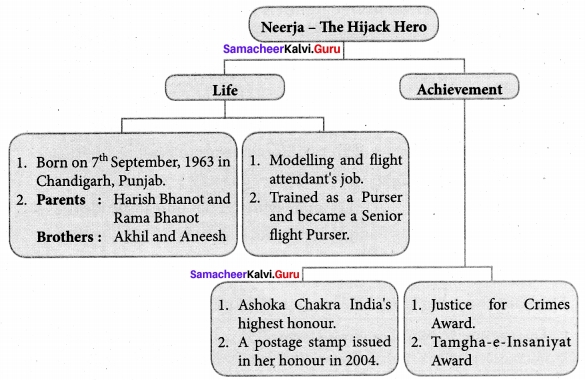
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Notes Chapter 3 Periodic Classification of Elements Notes
Elements known during 19th Century – 118 Elements. Out of 118 known 92 elements are found in nature.
Johann Dobereiner’s classification – Law of triads – It was seen that invariably, the atomic weight of the middle member of the triad was nearly equal to the arithmetic mean of the weight of the other two members of the triad. He noted that elements with similar properties occur in groups of three which he called triads.
Chancourtois classification – In this system, elements that differed from each other in atomic weight by 16 or multiples of 16 fell very nearly on the same vertical line. Elements lying directly under each other showed a definite similarity. This was the First periodic law.
Newland’s classification – Law of octaves – This law states that, when elements are arranged in the order of increasing atomic weights, the properties of the eighth element are a repetition of the properties of the first element. This law was seemed to be applicable only for elements upto atomic number 20 (Calcium).
Mendeleev’s classification – Mendeleev’s periodic law – This law states that the properties of the elements can be represented as periodic function of their atomic weights.
Modern periodic law – It was given by Henry Moseley in 1913. This law states that “The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers”.
Moseley’s correlation – between atomic number and the frequency of X-rays.
√v = a (Z – b), where u = frequency of the X-rays emitted by the elements concerned.
Z = atomic number; a and b = constants and have same values for all the elements.
Periodicity – The repetition of physical and chemical properties at regular intervals is called periodicity.
Groups – The vertical columns in the periodic table are called groups. There are 18 vertical columns which constitute 18 groups or families.
Periods – There are 7 horizontal rows in the periodic table known as periods.

Electronic configuration – The distribution of electrons into orbitals, s, p, d and f, of an atom is called its electronic configuration.
Lanthanides – The first f-transition series consisting of 14 elements placed separately as panel at the bottom of the periodic table.
Actinoids – The second f – transition series consisting of 14 elements placed separately as panel at the bottom of the periodic table.
Group 17 – Halogen family.
Group 16 – Chalcogen family (or) oxygen family.
Division of elements based on electronic configuration – The entire periodic table can be divided into s, p, d and f blocks.
Group 18 – Noble gases.
Group 1 – Alkali metals.
Group 2 – Alkaline earth metals.
d-block elements – The elements of the groups 3 to 12 are called d-block elements or transition elements with general valence shell electronic configuration ns1-2, (n-1)d1-10
p-block elements – The elements of groups 13 to 18 are called p-block elements or representative elements and have a general electronic configuration ns2, np1-6
s-block elements – The elements of group 1 and group 2 are called s-block elements, since the last valence electron enters the ns orbital.
f-block elements – The lanthanides (4f1-14, 5d0-1 6s2) and the actinides (5f0-14, 6d0-2, 7s2) are called f-block elements.
Types of elements –
| Basis of chemical behaviour | Basis of physical properties |
| Main group elements | Metals |
| Noble gases | Non-metals |
| Transition elements | Metalloids |
| Inner transition elements |
Example for periodic properties – (i) Atomic radius (n) Ionic radius (Hi) Ionization enthalpy (iv) Electron gain enthalpy (v) Electronegativity.
Atomic radius – It is the distance between the centre of the nucleus of an atom and the outermost shell containing the valence electron.
Covalent radius – It is one-half of the intemuclear distance between two identical atoms linked together by a single covalent bond.
Metallic radius – It is defined as one half of the distance between two adjacent metal atoms in the closely packed metallic crystal lattice.
Ionic radius – It is defined as the distance from the centre of the nucleus of the ion up to which it exerts its influence on the electron cloud of the ion.
Isoelectronic ions – The ions of different elements having the same number of electrons are called isoelectronic ions. e.g. Na+ , Mg2+ , Al3+ , F– , O2- , N3-
Ionization enthalpy – The energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from the valence shell of an isolated neutral gaseous atom is called as Ionization energy.
The unit of Ionization energy = KJ mole-1.
Electron gain enthalpy (or) Electron affinity – The electron gain enthalpy of an element is the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom. The unit of electron affinity = KJ mole-1.
Electronegativity – The relative tendency of an element present in a covalently bonded molecule, to attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself.
Valency – It is defined as the combining capacity of an element.
Valence electrons – The total number of electrons in the valence shell or equal to eight minus the number of valence electrons.
Diagonal relationship – In a periodic table, a diagonal relationship exists among certain pairs of elements. Thus Li is similar to Mg, Be is similar to A1 and B is similar to Si.