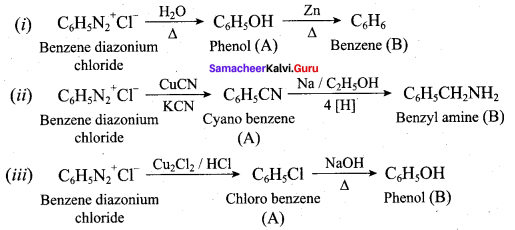
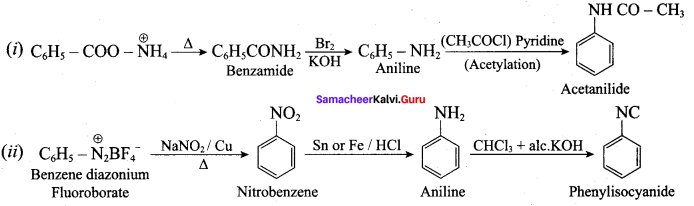
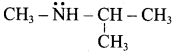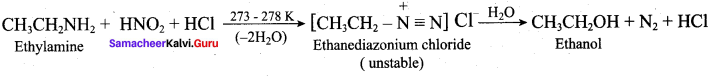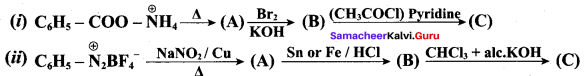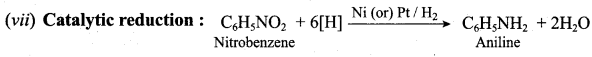Students can find the most related topics which helps them to analyse the concepts if they practice according to the chapter-wise page. It is necessary for the students to practice more Questions and Answers for Tamilnadu State Board Solutions of 11th Commerce are given in the pdf format in chapter 31 Discharge and Breach of a Contract Questions and Answers so that students can prepare in both online and offline modes. So, Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Book Solutions Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, to score good marks.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Solutions Chapter 31 Discharge and Breach of a Contract
Get the Questions and Answers, in Tamilnadu State Board 11th Commerce Solutions for Chapter 31 Discharge and Breach of a Contract. Learn the concepts of 11th Commerce Chapter-Wise by referring to the Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Chapter 31 Discharge and Breach of a Contract Questions and Answers. Hence we suggest the students to Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Book Solutions Questions and Answers pdf to enhance your knowledge.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Discharge and Breach of a Contract Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
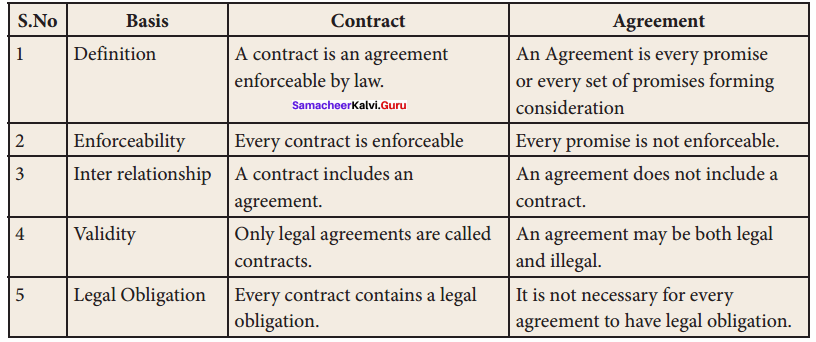
On the valid performance of the contractual obligation by the parties, the contract ……………….
(a) Is discharged
(b) Becomes enforceable
(c) Becomes void
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Is discharged
Question 2.
An agreement to do an act impossible in itself under Section 56 is ……………….
(a) Void
(b) Valid
(c) Voidable
(d) Unenforceable
Answer:
(a) Void
Question 3.
Any agreement which becomes impossible to perform under various circumstances.
(a) Voidable
(b) Void
(c) Valid
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Void
Question 4.
Discharge by mutual agreement may involve ……………….
(a) Novation
(b) Rescission
(c) Alteration
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 5.
The compensation given for breach of contract is ……………….
(a) Damage
(b) Remuneration
(c) Money
(d) Cheque
Answer:
(a) Damage
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the kinds of consent?
Answer:
The consent may be of the following types:
- Express
- Implied
Question 2.
What are the types of Impossibility of Performance?
Answer:
There are two types of impossibility of performance, such as –
- Impossibility existing at the time of agreement.
- Impossibility arising subsequent to the formation of contract.
Question 3.
What is Quantum merit?
Answer:
The meaning of the phrase quantum merit is ‘as much as earned’.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the different modes of discharge by implied consent?
Answer:
Different modes of discharge by implied consent are:
- Novation
- Alteration
- Recession
- Remission
- Accord and Satisfaction
- Waiver
- Merger
Question 2.
Define discharge by Performance.
Answer:
Performance implies carrying out the obligation of the contract. Performance must be completed according to the real intentions of the agreement. Performance must be done according to time and manner prescribed.
Question 3.
What are reasons for impossibility arising after the formation of contract?
Answer:
Impossibility arising subsequent to the formation of a contract or supervening impossibility may be:
- By some event beyond the control of the parties; or
- By some act either of the promisor or of the promisee.
Question 4.
What are the various rules regarding damages?
Answer:
Generally in the following cases, the court grants specific performance:
- When the act agreed to be done is such that compensation in money for its non – performance is not sufficient.
- When it is probable that compensation in money cannot be received for the non – performance of the act agreed to be done.
- When there is no standard for ascertaining the actual damage caused by the non – performance of the act agreed to be done.
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the ways of discharge of Contract?
Answer:
Different modes of discharge of contract have been provided under different sections of the Act:
1. Discharge by Performance : Performance implies carrying out the obligation of the contract. Performance must be completed according to the real intentions of the agreement. Performance must be done according to time and manner prescribed. Performance of contract may be of two types namely:
- Actual performance
- Attempted performance
2. By Agreement on Consent : Agreement between the parties comes to an end by mutually agreeing for it. Any contract is created by an agreement, hence in the same way, it can be discharged by an agreement. The consent may be of the following types:
- Express consent
- Implied consent
3. By Impossibility of Performance : A contract may be discharged if its performance becomes impossible. There are two types of impossibility of performance, such as –
- Impossibility existing at the time of agreement.
- Impossibility arising subsequent to the formation of contract.
4. By Lapse of Time : According to the Limitation Act, 1963 a contract must be performed within a specified time. If it is not performed within this specified time limit and against which if no action is taken by the promisee in the Court of Law within specified time, then the promisee is deprived of his remedy at law. In such cases, the contract is discharged.
5. By Operation of Law : A contract can be discharged by the operation of law. The operation of law by which contract can be discharged are as follows:
- By Death
- By Merger
- By Insolvency
- Unauthorized Alteration of the Terms of a Contract
- Rights and liabilities vesting in the same person
Question 2.
Write about the various remedies for breach of contract.
Answer:
There are various types of remedies for the injured parties listed as follows:
1. Recission of Contract – In case of breach of contract by one party, then the other parties may rescind the contract and thereby the party is absolved from his all obligations under the contract.
2. Claim for Specific Performance – In some specific cases if the damages are not the adequate remedy, then the court can direct the party in breach for the specific performance of the contract. In such case, the promise is carried out as per terms and conditions of the contract.
3. Claim for Injunction – Injunction is an order passed by a competent Court restraining a person from doing some act. Injunction can be defined as a mode of securing the specific performance of the negative terms of a contract.
4. Claim for Quantum Merit – The claim for quantum merit may arise if a contract performed by one party has become discharged by breach of the other party. The meaning of the phrase quantum merit is as much as earned’.
5. Claim for Damages – The claim for quantum merit may arise if a contract performed by one party has become discharged by breach of the other party. The meaning of the phrase quantum merit is as much as earned.
Question 3.
Discuss the different types of damages awarded to the injured party.
Answer:
Damages are a monetary compensation awarded by the court to the injured party for the loss or injury suffered by him. As per contract, one party can claim damages if other party breach the contract. The main purpose of awarding the damages is to make good the loss suffered by him. It is known as doctrine of restitution. The Section 73 of the Indian Contract Act, 1872 deals with the compensation for loss or damages caused by a party for breach of contract. There are mainly four types of damages, such as
- Ordinary damages
- Special damages
- Vindictive or exemplary damages; and
- Nominal damages
Share this Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for 11th Commerce Chapter 31 Discharge and Breach of a Contract Questions and Answers with your friends to help them to overcome the issues in exams. Keep visiting this site Tamilnadu State Board Solutions frequently to get the latest information on different subjects. Clarify your doubts by posting the comments and get the answers in an easy manner.
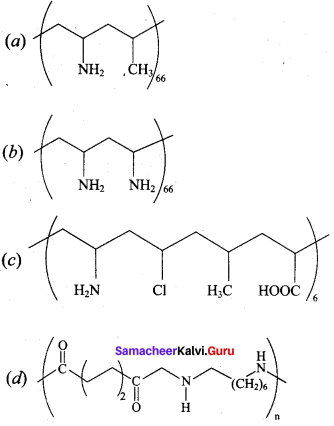
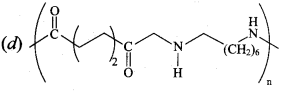
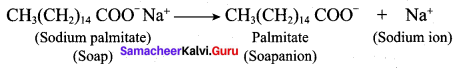
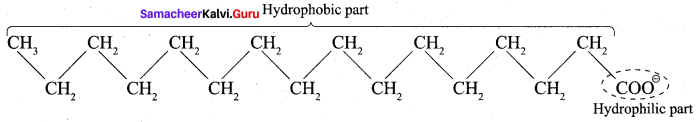
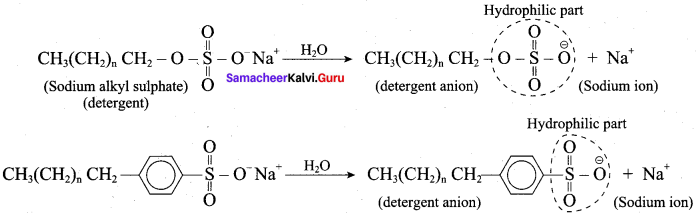
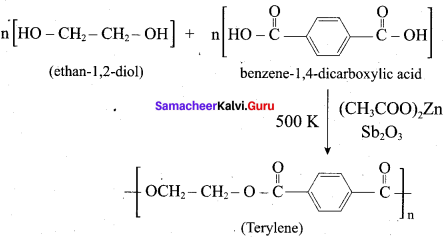
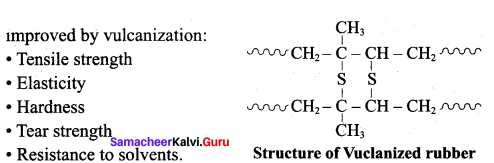
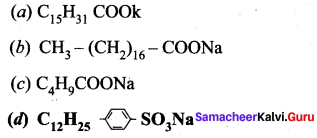
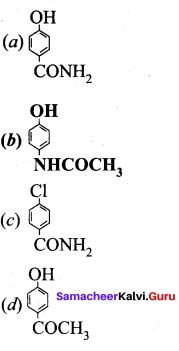
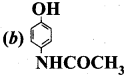
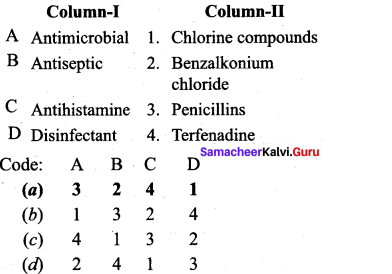
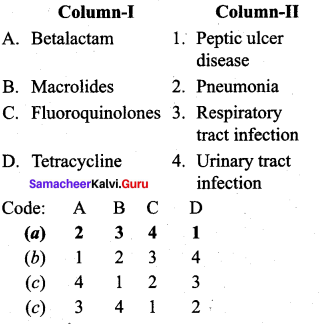
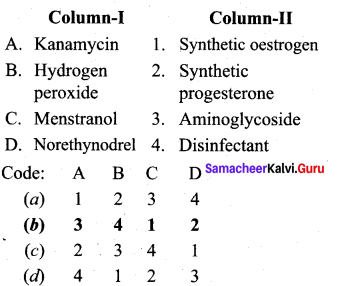
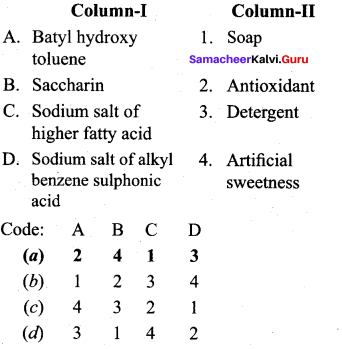
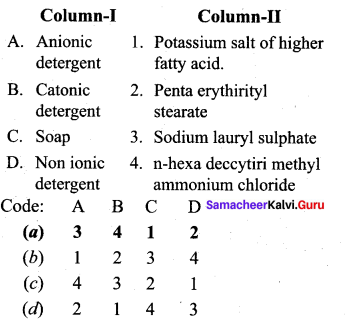
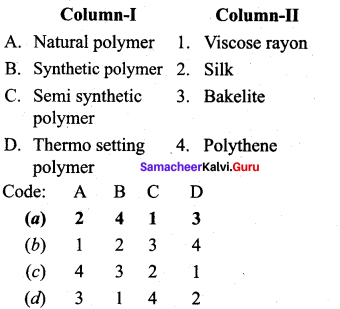
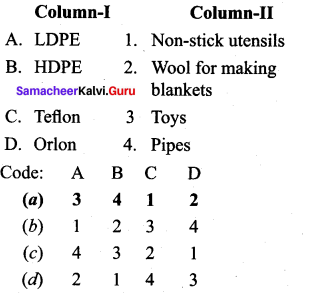
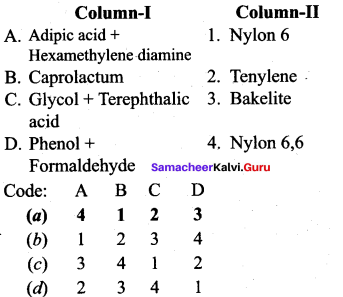
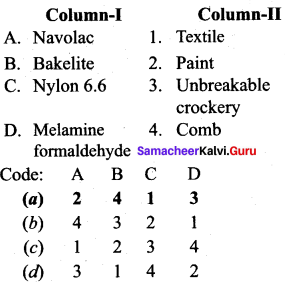
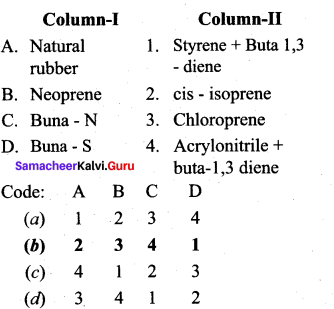
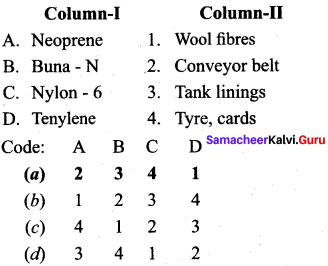

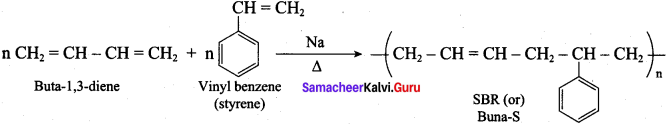
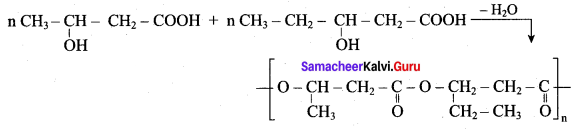

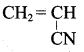
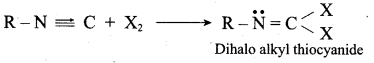
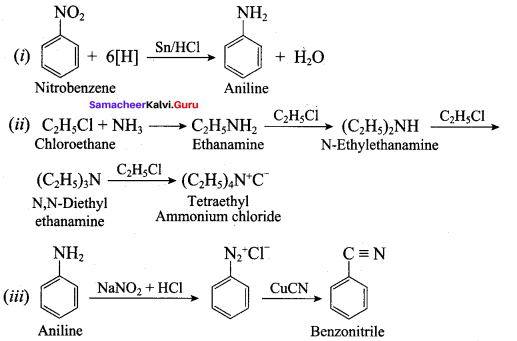
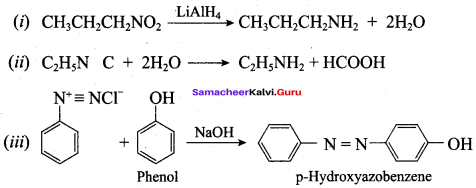
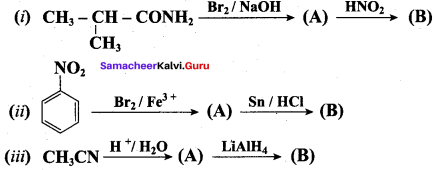
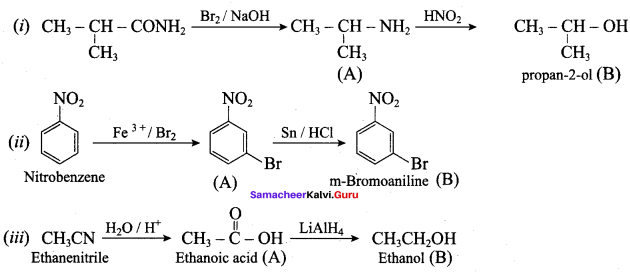
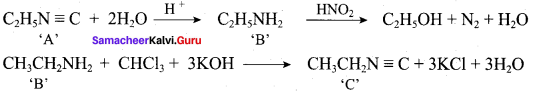
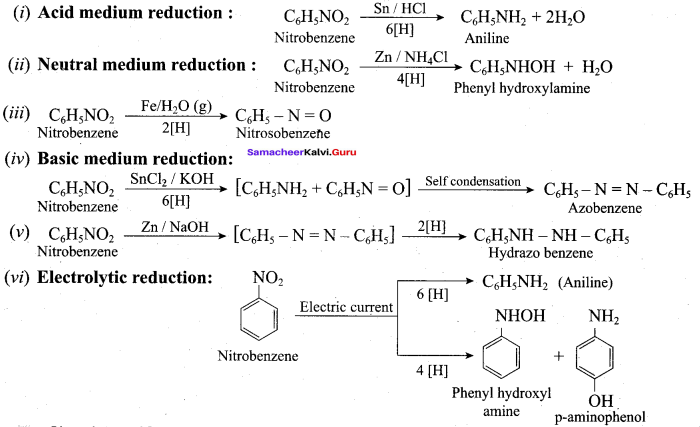
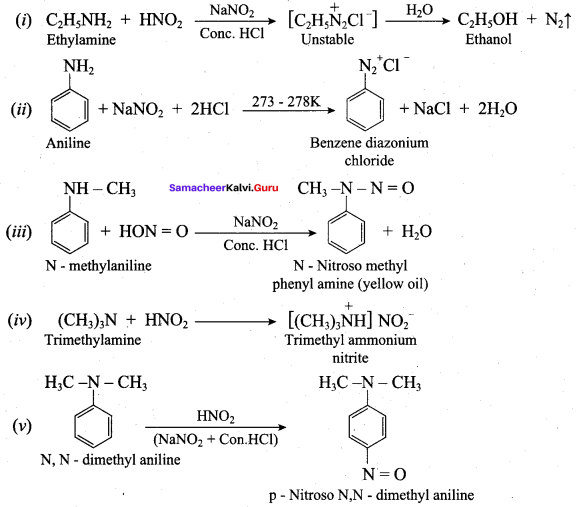
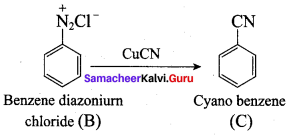
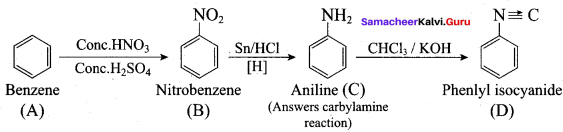
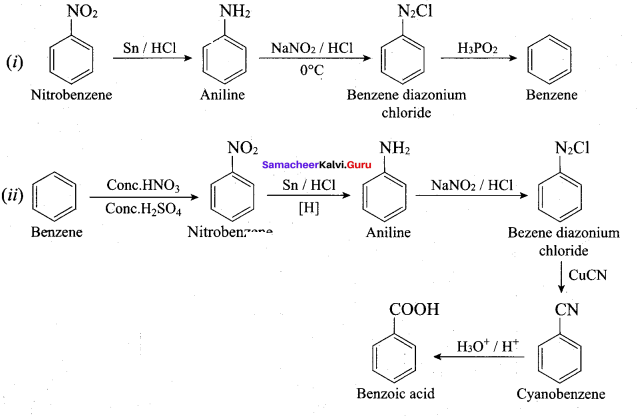
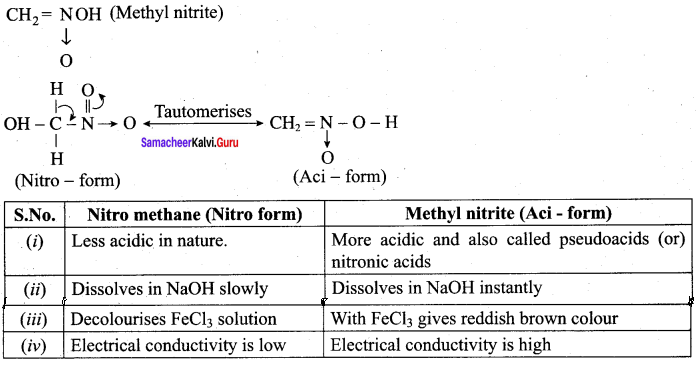
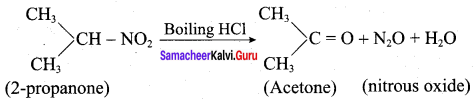
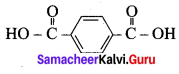 ; Ethylene glycol (Ethane – 1, 2 – diol)
; Ethylene glycol (Ethane – 1, 2 – diol)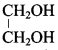
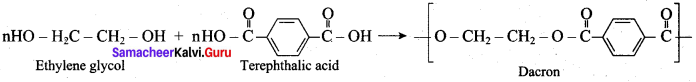

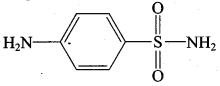

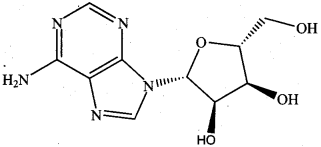
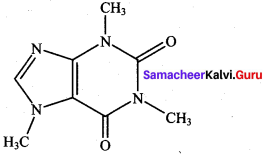
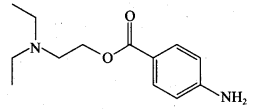


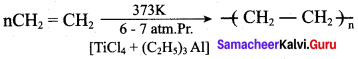
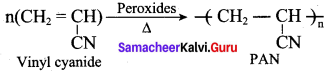
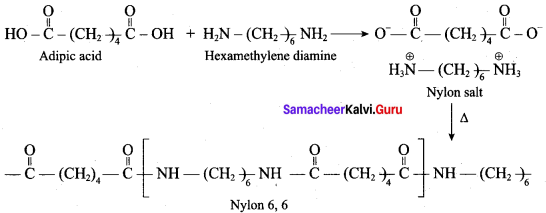
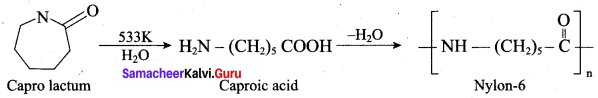
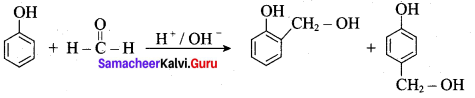
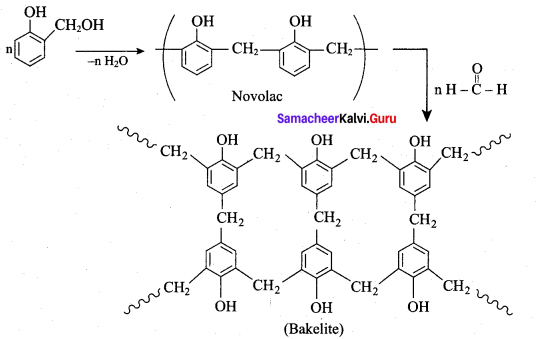
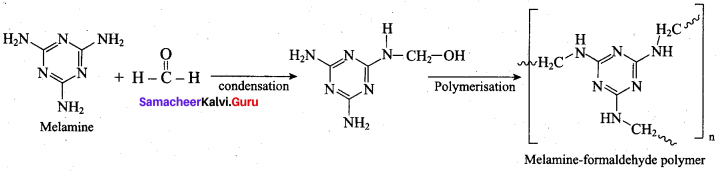
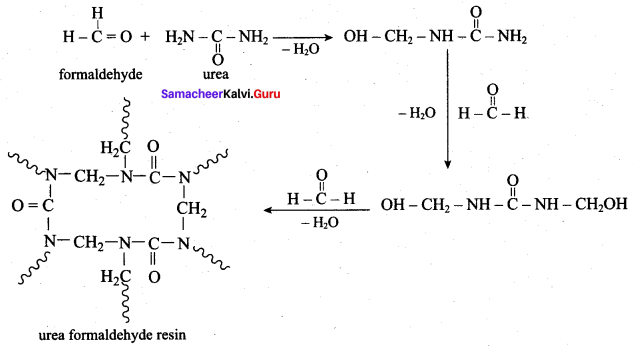
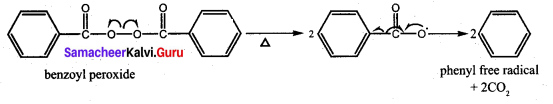
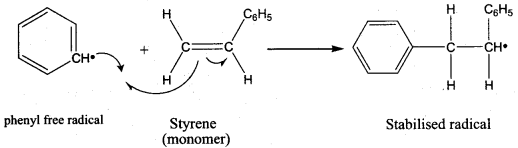
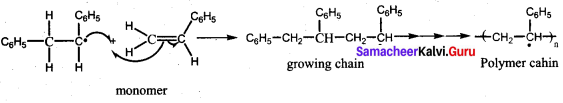
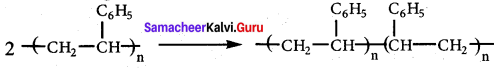
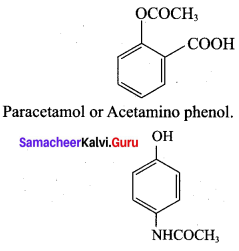
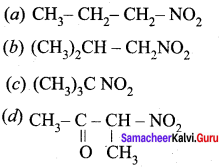
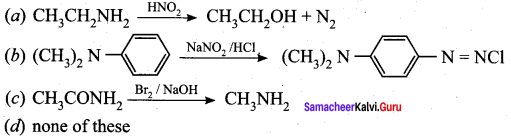
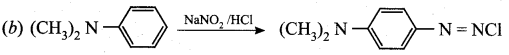
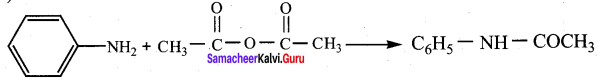
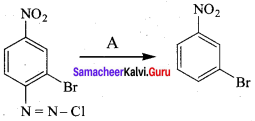
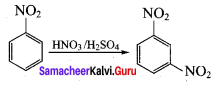

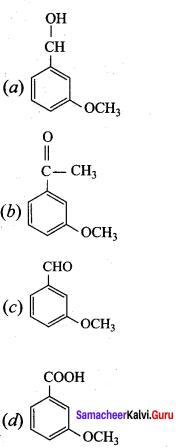
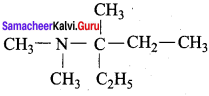 is ………………
is ………………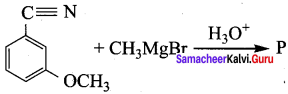
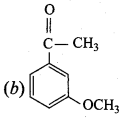
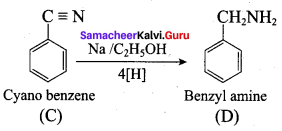
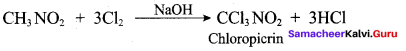
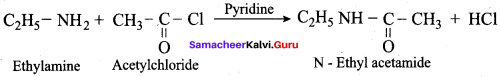
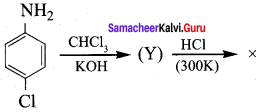 + Methanoic acid
+ Methanoic acid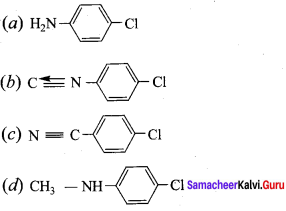
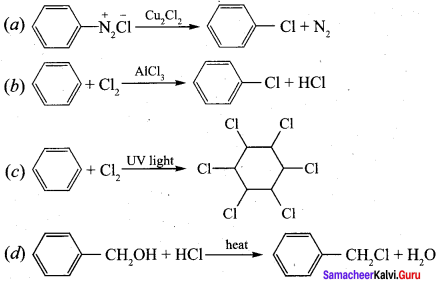
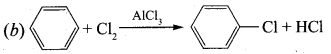
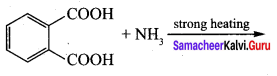
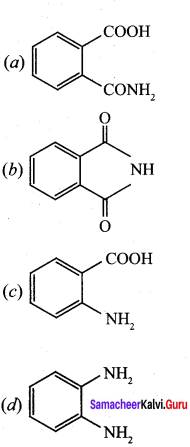
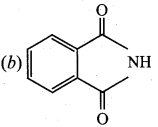
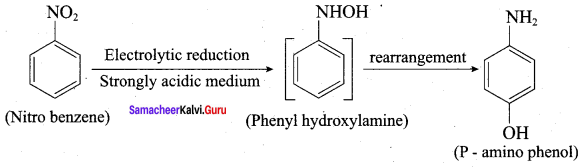
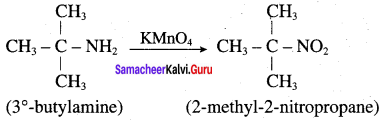
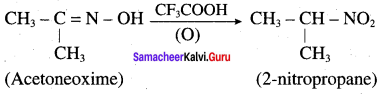
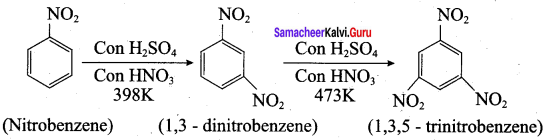
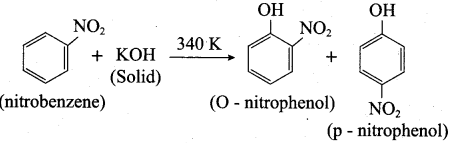
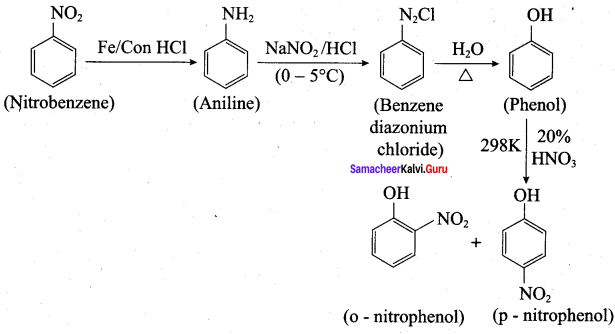
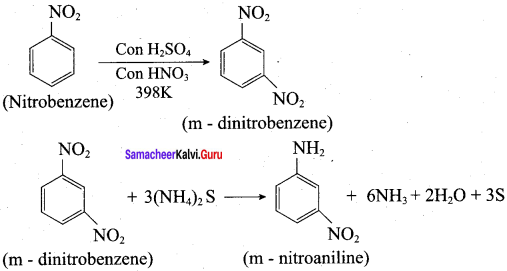
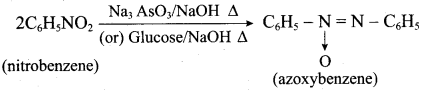
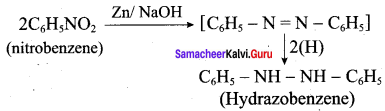
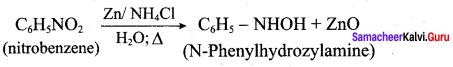
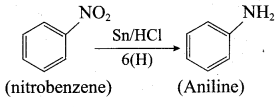
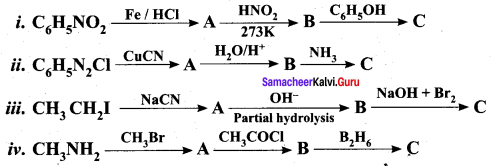
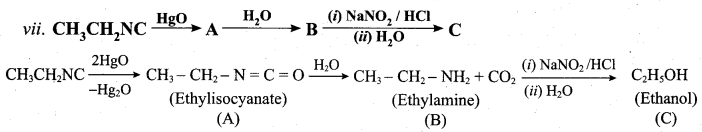
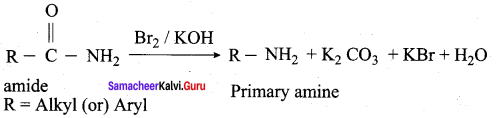
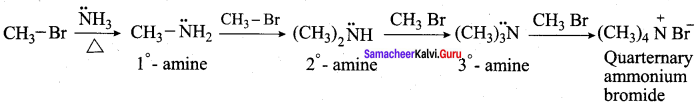
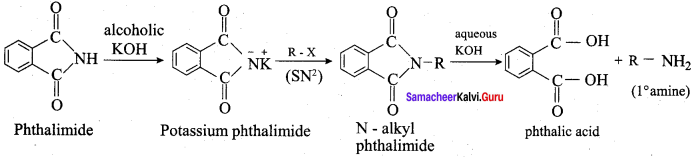
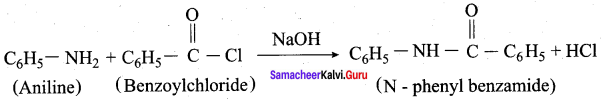
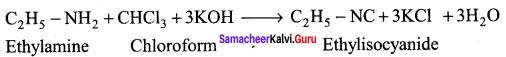
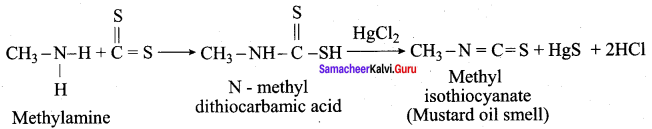
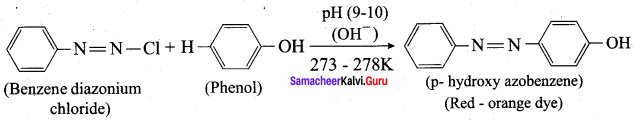
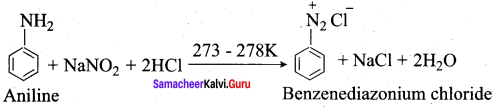
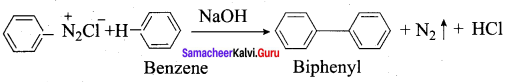
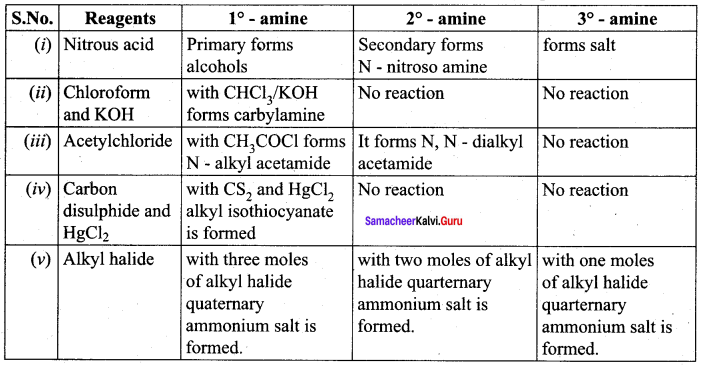
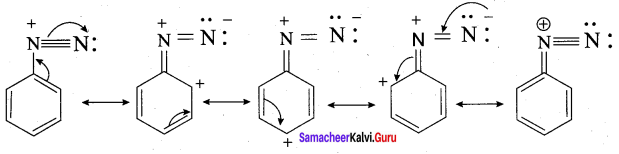
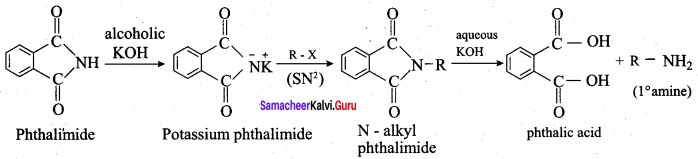
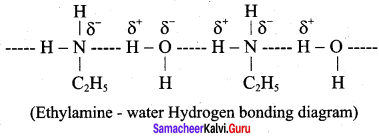
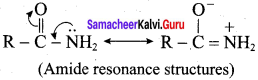
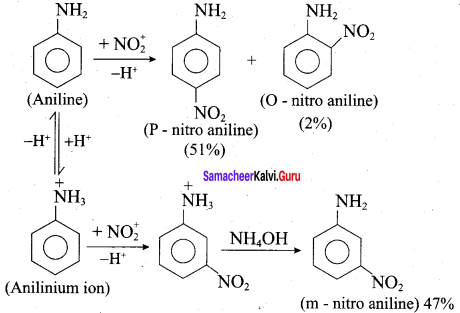
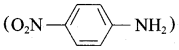
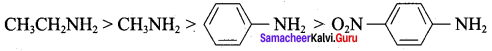
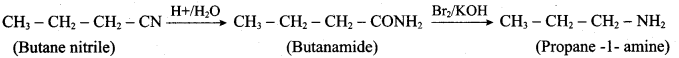
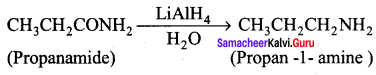
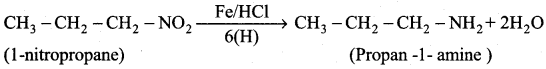


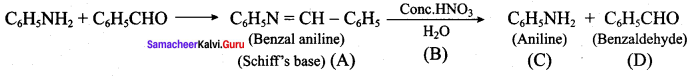
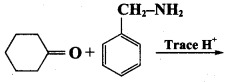
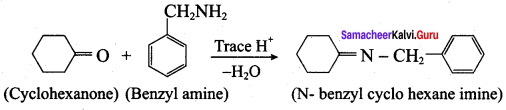
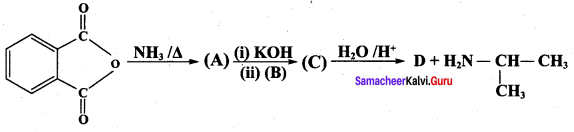
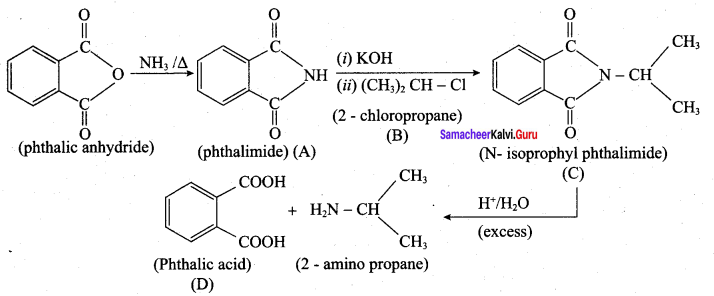
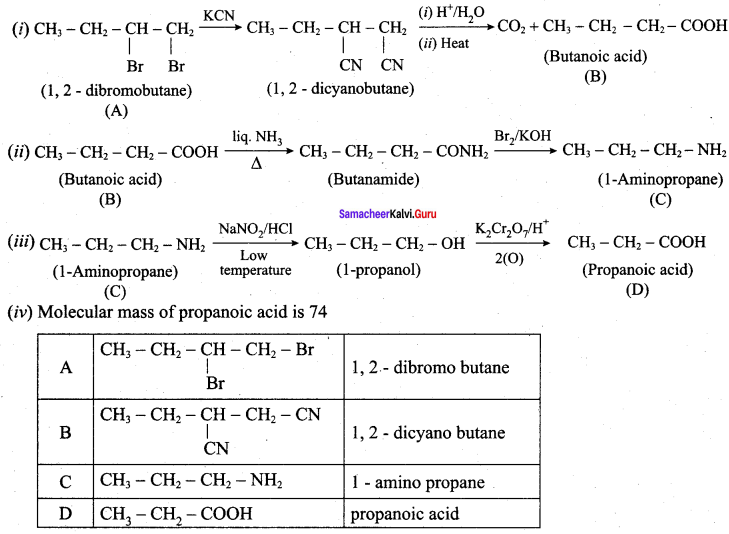
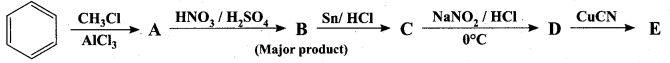
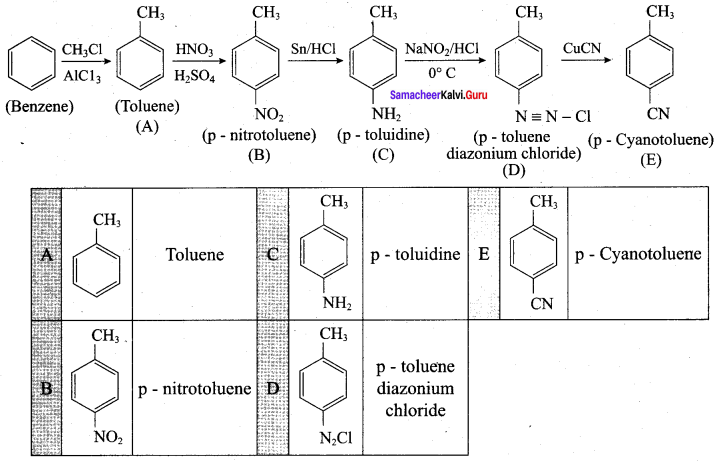
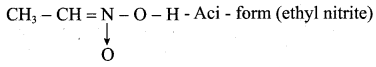

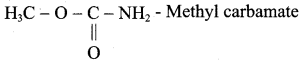
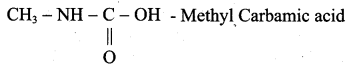
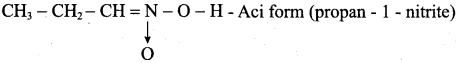


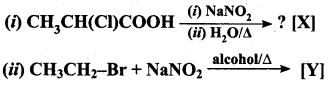
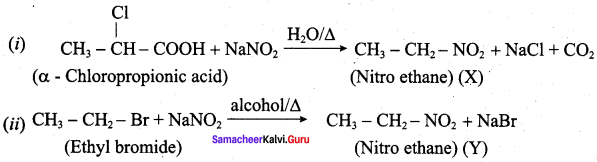
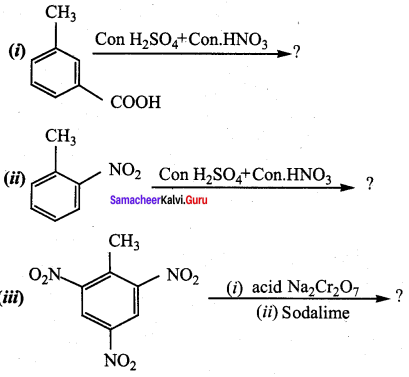
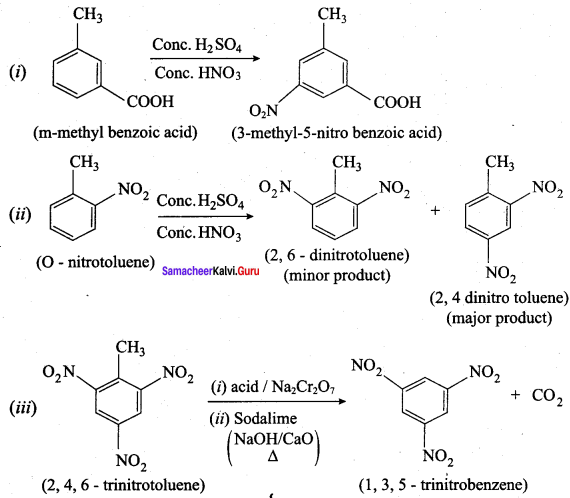
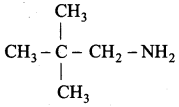
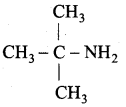
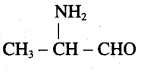
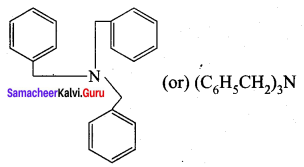
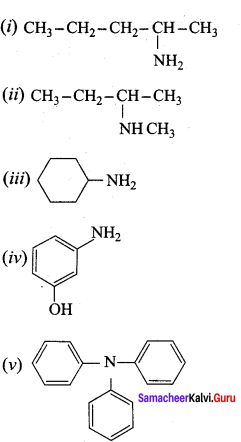
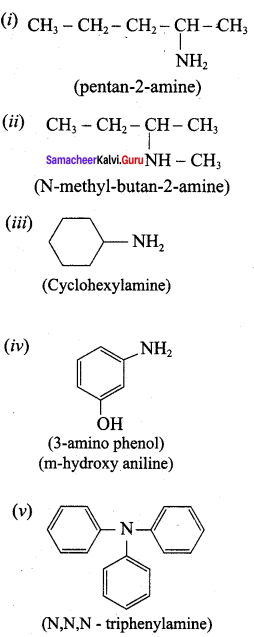
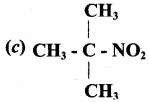
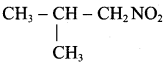 is ………………
is ………………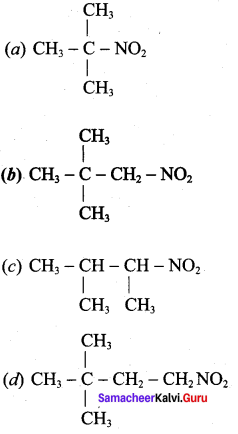
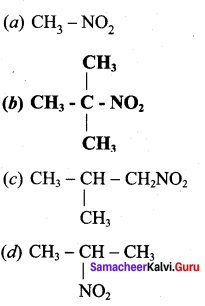
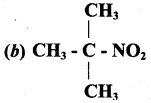
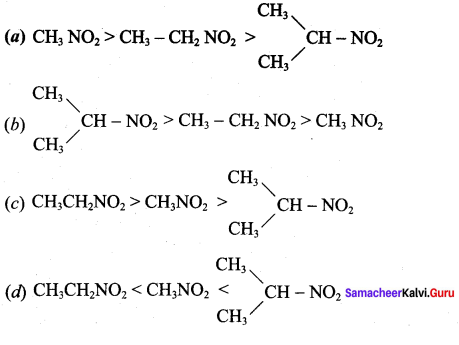
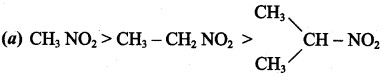
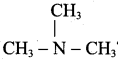
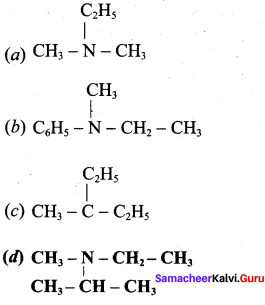
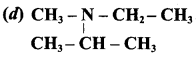
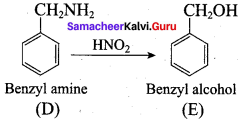
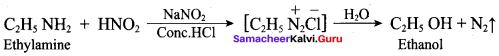
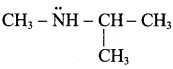 is ……………..
is ……………..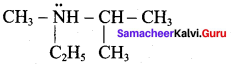
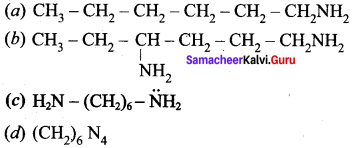
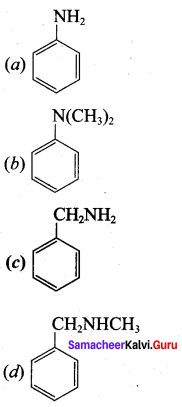
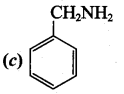
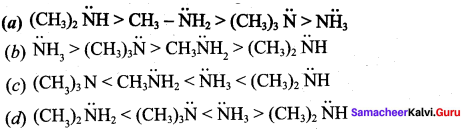
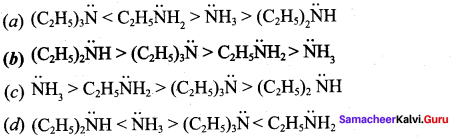
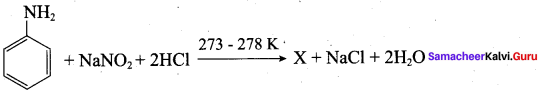
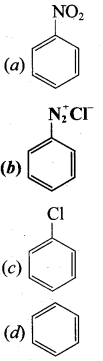
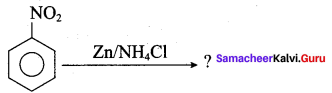
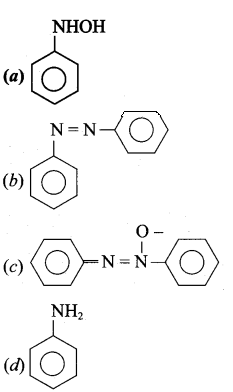
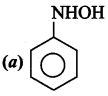
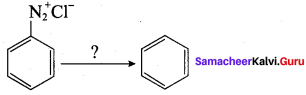
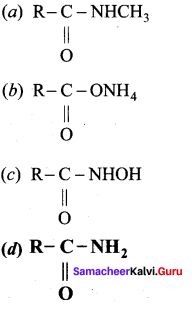
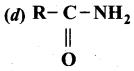
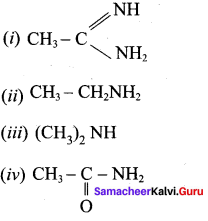
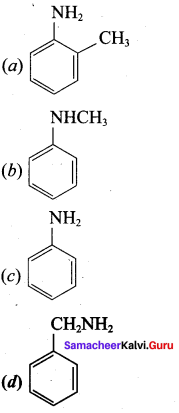
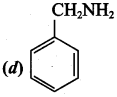
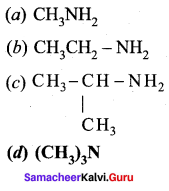
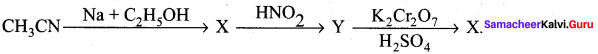

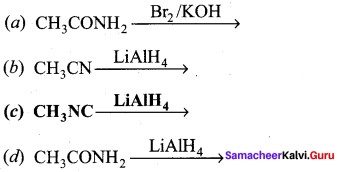
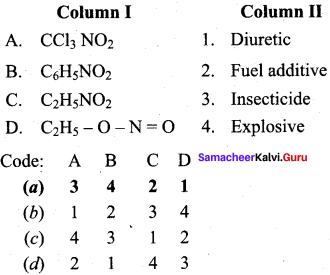
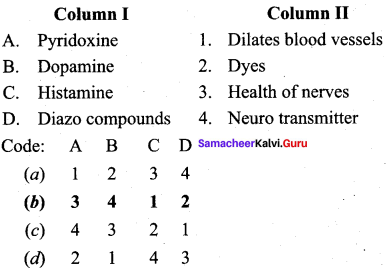
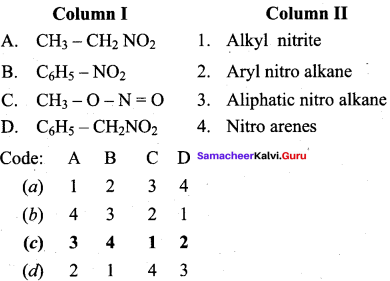

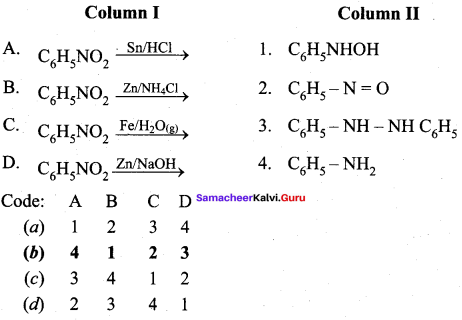
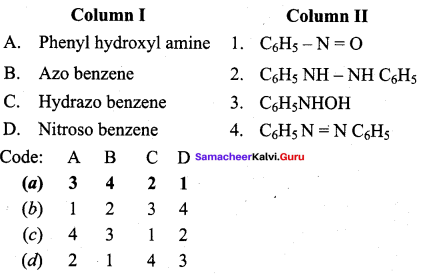
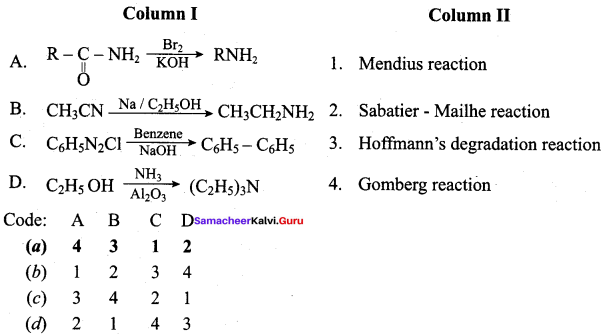

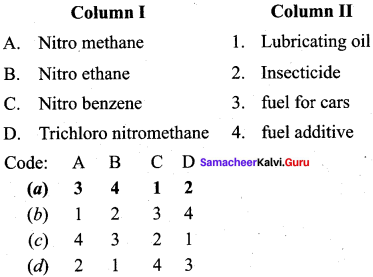
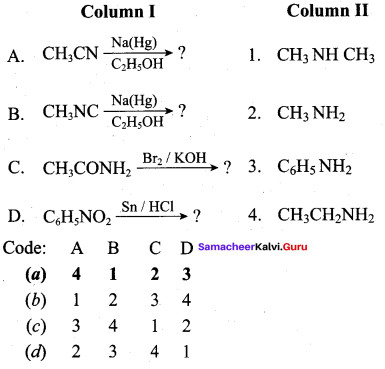

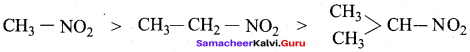
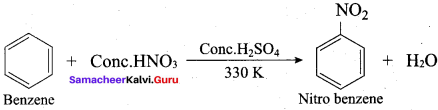
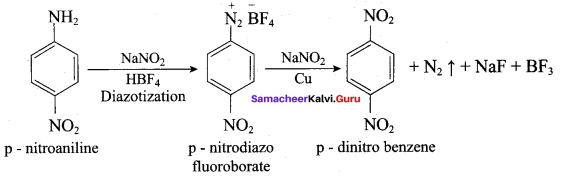
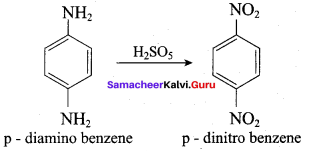
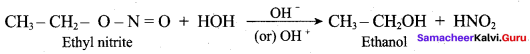

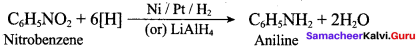
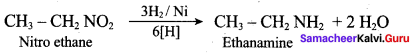
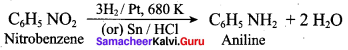
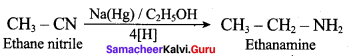
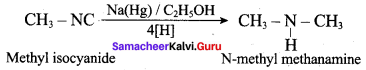

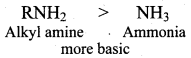
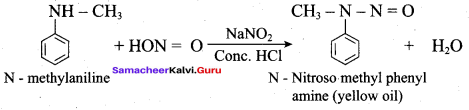
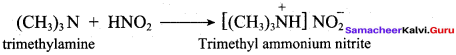
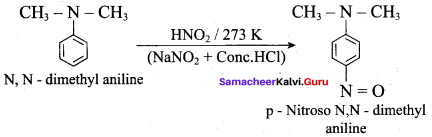
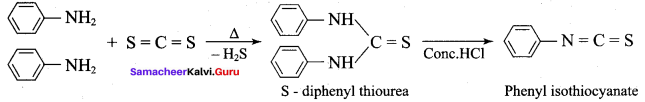
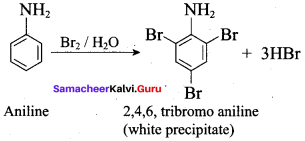
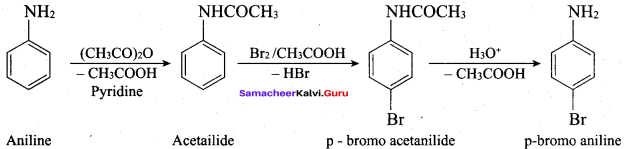
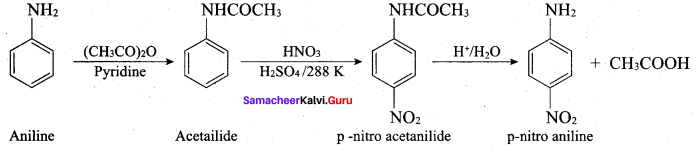
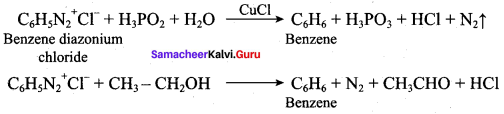
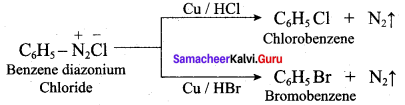
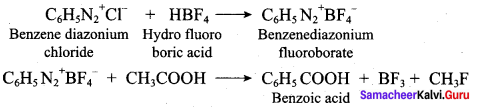
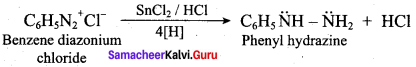

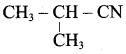
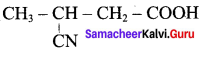
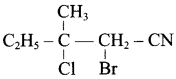
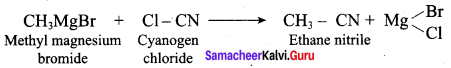
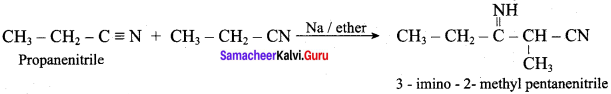
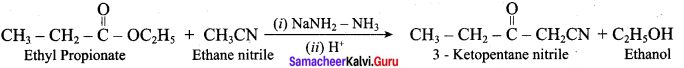
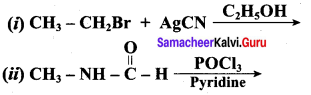
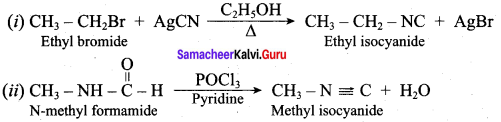
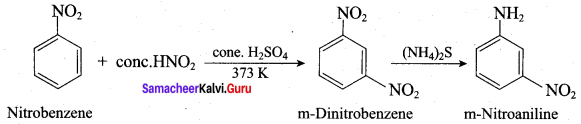
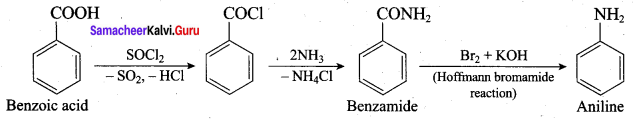
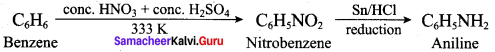
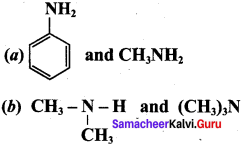
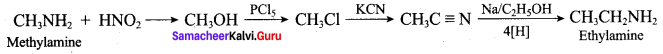
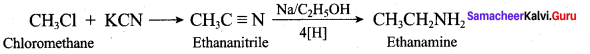
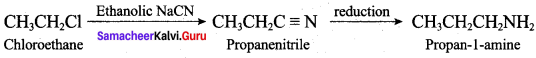
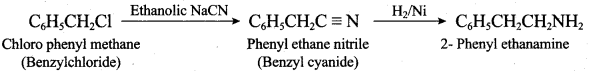
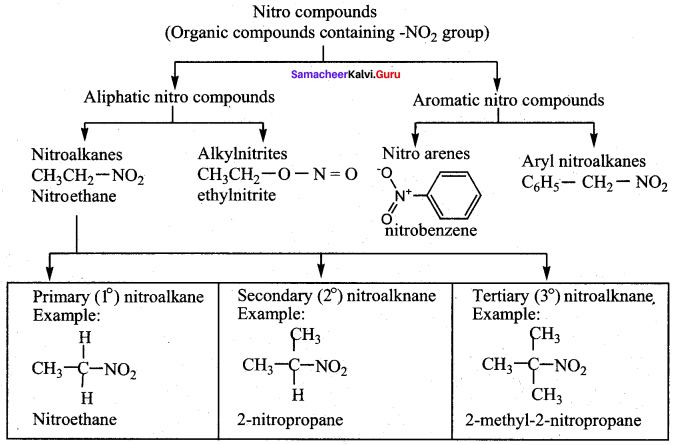
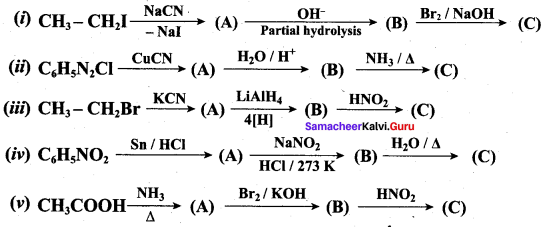
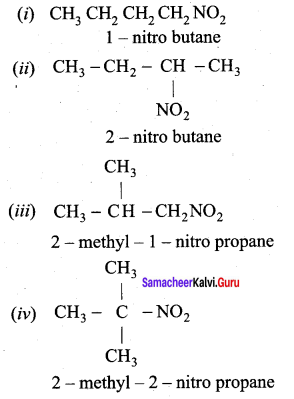
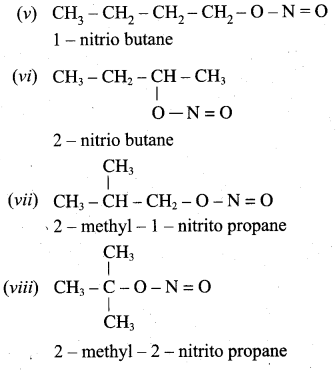
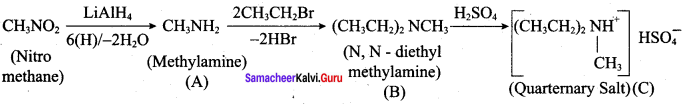
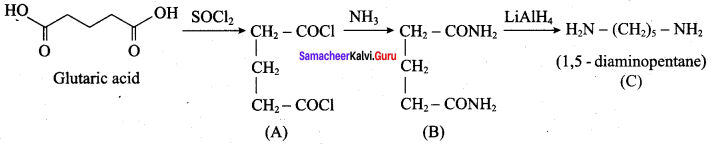
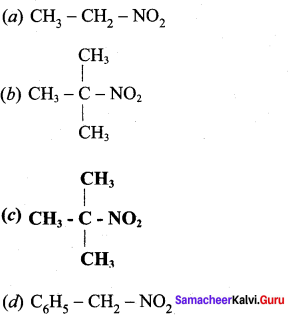
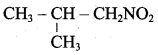 2 – methyl – 1 – nitropropane
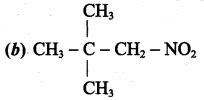
2 – methyl – 1 – nitropropane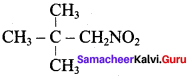 2, 2 – dimethyl – 1- nitropropane
2, 2 – dimethyl – 1- nitropropane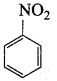 Nitrobenzene
Nitrobenzene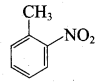 2 – nitro – 1 – methyl benzene
2 – nitro – 1 – methyl benzene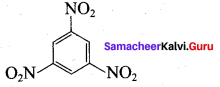 1, 3, 5 – trinitrobenzene
1, 3, 5 – trinitrobenzene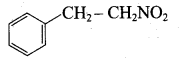 2 – phenyl – 1 – nitroethane
2 – phenyl – 1 – nitroethane
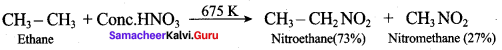
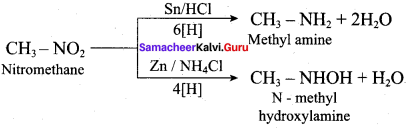
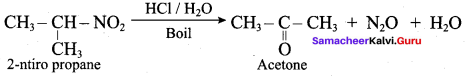
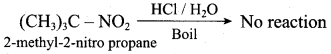
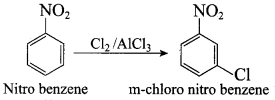
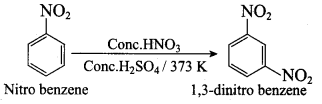
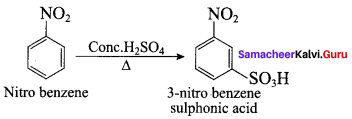
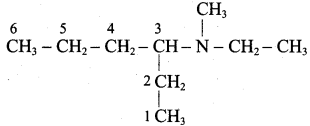
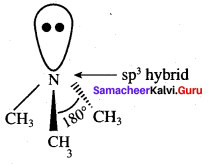
 Propan – 2 – amine
Propan – 2 – amine