You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 1 Chapter 1 Measurements
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Measurements Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
The girth of a tree can be measured by
(a) metre scale
(b) metre rod
(e) plastic ruler
(d) measuring tape
Answer:
(d) measuring tape
Question 2.
The conversion of 7 m into cm gives
(a) 70 cm
(b) 7 cm
(c) 700 cm
(d) 7000 cm
Answer:
(c) 700 cm
Question 3.
Quantity that can be measured Is called
(a) Physical quantity
(b) Measurement
(c) unit
(d) motion
Answer:
(a) Physical quantity
Question 4.
Choose the correct one
(a) km > mm > cm > m
(b) km > mm > m > cm
c) km > m > cm > mm
(d) km > cm > m > mm
Answer:
(c) km > m > cm > mm
Question 5.
While measuring length of an object using a ruler, the position of your eye should be
(a) Left side of the point.
(b) Vertically above the point where the measurement is to be taken.
(c) Right side of the point
(d) Any where according to one’s convenience.
Answer:
(b) Vertically above the
![]()
II. True or False.
- We can say that mass of an object is 126 kg.
- Length of one’s chest can be measured by using metre scale.
- Ten millimetres makes one centimetre.
- A hand span is a reliable measure of length.
- The SI system of units is accepted everywhere in the world.
Answers:
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
![]()
III. Fill in the blanks.
- SI Unit of length is symbolically represented as _____
- 500 gm = _____ kilogram
- Distance between Delhi and Chennai can be measured in _____
- 1 m = _____ cm.
- km = _____ m.
Answers:
- m
- 0.5
- Kilometre
- 100
- 5000
![]()
IV. Analogy
Question 1.
Sugar: Beam balance; Lime juice?
Answer:
Measuring Jar.
Question 2.
Height of a person : cm; length of your sharpened pencil lead?
Answer:
mm (mull metre)
Question 3.
Milk: volume; vegetables?
Answer:
mass
![]()
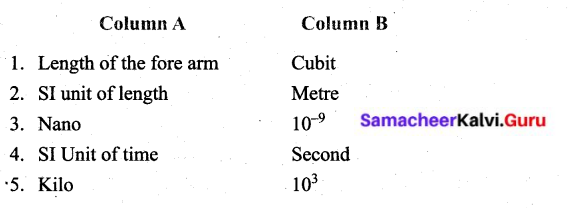
V. Match the following :
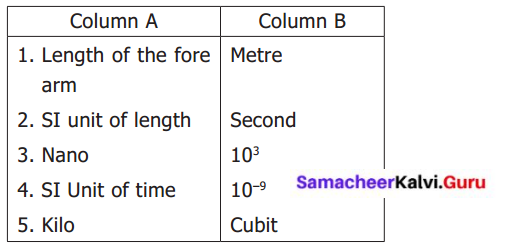
Answer:
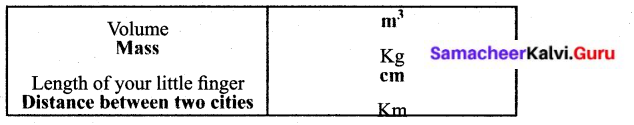
VI. Complete the given table
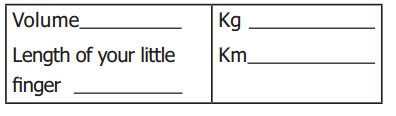
Answer:
VII. Arrange in increasing order of unit.
Question 1.
1 Metre, 1 centimetre, 1 kilometre, and 1 millimetre.
Answer:
1 millimetre < 1 centimetre < 1 Metre < 1 kilometre.
VIII. Find the answer for the following questions within the grid.
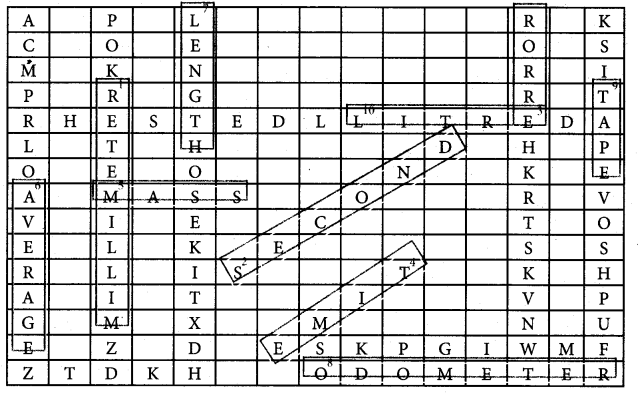
- 10-3 is one _____
- SI Unit of time _____
- Cross view of reading for a measurement leads to _____
- _____ is the one what a clock reads.
- _____ is the amount of substance present in an object
- _____ can be taken to get the final reading of the recordings of different of students for a single measurement.
- _____ is a fundamental quantity.
- _____ shows the distance covered by an automobile.
- A tailor use _____ to take measurements to stitch a cloth.
- Liquids are measured with this physical quantity.
Answers:
- Millimetre
- second
- error
- Time
- Mass
- Average
- Length
- Odometer
- Tape
- Litre
![]()
IX. Answer in a word or two.
Question 1.
What is the full form of SI system?
Answer:
An international system of unit
Question 2.
Name any one instrument used for measuring mass.
Answer:
Beam balance.
Question 3.
Find the odd one out: Kilogram, millimetre, centimetre, nanometre.
Answer:
Kilogram
Question 4.
What is the SI Unit of mass?
Answer:
Kilogram.
Question 5.
What are the two parts present in a measurement?
Answer:
- multiple
- sub
![]()
X. Answer in a sentence or two.
Question 1.
Define measurement.
Answer:
The comparison of an unknown quantity with some known quantity is known as measurement.
Question 2,
Define mass?
Answer:
Mass is the measure of the amount of matter in an object.
Question 3.
The distance between two places is 43.65 km. Convert it into metre and cm. 0
Answer:
(a) Convert km into metre
1 km = 1000m
∴ 43.65 km = 43.65 × 1000 = 43650.00 = 43650
= 43650 m.
(b) Convert km into cm.
1 km = 1000 m
1 m = 100 cm
1 km = 1000 × 100 cm
1 km = 100000 cm
∴ 43.65 km = 43.65 × 100000 = 4365000.00
= 4365000 cm.
Question 4.
What are the rules to be followed to make an accurate measurement with scale?
Answer:
- To avoid the parallax error.
- Your eye must be exactly in front of vertically above the point where the measurement has to be taken.
![]()
XI. Solve the following.
Question 1.
The distance between your school and your house is 2250 m. Express this distance in kilometre.
Answer:
Distance between school and house is 2250 m.
1000 m = 1 km
∴ 2250 m = 2250 ÷ 1000 = 2.25 km.
Question 2.
While measuring the length of a sharpened pencil, reading of the scale at one end is 2.0 cm and at the other end is 12.1 cm. What is the length of the pencil?
Answer:
The difference between the two readings is the length of the pencil.
= 12.1 cm – 2.0 cm
= 10.1 cm or 10 cm and 1 mm.
![]()
XII. Write in detail.
Question 1.
Explain two methods those you can use to measure the length of a curved line.
Answer:
Measuring the length of a curved line, by two methods.
First method – using a string.
- Draw a curved line AB on the paper.
- Place a string along the curved line.
- Make sure that the string covers e very bit of the curved line.
- Mark the points where the curved line begins and ends on the string.
- Now stretch the string along the length of a meter scale.
- Measure the distance between two markings of the string.
- This will give the length of a curved line.
Second method – using a divider.
- Draw a curved line AB on a paper.
- Separate the legs of the divider by 0.5 cm or 1 cm using a ruler.
- Place it on the curved line starting from one end. Mark the position of the other end.
- Move it along the line again and again cutting the line into number of segments of equal lengths.
- The remaining parts of the line can be measured using a scale.
- Count the number of segments.
- Length of the line = (No. of segments × length of each segment) + length of the left over part.
Question 2.
Fill in the following chart.

Answer:
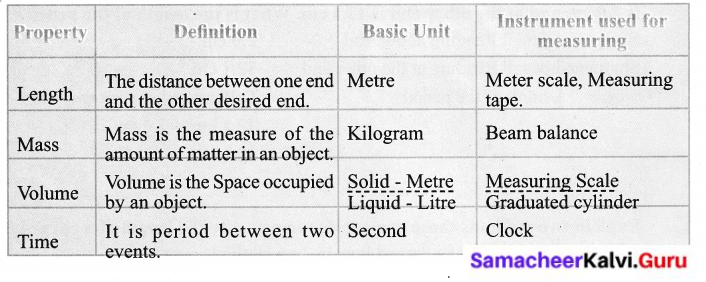
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Measurements Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
In which SI unit, you can measure you height?
(a) Kilogram
(b) Litre
(c) Metre
(d) Second
Answer:
(c) Metre
Question 2.
What is the unit of electric current in SI system?
(a) Kelvin
(b) Ampere
(c) seconds
(d) Volt.
Answer:
(b) Ampere
Question 3.
_____ is used to measure the accurate time of the activity.
(a) Clock
(b) Watch
(c) Stop clock
(d) Sundial
Answer:
(c) Stop dock
Question 4.
These are the measurements used in measuring the volume of liquid.
(a) cylinder
(b) pipettes
(c) burettes
(d) All.
Answer:
(d) All
Question 5.
S.I unit for Volume is _____
(a) m2
(b) m
(c) m3
(d) none
Answer:
(c) m3
Question 6.
Twenty decimetre is equal to _____
(a) 2 km
(b) 20 cm
(c) 2 metre
(d) 200 mm
Answer:
(c) 2 metre
Question 7.
_____ is used to measure mass.
(a) Stop clock
(b) Beam balance
(c) Sundial
(d) Graduated cylinder
Answer:
(b) Beam balance
Question 8.
The metric system of units was created by the _____ in 1790.
(a) Greek
(b) Australians
(c) Russians
(d) French
Answer:
(d) French
Question 9.
The moon’s gravitational pull is one _____ of the earth’s pull.
(a) seventh
(b) sixth
(c) fifth
(d) fourth
Answer:
(b) Sixth
![]()
II. Find whether the following sentences are true or false. If false Correct the statement.
Question 1.
Kerosene is measured with the help of the graduated cylinder.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Length is a fundamental quantity.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
On moon, the gravitational force is greater than earth.
Answer:
False. On moon the gravitational force is lesser than earth.
Question 4.
An electronic balance is a device used to find accurate mass.
Answer:
True.
Question 5.
Speedometer is a device used for indicating distance travelled by an automobile.
Answer:
False. Odometer js a device used for indicating distance travelled by an automobile.
Question 6.
A ruler or scale used now a days to measure length was invented by William Bedwell.
Answer:
True.
Question 7.
Length, mass and time are some of the derived quantities.
Answer:
False. Length, mass, and time are some of the fundamental quantities.
Question 8.
Leaves and piece of paper are heavier things.
Answer:
False. Leaves and piece of paper are lighter things.
Question 9.
National physical laboratory is located in Delhi.
Answer:
True.
![]()
III. Analogy.
Question 1.
Potatoes : Kilogram; Water?
Answer:
Litre.
Question 2.
Stop clock : accurate time; _______ : accurate weight
Answer:
Electronic balance.
Question 3.
Mass : Balance; Length?
Answer:
measuring tape.
Question 4
Amount of matter: mass; Gravitational Pull?
Answer:
Weight.
![]()
IV. Answer the following questions in one or two words.
Question 1
What are the materials needed to find the length of a banana?
Answer:
A meter scale, a string or thread, sketch pen..
Question 2.
What formula is used to measure area of your class room?
Answer:
My class room area = Length × Breadth
Question 3.
Give an example of a device used to find the accurate measurement of weight.
Answer:
Electronic balance.
Question 4.
In earlier days, which instruments are used to measure time?
Answer:
Sand clock and Sun dial.
Question 5.
What are the clocks used to measure a smaller duration of time?
Answer:
Electronic clock, Stop watch.
Question 6.
Who invented a ruler or scale?
Answer:
William Bedwell.
Question 7.
Which alloy is used to make the standard metre rod?
Answer:
An alloy of Platinum and iridium.
![]()
V. Match the following
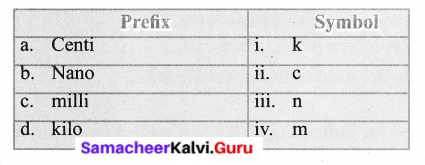
Answers:
a. ii
b. iii
c. iv
d. i
VI. Answer the following In one or two sentences:
Question 1.
What is the international system of units or SI units?
Answer:
For the sake of uniformity all over the world, we have adopted a common set of units to express measurements that are called as an International system of units or SI units.
Question 2.
Give some examples of larger length measures.
- Height of the building,
- Length of a banner,
- Height of lamp post.
Question 3.
What are the unit of measurements of very small length?
Answer:
- Millimetre
- centimetre.
Question 4.
What is meant by parallax?
Answer:
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight.
Question 5.
What are the clock used by ancient people to measure day time?
Answer:
- sand clock
- sun clock.
Question 6.
Where are the electronic balances used?
Answer:
Electronic balances are used in grocery shops and jeweleries.
Question 7.
What is odometer?
Answer:
It is a device used for indicating distance travelled by automobile.