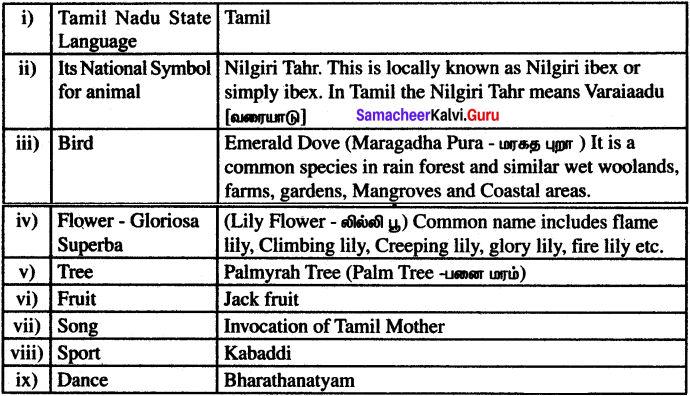
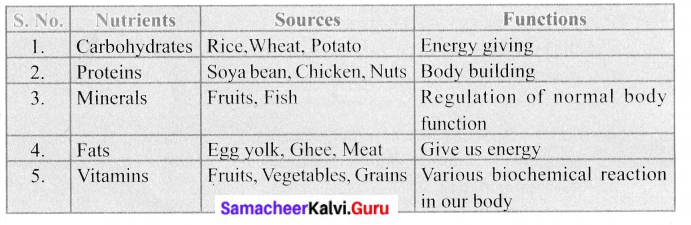
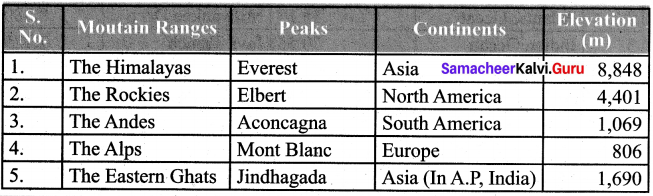
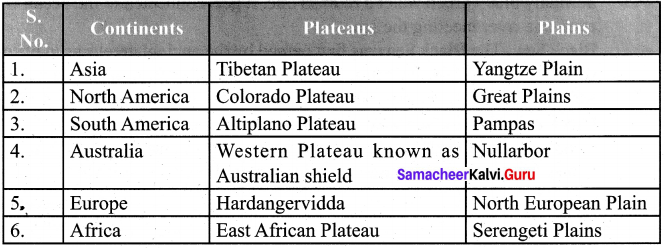
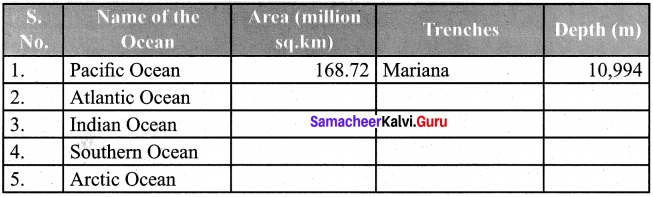
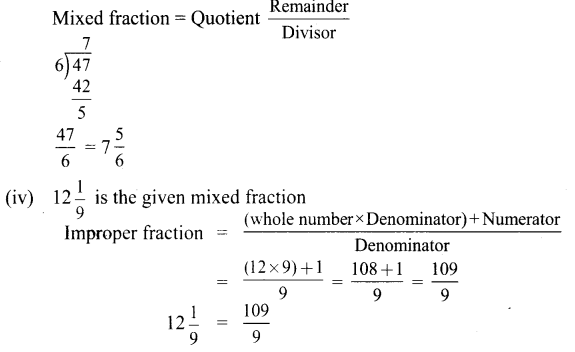
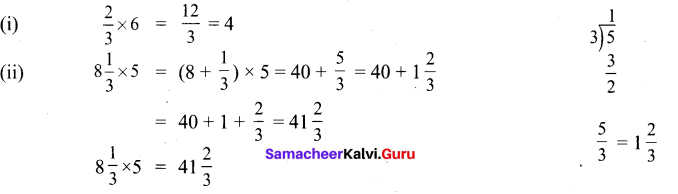
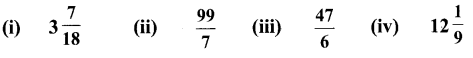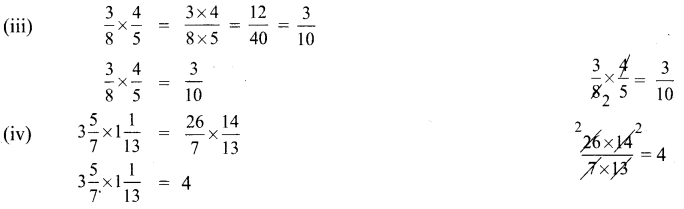Students can Download English Lesson 3 I Dream of Spices Questions and Answers, Summary, Activity, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th English Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th English Solutions Term 1 Poem Chapter 3 I Dream of Spices
I Dream Of Spices Poem Overview
|
No. |
Poem Line |
Explanation |
|
1-2 |
My mother would say: “Little hoy Raj… |
My mother would call out to me ‘Little boy Raj’. |
|
3-6 |
Go to Muthu s and get some cinnamon, betel leaves and ginger and garlic. ” |
She would say to go to Muthu’s shop and get some cinnamon, betel leaves and ginger and garlic. |
|
7-11 |
And so I go to the shops singing all the way and when Muthu asks me what l ‘d want ! rattle off a list: |
And so I would go to the shops, singing all the way and when Muthu asks me what I would want, I recite to him a list of items. |
|
12-13 |
“Sesame seeds, onions tomatoes and pickles” |
Sesame seeds, onions, tomatoes and pickle I forget the things told by my mother. |
|
14-15 |
And back home, Mother twists my ears Ouch! |
And when I go home my mother gets angry and twists my ears. I had forgotten what she has told. I cry in pain. |
I Dream Of Spices Questions And Answers Glossary
cinnamon – the bark of a tree that gives a delicious flavour to food
garlic – a small bulb with a strong taste used in cooking
rattle off – recite
sesame seeds – gingelly seeds
ouch – sound that expresses pain
Read and Understand
A. Answer the following questions.
I Dream Of Spices Poem Summary Question 1.
Who is Raj?
Answer:
Raj is a little boy.
Dream Of Spices Question 2.
Where did Raj’s mother send him?
Answer:
Raj’s mother sent him to a shop.
I Dream Of Spices Poem Question 3.
Who is Muthu?
Answer:
Muthu is the owner of a shop.
I Dream Of Spices Mind Map Question 4.
What did mother ask Raj to buy?
Answer:
His mother asked him to buy some cinnamon, betel leaves, ginger and garlic.
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 6th English Question 5.
What did Raj buy?
Answer:
Raj bought sesame seeds,onions, tomatoes and pickles.
B. Choose the correct answers.
1. Mother called _______
(a) Muthu
(b) Raj
(c) Ram
Answer:
(b) Raj
2. Mother did not ask for _______
(a) cinnamon
(b) cardamom
(c) betel leaves
Answer:
(b) cardamom
Spices Poem Question 3.
Raj did not buy _______
(a) onions and sesame
(b) ginger and garlic
(c) tomato and pickles
Answer:
(b) ginger and garlic
Dream About Spices Appreciating The Poem
C Find an example of alliteration in the poem.
sesame – seeds
what – want
ginger – garlic
D. Listen to the poem read by your teacher.
Read the poem aloud in pairs. One person reads out Raj’s words and the other reads the mother’s. Take turns and read.
(To be done by the students)
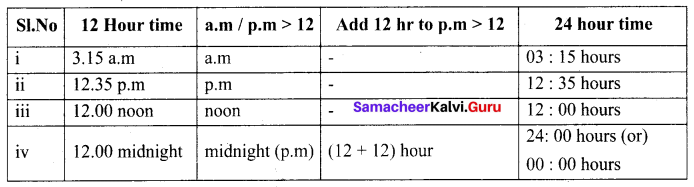
E. Tell the stoiy of the poem In three or four sentences with the help of the pictures given below.

Answer:
- Mother asks her son to go to shop and buy a few items.
- The boy goes to shop and buys different items.
- He returns home.
- Mother sees the items & punishes him.
Writing
F. Read the jumbled lines from the poem and rearrange them in correct order.
|
1. |
cinnamon, betel leaves |
9. tomatoes and pickles” |
|
2. |
and ginger and garlic” |
10. “Sesame seeds, onions |
|
3. |
Go to Muthu’s |
11. I rattle off a list: |
|
4. |
My mother would say : |
12. what I’d want |
|
5. |
and get some |
13. and when Muthu asks me |
|
6. |
“Little boy Raj… |
14. my mother twists my ears |
|
7. |
And so I go to the shops |
15. and back home |
|
8. |
singing all the way |
16 ouch! |
Answer:
4. My mother would say:
6. “Little boy Raj…
3. Go to Muthu’s
5. and get some
1. cinnamon, betel leaves
2. and ginger and garlic.”
7. And so I go to the shops
8. singing all the way
13. and when Muthu asks me
12. what I’d want
11. I rattle off a list:
10. “Sesame seeds, onions
9. tomatoes and pickles”
15. And back home,
14. My mother twists my ears
16. Ouch!
G. Fill in the blanks with different words and write, your own poem.
Your Title for the poem : Me and Mani!
My mom would say :
“Little boy / girl Mano
Go to Mani’s
and get some
Tomato, Brinjai
Carrot and Onion”
And so I go to the Mani’s
singing all the way
and when Mani asks me
what I want
I rattle off a list:
“Biscuit, Candies
Cakes and Wafers”
And back home,
My mom twists my ears
Ouch!
I Dream of Spices Additional Questions
I. Poem Comprehension.
1. My mother would say:
“Little boy Raj….
Go to Muthu s
Question a.
Who would say to go to shop?
Answer:
Raj’s mother.
Question b.
How does she call Raj?
Answer:
Little boy
2. get some
cinnamon, betel leaves
and ginger and garlic. ”
Question a.
Where will he get the items?
Answer:
Muthu’s shop.
Question b.
What should he buy?
Answer:
Cinnamon, betel leaves, ginger, garlic.
3. And so I go to the shops
singing all the way
Question a.
Who goes to shops?
Answer:
Raj goes to shops.
Question b.
How does he go?
Answer:
He goes singing all the way.
4. when Muthu asks me
what I’d want
I rattle off a list:
“Sesame seeds, onions
tomatoes and pickles ’’
Question a.
What does Muthu ask?
Answer:
Muthu asks Raj what he would want.
Question b.
List the things he will buy?
Answer:
Sesame seeds, onions, tomatoes and pickles.
5. And back home,
Mother twists my ears
Ouch!
Question a.
What does mother do?
Answer:
Mother twists Raj’s ears.
Question b.
Why does she do so?
Answer:
He forgot the list of items told by her.
II. Poetic Devices.
1. And back home
Mother twists my ears.
What Is the poetic devise used in the second line?
Answer:
Alliteration – Mother – my
2. Cinnamom, beetal leaves
and ginger and garlic
Pick out the Alliteration.
Answer:
Alliterati on – ginger – garlic.
III. Paragraph Questions.
Question 1.
Describe Raj’s experience in helping his mom at shopping?
Answer:
This is a simple and interesting poem by Raj Arumugam on a little boy’s memory while shopping for his Mom. One-day when Raj’s Mom asks him to buy cinnamon, betel leaves, ginger and garlic but Raj bought sesame seeds, onions, tomatoes and pickles. He gets lovingly punished by his Mom.
Question 2.
How did Raju react when his mother asked him to buy a list of items?
Answer:
Raju’s mother called him and gave him a list of items to be bought from Muthu’s shop. She told him to get some cinnamon, betel leaves, ginger and garlic. But, being a little boy, he goes to the shop, singing happily all the way. When the shop owner asks him what does he want, he forgets what his mother had told him to buy and recites different items like sesame seeds, onions, tomatoes and pickles. When he gets back home, his mother gets angry and twists his ears due to his poor memory.
I Dream of Spices Summary
This is a simple and interesting poem by Raj Arumugam on a little boy’s memory while shopping for his Mom. One-day when Raj’s Mom asks him to buy cinnamon, betel leaves, ginger and garlic but Raj bought sesame seeds, onions, tomatoes and pickles. He gets lovingly punished by his Mom.