Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Commerce Model Question Paper 4 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th commerce Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 11th Commerce Model Question Paper 4 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- questions of Part I, II. III and IV are to be attempted separately
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are objective type questions of one -mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer
- Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Parr III are three-marks questions, These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-marks questions. These are to be answered) in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
Part – I
Choose the correct answer. Answer all the questions: [20 × 1 = 20]
Question 1 .
……………. refers to occupation in which people work for others and get remuneration in the form of wages or salaries.
(a) Employment
(b) Profession
(c) Business
(d) Industry
Answer:
(a) Employment
![]()
Question 2.
The following are the disadvantages of a sole trader.
(i) Limited capital
(ii) Unlimited liability
(iii) Easy formation
(iv) Small capital
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(b) (i) and (ii)
Question 3.
Which of the following is not a function of RBI?
(a) Banker to the Government
(b) Acceptance of deposits
(c) Banker’s Bank
(d) Monopoly of Note issue
Answer:
(b) Acceptance of deposits
Question 4.
Which one of the following is a type of Marine insurance?
(a) Money back
(b) Mediclaim
(c) Health Insurance
(d) Cargo Insurance
Answer:
(d) Cargo Insurance
Question 5.
Registration of partnership is ……………
(a) Compulsory
(b) Optional
(c) Not necessary
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Optional
Question 6.
The relationship between the outsiders and the company is defined in …………….
(a) Prospectus
(b) Articles of Association
(c) Memorundum of Association
(d) Certificate of incorporate
Answer:
(a) Prospectus
![]()
Question 7.
In 1969 ……………. Banks were nationalised in India.
(a) 20
(b) 14
(c) 6
(d) 26
Answer:
(b) 14
Question 8.
MSMEs are important for the nations economy because they significantaly contributed to
(a) industrial production
(b) exports
(c) employment
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 9.
Co-operative fails because of …………….
(a) Unlimited membership
(b) Cash trading
(c) Mismanagement
(d) Loss making
Answer:
(c) Mismanagement
Question 10.
Which is not recent trend in transportation?
(a) Mono rail
(b) Pipeline transport
(c) Bullock cart
(d) Conveyor transport
Answer:
(c) Bullock cart
![]()
Question 11.
Which one of the following is a type of Marine insurance?
(a) Money back
(b) Mediclaim
(c) Hull insurance
(d) Cargo insurance
Answer:
(c) Hull insurance
Question 12.
Match List – I with List – II and select the correct answer using the codes given below:
List – I
(i) Limited liability
(ii) Unlimited liability
(iii) Voluntary organization
(iv) Special Statute
List – II
(1) Public corporation
(2) Co-operatives
(3) Joint stock company
(4) Partnership
Codes:
(a) (i) 1, (ii) 2, (iii) 3, (iv) 4
(b) (i) 3, (ii) 4, (iii) 1, (iv) 2
(c) (i) 3, (ii) 4, (iii) 2, (iv) 1
(d) (i) 2, (ii) 1, (iii) 4, (iv) 3
Answer:
(b) (i) 3, (ii) 4, (iii) 1, (iv) 2
Question 13.
Aids to trade is also called as …………….
(a) Trade
(b) Advertisement
(c) Warehousing
(d) Auxiliaries to trade
Answer:
(d) Auxiliaries to trade
![]()
Question 14.
Dispersion of decision making power to branches / subsidiaries to head office represents …………….
(a) Centralisation
(b) Decentralisation
(c) Power
(d) Integration
Answer:
(b) Decentralisation
Question 15.
Which one of the following is not correctly matched?
(a) Development Banks – Pallavan Grama Bank
(b) Specialised Banks – Private Sector Bank
(c) Regional Rural Banks – EXIM Bank
(d) Indian Bank – Industrial Bank
Answer:
(d) Indian Bank – Industrial Bank
Question 16.
The main benefit of outsourcing is …………….
(a) Productivity
(b) Cost reduction
(c) Skill
(d) Units
Answer:
(b) Cost reduction
Question 17.
Debenture holders are entitled to a fixed rate of …………….
(a) dividend
(b) profits
(c) interest
(d) ratio
Answer:
(c) interest
![]()
Question 18.
An ………………. is a document prepared by the importer and sent to the exporter to buy the goods.
(a) invoice
(b) indent
(c) enquiry
(d) charter party
Answer:
(b) indent
Question 19.
………………. acts as connective link between the producer and the consumer.
(a) Trade
(b) Industry
(c) Commerce
(d) Business
Answer:
(a) Trade
Question 20.
……………….. is the basic principle behind every insurance contract.
(a) Service
(b) Co-operation
(c) Fixed deposit
(d) Social service
Answer:
(b) Co-operation
Part-II
Answer any seven questions in which Question No. 30 is compulsory. [7 x 2 = 14]
Question 21.
What do you mean by business?
Answer:
Business refers to any human activity undertaken on a regular basis with the object to earn profit through production, distribution, sale or purchase of goods and services.
Question 22.
When two or more families agree to live and work together to earn profit – Identify the form of business organization. Also give any two features of it.
Answer:
The form of business organization is Joint Hindu Family Business. They are doing business with family property.
Features:
- Governed by Hindu Law
- Membership by birth
Question 23.
What is meant by barter system?
Answer:
In barter system, goods were exchanged for goods prior to invention of money.
![]()
Question 24.
Some enterprises operate in more than one country. But it is incorporated in one country. What does the organisation mean? What are the other names of the organisation?
Answer:
The name of the organisation is Multinational Corporation. The other names of MNC is known by:
(a) Global enterprise
(b) International enterprise
(c) World enterprise
(d) Transnational corporation
Question 25.
Are low taxes possible in Co-operative society?
Answer:
Yes, Low taxes are possible in co-operative society because it is a non-profit enterprise, and government provides various exemptions and tax concessions.
Question 26.
What are the services included in the service business?
Answer:
Educational, Medical, Hospitality and banking are the services included in service businesses. Bank service is the nerve center of industry and commerce in a country.
![]()
Question 27.
Who is called a partner?
Answer:
The persons who enter into partnership are individually called ‘Partners’.
Question 28.
Who are Rochdale pioneers?
Answer:
At first, the co-operative movement was started by Robert Owen, in the year 1844. He formed a consumer’s co-operative society in England with 28. workers as members, called “Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers”.
Question 29.
Give a short note on FCI.
Answer:
Food Corporation of India (FCI) provides storage facilities for food grains. It also hires storage capacity from other sources such as Central Warehousing Corporation, State Warehousing Corporation and Private parties. It was set up under the Food Corporation Act 1964.
Question 30.
Write a short note on debentures.
Answer:
Debentures are an important instrument for raising long term debt capital. A company can raise funds through issue of debentures which bear a fixed rate of interest.
Part-III
Answer any seven questions in which Question No. 40 is compulsory. [7 x 3 = 21]
Question 31.
What is charter party?
Answer:
When goods are to be consigned in large quantity, it is advantageous to hire the whole or substantial part of the ship. The document through which this contract is made is known as ‘Charter Party’ may also be known as ‘Voyage Charter’ or ‘Time Charter’. The person who hires the ship is known as ‘Charter’. The charter becomes responsible to the third parties for the acts of the master and crew of the ship.
Question 32.
What is meant by ‘Mail order retailing’?
Answer:
Mail order business is the retail trade that sells the goods through mail. There is no direct contact between the buyer and seller in this type of trading.
Procedure:
- Advertisements provide information about the products to consumers.
- Order receiving and processing: On receiving orders, the goods are sent to the customers through the post office by Value Payable Post (VPP).
- Receiving Payments: At the time of receiving goods, the customers have to make full payment of goods.
Question 33.
Mention the functions of ‘SAARC’
Answer:
- Monitoring and co-ordinating the development programme.
- Determining inter-sectoral priorities.
- Mobilizing cooperation within and outside the region.
- Dealing with modalities of financing!
Question 34.
Write any three characteristics of sole proprietorship.
Answer:
- Ownership by one man:
This is owned by single person. The sole trader contributes the required capital. He is not only the owner of the business but also manages the entire affairs. - Freedom of work and Quick Decisions:
Since an individual is himself as a owner, he need not consult anybody else. Hence he can take quick decisions. - Unlimited Liability:
When his business assets are not sufficient to pay off the business debts he has to pay from his personal property.
Question 35.
Distinguish between extractive and genetic industries.
Answer:
- Extractive Industries:
These industries extract or draw out products from natural sources.
Extractive industries supply some basic raw materials that are mostly products of geographical or natural environment. - Genetic Industries:
These industries remain engaged in breeding plants and animals for their use in further reproduction.
The seeds, nursery companies, poultry, diary, piggery, hatcheries, nursery, fisheries and apiary, etc.
Question 36.
What is meant by ATM?
Answer:
ATM means Automated Teller Machine. A customer can withdraw money any time, anywhere in India from the ATM machine using the ATM card given by his / her bank. The machine also shows the balance available in the customers’ account, provides statement print of the few past transactions, etc.
![]()
Question 37.
List the kinds of social responsibility.
Answer:
- Economic responsibility
- Legal responsibility
- Ethical responsibility
- Discretionary responsibility
Question 38.
List the steps in factoring process.
Answer:
- The firm enters into a factoring arrangement with a factor, which is generally a financial institution, for invoice purchasing.
- Whenever goods are sold on credit basis, an invoice is raised and a copy of the same is sent to the factor.
- The debt amount due to the firm is transferred to the factor through assignment and the same is intimated to the customer.
Question 39.
Write a note on agricultural income.
Answer:
Agricultural income is any rent or revenue derived from land which is situated in India and is used for agriculture purposes. It is fully exempted from tax u /s 10(1) and as such does not form part of total income.
![]()
Question 40.
There are two schools of Hindu law in Joint Hindu family business organisation. What are the two schools of Hindu law? Explain.
Answer:
In Joint Hindu Family business, there are two schools of Hindu Law: one is Dayabhaga which is prevalent in Bengal and Assam, and the other is Mitakshara prevalent in the rest of the country. In Mitakshara Law, there is a son’s right by birth in the property of joint family.
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [7 x 5 = 35]
Question 41 (a).
Business consists of many hindrances, while facilitating the production and distribution of goods.
(i) List out any five hindrances.
(ii) Explain any three.
(iii) How they are overcome?
Answer:
(i) For production of goods and services, there are so many hindrances. They are:
- Hindrance of person
- Hindrance of place _
- Hindrance of Time
- Hindrance of knowledge .
- Hindrance of Finance
(ii) 1. Hindrance of Person:
The problem of not knowing the place of consumers is called as hindrance of person. Because the manufacturer does not know the consumer, and the consumer does not know the producer. This difficulty is called Hindrance of person.
2. Hindrance of place:
The difficulty of connecting the place of production with the place of consumption is known as hindrance of place. The goods may be produced in one place but it may be used throughout the world, in many places. This problem is known as place hindrance.
![]()
3. Hindrance of Time:
Goods may be produced in certain period only. But it may be demanded throughout the year. Some goods may be produced throughout the year, but may be used in certain time only. This difficulty is known as hindrance of time.
(iii) Hindrance of person may be eliminated by the trader; the trader links the producer and consumer.
Hindrance of place can be overcome by the transport. The transport is connecting the place of production and place of consumption. Hindrance of time can be removed by warehouses. Goods can be stored in the warehouses till the time of demand.
[OR]
Question 41 (b).
Explain briefly about Business Process Outsourcing under the following headings:
(i) Meaning
(ii) Core activities
(iii) Any three benefits
(i) Meaning of outsourcing:
Business process outsourcing is a recent type of business in service sector. BPO (Business process sector) refers to outsourcing the work which is routine in nature to an outside agency. This practice was in USA in few companies.
(ii) Core Activities:
Companies can benefit in the long run provided they are keen on their core activities. A core activity involves experience, expertise, efficiency and even investment in the field of specialisation.
(iii) Benefits:
- Focusing on the core activities:
Companies can focus on their core competence, a few areas where the company has distinct capability. - To fill up economic development:
Outsourcing stimulates entrepreneurship, encouraging employment opportunities, which increases economic development. - Reduction in investment:
Companies through outsourcing avails the services of outsiders which in turn reduces the investment requirements.
Question 42 (a).
TO manage the government, revenue is needed. For the revenue, the government is collecting income from various methods. That revenue is used to meet the expenses of the government.
(i) How the government is collecting revenue from the public?
(ii) Also explain the methods of collecting tax.
Answer:
(i) The government is levying Tax for getting revenue. Tax is a compulsory payment by the public. It is the basic source of revenue to the government.
![]()
(ii) Tax is divided into two types:
- Direct Tax:
If a tax is levied on the income or wealth of a person and paid by that person directly to the government, it is called direct tax. Example: Income Tax, Wealth Tax and Capital Gains Tax. - Indirect Tax:
If a tax is levied on the goods or services of a person (seller); it is collected from the buyers and is paid by seller to the Government, it is called indirect tax. Example:
[OR]
Question 42 (b).
Explain the functions of wholesalers, (any 5)
Answer:
Meaning of wholesalers:
The traders who are engaged in wholesale trade are called wholesalers. A wholesaler buys goods in bulk directly from manufacturers and sells them in small lots to customers.
Functions of Wholesalers – The following are the functions of wholesalers:
(1) Collection of Goods:
Wholesaler collects the goods from the manufacturers or producers in bulk.
![]()
(2) Storage of Goods:
Wholesaler collects and stores them safely in warehouses, till they are sold out.
- Distribution:
Wholesaler sells goods to different retailers. Thus he performs the function of distribution. - Financing:
Wholesalers provide financial support to producers and manufacturers by providing money in advance to them. He also sells goods to retailer on credit. - Risk Taking:
Wholesaler buys finished goods from the producer and stores them in the warehouses till they are sold out. The wholesalers bear the risk arising from price, and damage of goods. - Grading and Packing:
Wholesaler classifies the goods into different categories. He grades the goods on the basis of quality, size and weight, etc. - Providing Information:
Wholesalers provide valuable information to retailers and producers.
Question 43(a).
Explain the types of Mercantile agents.
Answer:
Mercantile Agents are also called functional middlemen. A businessman appoints a person to buy and sell goods on his behalf. There are many types of Mercantile Agents:
(1) Brokers:
A broker is one who bargains for another and receives commission for his service. He brings the buyer and the seller to negotiate the contract.
(2) Factors:
A factor is a mercantile agent to whom goods are entrusted for sale by a principal. He takes physical possession of the goods, but does not obtain ownership of the goods.
(3) Commission Agent or Consignees:
A commission agent buys and sells goods on behalf of the principal for a fixed rate of commission. All risks connected with his transactions are borne by the principal.
![]()
(4) Del-credere Agents:
The agent who guarantees to the principal the collection of cash from credit sales is called ‘del-credere agent’. He is paid an additional commission known as del-credere commission for bearing the risk.
(5) Auctioneers:
They are agents who sell goods by auction on behalf of their principals. They are selling by giving notification to the public. The notice gives details about the date, time, place and details of goods for sales.
[OR]
Question 43 (b).
What are the objectives of GST?
Answer:
- To create a common market with uniform tax rate in India. (One Nation, One Tax and One
Market) - To eliminate the cascading effect of taxes, GST allows set-off of prior taxes for the same transactions as input tax credit.
- To boost Indian exports, the GST already collected oh the inputs will be refunded and thus there will be no tax on all exports.
- To increase the tax base by bringing more number of tax payers and increase tax revenue.
- To simplify tax return procedures through common forms and avoidance of visiting tax departments.
- To provide online facilities for payment of taxes and submission of forms.
Question 44 (a).
Explain any five principles of Co-operative society.
Answer:
(1) Voluntary and Open Membership:
Co-operatives are voluntary organisations, open to all people able to use its services and willing to accept the responsibilities of membership, without gender, social, racial, political or religious discrimination.
(2) Democratic Member Control:
Co-operatives are democratic organisations controlled by their members – those who buy the goods or use the services of the co-operative-who actively participate in setting policies and making decisions.
(3) Member’s Economic Participation:
Members contribute equally to, and democratically control, the capital of the co-operative. This benefits members in proportion to the business they conduct with the co-operative rather than on the capital invested.
![]()
(4) Autonomy and Independence:
Co-operatives are autonomous, self-help organisations controlled by their members. If the co-operative enters into agreements with other organisations or raises capital from external sources, it is done so based on terms that ensure democratic control by the members and maintains the co-operative’s autonomy.
(5) Education, Training, and Information:
Co-operatives provide education and training for members, elected representatives, managers and employees so they can contribute effectively to the development of their co-operative. Members also inform the general public about the nature and benefits of co-operatives.
[OR]
Question 44 (b).
Explain the advantages of warehousing.
Answer:
- It safeguards the stock for the merchants who do not have storage place.
- Warehouses reduce the distribution cost of the traders by storing the goods in bulk and allow the trader to take the goods in small lots to his shop.
- It helps in selection of channel of distribution. The producer will prefer whether to a wholesaler or retailer.
- It assists in maintaining the continuous sale and avoid the possibilities of “Out of Stock”.
- It creates employment opportunities for both skilled and unskilled workers to improve their standard of living.
Question 45 (a).
Distinguish between economic activity and non-economic activity.
Answer:
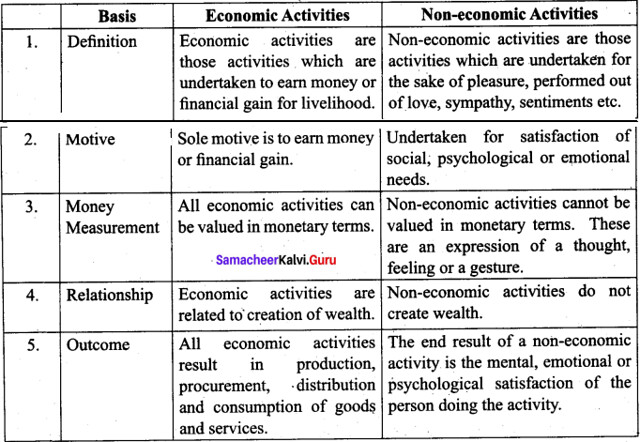
[OR]
Question 45 (b).
State the constraints of barter system.
Answer:
The constraints of barter system are:
(1) Lack of Double Coincidence of Wants:
Unless two persons who have surplus have the demand for the goods possessed by each other, barter could not materialize. If this “coincidence of wants” does not exist, barter cannot take place.
(2) Non-existence of Common Measure of Value:
Barter system could not determine the value of commodities to be exchanged as they lacked commonly acceptable measures to evaluate each and every commodity.
(3) Lack of Direct Contact between Producer and Consumers:
It was not possible for buyers and sellers to meet face to face in many contexts for exchanging the commodities for commodities.
(4) Lack of surplus stock:
Absence of surplus stock was one of the impediments in barter system. If the buyers and sellers do not have surplus then no barter was possible.
![]()
Question 46 (a).
Explain the classification of companies on the basis of nationality.
Answer:
1. Domestic Companies:
A company which cannot be termed as foreign company under the provision of the Companies Act should be regarded as a domestic company.
2. Foreign Companies:
A foreign company means a company which is incorporated in a country outside India under the law of that country. The following documents must be filed with the Registrar of Companies-
- A certified copy of the charter or statutes under which the company is incorporated.
- The full address of the registered office of the company.
- A list of directors and secretary of the company.
- The name and address of any Indian resident who is authorised to accept legal documents on behalf of the company.
- The full address of the company’s principal place of business in India.
3. Multi National Companies:
A Multi National Company (MNC) is a huge industrial organisation which-
- Operates in more than one country.
- Carries out production, marketing and research activities.
- Seeks to maximise profits world over. A domestic company or a foreign company can be a MNC.
[OR]
Question 46 (b).
Every nation has one central bank. It controls the entire banking system of the country.
- What is the name of our central bank?
- Explain the organisational structure of our central bank.
Answer:
- In India the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central bank
- The head office of the RBI is situated in Mumbai. This central office has 33 departments in 2017. It has four zonal offices in Mumbai, Delhi, Calcutta and Chennai functioning under local boards with deputy governors as their heads. It also has 19 regional offices and 11 sub-offices (2017).
The RBI is governed by a central board of directors. The 21 member board is appointed by the Government of India. It consists of:
- One Governor and four deputy governors appointed for a period of four years
- Ten Directors from various fields
- Two Government officials
- Four Directors – one each from local boards
Question 47 (a).
What are the advantages of warehousing?
Answer:
- It safeguards the stock for the merchants who do not have storage place.
- Warehouses reduce the distribution cost of the traders by storing the goods in bulk and allow the trader to take the goods in small lots to his shop.
- It helps in selection of channel of distribution. The producer will prefer whether to a wholesaler or retailer.
- It assists in maintaining the continuous sale and avoid the possibilities of “Out of Stock”.
- It creates employment opportunities for both skilled and unskilled workers to improve their standard of living. .
[OR]
Question 47 (b).
Short term and medium term loans are provided by commercial banks. It is repayable in one lump sum or in installments. Loans may be of various types. Explain the various kinds of loan granted by the commercial banks.
Answer:
Banks can provide various kinds of loan to the customers. They are as follows:
- Housing Loan:
Accepting the title deeds of the house as security, banks provide medium and long term loans, based on the monthly income of the customer. It is a boon to the middle class salaried employees who cannot afford to pay the full price of a house in a lump sum. - Consumer Loans:
Loan is granted to the customer to purchase durables like refrigerator, air-conditioner, laptop, washing machine, television, etc. - Vehicle Loans:
Two wheelers, cars, buses and other vehicles can be purchased by individuals as well as organisations obtaining vehicle loans from the banks. - Educational Loan:
Loan is provided by banks to students for studying undergraduate, post graduate or professional courses. Loan may be received in instalments to pay the educational fees. - Jewel Loan:
Customers can pledge their gold jewels and obtain loans from banks. Interest should be paid every month.