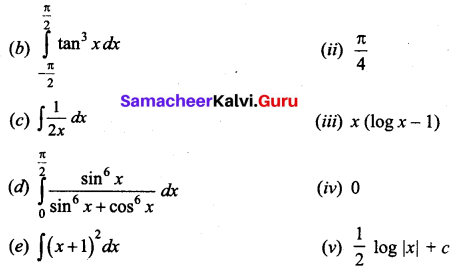
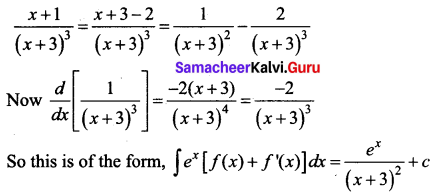
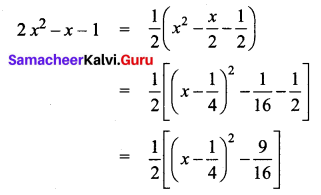
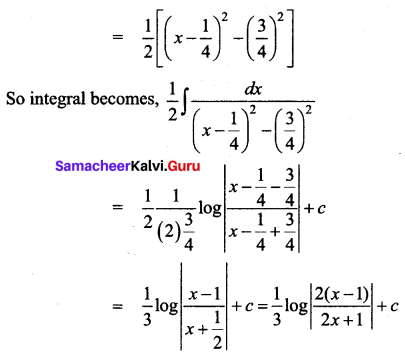
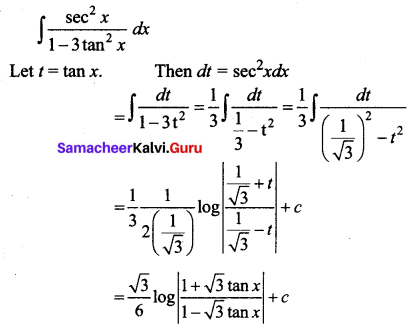
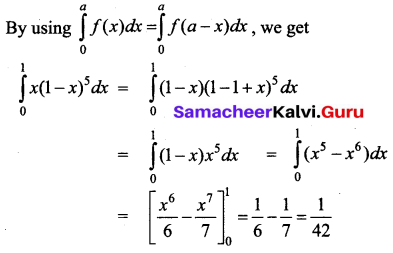
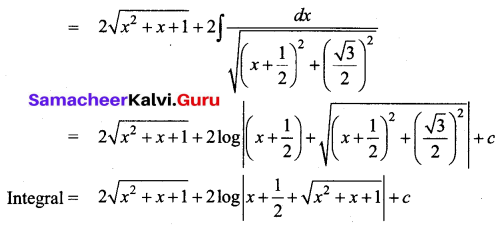
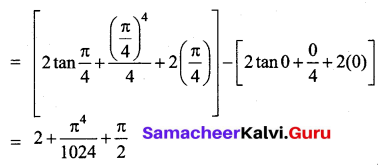
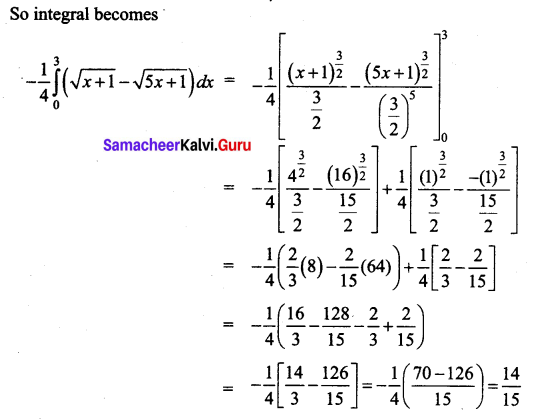
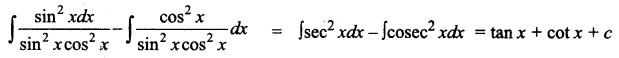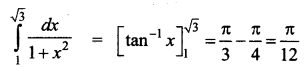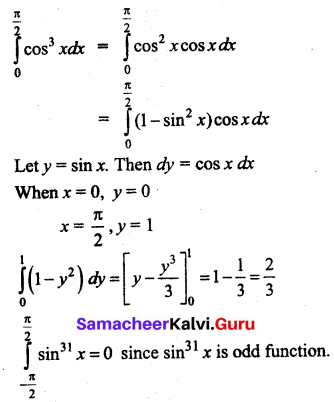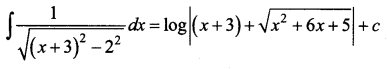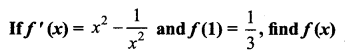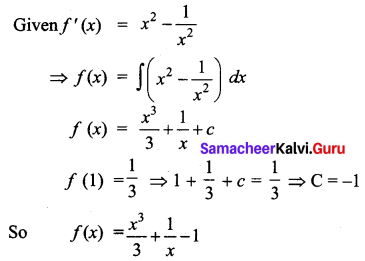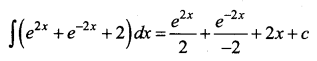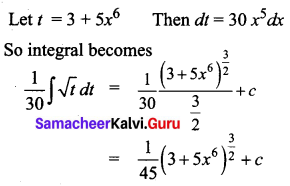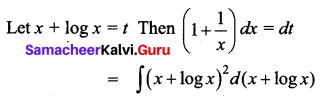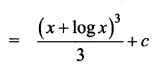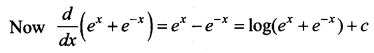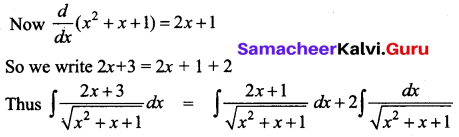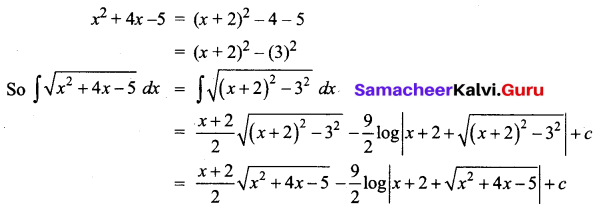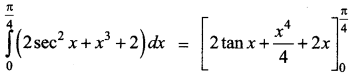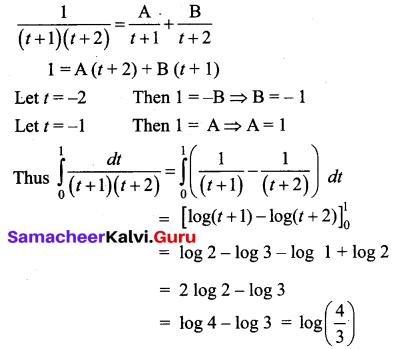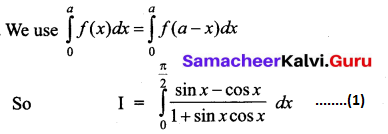Students can download 12th Business Maths Chapter 3 Integral Calculus II Ex 3.1 Questions and Answers, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Integral Calculus II Ex 3.1
Question 1.
Using Integration, find the area of the region bounded the line 2y + x = 8, the x-axis and the lines x = 2, x = 4
Solution:
The given lines are 2y + x = 8, x-axis, x = 2, x = 4
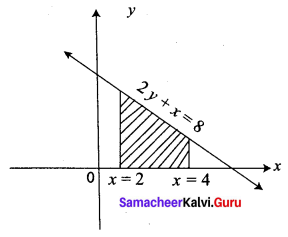

Question 2.
Find the area bounded by the lines y – 2x – 4 = 0, y = 1, y = 3 and the y-axis.
Solution:
Given lines are y – 2x – 4 = 0, y = 1, y = 3, y-axis
y – 2x = 4 = 0 ⇒ x = \(\frac{y-4}{2}\)
We observe that the required area lies to the left to the y-axis
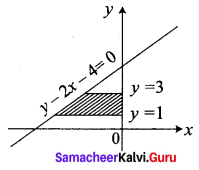
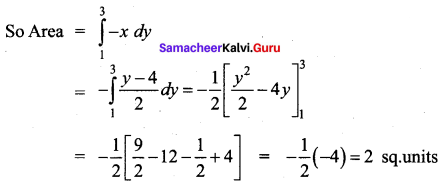
Question 3.
Calculate the area bounded by the parabola y2 = 4ax and its latus rectum.
Solution:
Given parabola is y2 = 4ax
Its focus is (a, 0)
Equation of latus rectum is x = a
The parabola is symmetrical about the x-axis
Required area = 2[Area in the first quadrant between the limits x = 0 and x = a]
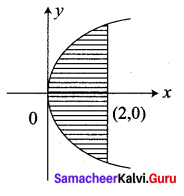
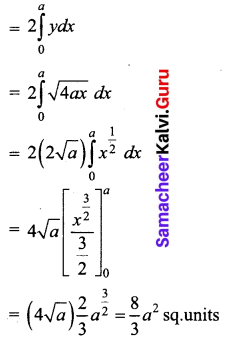
Question 4.
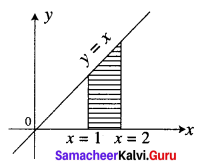
Find the area bounded by the line y = x, the x-axis and the ordinates x = 1, x = 2.
Solution:
Given lines are y = x, x-axis, x = 1, x = 2
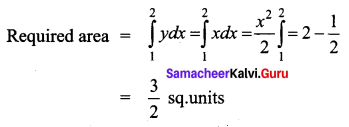
Question 5.
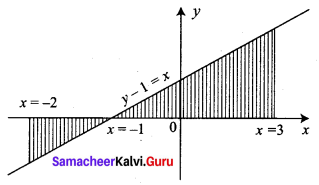
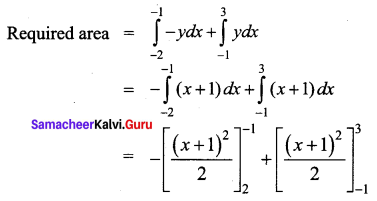
Using integration, find the area of the region bounded by the line y – 1 = x, the x axis and the ordinates x = -2, x = 3
Solution:
Given lines are y – 1 = x, x-axis, x = -2, x = 3
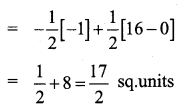
Question 6.
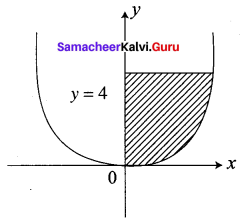
Find the area of the region lying in the first quadrant bounded by the region y = 4x2, x = 0, y = 0 and y = 4.
Solution:
The given parabola is y = 4x2
\(x^{2}=\frac{y}{4}\)
comparing with the standared form x2 = 4ay
\(4 a=\frac{1}{4} \Rightarrow a=\frac{1}{16}\)
The parabola is symmetric about y-axis
We require the area in the first quadrant.
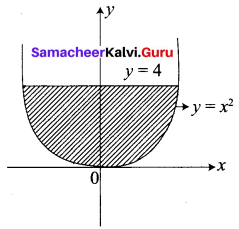
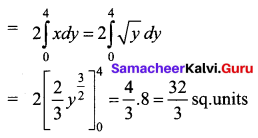
Question 7.
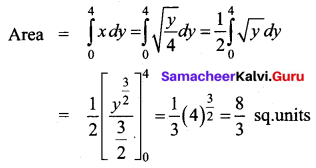
Find the area bounded by the curve y = x2 and the line y = 4
Solution:
Given the parabola is y = x2 and line y = 4
The parabola is symmetrical about the y-axis.
So required area = 2 [Area in the first quadrant between limits y = 0 and y = 4]