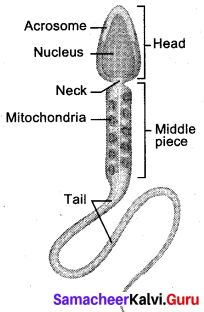
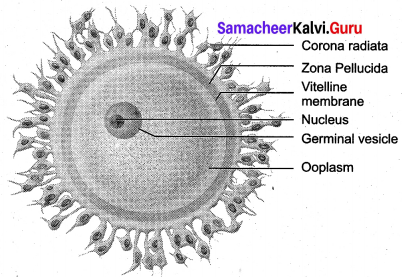
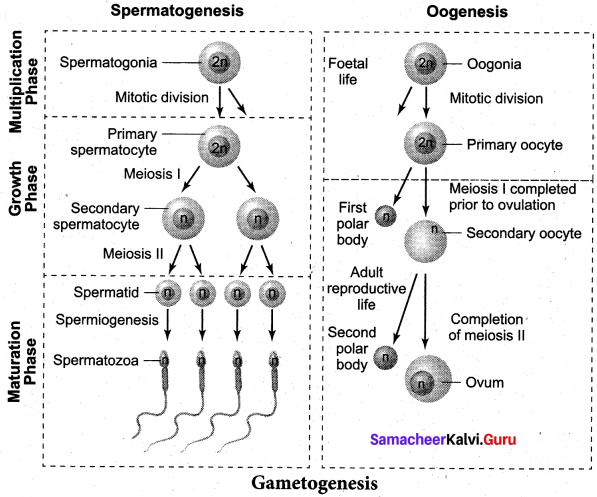
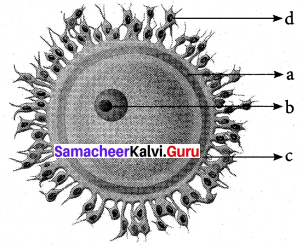
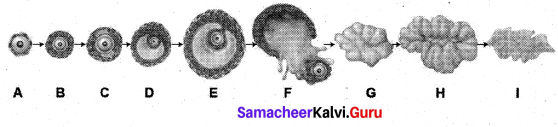
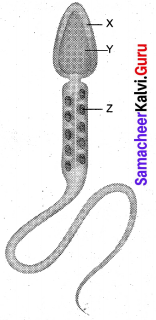
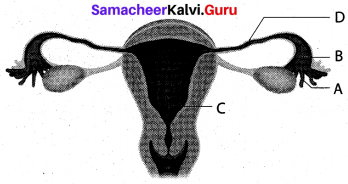
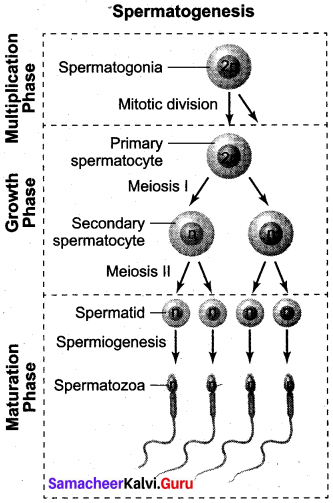
Get Tamilnadu Board Class 12 Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter wise Study Material to score good marks in the exam. Various chapters with subtopics are explained clearly in Samacheer Kalvi Class 12 Bio Zoology Solutions Material. All the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12 Bio Zoology Book Solutions Chapter 10 Organisms and Population Questions, answers, Notes, Guide, Pdf along with the explanations are provided by the subject experts. Students can easily learn Tamilnadu Board Class 12 Chapter wise Bio Zoology with the help of the step by step guide provided on our site. Learn all the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12 Bio Zoology concepts to attempt the exam with more confidence. Read all the concepts of Tamilnadu Board Solutions for Class 12 Bio Zoology Chapter 10 Organisms and Population.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 10 Organisms and Population
Whether you want to become an expert in Bio Zoology or to get good marks in the exam, you have one and only solution is practicing with Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Chapter wise Solutions. Strengthen your weakness by learning the Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Chapter 10 Organisms and Population Questions and Answers on our site. You can learn directly online on our website or learn offline by downloading Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Chapter wise material. Save your time and read Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Subject at your comfort level.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Organisms and Population Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Question 1.
All populations in a given physical area are defined as ___________
(a) Biome
(b) Ecosystem
(c) Territory
(d) Biotic factors
Answer:
(a) Biome
Question 2.
Organisms which can survive a wide range of temperature are called ___________
(a) Ectotherms
(b) Eurytherms
(c) Endotherms
(d) Stenotherms
Answer:
(b) Eurytherms
Question 3.
The interaction in nature, where one gets benefit on the expense of other is _________
(a) Predation
(b) Mutualism
(c) Amensalism
(d) Commensalism
Answer:
(d) Commensalism
Question 4.
Predation and parasitism are which type of interactions?
(a) (+,+)
(b) (+, O)
(c) (-, -,)
(d) (+, -)
Answer:
(d) (+, -)
Question 5.
Competition between species leads to ___________
(a) Extinction
(b) Mutation
(c) Amensalism
(d) Symbiosis
Answer:
(a) Extinction
Question 6.
Which of the following is an r-species?
(a) Human
(b) Insects
(c) Rginoceros
(d) Whale
Answer:
(b) Insects
Question 7.
Match the following and choose the correct combination from the options given below.

Dispersal
(a) A – 4, B – 5, C – 2, D -3, E – 1
(b) A – 3, B – 1, C – 4, D – 2, E – 5
(c) A – 2, B – 3, C – 1, D – 5, E – 4
(d) A – 5, B – 4, C – 2, D – 3, E – 1
Answer:
(a) A – 4, B – 5, C – 2, D -3, E – 1
Question 8.
The figure given below is a diagrammatic representation of response of organisms to abiotic factors. What do A, B and C represent respectively
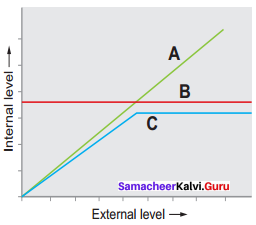
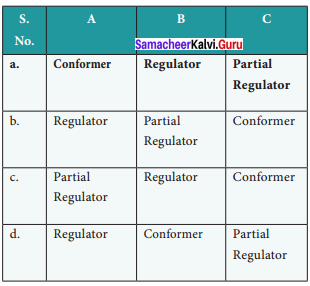
Answer:
(a) Conformer, Regulator, Partial Regulator
Question 9.
The relationship between sucker fish and shark is ___________
(a) Competition
(b) Commensalism
(c) Predation
(d) Parasitism
Answer:
(b) Commensalism
Question 10.
What type of human population is represented by the following age pyramid?
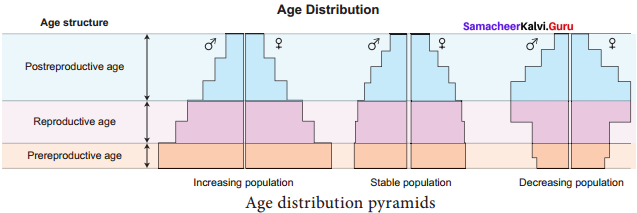
(a) Vanishing population
(b) Stable population
(c) Declining population
(d) Expanding population
Answer:
(b) Stable population
Question 11.
Which of the following is correct for r-selected species?
(a) large number of progeny with small size
(b) large number of progeny with large size
(c) small number of progeny with small size
(d) small number of progeny with large size
Answer:
(a) large number of progeny with small size
Question 12.
Animals that can move from fresh water to sea called as ___________
(a) Stenothermal
(b) Eurythermal
(c) Catadromous
(d) Anadromous
Answer:
(c) Catadromous
Question 13.
Some organisms are able to maintain homeostasis by physical means ___________
(a) Conform
(b) Regulate
(c) Migrate
(d) Suspend
Answer:
(b) Regulate
Question 14.
What is a Habitat?
Answer:
A habitat can be considered as the ‘address’ of the organism. Organisms in a habitat interact with each other and can be part of trophic levels to form food chains and food webs.
Question 15.
Define ecological niche.
Answer:
Niche of an organism can be defined as the total position and function of an individual in its environment.
Question 16.
What is Acclimatisation?
Answer:
Animals are known to modify their response to environmental changes (stress) in reasonably short time spans. This is known as Acclimatization. This is observed when people who have moved from the plains to higher altitudes show enhanced RBC count within a few days of settling in their new habitat. This helps them cope with lower atmospheric oxygen and higher oxygen demand.
Question 17.
What is Pedogenesis?
Answer:
Pedogenesis is the process of formation of soil (embryonic soil) from the rock materials by weathering.
Question 18.
What is Zero Stress?
Answer:
Stress refers to any environmental factor causing a change in the biological system which is potentially injurious.
Question 19.
What is soil permeability?
Answer:
The characteristic of soil that determines the movement of water through pore spaces is known as soil permeability. Soil permeability is directly dependent on the pore size. Water holding capacity of the soil is inversely dependent on soil porosity.
Question 20.
Differentiate between Eurytherms and Stenotherms.
Answer:
Eurytherms:
- Organism that can tolerate wide range of temperature.
- E.g: Human beings
Stenotherms:
- Organism that can tolerate narrow range of templerature.
- E.g: Fish
Question 21.
Explain hibernation and aestivation with examples.
Answer:
In certain conditions, if the organisms is unable to migrate, it may avoid the stress by becoming inactive. This is seen commonly in bears going into hibernation during winter. Some snails and fish go into aestivation to avoid summer related problems like heat and desiccation.
Question 22.
Give the diagnostic characters features of a Biome.
Answer:
- Location, Geographical position (Latitude and Longitude)
- Climate and physiochemical environment
- Predominant plant and animal life
- Boundaries between biomes are not always sharply defined. Transition or transient zones are seen.
Question 23.
Classify the aquatic biomes of Earth.
Answer:
- Freshwater (Lakes, ponds and rivers)
- Brackish water (Estuaries / Wetlands)
- Marine (Coral reefs, pelagic zones and abyssal zones)
Question 24.
What are the ways by which organisms respond to abiotic factors?
Answer:
The ways by which organism respond to abiotic stress are Regulate, Conform, Migrate and Suspends, etc.
Question 25.
Classify the adaptive traits found in organisms.
Answer:
The adaptive traits may be structural adaptation, behavioural adaptation and physiological adaptation.
Question 26.
Differentiate Natality and Mortality?
Answer:
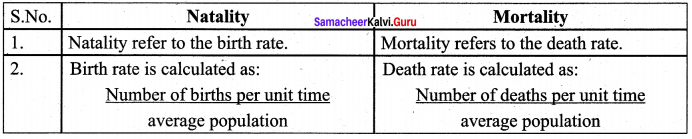
Question 27.
Differentiate J and S shaped curve.
Answer:
J-shaped growth:
- Population increase rapidly and exponentally and stops suddenly due to environmental stress.
- Population declines due to mass mortality.
- E.g: Insects
S-shaped growth:
- Population increases slowly at first then more rapidly and then slows down due to this environmental stress.
- Population is maintained.
- E.g: Small mammals
Question 28.
Give an account of population regulation.
Answer:
The inherent tendency of all animal populations is to increase in number. But it does not increase indefinitely. Once the carrying capacity of the environment is reached, population numbers remain static or fluctuate depending on environmental conditions. This is regulated by many factors which are
- Density independent – Extrinsic factors
- Density dependent – Intrinsic factors
Extrinsic factors include availability of space, shelter, weather and food, etc. Intrinsic factors include competition, predation, emigration, immigration and diseases.
Question 29.
What is ecological density, crude density and population density?
Answer:
| S.No. | Indices of Density | Keys |
| 1. | Population density | It is usually expressed as the number of individuals per unit area or volume. E.g. 100 trees per acre. |
| 2 | Crude density | It is the size of a population in relation to the numbers per unit of total space. E.g. 1000 fish in a pond. |
| 3 | Ecological density | It is the size of a population in relation to the numbers per unit of habitat space. (Available area or volume that can be colonized by a population). E.g. 1000 fish in the volume of water in the pond. |
Question 30.
Give an account of the properties of soil.
Answer:
- Texture of soil – The texture of soil is determined by the size of the soil particles. The types of soil include sand, silt and clay on the basis of their size differences.
- Porosity – The space present between soil particles in a given volume of soil are called pore spaces. The percentage of soil volume occupied by pore space or by the interstitial spaces is cal Ted porosity of the soil.
- Permeability of soil – The characteristic of soil that determines the movement of water through pore spaces is known as soil permeability. Soil permeability is directly dependent on the pore size. Water holding capacity of the soil is inversely dependent on soil porosity.
- Soil Temperature – Soil gets its heat energy from solar radiation, decomposing organic matter, and heat from the interior of Earth. Soil temperature effects the germination of seeds, growth of roots and biological activity of soil-inhabiting micro-and macroorganisms.
- Soil water – In soil, water is not only important as a solvent and transporting agent, but also maintains soil texture, arrangement and compactness of soil particles, making soil habitable for plants and animals.
Question 31.
Differentiate between Tundra and Taiga Biomes.
Answer:
Tundra Biome:
- Tundras are Treeless plains with grasses.
- Precipitation is less than 250 mm per year.
Taiga Biome:
- Taiga biome is composed of conifers with needle shaped leaves and scaly leaves.
- Precipitation is about 380-1000 mm per year
Question 32.
List the adaptations seen in terrestrial animals.
Answer:
- Earthworms, land Planarians secrete a mucus coating to maintain a moist situation for burrowing, coiling and respiration, etc.
- Arthropods have an external covering over the respiratory surfaces and well – developed tracheal systems.
- In vertebrate skin, there are many cellular layers besides the well-protected respiratory surfaces that help in preventing loss of water.
- Some animals obtain their water requirement from food as partial replacement of water lost through excretion.
- Birds make nests and breed before the rainy season as there is availability of abundant food. But during drought birds rarely reproduce.
- Camels are able to regulate water effectively for evaporative cooling through the-skin and respiratory system and excrete highly concentrated urine, and can also withstand dehydration up to 25% of their body weight.
Question 33.
Describe Population Age Distribution.
Answer:
The proportion of the age groups (pre-reproductive, reproductive and post reproductive) in a population is its age distribution attribute. This determines the reproductive status of the population at the given time and is an indicator of the future population size. Usually a rapidly growing population will have larger proportion of young individuals. A stable population will have an even distribution of various age classes. A declining population tends to have a larger proportion of older individuals.
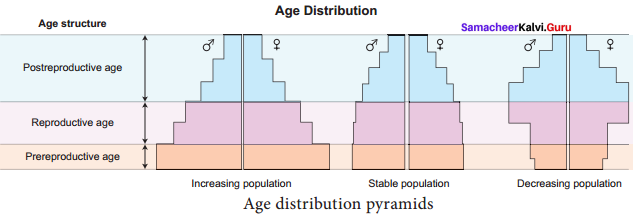
Question 34.
Describe Growth Models/Curves.
Answer:
Populations show characteristic growth patterns or forms. These patterns can be plotted and termed as J-shaped growth form and S-shaped growth form (Sigmoid form). Their growth is represented by S shaped growth curve. J shaped growth form: When a population increases rapidly in an exponential fashion and then stops abruptly due to environmental resistance or due to sudden appearance of a limiting factor, they are said to exhibit J-shaped growth form. Many insects show explosive
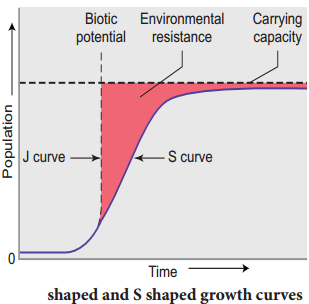
increase in number during the rainy season followed by their disappearance at the end of the season. S-Shaped growth form (sigmoid growth) Some populations, as in a population of small mammals, increase slowly at first then more rapidly and gradually slow down as environmental resistance increases whereby equilibrium is reached and maintained. Their growth is represented by S shaped growth curve
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Organisms and Population Additional Questions and Answers
1 – Mark Questions
Question 1.
The study dealing with animal behaviour is called as ________
(a) Euthenics
(b) Ethology
(c) Ecology
(d) Pedogenesis
Answer:
(b) Ethology
Question 2.
Identify the proper sequence in increasing order of population ________
(a) Species → Population → Community → biome
(b) Population → Community → Species → biome
(c) Biome → Species → Community → Population
(d) Community → Population → Biome → Species
Answer:
(a) Species → Population → Community → biome
Question 3.
Functional status of an organism in its community is ________
(a) Biome
(b) Niche
(c) Species
(d) Population
Answer:
(b) Niche
Question 4.
Pick out the eurythermal organism ________
(a) Fish
(b) Frog
(c) Tiger
(d) Lizards
Answer:
(c) Tiger
Question 5.
Locomotary speed of an organism changes due to light. This phenomenon is referred as ________
(a) Photonasty
(b) Photokinesis
(c) Phototropism
(d) Phototaxis
Answer:
(b) Photokinesis
Question 6.
Identify the incorrect statement
(a) Water is a universal solvent
(b) Water has less surface tension
(c) Water is heavier than air
(d) When freezes water contracts
Answer:
(b) Water has less surface tension
Question 7.
The soil zone is known as ________
(a) Pedosphere
(b) Atmosphere
(c) Hydrosphere
(d) Stratosphere
Answer:
(a) Pedosphere
Question 8.
Assertion (A): Snake is a stenotherm.
Reason (R): Organism can tolerate narrow temperature fluctuations.
(a) Both A and R are correct R explain A
(b) A is correct R is incorrect
(c) R doesnot explain A
(d) Both A and R are incorrect
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct R explain A
Question 9.
Assertion (A): Diapause is carried out to overcome abiotic stress.
Reason (R): Animals become inactive during winter.
(a) Both A and R are correct R explain A
(b) A is correct R is incorrect
(c) R doesnot explain A
(d) Both A and R are incorrect
Answer:
(b) A is correct R is incorrect
Question 10.
Assertion (A): Movement of organism from one place to another and back is called migration.
Reason (R): Eel is an example for aradromous migration.
(a) Both A and R are correct R explain A
(b) A is correct R is incorrect
(c) R doesnot explain A
(d) Both A and R are incorrect
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct R explain A
Question 11.
Which is not a feature of Tundra?
(a) Large population oscillation
(b) Short season of growth and reproduction
(c) Low biotic diversity
(d) Extremely hot climate
Answer:
(d) Extremely hot climate
Question 12.
Pick out the correct statement regarding K-selected species
(a) Produce many offsprings
(b)Only few reach adulthood
(c) Unstable environment
(d) Long life expectancy
Answer:
(d) Long life expectancy
Question 13.
Maximum reproductive capacity of an organism under favourable condition is referred as ________
(a) Carrying capacity
(b)Biotic potential
(c) Natality
(d) Fecundity
Answer:
(b) Biotic potential
Question 14.
During breeding season, Salmon migrates from sea to fresh water. This is an example for ________
Answer:
Anadromous migration.
Question 15.
Exponential growth shows ________ growth patterns.
Answer:
J-shaped
Question 16.
Interaction between Ascaris in human gut is an example for ________
Answer:
Parasitisim
Question 17.
If both the species of an interaction is benefitted then it is said to be ________
Answer:
Mutualism
Question 18.
Match the following

Answer:
(a) a – ii, b – i, c – iv, d – iii
(b) a – iii, b – ii, c – i, d – iv
(c) a – iv, b – iii, c – iii, d – i
(d) a – i, b – iv, c – iii, d – ii
Question 19.
As altitude increases ________
(a) O2 density increases
(b) Precipitation decreases
(c) Temperature increases
(d) Snowing decreases
Answer:
(b) Precipitation decreases
2 – Mark Questions
Question 1.
What is ecosphere?
Answer:
The largest and most nearly self-sufficient biological system is often designated as the Ecosphere, which includes all the living organisms of the Earth, interacting with the physical environment to regulate their distribution, abundance, production and evolution.
Question 2.
List out the adaptation of fish to survive in aquatic environment.
Answer:
Fishes possess fins for locomotion, streamlined body (aerodynamic) sensory lateral line system, gills for respiratory purpose and air sacs for floatation.
Question 3.
Define niche.
Answer:
Niche of an organism can be defined as the total position and function of an individual in its environment.
Question 4.
Name few abiotic factors that influence organisms in an environment.
Answer:
Temperature, light, water, soil, humidity and altitude, etc.
Question 5.
State Allen’s rule and Bergmann’s rule.
Answer:
Allen’s rule: Warm blooded animals living in cold climates have shorter limbs, ears and other appendages than the same species in warm climates.
Beegmann’s rule: Birds and mammals have larger body size in cold regions than warmer regions.
Question 6.
What does Jordon’s rule state?
Answer:
In some aquatic environments, an inverse relationship between water temperature and fish meristic characters is observed – lower the temperature, more the vertebrae.
Question 7.
State Van’t Hoff’s rule.
Answer:
Van’t Hoff’s rule states that with the increase of every 10°C, the rate of metabolic activity is doubled or the reaction rate is halved with the decrease of 10°C.
Question 8.
What is Q10 value? How it is calculated?
Answer:
The effect of temperature on the rate of reaction is expressed in terms of temperature coefficient or Q10 value. The Q10 values are estimated taking the ratio between the rate of reaction at X°C and rate of reaction at (X-10°C).
Question 9.
Differentiate between Eurytherms and Stenotherm
Answer:
Eurytherm:
- Organism that can tolerate wide range of temperature.
- E.g: Human beings.
Stenotherm:
- Organism that can tolerate narrow range of temperature.
- E.g: Fishes.
Question 10.
Snakes are stenotherms. Why?
Answer:
Snakes are stenotherms since they can tolerae only a narrow range of temperature fluctuation.
Question 11.
Define phototaxis.
Answer:
The movement of organism in response to light, either towards the source of light as in Moths (positive phototaxis) or away from light (Earthworm (negative phototaxis).
Question 12.
What is photokinesis?
Answer:
A change in the speed of locomotion (or frequency of turning) in a motile organism or cell which is made in response to a change in light intensity is called photokinesis. It involves undirected random movement in response to light.
Question 13.
What is pedosphere and soil profile?
Answer:
- Pedosphere: The outer soil zone of the Earth.
- Soil profile: Soil is formed by many horizontal layers called soil profile.
Question 14.
Point out the major functions of soil.
Answer:
Soil has four major functions
- medium for plant growth
- means for water storage and purification
- modifier of Earth’s atmosphere
- habitat for many organisms, which in turn modify the soil
Question 15.
Define humidity and mention its types.
Answer:
Moisture in the form of invisible vapor in the atmosphere is called humidity, which is generally expressed in terms of absolute humidity, relative humidity or specific humidity.
Question 16.
What is a Biome?
Answer:
Biomes are large regions of Earth that have similar or common vegetation and climatic conditions. They play a crucial role in sustaining life on Earth. They are defined by their soil,climate, flora and fauna. Biomes have distinct biological communities that have been formed in response to a shared physio-chemical climate.
Question 17.
Enumerate the characters of a Biome.
Answer:
- Location, Geographical position (Latitude and Longitude)
- Climate and physiochemical environment
- Predominant plant and animal life
- Boundaries between biomes are not always sharply defined. Transition or transient zones are seen.
Question 18.
Which is the largest biome on Earth? Classify it.
Answer:
Aquatic biome is the largest biome occupying 71% of biosphere.
The aquatic biomes on Earth are:
- Fresh water biome (Lakes and Ponds)
- Brackish water biome (Estuaries / Wetlands)
- Marine biome (Coral reefs and abyssal zones)
Question 19.
Define alpine zone.
Answer:
The alpine zone between timber line and snow zone includes in the descending order, a sub¬snow zone immediately below the snow zone, a meadow zone in the centre and a shrub zone which gradually merges into the timber zone.
Question 20.
What is a forest? Name the major forest biomes.
Answer:
Forest is a broad term used to describe areas where there are a large number of trees. The major forest biomes are the Tropical forests and the Temperate forests.
Question 21.
What are the types of tropical forest?
Answer:
- Evergreen rain forest
- Seasonal rain forest
- Semi evergreen forest
- Dry deciduous forest
Question 22.
How the cold deserts are characterized? Give an example.
Answer:
- Cold deserts are characterized by cold winters with snow fall and high overall rainfall throughout the winter and occasionally over the summer.
- E.g: Ladakh region in India.
Question 23.
Fishes are said to be conformers – Justify.
Answer:
In fishes, the osmotic concentration of the body fluids changes with that of surrounding water osmotic concentration. Hence they are called conformers.
Question 24.
When and why do snails go into aestivation?
Answer:
Snails undergo aestivation during summer to avoid heat and overcome dessication.
Question 25.
How do animals like fishes and bears avoid unfavourable climatic conditions?
Answer:
- Fishes undergo aestivation to avoid summer related problems.
- Bears undergo hibernation to avoid winter related problems.
Question 26.
What are cryptic animals? How cryptic adaptation helps them?
Answer:
Cryptic animals are those which camouflage perfectly with their environment and are almost impossible to detect. Certain reptiles and insects such as chameleons and stick insects show this type of adaptation, which helps in prey capture or to evade from predators.
Question 27.
Explain any two behavioural adaptations?
Answer:
The two most characteristic forms of behavioral adaptations are migration and courtship. Migration allows the animals to find better resources or evade threat. Courtship is a set of behavioral patterns to find a mate to reproduce.
Question 28.
Define population.
Answer:
Population is defined as any group of organisms of the same species which can interbreed among themselves, and occupy a particular space and function as part of a biotic community.
Question 29.
What are the attributes of population?
Answer:
- Population density
- Natality, Mortality
- Age distribution
- dispersion (immigration and emigration).
Question 30.
Camels are well adapted to xeric conditions, how?
Answer:
Camels are able to regulate water effectively for evaporative cooling through the skin and respiratory system and excrete highly concentrated urine, and can also withstand dehydration up to 25% of their body weight.
Question 31.
How natality and mortality can be calculated?
Answer:

Question 32.
Define biotic potential.
Answer:
It is the maximum reproductive capacity of an organism under optimum environmental conditions.
Question 33.
Which type of species interaction is noticed between:
- Cat and Rat
- Crocodile and birds
Answer:
- Amensalism
- Mutualism
Question 34.
Define Commensalism.
Answer:
Commensalism is species interaction in which one species (the commensal) is benefitted whereas the host is neither benefitted nor affected.
Example: Sucker fish on Shark.
3 – Mark Questions
Question 35.
Define the terms
- guilds
- ecological equivalents
Answer:
- Groups of species with comparable role and niche dimensions within a community are termed ‘guilds’.
- Species that occupy the same niche in different geographical regions, are termed ‘ecological equivalents’
Question 36.
Define temperature. How it impacts the life of an organism?
Answer:
Temperature or degree of hotness and coldness is an essential and variable factor in any environment. It influences all forms of life by affecting many vital activities of organisms like metabolism, behaviour, reproduction, development and even death in the Biosphere.
Question 37.
Light is essential for life. Why?
Answer:
Light influences growth, pigmentation, migration and reproduction. The intensity and frequency of light influences metabolic activity, induce gene mutations (UV, X-rays). Light is essential for vision. This is proved by the poorly developed or absence of eyes in cave dwelling organisms. Diapause is also influenced by light in animals. Gonads of birds become more active with increasing light in summer. Light influences the locomotion and movement of lower animals.
Question 38.
What is Acclimatization? Explain with example.
Answer:
Animals are known to modify their response to environmental changes (stress) in reasonably short time spans. This is known as Acclimatization. This is observed when people who have moved from the plains to higher altitudes show enhanced RBC count within a few days of settling in their new habitat. This helps them cope with lower atmospheric oxygen and higher oxygen demand.
Question 39.
Enlist the characteristics of Tundra.
Answer:
- Extremely cold climate
- Low biotic diversity
- Simple vegetation structure
- Limitation of drainage
- Short season of growth and reproduction
- Energy and nutrients in the form of dead organic material
- Large population oscillations
Question 40.
Name the major biomes of the Earth.
Answer:
Tundra biome, Taiga biome, Grassland biome, Alpine biome, Forest biome and Desert biome.
Question 41.
Why do organisms migrate? Give example.
Answer:
Organisms tend to move away temporarily from a stressful habitat to a new, hospitable area and return when the stressful period is over. Birds migrate from Siberia to Vedanthangal in Tamilnadu to escape from the severe winter periods.
Question 42.
Define
- Diapause
- Ethology
Answer:
- Diapause: Some lower animals suspend a certain phase of their life cycle, which is referred to as diapause.
- Ethology: The study of animal behaviour, under natural conditions.
Question 43.
Comment on the J-shaped growth form.
Answer:
When a population increases rapidly in an exponential fashion and then stops abruptly due to environmental resistance or due to sudden appearance of a limiting factor, they are said to exhibit J-shaped growth form. Many insects show explosive increase in number during the rainy season followed by their disappearance at the end of the season.
Question 44.
Explain sigmoid growth.
Answer:
Some populations, as in a population of small mammals, increase slowly at first then more rapidly and gradually slow down as environmental resistance increases whereby equilibrium is reached and maintained. Their growth is represented by S shaped growth curve.
5 – Mark Questions
Question 45.
Enumerate the properties of water.
Answer:
- Water is one of the main agents in Pedogenesis (soil formation).
- It is the medium for several different ecosystems.
- It is present as moisture in the atmosphere and the outer layers of the lithosphere and is uneven in distribution on the Earth.
- Water is heavier than air and imparts greater buoyancy to the aquatic medium. This enables organism to float at variable levels.
- Water has high heat capacity and latent heat, due to which it can withhold large amounts of heat. Thus, oceans and lakes tend to maintain a relatively constant temperature, and the biosphere is relatively thermostable.
- Water is physically unique because it is less dense as a solid (ice) than as a liquid.
- When water freezes (0°C), it contracts. The maximum density of liquid water occurs at 4°C. Below that, it expands markedly. This enables ice to float on the top of water bodies. Hence, only the surface of water bodies will freeze, while below the surface, water will be in liquid form, sustaining life.
Question 46.
Give an account of grass land biome.
Answer:
- Grasslands occur in temperate and in the tropical regions.
- They have hot summers, cold winters, and irregular rainfall.
- Often they are characterized by high winds.
- The low irregular rainfall is the factor which makes the difference between a temperate deciduous forest and a temperate grassland.
- Herbivores like antelope, bison, wild horse, jack rabbit, ground squirrel and prairie dogs are abundant.
- Predators include coyotes, foxes, hawks and snakes.
- In India, fauna of grasslands includes Elephant, Gaur, Rhino and Antelope.
- Flora of grasslands include purple needle grass, wild oats, foxtail, ryegrass and buffalo grass.
Question 47.
Write in detail about Temperate forest and its types.
Answer:
- These forests occur in eastern North America, northeastern Asia and western and central Europe.
- Have well-defined seasons with a distinct winter. Moderate climate and a growing season of 140-200 days during 4-6 frost-free months distinguish temperate forests.
- Annual temperature varies from -30° C to 30° C.
- Precipitation (750-1500 mm) is distributed evenly throughout the year.
- Soil is fertile, enriched with decaying litter.
Canopy is moderately dense and allows light to penetrate, resulting in well-developed and richly diversified understorey vegetation and stratification of animals. - Flora is characterized by 3-4 tree species per km2. Trees have broad leaves that are lost annually such as oak, hickory, beech, hemlock, maple, basswood, cottonwood, elm, willow, and spring-flowering herbs.
- Fauna consists of squirrels, rabbits, skunks, birds, deer, mountain lion, bobcat, timber wolf, fox, and black bear. Based on seasonal distribution of rainfall, the types of temperate forests are:
- Moist conifer and evergreen broad-leaved forests: wet winters and dry summers.
- Dry conifer forests: dominate higher elevation zones; low precipitation.
- Mediterranean forests: precipitation is concentrated in winter (<1000 mm /year).
- Temperate coniferous forests: mild winters, high annual precipitation (> 2000 mm /year).
- Temperate broad-leaved rainforests: mild, frost-free winters, high precipitation (> 1500 mm/year), evenly distributed throughout the year.
Question 48.
Point out the adaptitive traits of aquatic animals.
Answer:
- The pectoral fins and dorsal fins act as stabilizers or balancers and the caudal fin helps in changing the direction as a rudder.
- Arrangement of body muscles in the form of bundles (myotomes) help in locomotion.
- Stream lined structure helps in the swift movement of the animals in water.
- Respiration by gills making use of gases dissolved in water.
- Presence of air-bladders filled with air for buoyancy.
- Presence of lateral-line system. They function as rheoreceptors which is helpful in echolocating objects in water.
- Integuments rich in mucous glands are protected by scales.
- Maintain water and ionic balance in its body with excretory structures.
Question 49.
Differentiate between r-selected species and k-selected species.
Answer:
r-selected species:
- Smaller sized organisms
- Produce many offspring
- Mature early
- Short life expectancy
- Each individual reproduces only once or few times in their life time
- Only few reach adulthood
- Unstable environment, density independent
k-seleced species:
- Larger sized organisms
- Produce few offspring
- Late maturity with extended parental care
- Long life expectancy
- Can reproduce more than once in lifetime
- Most individuals reach maximum life span
- Stable environment, density dependent
Question 50.
Describe in detail on population interaction.
Answer:
Organisms belonging to different populations interact for food, shelter, mating or for other necessities. Interaction may be intra specific (interaction within the members of same species) or inter specific (among organisms of different species). Intra specific association is observed for all livelihood processes like feeding, territoriality, breeding and protection.
Interspecific associations or interactions can be:
- Neutral: where different species live together but do not affect each other.
- Positive: it is a symbiotic relationship in which no organism in association is harmed and either one or both may be benefitted. It is of two types Mutualism and Commensalism. Negative: One or both of the interacting organisms will be affected as in case of competition, predation and parasitism.
Question 51.
Explain structural and behavioural adaptations seen in organism.
Answer:
The two most characteristic forms of behavioral adaptations are migration and courtship. Migration allows the animals to find better resources or evade threat. Courtship is a set of behavioral patterns to find a mate to reproduce. Most nocturnal animals remain underground or inactive during daytime. This is a modification of their feeding and activity pattern or habit or behaviour.
Higher Order Thinking (HOTs) Questions
Question 1.
Name the kind of interaction in the following pairs.
- Shark and Sucker fish
- Cat and Rat
- Lion and Deer
Answer:
- Commensalism
- Amensalism
- Predation
Question 2.
What are the four ways through which the living organisms respond to abiotic factor?
Answer:
Regulate, Conform, Migrate and Suspend
Question 3.
List out the different attributes that a population has and not an individual organism.
Answer:
Population density, Birth rate, Death rate, Age distribution and Population dispersion.
Question 4.
Census refers to the official count or survey of population. Every 10 years our government undertake census. In India the next census will be carried out in 2021. Mention any four characters that are employed in human population census.
Answer:
Birth rate, Death rate, Growth rate and Sex ratio.
Question 5.
Fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) are the most widely used genetic tool by molecular geneticists. The life cycle of a fruit fly completes within a time span of 15 days. Calculate the death rate if 12 individuals in a laboratory population of 148 fruit flies died during a particular week.
Answer:

Question 6.
People leaving in high altitudes show increased RBC count. Give reason.
Answer:
Higher the altitude, lower the atmospheric oxygen. Hence to compensate the oxygen demand they adapt themselves showing enhanced RBC count in the blood.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Chapter Wise Solutions PDF will help you to clear all doubts. Learn perfectly by using Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chapter 10 Organisms and Population Questions and Answers Bio Zoology Solutions PDF. Leave us a comment to clear your queries. Get instant updates by bookmarking our site. Get the best learning with the effective and excellent step by step Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Guide.