You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Solutions Term 1 Chapter 2 Introduction to Algebra Ex 2.3
Miscellaneous Practice Problems
![]()
Question 1.
Complete the following pattern.
9 – 1 =
98 – 21 =
987 – 321 =
9876 – 4321 =
98765 – 54321 =
What comes next?
Solution:
9 – 1 = 8
98 – 21 = 77
987 – 321 = 666
9876 – 4321 = 5555
98765 – 54321 = 44444
Next will be 987654 – 654321 = 333333
Question 2.
A piece of wire is ’12s’ cm long. What will be the length of the side, if it is formed as
(i) an equilateral triangle
(ii) a square?
Solution:
(i) 4s
(ii) 3s
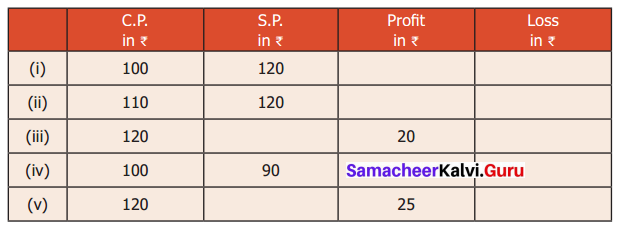
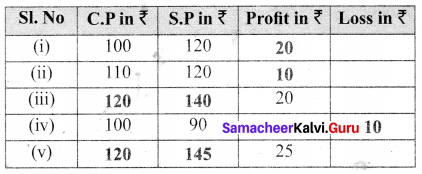
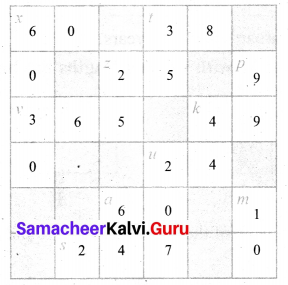
Question 3.
Identify the value of the shapes and figures in the table given below the verify their addition horizontally and vertically.
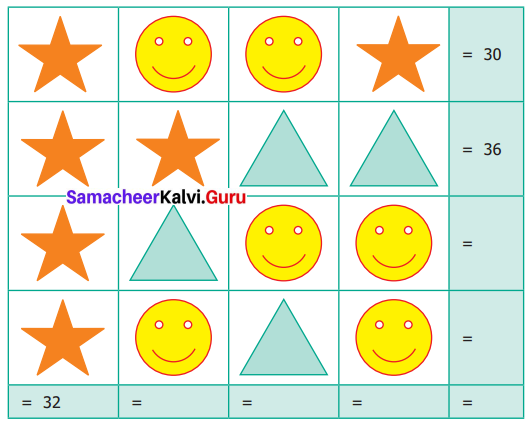
Solution:
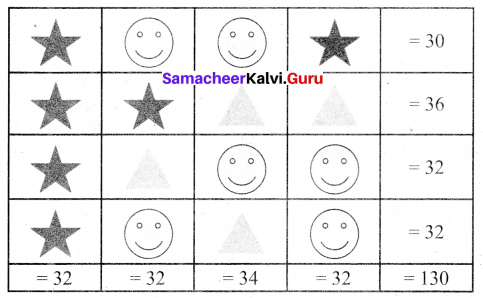
![]()
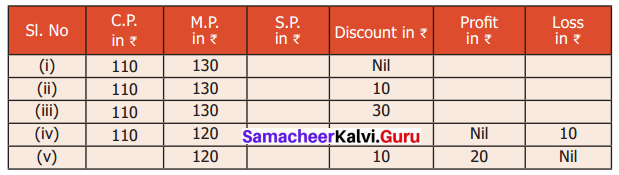
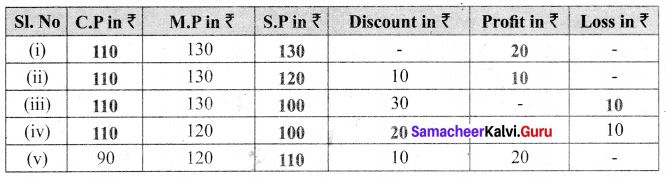
Question 4.
The table given below shows the results of the matches played by 8 teams in a Kabaddi championship tournament.
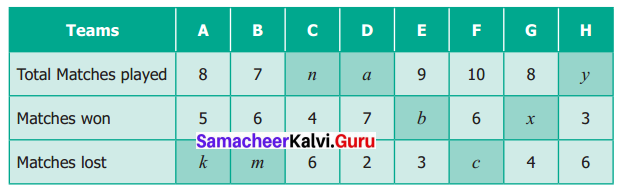
Find the value of all the variables in the table given above.
Solution:
We know that
Total matches played = Matches wont + Matches lost.
5 + k = 8
⇒ k = 3
7 + 2 = a
a = 9
7 = 6 + m
⇒ m = 1
b + 3 = 9
⇒ b = 6
4 + 6 = n
⇒ n = 10
6 + c = 10
⇒ c = 4
x + 4 = 8
⇒ x = 4
3 + 6 = y
⇒ y = 10
Challenging Problem (Text book Page No. 53)
Question 5.
Gopal is 8 years younger to Karnan. If the sum of their ages is 30, how old is Karnan?
Solution:
Let Kaman’s age be x years
Gopal age is x – 8 years
Given sum of their ages is 30. i.e, x + (x – 8) = 30
Now we will form the table to find their sums = 30.
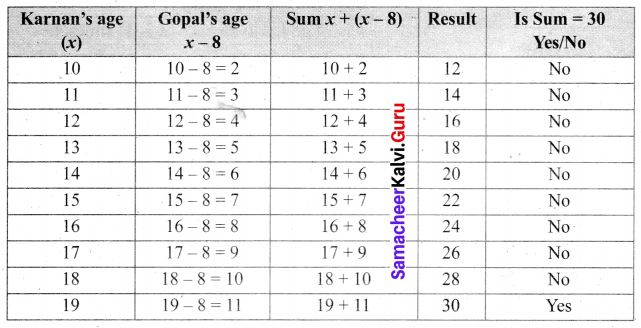
For x = 19 (Karnan’s age)
the sum = 30
Kaman’s age = 19 years.
![]()
Question 6.
The rectangles made of identical square blocks with varying lengths but having only two square blocks as width are given below.
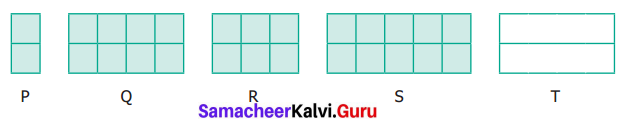
(i) How many smallest squares are there in each of the rectangles P, Q, R and S?
(ii) Fill in the boxes.
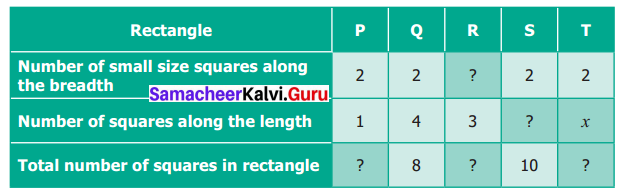
Solution:
(i) No. of smallest squares in P, Q, R and S are 2, 8, 6 and 10 respectively.
(ii)

Question 7.
Find the variables from the clues given below and solve the crossword puzzle.
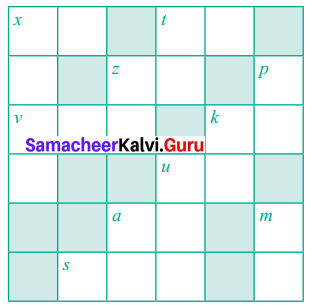
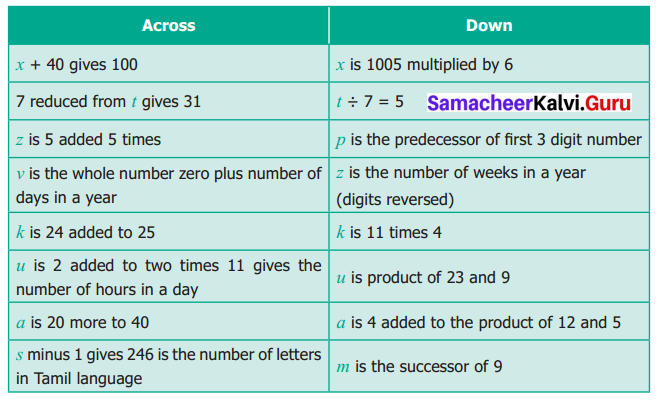
Solution:
![]()
Please Check This Post: