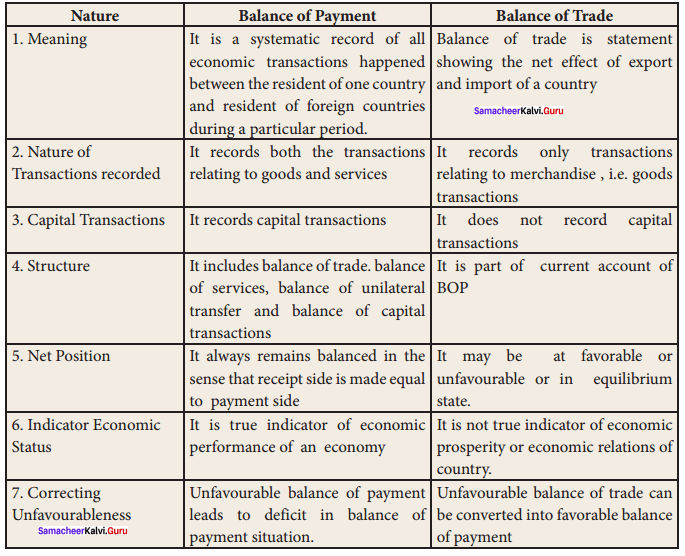
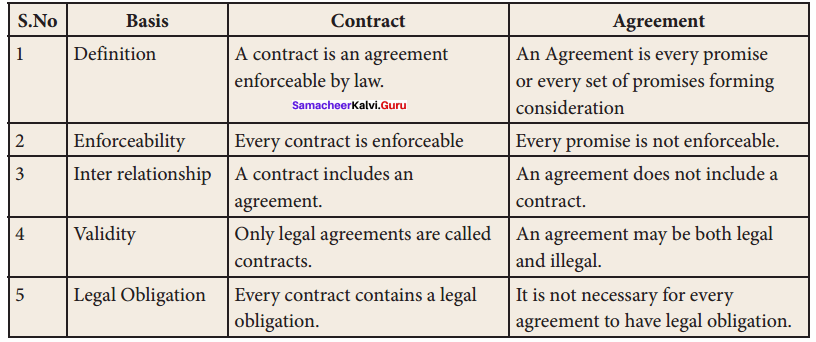
Students can find the most related topics which helps them to analyse the concepts if they practice according to the chapter-wise page. It is necessary for the students to practice more Questions and Answers for Tamilnadu State Board Solutions of 11th Commerce are given in the pdf format in chapter 33 Indirect Taxation Questions and Answers so that students can prepare in both online and offline modes. So, Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Book Solutions Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, to score good marks.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Solutions Chapter 33 Indirect Taxation
Get the Questions and Answers, in Tamilnadu State Board 11th Commerce Solutions for Chapter 33 Indirect Taxation. Learn the concepts of 11th Commerce Chapter-Wise by referring to the Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Chapter 33 Indirect Taxation Questions and Answers. Hence we suggest the students to Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Book Solutions Questions and Answers pdf to enhance your knowledge.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Indirect Taxation Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
Who is the chairman of the GST council?
(a) RBI Governor
(b) Finance Minister
(c) Prime Minister
(d) President of India
Answer:
(b) Finance Minister
Question 2.
GST Stands for …………….
(a) Goods and Supply Tax
(b) Government sales Tax
(c) Goods and Services Tax
(d) General Sales Tax
Answer:
(c) Goods and Services Tax
Question 3.
What kind of Tax the GST is?
(a) Direct Tax
(b) Indirect Tax
(c) Dependence on the Type of Goods and Services
(d) All Business Organisations
Answer:
(b) Indirect Tax
Question 4.
What is IGST?
(a) Integrated Goods and Service Tax
(b) India Goods and Service Tax
(c) Initial Goods and Service Tax
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) Integrated Goods and Service Tax
Question 5.
In India GST became effective from?
(a) 1st April, 2017
(b) 1st January, 2017
(c) 1st July, 2017
(d) 1st March, 2017
Answer:
(d) 1st March, 2017
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Indirect tax.
Answer:
Indirect Tax is levied on the goods and services. It is collected from the buyers by the sellers and paid by the sellers to the Government. Since it is indirectly imposed on the buyers it is called indirect tax.
Question 2.
List out any four types of indirect taxes levied in India.
Answer:
- CGST
- SGST
- UGST
- IGST
Question 3.
What do you mean by Goods and Services Taxes?
Answer:
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is the tax imposed on the supply (consumption) of goods and services. It is a destination based consumption tax and collected on those value added items at each stage of the supply chain.
Question 4.
Write a note on SGST.
Answer:
SGST – State Goods and Services Tax – is imposed and collected by the State Governments under State GST Act. (Tamil Nadu GST Act 2017 passed by Tamil Nadu Govt.)
Question 5.
What is CGST?
Answer:
CGST – Central Goods and Services Tax – is imposed and collected by the Central Government on all supply of goods within a state (intra – state) under CGST Act 2017.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write any two differences between direct taxes and indirect taxes?
Answer:
| Basis | Direct Taxes | Indirect Taxes |
| 1. Meaning | If a tax levied on the income or wealth of a person is paid by that person (or his office) directly to the Government, it is called direct tax. | If tax is levied on the goods or services of a person is collected from he buyers by another person (seller) and paid by him to the Government it is called indirect tax. |
| 2. Incidence and Impact | Falls on the same person. Imposed on the income of a person and paid by the same person. | Falls on different persons. Imposed on the sellers but collected from the consumers and paid by sellers. |
Question 2.
What are the objectives of GST?
Answer:
- To create a common market with uniform tax rate in India. (One Nation, One Tax, One Market)
- To eliminate the cascading effect of taxes, GST allows set-off of prior taxes for the same transactions as input tax credit.
- To boost Indian exports, the GST already collected on the inputs will be refunded and thus there will be no tax on all exports.
- To increase the tax base by bringing more number of tax payers and increase tax revenue.
- To simplify tax return procedures through common forms and avoidance of visiting tax departments.
- To provide online facilities for payment of taxes and submission of forms.
Question 3.
Briefly explain the functions of GST council.
Answer:
- The GST Council will oversee the implementation of the GST. But the Central Board of Excise and Customs is responsible for administration of the CGST and IGST Acts.
- The Council makes recommendations on rate of GST, apportionment of IGST, exemptions, model GST laws, etc.
- The Minister of State in the Finance Ministry and all Finance Ministers of the State Governments shall be its members.
- All decisions of the Council can be passed only with Atb of the total votes. Each state has one vote, irrespective of its size or population.
Question 4.
Explain IGST with an example.
Answer:
IGST – Inter-State Goods and Services Tax is imposed and collected by the Central Government and the revenue is shared with States under IGST Act 2017.
Question 5.
Write any three demerits of UGST.
Answer:
- Several Economists says that GST in India would impact negatively on the real estate market. It would add up to 8 percent to the cost of new homes and reduce demand by about 12 percent.
- Another criticism is that CGST, SGST are nothing but new names for Central Excise/ Service Tax, VAT and CST. Hence, there is no major reduction in the number of tax layers.
- A number of retail products currently have only four percent tax on them. After GST, garments and clothes could become more expensive.
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between direct taxes and indirect taxes.
Answer:
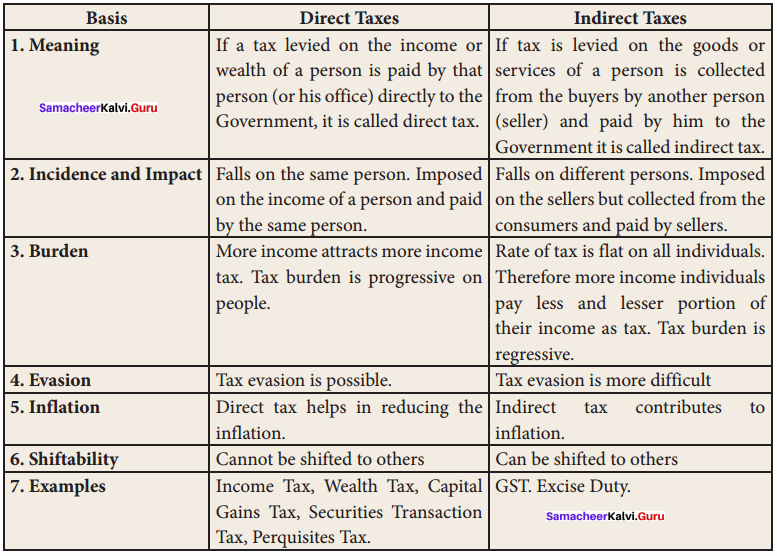
Question 2.
Discuss the different kinds of GST.
Answer:
GST is of three kinds: CGST, SGST/UGST, and IGST.
1. CGST – Central Goods and Services Tax – imposed and collected by the Central Government on all supply of goods within a state (intra-state) under CGST Act 2017.
2. SGST – State Goods and Services Tax – imposed and collected by the State Governments under State GST Act. (Tamil Nadu GST Act 2017 passed by Tamil Nadu Govt.)
3. UGST – Union Territory Goods and Services Tax – imposed and collected by the five Union Territory Administrations in India under UGST Act 2017.
4. IGST – Inter-State Goods and Services Tax – imposed and collected by the Central Government and the revenue shared with States under IGST Act 2017.
5. IGST on exports – All exports are treated as Inter-State supply under GST. Since exports are zero rated, GST is not imposed on all goods and services exported from India. Any input credit paid already on exports will be refunded.
Question 3.
Elucidate the merits of GST.
Answer:
A. To the Society and country:
- Unified common national market will attract more foreign investment. GST has integrated the economy of all States and Union Territories.
- It brings parity in taxation among imported goods and Indian manufactured goods. All imported goods will be charged with IGST which will be more or less equivalent to the total of CGST and SGST levied on manufactured goods. Removal of several taxes will make the price of Indian products more competitive at world market.
- It will boost manufacturing, export, GDP leading to economic growth through increase in economic activity.
- Creation of more employment opportunities which will result in poverty eradication.
- It will bring more tax compliance (more tax payers) and increase revenue to the Governments.
- It is transparent and will improve India’s ranking in the Ease of Doing Business in the world.
- Uniform rates of tax will reduce tax evasion and rate arbitrage between States.
B. To Business Community:
- Simpler Tax System with fewer exemptions. 17 taxes were abolished and one tax exists today.
- Input tax credit will reduce cascading effect of taxes. Reduction in average tax burden will encourage manufacturers and help “Make in India” campaign and make India as a manufacturing hub.
- Common procedures, common classification of goods and services and timelines will lend greater certainty to taxation system.
- GSTN facility will reduce multiple record keeping, lesser investment in manpower and resources and improve efficiency.
- All interactions will be through common GSTN portal and will ensure corruption free administration
- Uniform prices throughout the country. Expansion of business to all states is made easy.
C. To Consumers:
- Input tax credit allowed will lower the prices to the consumers.
- All small retailers will get exemption and purchases from them will cost less for the consumers.
Question 4.
Compare CGST, SGST and IGST.
Answer:
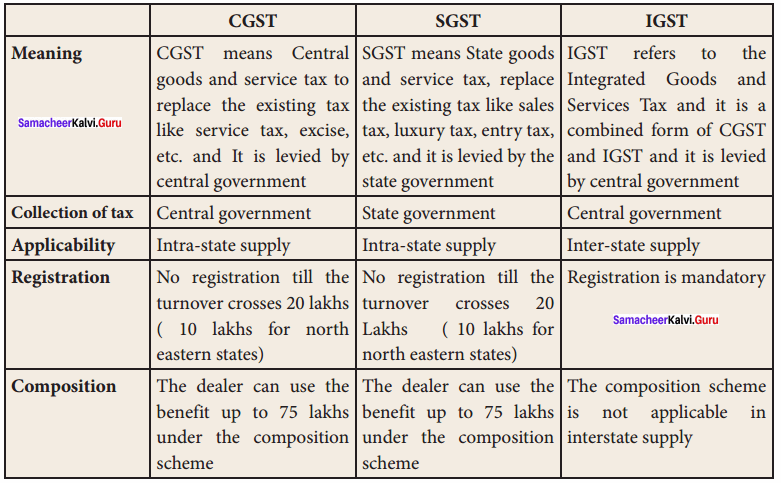
Share this Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for 11th Commerce Chapter 33 Indirect Taxation Questions and Answers with your friends to help them to overcome the issues in exams. Keep visiting this site Tamilnadu State Board Solutions frequently to get the latest information on different subjects. Clarify your doubts by posting the comments and get the answers in an easy manner.