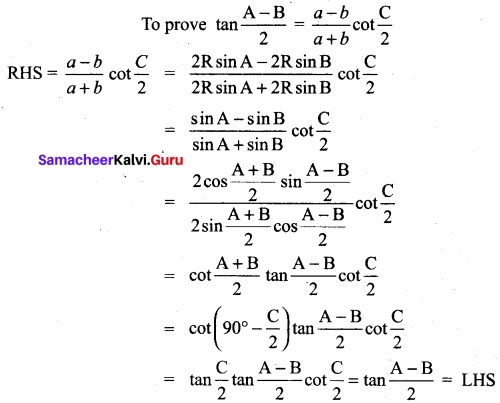
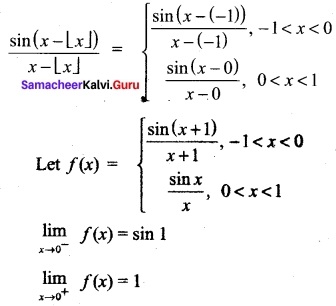
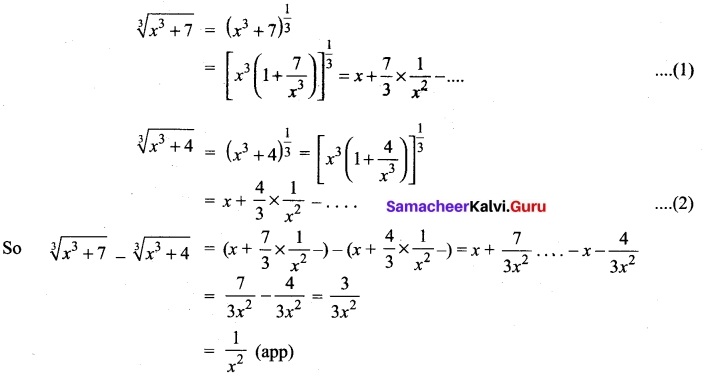
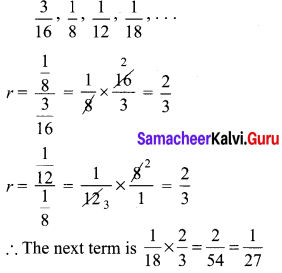
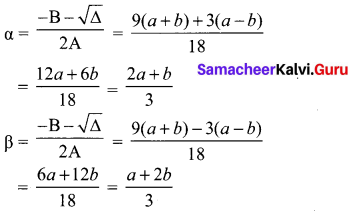
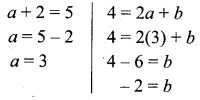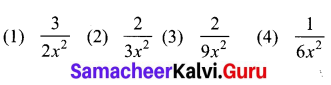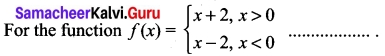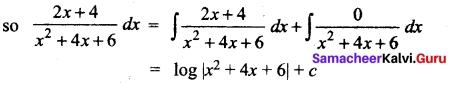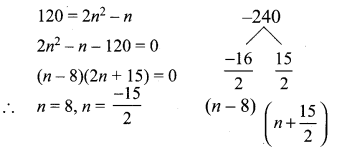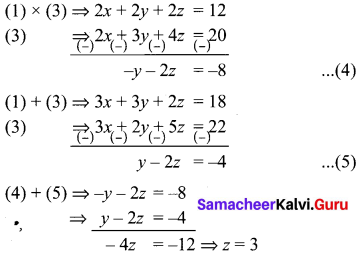You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Relations and Functions Additional Questions
Question 1.
Let A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12} Let R = {(1, 3), (2, 6), (3,10), (4, 9)} ⊂ A × B be a relation. Show that R is a function and find its domain, co-domain and the range of R.
Answer:
Domain of R = {1, 2, 3, 4}
Co-domain of R = B = {-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12}
Range of R= {3, 6, 10, 9}
Question 2.
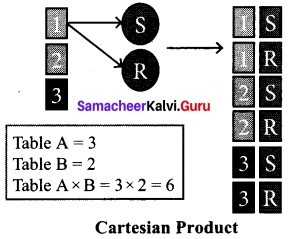
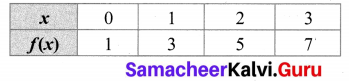
Let A = {0, 1, 2, 3} and B = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9} be two sets. Let f: A → B be a function given by f(x) = 2x + 1. Represent this function as (i) a set of ordered pairs (ii) a table (iii) an arrow and (iv) a graph.
Solution:
A = {0, 1, 2, 3}, B = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}
f(x) = 2x + 1
f(0) = 2(0) + 1 = 1
f(1) = 2(1) + 1 = 3
f(2) = 2(2) + 1 = 5
f(3) = 2(3) + 1 = 7
(i) A set of ordered pairs.
f = {(0, 1), (1, 3), (2, 5), (3, 7)}
(ii) A table
(iii) An arrow diagram
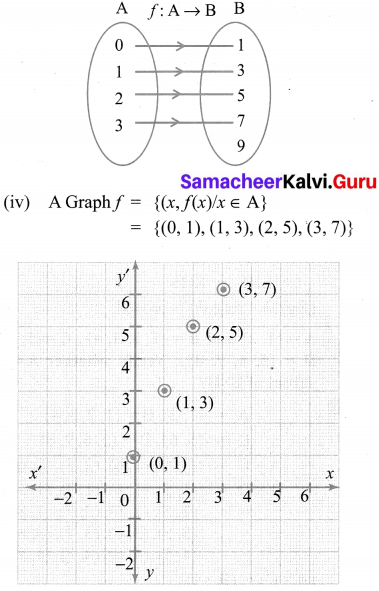
![]()
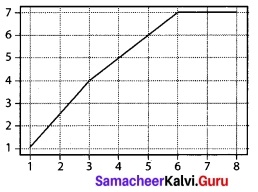
Question 3.
State whether the graph represent a function. Use vertical line test.
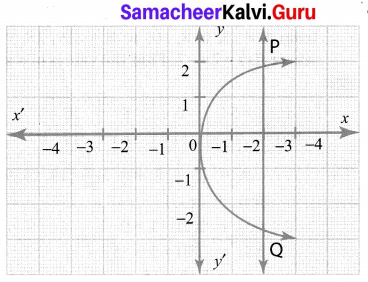
Solution:
It is not a function as the vertical line PQ cuts the graph at two points.
Question 4.
Let f = {(2, 7), (3, 4), (7, 9), (-1, 6), (0, 2), (5, 3)} be a function from A = {-1, 0, 2, 3, 5, 7} to B = {2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9}. Is this (i) an one-one function (ii) an onto function, (iii) both one- one and onto function?
Solution:
It is both one-one and onto function.
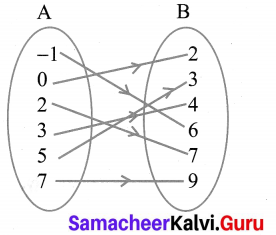
All the elements in A have their separate images in B. All the elements in B have their preimage in A. Therefore it is one-one and onto function.
Question 5.
A function f: (-7,6) → R is defined as follows.
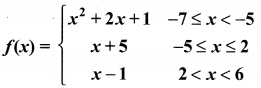
Find (i) 2f(-4) + 3 f(2)
(ii) f(-7) – f(-3)
Solution:
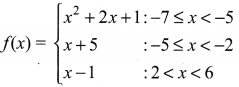
(i) 2f(-4) + 3f(2)
f(-4) = x + 5 = -4 + 5 = 1
2f(-4) = 2 × 1 = 2
f(2) = x + 5 = 2 + 5 = 7
3f(2) = 3(7) = 21
∴ 2f(-4) + 3f(2) = 2 + 21 = 23
(ii) f(-7) = x2 + 2x + 1
= (-7)2 + 2(-7) + 1
= 49 – 14 + 1 = 36
f(3) = x + 5 = -3 + 5 = 2
f(-7) – f(-3) = 36 – 2 = 34
![]()
Question 6.
If A = {2,3, 5} and B = {1, 4} then find
(i) A × B
(ii) B × A
Answer:
A = {2, 3, 5}
B = {1, 4}
(i) A × B = {2,3,5} × {1,4}
= {(2, 1) (2, 4) (3, 1) (3, 4) (5,1) (5, 4)}.
(ii) B × A = {1,4} × {2,3,5}
= {(1,2) (1,3) (1,5) (4, 2) (4, 3) (4, 5)}
Question 7.
Let A = {5, 6, 7, 8};
B = {- 11, 4, 7, -10, -7, – 9, -13} and
f = {(x,y): y = 3 – 2x, x ∈ A, y ∈ B}.
(i) Write down the elements of f.
(ii) What is the co-domain?
(iii) What is the range?
(iv) Identify the type of function.
Answer:
Given, A = {5, 6, 7, 8},
B = {- 11,4, 7,-10,-7,-9,-13}
y = 3 – 2x
ie; f(x) = 3 – 2x
f(5) = 3 – 2 (5) = 3 – 10 = – 7
f(6) = 3 – 2 (6) = 3 – 12 = – 9
f(7) = 3 – 2(7) = 3 – 14 = – 11
f(8) = 3 – 2 (8) = 3 – 16 = – 13
(i) f = {(5, – 7), (6, – 9), (7, – 11), (8, – 13)}
(ii) Co-domain (B)
= {-11,4, 7,-10,-7,-9,-13} i
(iii) Range = {-7, – 9, -11,-13}
(iv) It is one-one function.
Question 8.
A function f: [1, 6] → R is defined as follows:
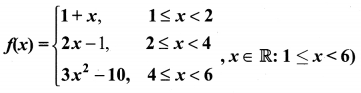
Find the value of (i) f(5)
(ii) f(3)
(iii) f(2) – f(4).
Solution:

(i) f(5) = 3x2 – 10
= 3 (52) – 10 = 75 – 10 = 65
(ii) f(3) = 2x – 1
= 2(3) – 1 = 6 – 1 = 5
(ii) f(2) – f(4)
f(2) = 2x – 1
= 2(2) – 1 = 3
f(4) = 3x2 – 10
= 3(42) – 10 = 38
∴ f(2) – f(4) = 3 – 38 = 35
![]()
Question 9.
The following table represents a function from A = {5, 6, 8, 10} to B = {19, 15, 9, 11}, where f(x) = 2x – 1. Find the values of a and b.
Solution:
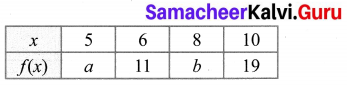
A = {5, 6, 8, 10}, B = {19, 15, 9, 11}
f(x) = 2x – 1
f(5) = 2(5) – 1 = 9
f(8) = 2(8) – 1 = 15
∴ a = 9, b = 15
Question 10.
If R = {(a, -2), (-5, 6), (8, c), (d, -1)} represents the identity function, find the values of a,b,c and d.
Solution:
R = {(a, -2), (-5, b), (8, c), (d, -1)} represents the identity function.
a = -2, b = -5, c = 8, d = -1.