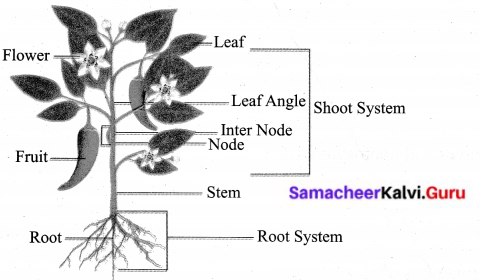
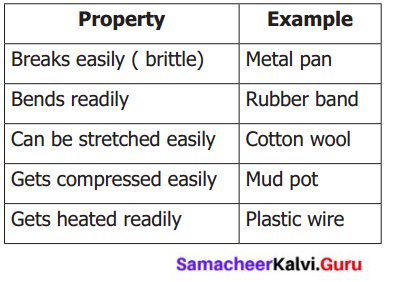
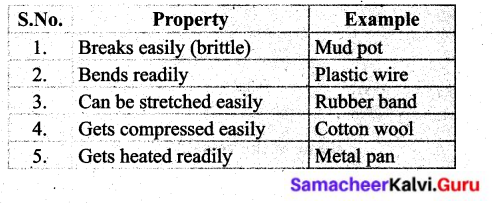
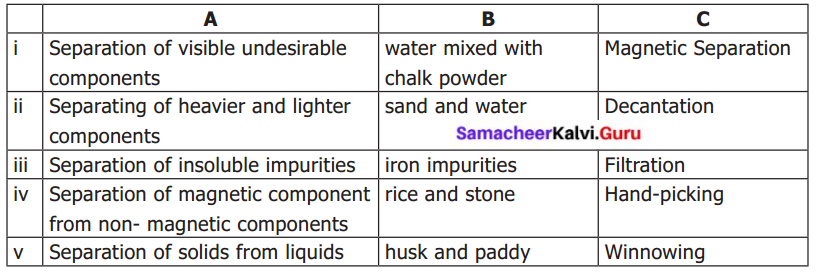
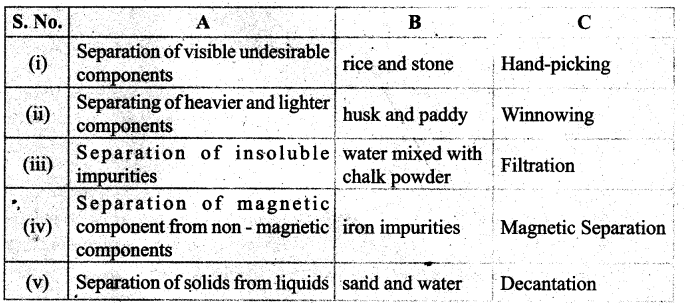
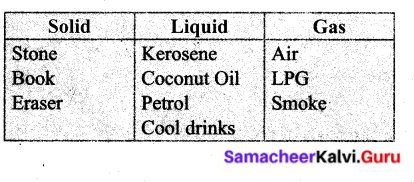
Students can Download English Lesson 2 The Apple Tree and The Farmer Questions and Answers, Summary, Activity, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th English Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th English Solutions Term 1 Supplementary Chapter 2 The Apple Tree and The Farmer
A. Read the following statements. Say True or False.
- The farmer had spent his childhood playing under the tree.
- The farmer felt the space could be used to build a house.
- The apple tree requested the farmer not to cut it.
- All the little animals were happy about the farmer’s decision.
- The apple tree was home for all the little animals.
Answers:
- True
- False
- False
- False
- True
B. Identify the speaker / character
The Apple Tree And The Farmer Questions And Answers Question 1.
Please don’t cut the tree.
Answer:
Farmer’s daughter and her friends.
The Apple Tree And The Farmer Question 2.
You can enjoy the shade when you become old.
Answer:
Farmer’s daughter and her friends.
The Apple Tree And The Farmer Summary Question 3.
I promise that I will never cut this tree.
Answer:
Farmer to his daughter.
Identify The Character/Speaker:Additional
- ‘We play here just like you did’. – The farmer’s daughter and her friends.
- He wanted his little girl to have the childhood that he had had. – The farmer.
- ‘You and your friends will have your tree and your playground’. – The farmer to his daughter.
- He lived in a village, up in the hills, beside a forest’. The farmer.
- They climbed the tree and swung on it. – The farmer and his friends.
C. Choose the right option.
1. The animals became worried because
(a) there was heavy rain.
(b) the farmer began to chop the tree.
(c) the farmer chased them away.
(d) the tree became old.
Answer:
(b) the farmer began to chop the tree.
2. The farmer’s daughter and her friends came out because
(a) they wanted to play under the tree.
(b) they heard the commotion of the creatures.
(c) the farmer called them.
(d) they heard the farmer’s voice.
Answer:
(b) they heard the commotion of the creatures.
3. The farmer promised that he would
(a) grow more trees.
(b) provide shelter to all the little animals.
(c) not cut the tree.
(d) be thankful to the children.
Answer:
(c) not cut the tree.
Apple Tree And The Farmer MCQ; Additional
6th Standard The Apple Tree And The Farmer Questions 1.
For many years, the farmer and his family
(a) enjoyed living in the village
(b) enjoyed the tastiest apples from the tree
(c) enjoyed farming and cultivation
Answer:
(b) enjoyed the tastiest apples from the tree
The Apple Tree Was Home For All The Little Animals Question 2.
The farmer felt he could use the wood from the tree
(a) to build a new room in his house
(b) to build a new boat
(c) to sell it in the market
Answer:
(a) to build a new room in his house
The Apple Tree Questions And Answers Questions 3.
The farmer decided to cut the tree because
(a) the tree was big and its branches were entering the house
(b) the tree was dying
(c) the tree bear fewer and fewer fruits
Answer:
(c) the tree bear fewer and fewer fruits
The Apple Tree And The Farmer Book Back Answers Questions 4.
When the farmer began chopping the tree , the farmer’s daughter and her friends
(a) pleaded him not to cut the tree
(b) helped the farmer to cut the tree
(c) collected the woods from the chopped tree.
Answer:
(a) pleaded him not to cut the tree
The Apple Tree And The Farmer Lesson Plan Question 5.
When the farmer bit into the juicy fruit from the tree,
(a) he felt it was bitter in taste
(b) memories of the fun he had as a boy came rushing back
(c) he fainted and fell on the floor.
Answer:
(b) memories of the fun he had as a boy came rushing back
D. Read the passage and answer the following.
All of a sudden, the farmer noticed a small fruit hanging from a branch. It was an apple and looked as delicious as the ones he ate as a boy. He plucked it and bit into the juicy fruit. The memories of the fun he had had as a boy came rushing back. When his daughter saw the changed expression in her father’s face, she started pleading harder.
The Apple Tree And The Farmer Short Summary Questions 1.
What did the farmer notice?
Answer:
The farmer noticed a small fruit hanging from a branch.
The Apple Tree And The Farmer Story Questions 2.
What made him recall his childhood?
Answer:.
The delicious apple made him recall his childhood.
The Apple Tree Complex Class 6 Questions And Answers Question 3.
Why did his daughter start pleading?
Answer:.
When his daughter saw the changed expression in her father’s face, she started pleading harder.
Read The Passage And Answer the Questions; Additional
1. For many years the farmer and his family had enjoyed the tastiest apples from the tree. As a boy the farmer and his friends played hide and seek around the apple tree. In mean time many small animals and birds started living in the tree.
The Apple Tree Complex Questions And Answers Question a.
What did the the farmer and his family enjoy?
Answer:
The farmer and his family had enjoyed the tastiest apples from the tree.
The Apple Tree And The Farmer Story In English Question b.
What is the game mentioned in the passage?
Answer:
The game mentioned in the passage is hide and seek.
Question c.
Who lived in the tree?
Answer:
Many small animals and birds lived in the tree.
2. Once upon a time there was a farmer. He lived in a village, up in the hills, beside a forest. In his farm where he grew many kinds of vegetables, he also had an apple tree. For many years the farmer and his family had enjoyed the tastiest apples from the tree. As a boy, the farmer and his friends played under the apple tree. They played hide and seek around the tree. They climbed the tree and swung on it and in season they plucked and ate the apples.
Question a.
Where did the farmer live?
Answer:
Farmer lived in a village, up in the hills, beside a forest.
Question b.
What did the farmer grow in his farm ?
Answer:
The farmer grew many kinds of vegetables and also had an apple tree in his farm.
Question c.
How did the farmer as a boy and his friends enjoy the apple tree ?
Answer:
As a boy, the farmer and his friends played hide and seek around the tree. They climbed the tree and swung on it and in season they plucked and ate the apples.
3. As the years passed the boy grew into a man. He took over the farm and continued to enjoy ’> the fruits from the tree. In the meantime many small animals and birds started living in the tree. The man’s children and their friends started playing under it. The large and shady apple tree now grew old and was bearing fewer and fewer fruits. It was nice to sit under its shade in the summer but nothing grew under it. The farmer felt the space could be used to grow some vegetables. He also felt he could use the wood to build a new room in his house. Therefore, he decided to cut the tree.
Question a.
What did animals and birds do ?
Answer:
The small animals and birds started living in the tree.
Question b.
What happened to the apple tree?
Answer:
The apple tree grew old and was bearing fewer and fewer fruits.
Question c.
What did the farmer decide to do?
Answer:
The Farmer felt he could use the wood of the apple tree to build a new room in his house. So decided to cut the tree.
4. When the farmer took his axe and began chopping the tree, all the little animals, birds and insects that lived in the tree came rushing down. They started running around in alarm, chirping and squeaking all over the place. The farmer was adamant. He raised his axe and the uproar grew.
Question a.
What did the animals and birds do?
Answer:
When the farmer took the axe and began to cut the tree, the animals, birds and insects that lived in the tree came rushing down.
Question b.
How did the animals and birds react when the farmer chopped the tree ?
Answer:
The animals ,birds and insects started running around in alarm, chirping and squeaking all over the place.
Question c.
What did the farmer do then ?
Answer:
As the farmer was adamant, he raised his axe and the uproar grew.
5. All of a sudden, the farmer noticed a small fruit hanging from a branch. It was an apple and looked as delicious as the ones he ate as a boy. He plucked it and bit into the juicy fruit. The memories of the fun he had had as a boy came rushing back. When his daughter saw the changed expression in her father’s face, she started pleading harder.
Question a.
What did the former notice?
Answer:
Suddenly, the farmer noticed a small fruit hanging from a branch.
Question b.
How did the apple look like ?
Answer:
The apple looked delicious like the ones the farmer had eaten when he was a boy.
Question c.
What came to Farmer’s mind when he ate the apple ?
Answer:
The farmer plucked the apple and bit into the juicy fruit; The memories of the fun he had had as a boy came rushing back.
6. The farmer put down his axe. He understood that the tree was home to many lovely animals and provided them with so many things. He wanted his little girl to have the childhood that he had had. He threw away the axe and said to his daughter, “I promise that I will never cut this tree. You and your friends will have your tree and your playground.”
Question a.
What did the Farmer do ?
Answer:
The farmer put down the axe.
Question b.
What did the former promise his daughter ?
Answer:
The farmer promised his daughter that he will never cut the tree.
Question c.
What is the moral of the story ?
Answer:
The moral of the story is we should not cut down the tree. We should try to grow more trees and preserve the trees for future generations to come.
E. Rearrange the jumbled sentences.
1. He did not listen to their cries.
2. The farmer continued cutting the tree.
3. His childhood memories made him realize his mistake.
4 He decided to cut the tree thinking that it was useless.
5. The taste of the apple brought back his childhood memories.
6. The farmer had an old apple tree in his garden.
7. All the little animals in the tree pleaded with him.
8. He spent all his childhood playing under the apple tree.
Answer:
(6, 8, 4, 7, 1, 2, 5, 3)
6. The farmer had an old apple tree in his garden.
8. He spent all his childhood playing under the apple tree.
4. He decided to cut the tree thinking that it was useless.
7. All the little animals in the tree pleaded with him.
1. He did not listen to their cries.
2. The farmer continued cutting the tree.
5. The taste of the apple brought back his childhood memories.
3. His childhood memories made him realize his mistake.
Rearrange The Following Jumbled Sentences : Additional
A. 1. We play here just like you did. These small animals live here.
2. If you cut the tree, where will they go? You can enjoy the shade when you become old.
3. The farmer’s daughter and her friends began to plead with him.
4. It is a beautiful tree.”
5. They gathered around the farmer and said, “Please don’t cut the tree.
Answer:
(3, 5,1, 2, 4)
3. The farmer’s daughter and her friends began to plead with him.
5. They gathered around the farmer and said, “Please don’t cut the tree.
1. We play here just like you did. These small animals live here.
2. If you cut the tree, where will they go? You can enjoy the shade when you become old.
4. It is a beautiful tree.”
B. 1. Rather he felt the tree had outlived its usefulness and should be cut down.
2. He did not think about the wonderful times he and his friends had playing around the tree or the delicious apples they ate.
3. Therefore, he decided to cut the tree.
4. He also felt he could use the wood to build a new room in his house.
5. The farmer felt the space could be used to grow some vegetables.
Answer:
(5. 4, 3, 2,1)
5. The farmer felt the space could be used to grow some vegetables.
4. He also felt he could use the wood to build a new room in his house.
3. Therefore, he decided to cut the tree.
2. He did not think about the wonderful times he and his friends had playing around the tree or the delicious apples they ate.
1. Rather he felt the tree had outlived its usefulness and should be cut down.
F. Think and answer :
Question 1.
Which part of the story do you like? why?
Answer:
I like the last part of the story because the farmer realizes his mistake and puts down his axe. He understands that the tree was a home to many lovely animals and provided them so many things.
Question 2.
If the little animals become homeless, what will happen?
Answer:
They will become desperate, suffer and sometimes die.
Question 3.
What made the farmer realise his mistakes?
Answer:
The memories of the fun, he had had as a boy came rushing back, when the farmer ate a juicy apple, which was hanging from a branch. This made the farmer realise his mistakes.
Project
G. Look at the table. Read any story. Then fill the table
| Title of the story | The selfish Gaint |
| Name of the author | Oscar wilde |
| No of characters | Two |
| The character you like the most | The little child |
| Main points | The giant built a wall. The little child kissed him. The giant became kind hearted. The boy took him to paradise. |
Connecting To Self
H. Lilly was on a trip to the beach with her friends. Some of her friends carelessly threw plastic bags on the road after eating their snacks. She wants to convince them that what they were doing was not correct and they should be good citizens.
Discuss in your group. What could Lilly say? Role play die conversation with one person being Lilly and the other a friend.
(To be done by the students)
Steps To Success
I. For each item write the word that has the same relationship as the pair on the left.
Example: desert : dry :: valley : fertile
Question 1.
creeper : tendril :: tree : ?
(a) leaf
(b) bough
(c) flower
(d) fruit
Answer:
(b) bough
Question 2.
river : flow :: mountain : ?
(a) beautiful
(b) high
(c) trees
(d) still
Answer:
(d) still
Question 3.
breeze : gentle :: storm: ?
(a) violent
(b) wind
(c) sea
(d) rain
Answer:
(a) violent
Question 4.
mango : sweet :: lime: ? ‘
(a) fruit
(b) sour
(c) tree
(d) juice
Answer:
(b) sour
Question 5.
hark : timber :: flower : ?
(a) branch
(b) plant
(c) fruit
(d) stem
Answer:
(c) fruit
The Apple Tree and The Farmer Additional Questions
I. What is the logical sequence for these words? Tick the right option
Questions 1.
1. leaves, 2. fruit , 3. seed, 4. flowers, 5. root
(a) 2,4,5,1,3, (b) 3,5,1,4,2, (c) 1,2,3,4,5, (d) 5,3,1,2,4
Answer:.
(b) 3,5,1,4,21
Questions 2.
1. Timber, 2. Furniture, 3. Sapling, 4. Tree, 5. wood
(a) 2,1,4,5,3, (b) 5,2,3,1,4, (c) 3,4,5,1,2, (d) 5,3,1,4,2
Answer:
(c) 3,4,5,1,21
Question 3.
1. Sow, 2. Weed, 3. Water, 4. Harvest, 5. Plough
(a) 1,3,5,2,4, (b) 5,1,3,2,4, (c) 3,5,4,2,1, (d) 2,3,4,1,5
Answer:
(b) 5,1,3,2,4
Question 4.
1. Plant, 2. Butterfly, 3. Flower, 4. Honey, 5. Seed
(a) 5,1,3,4,2, (b) 3,4,5,2,1, (c) 5,4,2,3,1, (d) 2,3,4,5,1
Answer:
(a) 5,1,3,4,21
Question 5.
1. Paper, 2. Bamboo, 3. Book, 4. Bulb, 5. Sapling
(a) 2,4,5,1,3, (b) 3,4,5,2,1, (c) 5,2,4,1,3, (d) 4,5,2,3,1
Answer:
(c) 5,2,4,1,3
II. Paragraph Questions.
Question 1.
How did the farmer enjoy his childhood days ?
Answer:
The farmer lived in a village, up in the hills, beside a forest. In his farm, he grew many kinds of vegetables and an apple tree. For many years, the farmer his family had enjoyed the tastiest apples from the tree. As a boy, he played under the apple tree with his friends. They played hide and seek, climbed the tree, swung on it and ate the tasty apples.
Question 2.
Why did the’ farmer decided to- cut, the apple tree?
Answer:
The large and the shady apple tree grew old and w’as bearing fewer and fewer fruits. It gave them shade but nothing grew under it. The farmer felt that the space could be used to grow some vegetables. He also felt that he could use the wood to build a new room in his house. Therefore, he decided to cut the tree. He did not think about the wonderful times, he and his friends had, playing around the tree or the delicious apples, they ate. Rather, he felt that the tree had outlived its usefulness and should be cut down.
Question 3.
What happened, as soon as the farmer took his axe and began to chop the tree?
Answer:
When the farmer took his axe and began chopping the tree, all the little animals, birds and insects that lived in the tree came rushing down. They started running around in alarm, chirping and squeaking all over the place. The farmer was adamant. He raised his axe and the uproar grew. He began to chop the tree harder. All the little animals became desperate and wanted to protect the apple tree at any cost. They ran around in circles making a huge commotion.
Question 4.
Write a paragraph op “Uses of trees”.
Answer:
Trees provide food, notably fruit trees such as apple, pear, apricot, peach, cherry, lemon, orange and grapefruit. They also provide shade and protect us from solar radiation. They offer habitation and food for birds, insects, lichen, etc. They help to prevent flooding and soil erosion. They absorb carbon dioxide and help to slow the rate of global warming.
The Apple Tree and The Farmer Summary
A farmer had an apple tree is his farm. Many small animals and birds lived in that tree. The apple tree grew old and bore less fruits. It gave shade, so his daughter and her friends played under it. The farmer decided to cut the tree for timber and more space to grow vegetables. He took his axe and began chopping. The little animals, birds and insects created commotion and brought his daughter out. The daughter pleaded in vain. The farmer saw a small fruit. He plucked it & tasted and recollected his childhood. The farmer put the axe down and promised his daughter that he would never cut the apple tree.