c) Public
(d) Co – operative
Answer:
(d) Co – operative
Question 2.
The FCI was setup under the Food Corporation Act,
(a) 1964
(b) 1985
(c) 1995
(d) 2013
Answer:
(a) 1964
Question 3.
CWC was established in
(a) 1964
(b) 1957
(c) 1956
(d) 1956
Answer:
(b) 1957
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Give a not on SWC.
Answer:
State Warehousing Corporation (SWC) : Every state government is given power to establish its own Warehousing Corporation after getting approval from the CWC. 50% of the capital is contributed by the CWC and the balance 50% contributed by State Government.
Question 2.
Write a note on TNWC.
Answer:
Tamil Nadu Warehousing Corporation (TNWC) : Tamil Nadu Warehousing Corporation was established in 1959. The available storage capacity of TNWC is 6.83 Lakh MT with 7 Regional offices and 256 Godowns across the state.
III. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the warehousing in India.
Answer:
India is an agrarian country but the importance of warehousing was not felt till 1950. Agriculture contributes 16 percent of the overall GDP and accounts for employment of approximately 52 percent of the Indian population. It is estimated that more than 40 percent of our agricultural .productions wasted due to poor storage facilities.
On the recommendation of the All India Rural Credit Survey Committee, the Agricultural Produce (Development and warehousing) Corporation Act enacted in 1956, authorized the Government to setup National Co-operative Development and Warehousing Board to develop agricultural Co-operatives and warehousing.
For future Learning
Question a.
The warehouse of the future : How will it impact efficiency?
Answer:
From 2019, new technology could be revolutionary and improving efficiency in warehouse by Warehousing Management System (WMS). Technologies including artificial intelligence, 3D printing and self-driving vehicle could be more widely used in warehouses everywhere sooner than you think. By 2030, warehouses will be a part of initiative to achieve Zero net energy. Warehouse buildings will operate 24 x 7 x 365 and be designed with sustainability. By creating strategies, warehouse will save costs and prevent harmful emissions. Solar panels will become the main sources of energy for warehouses.
Share this Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for 11th Commerce Chapter 13 Warehousing Questions and Answers with your friends to help them to overcome the issues in exams. Keep visiting this site Tamilnadu State Board Solutions frequently to get the latest information on different subjects. Clarify your doubts by posting the comments and get the answers in an easy manner.