Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Guide Pdf Term 1 Chapter 1 அளவீடுகள் Questions and Answers, Notes.
TN Board 6th Science Solutions Term 1 Chapter 1 அளவீடுகள்
6th Science Guide அளவீடுகள் Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. சரியான விடையைத் தேர்ந்தெடு:
Question 1.
ஒரு மரத்தின் சுற்றளவை அளவிடப் பயன்படுவது.
அ) மீட்டர் அளவு கோல்
ஆ) மீட்டர் கம்பி
இ) பிளாஸ்டிக் அளவுகோல்
ஈ) அளவு நாடா
விடை:
ஈ) அளவு நாடா
Question 2.
7மீ என்பது செ.மீ -ல்
அ) 70 செ.மீ
ஆ) 7 செ.மீ
இ) 700 செ.மீ
ஈ) 7000 செ.மீ
விடை:
இ) 700 செ.மீ
![]()
Question 3.
ஒரு அளவை அளவிடும் முறைக்கு என்று பெயர்
அ) இயல் அளவீடு
ஆ) அளவீடு
இ) அலகு
ஈ) இயக்கம்
விடை:
ஆ) அளவீடு
Question 4.
சரியானதைத் தேர்ந்தெடு
அ) கி.மீ > மி.மீ > செ.மீ > மீ
ஆ) கி.மீ > மி.மீ > செ.மீ > மீ
இ) கி.மீ > மீ > செ.மீ > மி.மீ
ஈ) கி.மீ > செ.மீ > மீ > மி.மீ
விடை:
இ) கி.மீ > மீ > செ.மீ > மி.மீ
Question 5.
அளவுகோலைப் பயன்படுத்தி, நீளத்தை அளவிடும் போது, உனது கண்ணின் நிலை _____ இருக்க வேண்டும்.
அ) அளவிடும் புள்ளிக்கு இடது புறமாக
ஆ) அளவிடும் புள்ளிக்கு மேலே, செங்குத்தாக
இ) புள்ளிக்கு வலது புறமாக
ஈ) வசதியான ஏதாவது ஒரு கோணத்தில்
விடை:
ஆ) அளவிடும் புள்ளிக்கு மேலே, செங்குத்தாக
II. சரியா தவறா என எழுதுக.
Question 1.
நிறையை 126 கிகி எனக் கூறுவது சரியே.
விடை:
சரி
Question 2.
ஒருவரின் மார்பளவை அளவுகோல் பயன்படுத்தி அளவிட முடியும்.
விடை:
தவறு
Question 3.
10 மி.மீ என்பது 1 செ.மீ ஆகும்.
விடை:
சரி
Question 4.
முழம் என்பது நீளத்தை அளவிடும் நம்பத் தகுந்த முறையாகும்.
விடை:
தவறு
Question 5.
SI அலகு முறை என்பது உலகம் முழுவதும் ஏற்றுக்கொள்ளப்பட்ட ஒரு அலகு முறையாகும்.
விடை:
சரி
![]()
III. கோடிட்ட இடத்தை நிரப்புக.
Question 1.
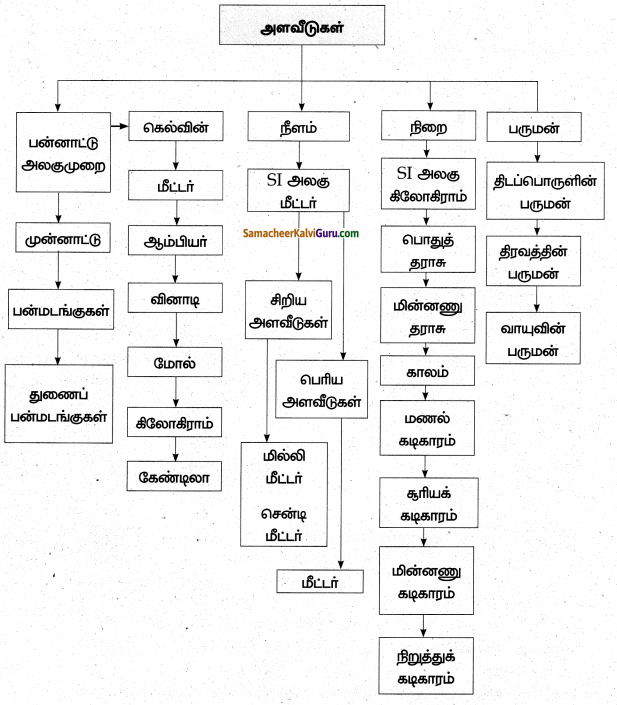
SI அலகு முறையில் நீளத்தின் அலகு _______
விடை:
மீட்டர்
Question 2.
500 கிராம் = _____ கிலோகிராம்.
விடை:
0.5.
Question 3.
டெல்லிக்கும், சென்னைக்கும் இடையில் உள்ள தொலைவு _____ என்ற அலகால் அளக்கப்படுகிறது
விடை:
கிலோ மீட்டர்
Question 4.
1மீ = _____ செ.மீ என அளவிடப்படுகிறது.
விடை:
100
Question 5.
5 கி.மீ = ______ மீ.
விடை:
5000
IV. ஒப்புமை தருக.
Question 1.
சர்க்கரை : பொதுத்தராசு; எலுமிச்சை சாறு : ______ ?
விடை:
அளவுசாடி.
Question 2.
மனிதனின் உயரம் : செ.மீ; கூர்மையான பென்சிலின் முனையின் நீளம் : ______?
விடை:
மி.மீட்டர்
Question 3.
பால் : பருமன்; காய்கறிகள் : _____
விடை:
எடை
![]()
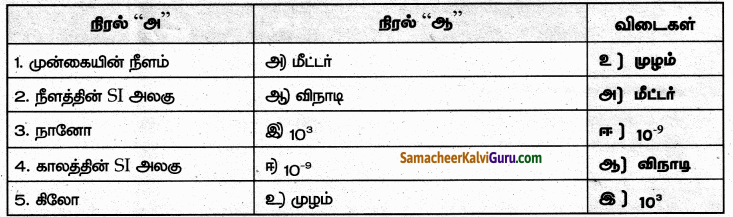
V. பொருத்துக.
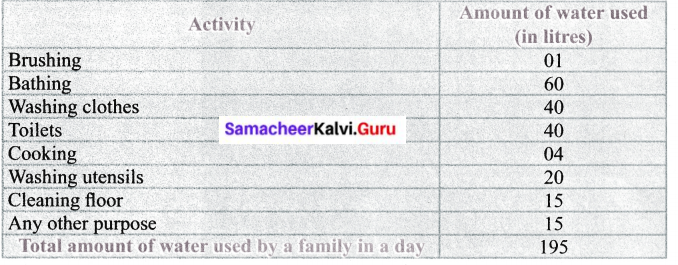
VI. அட்டவணையை நிரப்புக.
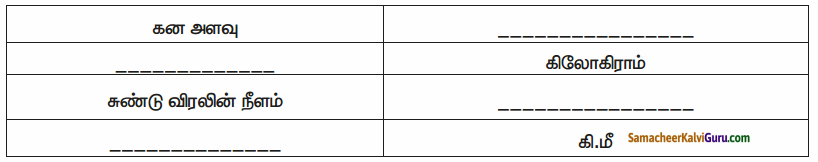
விடை:

VII. பின்வரும் அலகினை ஏறு வரிசையில் எழுதுக.
Question 1.
மீட்டர், 1 சென்டி மீட்டர், 1 கிலோ மீட்டர் மற்றும் 1 மில்லிமீட்டர்.
விடை:
1 மில்லிமீட்டர், 1 சென்டிமீட்டர், 1 மீட்டர், 1 கிலோ மீட்டர்.
VIII. கீழ்க்கண்ட வினாக்களுக்கான விடையை கட்டத்திற்குள் தேடுக
Question 1.
10-3 என்பது
விடை:
மில்லிமீட்டர்
Question 2.
காலத்தின் அலகு
விடை:
விநாடி
Question 3.
சாய்வாக அளவிடுவதால் ஏற்படுவது
விடை:
![]()
Question 4.
கடிகாரம் காட்டுவது
விடை:
நேரம்
Question 5.
ஒரு பொருளில் உள்ள பருப்பொருளின் அளவு
விடை:
நிறை
Question 6.
பல மாணவர்களின் பதிவுகளிலிருந்து கடைசியாக எடுக்கப்படும் ஒரு தனி அளவீடு
விடை:
சராசரி
![]()
Question 7.
_____ என்பது ஒரு அடிப்படை அளவு
விடை:
நீளம்
Question 8.
வாகனங்கள் கடக்கும் தொலைவைக் காட்டுவது
விடை:
ஒடோமீட்டர்
Question 9.
தையல்காரர் துணியைத் தைக்க அளவிடப் பயன்படுத்துவது.
விடை:
நாடா
Question 10.
நீர்மங்களை அளவிட உதவும் அளவீடு.
விடை:
லிட்டர்
விடை:
IX. ஓரிரு வார்த்தைகளில் விடை தருக.
Question 1.
SI என்பதன் விரிவாக்கம் என்ன?
விடை:
பன்னாட்டு அலகு முறை [International System of units]
Question 2.
நிறையை அளவிடப் பயன்படும் ஒரு கருவி.
விடை:
பொதுத்தராசு.
Question 3.
பொருந்தாததைத் தேர்ந்தெடு.
விடை:
விடை:
கிலோகிராம், மில்லி மீட்டர், சென்டி மீட்டர், நேனோ மீட்டர்.
Question 4.
நிறையின் SI அலகு என்ன?
விடை:
கிலோகிராம்.
Question 5.
ஒரு அளவீட்டில் இருக்கும் இரு பகுதிகள் என்ன?
விடை:
- பன்மடங்கு
- துணைப் பன்மடங்குகள்.
X. ஓரிரு வரிகளில் விடையளி:
Question 1.
அளவீடு – வரையறு.
விடை:
தெரிந்த ஒரு அளவைக் கொண்டு தெரியாத அளவை ஒப்பிடுவது ‘அளவீடு’ எனப்படும்.
Question 2.
நிறை வரையறு.
விடை:
நிறை என்பது ஒரு பொருளில் உள்ள பருப்பொருளின் அளவே ஆகும்.
![]()
Question 3.
இரு இடங்களுக்கு இடையே உள்ள தொலைவு 43.65 கி.மீ இதன் மதிப்பை மீட்டரிலும், சென்டிமீட்டரிலும் மாற்றுக.
விடை:
தொலைவு = 43.65 கி.மீ (1 கி.மீ = 1000 மீட்டர்)
தொலைவு = 43650 மீட்டர் (1 மீட்டர் = 100 செ.மீ)
தொலைவு = 4365000 செ.மீ
Question 4.
அளவுகோலில் அளவிடும் போது, துல்லியமான அளவீடு பெறப் பின்பற்றப்படும் விதிமுறைகள் என்ன?
விடை:
- இடமாறு தோற்றப் பிழையைத் தவிர்க்கவும்.
- அளவீட்டை கீழ்நோக்கி செங்குத்தாகப் பார்ப்பதன் மூலம் துல்லியமான அளவீட்டை பெறலாம்.
XI. கீழ்க்கண்டவைகளைத் தீர்க்க.
Question 1.
உனது வீட்டில் இருந்து உனது பள்ளிக்கு இடையே உள்ள தொலைவு 2250மீ. இந்தத் தொலைவினை கிலோமீட்டராக மாற்றுக.
விடை:
வீட்டிற்கும் பள்ளிக்கும் இடையே உள்ள தொலைவு = 2250 மீ
தொலைவு = 2.250 கிலோமீட்டர்.
Question 2.
கூர்மையான ஒரு பென்சிலின் நீளத்தை அளவிடும் போது அளவு கோலின் ஒரு முனை 2.0 செ.மீ மற்றும் அடுத்த முனை 12.1 செ.மீ என்ற இரு அளவுகளைக் காட்டினால் பென்சிலின் நீளம் என்ன?
விடை:
அளவு கோலின் ஒரு முனை = 2.0 செ.மீ
அடுத்த முனை = 12.1 செ.மீ
பென்சிலின் நீளம் = 10.1 செ.மீ (அல்லது) 10 செ.மீ மற்றும் 1 மி.மீ
XII. விரிவாக எழுதுக.
Question 1.
வளைகோடுகளின் நீளத்தை அளக்க நீ பயன்படுத்தும் இரண்டு முறைகளை விளக்குக.
விடை:
1. ஆவது முறை:
- ஒரு வளைகோட்டின் மீது ஒரு கம்பியை வைக்கவும்
- கம்பியானது வளைகோட்டின் எல்லாப் பகுதியையும் தொடுவதை உறுதி செய்ய வேண்டும்.
- வளைகோட்டின் தொடக்கப் புள்ளியையும் முடிவுப் புள்ளியையும் கம்பியின் மீது குறிக்க வேண்டும்.
- கம்பியை நேராக நீட்டி குறிக்கப்பட்ட தொடக்கப்புள்ளிக்கும், முடிவுப் புள்ளிக்கும் இடையிலான தொலைவை அளவுகோல் கொண்டு அளவிடவும்.
- இதுவே வளைகோட்டின் நீளமாகும்.
2 ஆவது முறை :
- கவையின் இரு முனைகளை 0.5 செ.மீ அல்லது 1 செ.மீ இடைவெளி உள்ளவாறு பிரிக்க வேண்டும்.
- வளைகோட்டின் ஒரு முனையிலிருந்து கவையை வைத்து தொடங்கவும். மறுமுனை வரை அளந்து குறிக்க வேண்டும்.
- வளைகோட்டின் மேல் சம அளவு பாகங்களாகப் பிரிக்கவும். குறைவாக உள்ள கடைசிப் பாகத்தை அளவுகோல் பயன்படுத்தி அளவிட வேண்டும்.
- வளைகோட்டின் நீளம் = (பாகங்களின் எண்ணிக்கை × ஒரு பாகத்தின் நீளம்) + மீதம் உள்ள கடைசி பாகத்தின் நீளம்.
Question 2.
கீழ்க்கண்ட அட்டவணையை நிரப்புக்
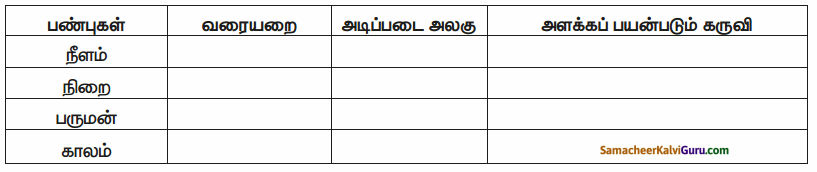
விடை:

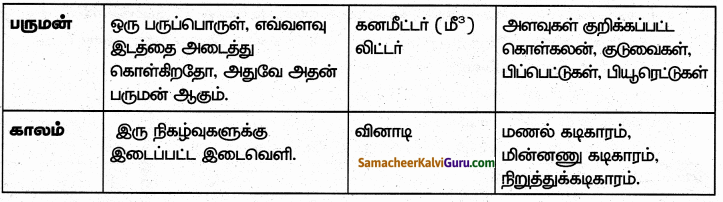
6th Science Guide அளவீடுகள் Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. சரியான விடையைத் தேர்ந்தெடுத்து எழுதுக.
Question 1.
7 மீ என்ப து மி.மீ ல்
அ) 0.7 மி.மீ
ஆ) 700 மி.மீ
இ 7000 மி.மீ
ஈ) 70 மி.மீ
விடை:
இ) 7000 மி.மீ
![]()
Question 2.
SI அலகுமுறையில் மின்னோட்டத்தின் அலகு.
அ) கெல்வின்
ஆ) ஆம்பியர்
இ) வினாடி
ஈ) வோல்ட்
விடை:
ஆ) ஆம்பியர்
Question 3.
நீளத்தின் அலகு
அ) மீட்டர்
ஆ) லிட்டர்
இ) வினாடி
ஈ) கிலோகிராம்
விடை:
அ) மீட்டர்
Question 4.
திரவத்தின் பருமனை அளவிட உதவும் கருவிகள்
அ) குடுவைகள்
ஆ) ![]()
இ) பியூரெட்டுகள்
ஈ) அனைத்தும்
விடை:
ஈ) அனைத்தும்
Question 5.
ஒழுங்கற்ற பொருள்களின் பருமனை அளந்தறிய ____ முறை பயன்படுகிறது.
அ) தராசு
ஆ) மின்னணுதராசு
இ) நீர் இடப்பெயர்ச்சி
ஈ) மணல் கடிகாரம்
விடை:
இ) நீர் இடப்பெயர்ச்சி
II. சரியா? தவறா? என எழுதுக.
Question 1.
தெரிந்த ஒரு அளவைக் கொண்டு தெரியாத அளவை ஒப்பிடுவது நிறை எனப்படும்.
விடை:
தவறு
Question 2.
நீளம், அகலம் என இருவகையான நீளத்தைப் பயன்படுத்தி பரப்பளவை கணக்கிடலாம்.
விடை:
சரி
Question 3.
மின்னணுத்தராசைப் பயன்படுத்தி மிகத்துல்லியமாக எடையை அளக்கலாம்.
விடை:
சரி
![]()
III. கோடிட்ட இடத்தை நிரப்புக
Question 1.
7875 செ.மீ = ____ மீ ____ செ.மீ
விடை:
78.மீ;75.செ.மீ
Question 2.
1195 மீ = ____ கி.மீ. _____ மீ.
விடை:
1 கி.மீ; 195 மீ
Question 3.
15 செ.மீ 10 மி.மீ = ____ மி.மீ
விடை:
160 மி.மீ
Question 4.
45 கி.மீ 33மீ = _____ மீ
விடை:
45033 மீ
Question 5.
மெட்ரிக் முறை அலகுகள் _____ ஆண்டு ஃபிரெஞ்சு காரர்களால் 1790
விடை:
உருவாக்கப்பட்டது.
IV. பொருத்துக
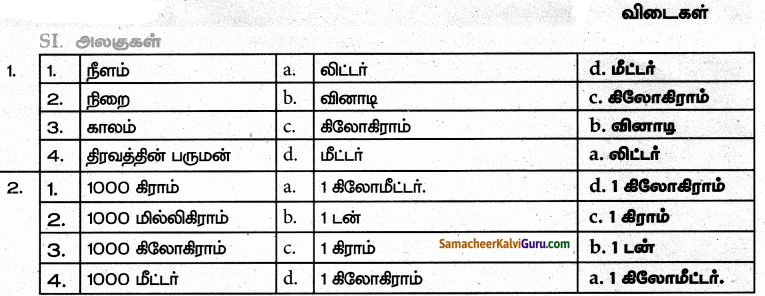
V. பின்வரும் அலகினை ஏறுவரிசையில் எழுதுக.
Question 1.
டன் → கிராம் → கிலோகிராம் → மெட்ரிக் டன்.
விடை:
கிராம் → கிலோகிராம் → டன் → மெட்ரிக் டன்.
VI. மிகக் குறுகிய விடையளி (2 மதிப்பெண்கள்)
Question 1.
பன்னாட்டு அலகு முறை அல்லது SI அலகு என்றால் என்ன?
விடை:
ஒரே மாதிரியான அளவிடும் முறைக்காக உலகம் முழுவதும் உள்ள அறிவியல் அறிஞர்கள் ஏற்றுக் கொண்ட அலகுகளுக்கு பன்னாட்டு அலகு முறை அல்லது SI அலகு என்று பெயர்.
![]()
Question 2.
நிறை எடை வேறுபடுத்துக?
விடை:

Question 3.
மிகக் குறுகிய நீளங்களை அளக்க உதவும் அளவீடுகள் யாவை?
விடை:
- மில்லி மீட்டர்
- சென்டி மீட்டர்
Question 4.
அடிப்படை இயற்பியல் அளவுகள் யாவை?
விடை:
1- நீளம்;
2 – நிறை;
3 – காலம்,
4 – மின்னோட்டம்,
5 – வெப்பநிலை,
6 – ஒளிச்செறிவு,
7 – பொருளின் அளவு
Question 5.
முற்காலத்தில் மக்கள் பகல் நேரத்தை கணக்கிட பயன்படுத்திய கடிகாரங்கள் யாவை?
விடை:
1- மணல் கடிகாரம்;
2 – சூரியக் கடிகாரம்
Question 6.
நேரத்தை துல்லியமாக கணக்கிட உதவும் கடிகாரங்கள் யாவை?
விடை:
1 – மின்ன ணு கடிகாரம்;
2 – நிறுத்துக் கடிகாரம்
Question 7.
ஒடோமீட்டர் என்றால் என்ன?
விடை:
தானியங்கி வாகனங்கள் கடக்கும் தொலைவைக் கணக்கிட உதவும் கருவி.
VII. விரிவான விடை எழுதுக.
Question 1.
அளவு கோலைப் பயன்படுத்தி அளக்கும் போது ஏற்படும் கவனிக்க வேண்டிய வழிமுறைகளைக் கூறு?
விடை:
- அளக்க வேண்டிய பொருளை எப்போதும் அளவு கோலின் சுழியில் “O” பொருந்துமாறு வைக்க வேண்டும்.
- அளக்க வேண்டிய பொருளை அளவு கோலுக்கு இணையாக வைக்க வேண்டும்
- எப்போதும் சுழியிலிருந்து (‘O’) அளவிட வேண்டும்.
- முதலில் பெரிய பிரிவுகளையும் (செ.மீ) பிறகு சிறிய பிரிவு (மி.மீ) களையும் அளவிட வேண்டும்
- அளவுகளைக் குறிக்கும் போது பெரிய அளவுகளை முதலிலும், அதன் பின் புள்ளி வைத்த பின் சிறிய அளவுகளைக் குறிக்க வேண்டும்.
எ.கா. ஒரு பென்சிலின் நீளம் 6 செ.மீ, 2 மி.மீ என்றால் (6.2 செ.மீ)
![]()
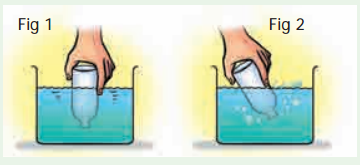
Question 2.
ஒரு ஒழுங்கற்ற வடிவம் கொண்ட கல்லின் பருமனை எவ்வாறு காண்பாய்?
விடை:
- அளவுகள் குறிக்கப்பட்ட ஒரு உருளை வடிவ குவளையில் 50 மி.லி அளவு வரை நீரால் நிரப்பவும்.
- கன அளவு காண வேண்டிய கல்லை ஒரு நூலில் கட்டி ஜாடியில் உள்ள நீரினுள் அடிமட்டம் வரை மெதுவாக விடவும்.
- இப்போது ஜாடியில் நீர்மட்டம் உயர்ந்துள்ளது. இதன் நீர்மட்டம் 75 மி.லி.
- கல் நீரை இடப்பெயர்ச்சி செய்ததால், நீர் மட்டம் உயர்ந்துள்ளது.
- இடப்பெயர்ச்சி செய்த நீரின் அளவே கல்லின் பருமனாகும்.
மனவரைபடம்