You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 1 Chapter 6 Health and Hygiene
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Health and Hygiene Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the appropriate answer
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 6th Science Question 1.
Our body needs _______ for muscle-building.
(a) Carbohydrate
(b) Fat
(c) Protein
(d) Water
Answer:
(c) Protein
Health And Hygiene Class 6 Questions And Answers Samacheer Question 2.
Scurvy is caused due to the deficiency of ………..
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Vitamin B
(c) Vitamin C
(d) Vitamin D
Answer:
(c) Vitamin C
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Question 3.
Calcium is an example of a _______
(a) Carbohydrate
(b) Fat
(c) Protein
(d) Minerals
Answer:
(d) Minerals
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Guide Question 4.
We should include fruits and vegetables in our diet, because ……….
(a) They are the best source of Carbohydrates.
(b) They are the best source of Proteins.
(c) They are rich in minerals and vitamins.
(d) They have high water content.
Answer:
(c) They are rich in minerals and vitamins.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Book Back Answers Question 5.
Bacteria are very small _______ microorganism.
(a) Prokaryotic
(b) Eukaryotic
(c) Protozoa
(d) Acellular
Answer:
(a) Prokaryotic
II. True or false
6th Science Samacheer Kalvi Question 1.
There are three main nutrients present in food.
Answer:
False. There are six main nutrients present in food.
Samacheer Kalvi.Guru 6th Science Question 2.
Fats are used as an energy store by our body.
Answer:
True.
Samacheer Kalvi Science 6th Standard Question 3.
All bacteria have flagella.
Answer:
False. Not all bacteria have flagella only, some bacteria have flagella.
Samacheer Kalvi 6 Science Question 4.
Iron helps in the formation of haemoglobin.
Answer:
True
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solution Question 5.
Virus can grow and multiply outside host.
Answer:
False. Virus can grow and multiply inside host.
III. Fill in the Blanks.
- Malnutrition leads to _______
- Iodine deficiency leads to _______ in adults.
- Vitamin D deficiency causes _______.
- Typhoid is transmitted due to contamination of _______ and water.
- Influenza is a _______ disease.
Answers:
- deficiency disease
- goitre
- Rickets
- food
- viral (virus)
IV. Complete the Analogy.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Standard Question 1.
Rice: Carbohydrate :: Pulses: _______
Answer:
Protein.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Question 2.
Vitamin D : Rickets :: Vitamin C: _______
Answer:
Scurvy.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Book Question 3.
Iodine: Goitre :: Iron: _______
Answer:
Anaemia.
Samacheer Kalvi Class 6 Science Solutions Question 4.
Cholera: Bacteria :: Smallpox: _______
Answer:
Virus.
V. Match the following
- Vitamin A – Rickets
- Vitamin B – Night blindness
- Vitamin C – Sterility
- Vitamin D – Beriberi
- Vitamin E – Scurvy
Answer:
- Vitamin A – Night blindness
- Vitamin B – Beri beri
- Vitamin C – Scurvy
- Vitamin D – Rickets
- Vitamin E – Sterility
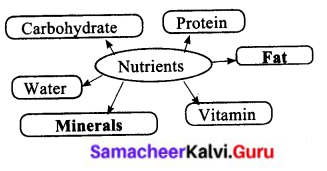
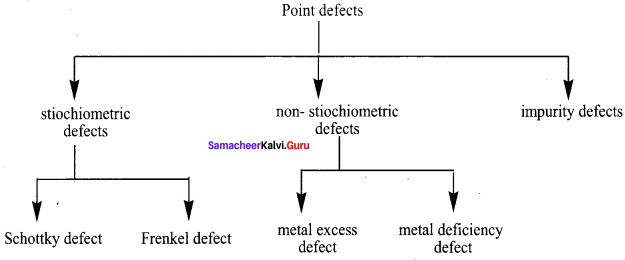
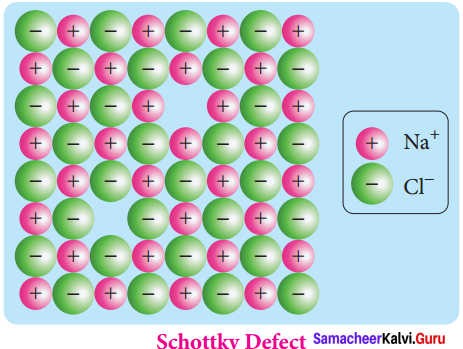
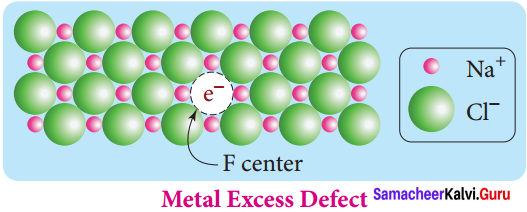
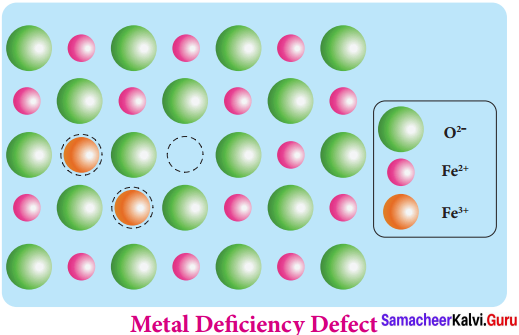
VI. Complete the diagram
Question:
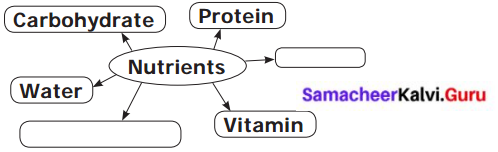
Answer:
VII. Write a Short Answer.
Samacheer Kalvi Science 6th Question 1.
Write two examples for each of the following.
Answer:
(a) Food items were rich in fat – Egg yolk, meat.
(b) Vitamin deficiency – diseases.
(c) Vitamin C – Scurvy
(d) Vitamin D – Rickets.
6th Samacheer Kalvi Science Question 2.
Differentiate between carbohydrate and protein.
Answer:
Carbohydrate:
- Energy giving component of the food.
- The sources of carbohydrate are nuts, fruits, rice and maize.
Protein:
- It is body building foods.
- The sources of proteins are pulses, soyabean, nuts, egg, and fish.
6th Standard Science Question 3.
Define the term ‘balanced diet’?
Answer:
A balanced diet is a diet which contains an adequate amount of all the necessary nutrients like carbohydrate fat protein minerals and vitamins required for healthy growth and activity.
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 6th Question 4.
Why should the fruits and vegetables not to be washed after cutting?
Answer:
We should not wash the fruits and vegetables after cutting, because the minerals and protein in the fruits and vegetables will also be washed away.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Solutions Question 5.
Write any two viral diseases.
Answer:
- AIDS
- Hepatitis.
Samacheerkalvi.Guru 6th Science Question 6.
What is the main feature of a microorganism?
Answer:
Microorganism will be seen with the help of microscope. They are very small in size.
VIII. Long Answer.
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 6th Standard Science Question 1.
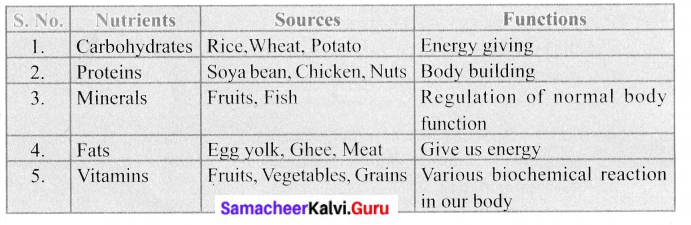
Tabulate the vitamins and their corresponding deficiency diseases.
Answer:
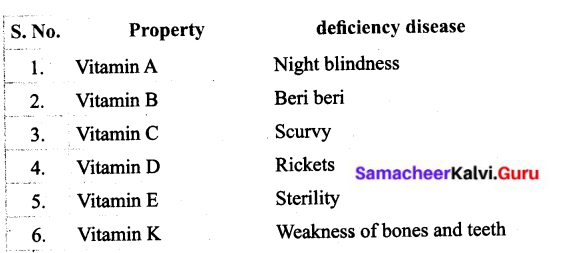
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Health and Hygiene Intext Activities
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 6th Science Guide Activity 1
Identify the following food items and complete the table given below.

Answer:
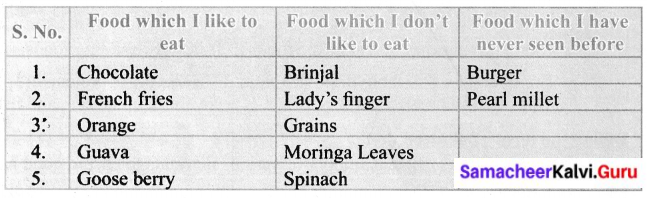
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 6 Science Question 1.
Do your favorite foods make you healthy?
Answer:
Some of my favorite foods make me healthy.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Question 2.
Do you choose your food by taste or by its nutritive value?
Answer:
I choose my food by taste and also by its nutritive value.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Guide Activity 2
Collect as many food items as you can and classify them according to the major nutrient content in it.
Answer:
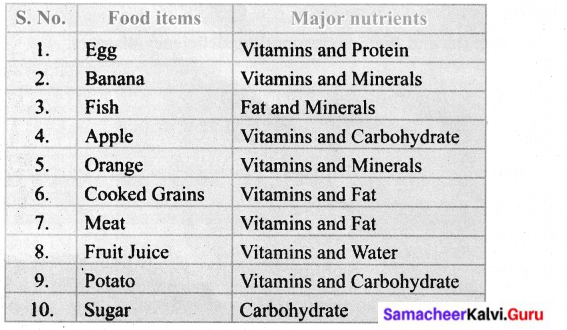
Activity 3
Aim: To test the presence of Carbohydrate as Starch in the given food item.
Question 1.
What do you need?
Answer:
Boiled potato, dropper and dilute Iodine solution.
Question 2.
How to do?
Answer:
Smash the boiled potato. Add two or three drops of dilute Iodine solution on the Sample.
Question 3.
What do you observe?
Answer:
The potato turns blue-black in colour.
Question 4.
What do you infer?
Answer:
Iodine reacts with Starch to form Starch-Iodine complex which is blueblack in colour. Thus, the appearance of blue-black colour confirms the presence of Starch in the food item.
Activity 4
Aim: To test the presence of Fat in the given food item.
Question 1.
What do you need?
Answer:
Coconut Oil, groundnut oil, and any Paper.
Question 2.
How to do?
Answer:
Pour few drops of oil onto the paper and rub it gently with your finger. In case of ground nut, crush the groundnut and place it on a paper. Now rub the groundnut on the paper.
Question 3.
What do you see?
Answer:
The paper turns translucent and becomes greasy.
Question 4.
What do you learn?
Answer:
The given food sample contains fat.
Activity 5
Aim: To test the presence of Protein in the given food item.
Question 1.
What do you need?
Answer:
Egg white, Copper sulphate solution, Sodium hydroxide, Test tube and Bunsen burner.
Question 2.
How to do?
Answer:
Take a small amount of the food sample (egg white) and put in the test tube. Add some water to the test tube and shake it. Next, heat the test tube for about one minute. After the test tube has cooled down, add two drops each of Copper sulphate solution and Sodium hydroxide to it.
Question 3.
What do you see?
Answer:
The food sample turns purple or violet.
Question 4.
What do you learn?
Answer:
Change in colour of the given food sample turns purple or violet confirms the presence of Protein.
Just Think
A medical camp was conducted in School. Most of the children were healthy. Some of the students had some health issues
Priya had bleeding gums.
Raja could not see clearly in dim light.
Arun had bent legs .
Can you guess what could be the reasons?
- Priya was affected by Vitamin ‘C’ deficiency. So she had bleeding gums.
- Raja was affected by vitamin ‘A’ deficiency. So he could not see clearly in dim light.
- Arun was affected by vitamin ‘D’ deficiency. So he had bent legs.
Activity 6
Question 1.
Make your food little healthier. What do you need?
Answer:
A small cup of green gram seeds, Water and thin cloth.
Question 2.
How to do?
Answer:
Soak the green gram seeds in water over night. Take out the seeds and strain the water. Wrap the seeds in wet thin cloth. Keep it for a day or two. Sprinkle some water whenever it is dry.
Question 3.
What do you see?
Answer:
You can see white sprouts coming out of the seeds.
Question 4.
What do you learn?
Answer:
Green gram sprouts are low in calories, have fibre and Vitamin B. It has comparatively high amount of vitamin C and vitamin K.
Complete the following Table – 4
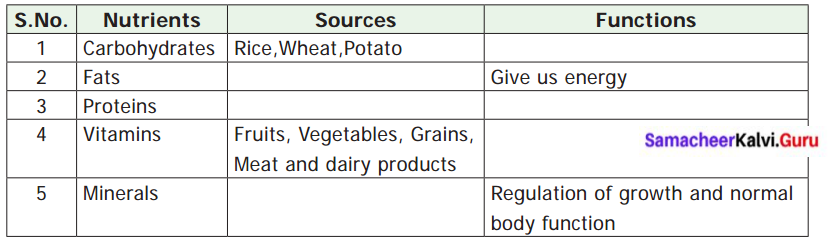
Answer:
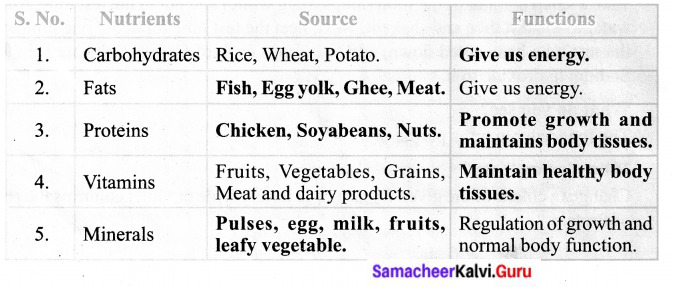
Activity 7
Question:
Why do we need a balanced diet?
Prepare a diet chart to provide balanced diet to a 12 year old child. The diet chart should include food item which are not expensive and are commonly available in your area.
Answer:
We need a balanced diet because,
a balanced diet contains sufficient amount of various nutrients to ensure good health.
Balance diet for 12 year old boy / girl.
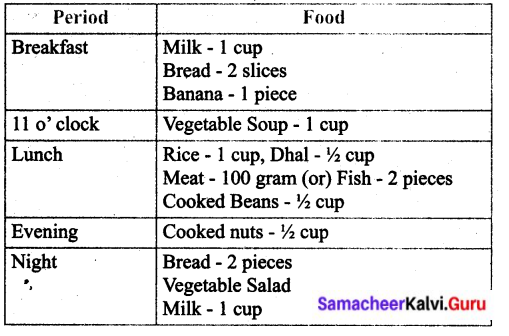
Activity 8
Question:
Visit a nearby Anganwadi centre and find the steps taken by the government to overcome malnutrition and ensure health in the age group 0-5 years.
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
Activity 9
One day Rahim, a class six boy vomited three times. He was looking tired and dehydrated. His mother who was a nurse prepared a solution and gave it to him drink. He felt better after sometime and asked his mother what the solution was. His mother said it was Oral Rehydration Solution – ORS. Shall we see what an ORS is? Vomiting or loose motions result in loss of water and cause salt imbalance in the body. Loss of water (dehydration) can lead to serious problems. This can be prevented by consuming ORS at short intervals.
Follow the steps to make ORS at home:
- Take a litre of boiled water. Cool it.
- Add half a teaspoon of salt and six teaspoons of sugar to it.
- You can also add a few drops of lemon juice to it. Stir it and give it to the person suffering from vomiting, loose motions or dehydration.
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
Discuss in your class room
“Is virus a living thing or non living thing?”
Answer:
Viruse is a non-living thing.
Reasons:
- Virus is an a cellular, meaning it lacks a cell membrane.
- It is an obligate parasite. It requires a host cell to reproduce.
- It lacks an energy-generating system. It cannot produce its own energy.
- It cannot perform metabolic activities.
- Viruses are not composed of cells and do not reproduce themselves from other pre-existing viruses.
- The genetic material (DNA or RNA) inside the virus invades the living host cell, and causes the cell to replicate virus parts and assemble them to make new viruses, which are released to infect more cells.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Health and Hygiene Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
_______ provides more energy than Carbohydrates.
(a) Fat
(b) Vitamin
(c) Protein
(d) Water
Answer:
(a) Fat
Question 2.
Name the vitamin which is rich in Gooseberry.
(a) C
(b) E
(c) B
(d) D
Answer:
(c) B
Question 3.
Among the Vitamins, which one is the water soluble Vitamin?
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Vitamin B
(e) Vitamin D
(d) Vitamin E
Answer:
(b) Vitamin B
Question 4.
Name the vitamin present in Muringa leaves
(a) A and B
(b) C and D
(c) K and A
(d) A and C
Answer:
(d) A and C
Question 5.
_______ is made in our skin using sunlight.
(a) Vitamin D
(b) Vitamin C
(c) Vitamin A
(d) Vitamin B
Answer:
(a) Vitamin D
Question 6.
_______ are required for growth as well as for the regulation of normal body function.
(a) Fats
(b) Proteins
(c) Carbohydrates
(d) Minerals
Answer:
(d) Minerals
Question 7.
80% of the world production of Moringa leaves is in _______
(a) China
(b) Germany
(c) India
(d) Canada
Answer:
(c) India
Question 8.
Any human being should take minimum _______ of water every day.
(a) 2 litres
(b) 3 litres
(c) 8 litres
(d) 6 litres
Answer:
(a) 2 litres
Question 9.
_______ is the bacterial disease and it transmits through contamination of wounds, with the bacteria.
(a) Cholera
(b) Tetanus
(c) Typhoid
(d) Pneumonia
Answer:
(b) Tetanus
Question 10.
_______ is a cellular agent that replicates only inside the cells of the other living organism.
(a) Bacteria
(b) Protozoa
(c) Fungi
(d) Virus
Answer:
(d) Virus
Il. Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
We can obtain Carbohydrates in the form of _______
Answer:
Sugar, Starch, Dietary Fibers
Question 2.
Vitamins are called as _______ food.
Answer:
Protective
Question 3.
The vitamins A, D, E, K are _______ soluble vitamins.
Answer:
Fat
Question 4.
_______ is a disease, due to the deficiency of Vitamin E.
Answer:
Nervous Weakness
Question 5.
Moringa leaves contains powerful anti _______
Answer:
Oxidantsl
Question 6.
Skinny appearance and slow body growth are the symptoms of _______ disease.
Answer:
Marasmusl
Question 7.
_______ is strengthening muscles and the cardiovascular system.
Answer:
Physical exercisel
Question 8.
_______ can kill damage or change the cells and make you sick.
Answer:
Virus
Question 9.
Sun screen lotion reduces your skin’s ability to produce _______ by up to 95%.
Answer:
Vitamin D
Question 10.
Goose bernes contain nearly _______ the vitamin C than orange.
Answer:
20 times
Question 11.
India has the _______ highest number of obese children ¡n the world.
Answer:
Second
III. True of false. If false give the correct answer.
Question 1.
Minerals are required for carrying out various biochemical reactions in our body.
Answer:
False. Vitamins are required for carrying out various biochemical reactions in our body.
Question 2.
Night blindness is a disease due to deficiency of Vitamin A.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
Vitamin D abundantly found in orange and gooseberry.
Answer:
False. Vitamin C abundantly found in orange and gooseberry.
Question 4.
Sun screen lotion reduces ability to produce Vitamin D. It leads to Vitamin D deficiency diseases.
Answer:
True.
Question 5.
Iodine maintains strong bones, teeth and helps in clotting of blood.
Answer:
False. Calcium maintains strong bones, teeth and helps in clotting of blood.
Question 6.
Moringa leaves are rich in the minerals potassium, calcium and iron.
Answer:
True.
IV. Complete the Analogy
Question 1.
Polio : Virus :: Tetanus : _______
Answer:
Bacteria
Question 2.
_______ : Diarrhoea:: Marasmus: Slow body growth.
Answer:
Kwashiorkar
Question 3.
Synthesis of thyroid harmone: Iodine:: Formation of haeniogiobin: _______
Answer:
Iron
Question 4.
Fish oil : Vitamin D :: Vegetable oil : _______
Answer:
Vitamin II
Question 5.
Vitamin K : Clotting of blood :: Vitamin E : _______
Answer:
Fertility
Question 6.
Protein: Soya bean:: Fat: _______
Answer:
Meat
V. Match the following.
Question 1.
- Carbohydrate – (a) Carrying out various biochemical reactions
- Proteins – (b) Regulation of normal body function
- Vitamins – (c) energy giving component
- Minerals – (d) Body building food
Answer:
- – c
- – d
- – a
- – b
Question 2.

Answer:
- – d
- – e
- – b
- – a
- – c
VI. Complete the diagram
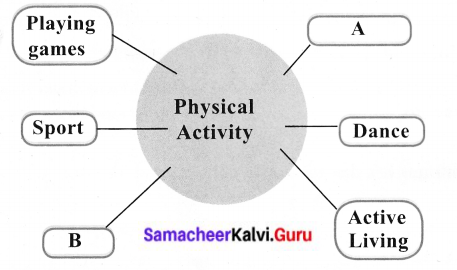
Answer:
A – Exercise
B – Yoga.
VII. Short Answers.
Question 1.
Define homeostasis.
Answer:
It is to maintain a stable equilibrium of body in accordance with the pressures and changes of body environment.
Question 2.
What are the nutrients obtained from food?
Answer:
- Carbohydrate
- Proteins
- Fats
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Water.
Question 3.
What is meant by deficiency diseases?
Answer:
The diseases that are caused due to lack of nutrients in the diet are called deficiency diseases.
Question 4.
Sun Screen lotion is not good for our health. Justify.
Answer:
Sun Screen lotion reduces our skin’s ability to produce vitamin D upto 95%. It may lead to Vitamin D deficiency. So it not for good our health.
Question 5.
Fill in the blanks.
A – Calcium – Rickets
Phosphorus – …………
Answer:
Osteomalacia
B – Iodine – cretinism
Iron – ………….
Answer:
anaemia
Question 6.
What are the nutrients present in Moringa leaves?
Answer:
Moringa leaves are rich in Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Potassium, Calcium, Iron and Protein. It also contains powerful anti-oxidants.
Question 7.
How does Balanced diet help in our body?
Answer:
Balanced diet helps in our body, in the following ways :
- An increased capacity to work
- Good physical and mental health
- Increased capacity to resist diseases.
- Help in proper growth of the body.
Question 8.
Give some mineral deficiency diseases.
Answer:
Rickets, Osteomalatia, Cretinism in Child, Goitre in adult, Anaemia are the mineral deficiency diseases.
Question 9.
How does Physical exercise help us?
Answer:
Physical exercise helps us in the following ways:
- increase in growth and development
- strengthening muscles and the cardiovascular system
- developing athletic skills
- weight loss or maintenance, and enjoyment.
Question 10.
How are the following bacterial diseases transmitted?
(i) Cholera
(ii) Tetanus
(iii) Typhoid
(iv) Tuberculosis
Answer:

Question 11.
Name the countries which import Moringa leaves.
Answer:
China, United States, German, Canada, South Korea and European Countries import Moringa leaves.
Question 12.
Define health.
Answer:
Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely absence of diseases. Eating a healthy diet keeps us physically and mentally fit.
Question 13.
Name the four major groups of Microbes.
Answer:
Microbes divided into four major groups. They are
- Bacteria
- Virus
- Protozoa
- Fungi
Question 14.
Define Disease.
Answer:
Disease is a definite pathological process having a characteristic set of signs and symptoms.
Question 15.
What is a Retrovirus?
Answer:
A Virus that contains R.N.A. instead of D.N.A. is called a Retrovirus.
VIII. Long Answer.
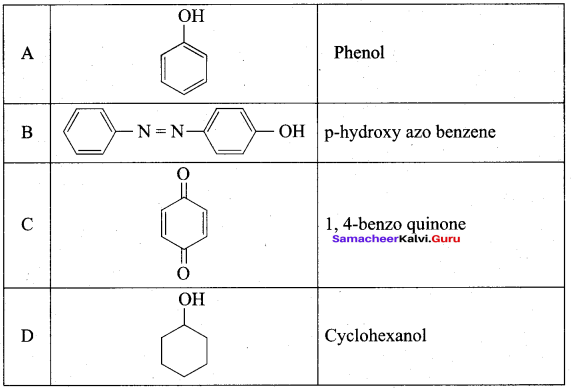
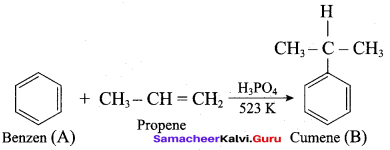
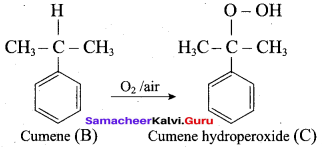
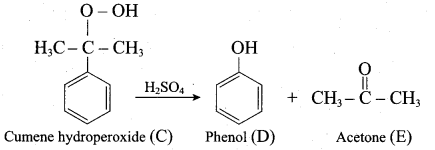
Question 1.
Fill in the Table :
Answer:
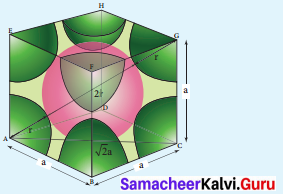
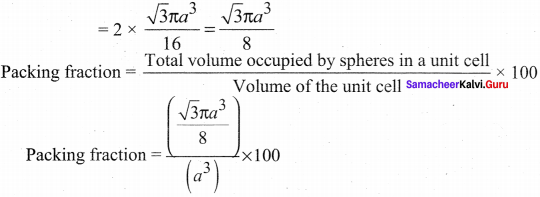
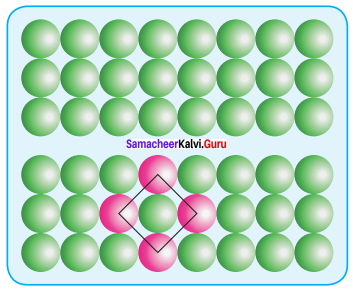
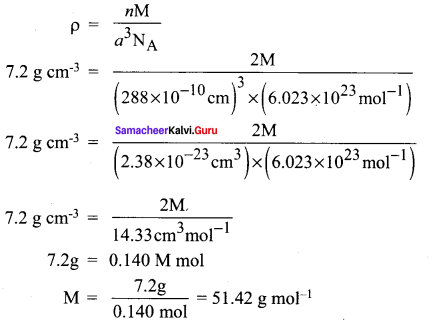











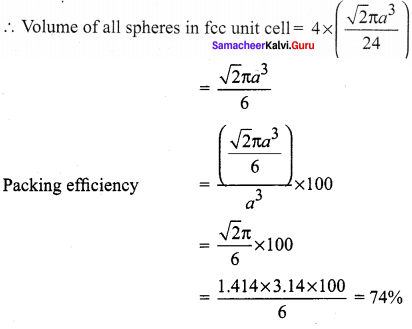
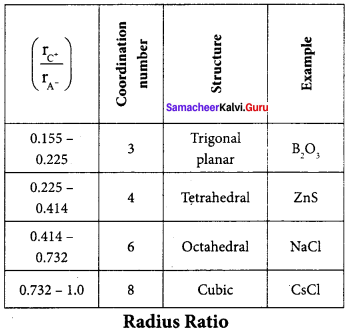

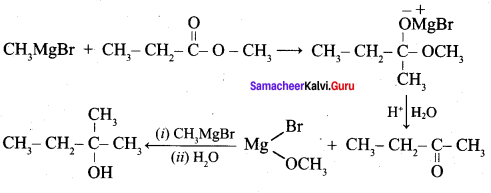
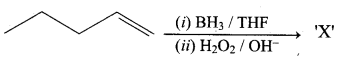
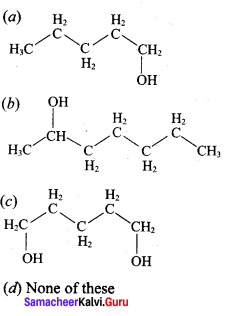
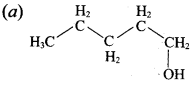
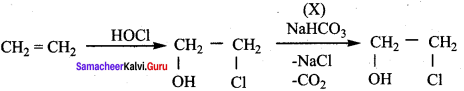
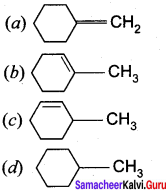
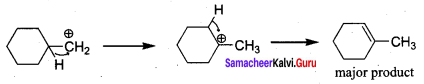
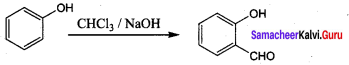
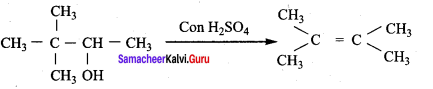
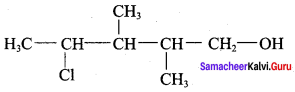
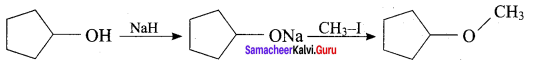
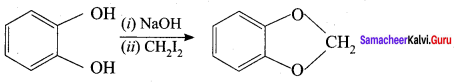
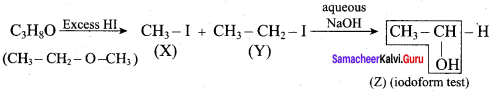
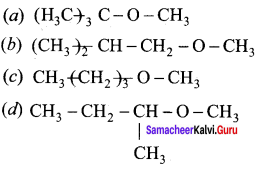
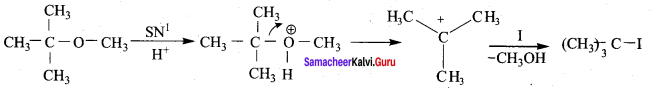
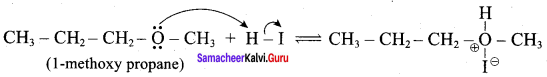
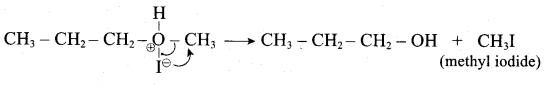
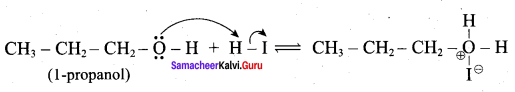
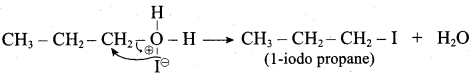
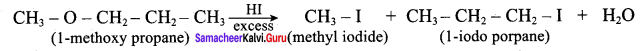
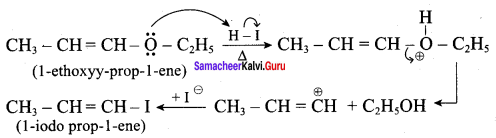
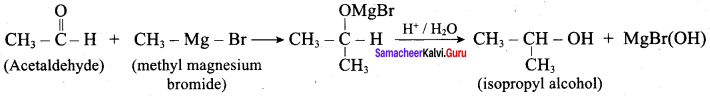
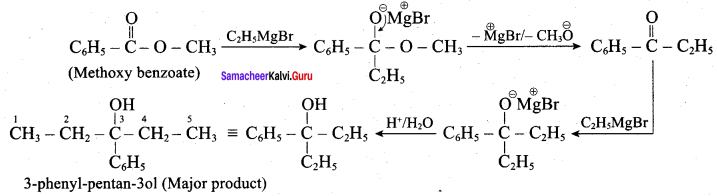
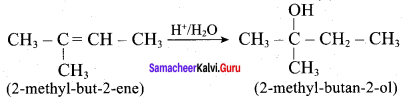
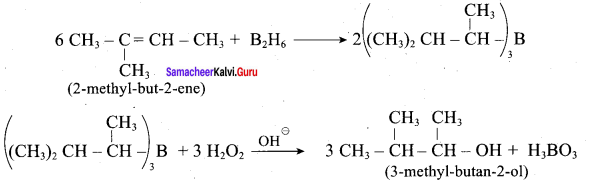
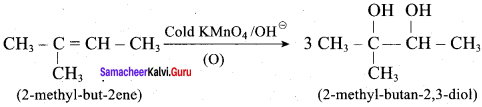
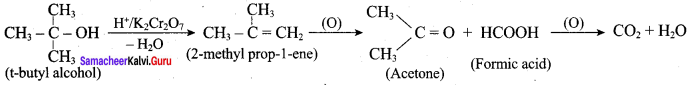
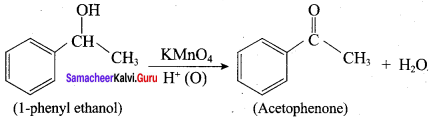
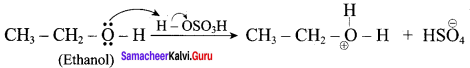
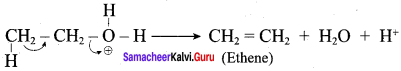
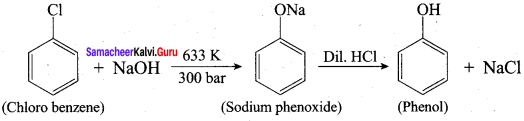
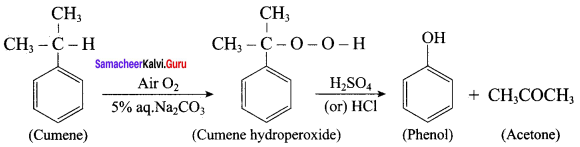
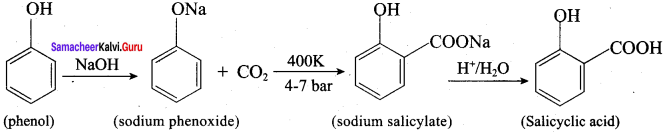
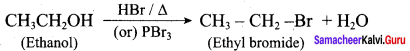
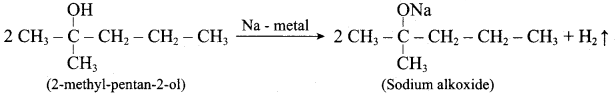
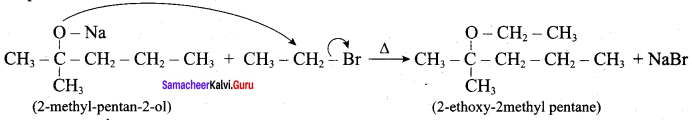
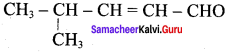
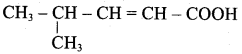
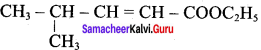
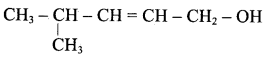
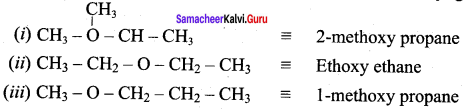
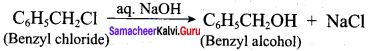
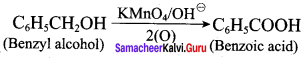
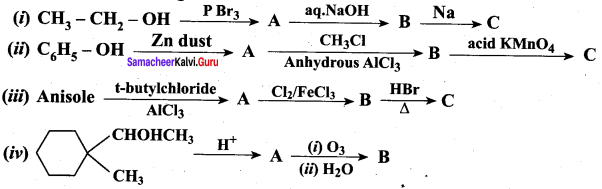
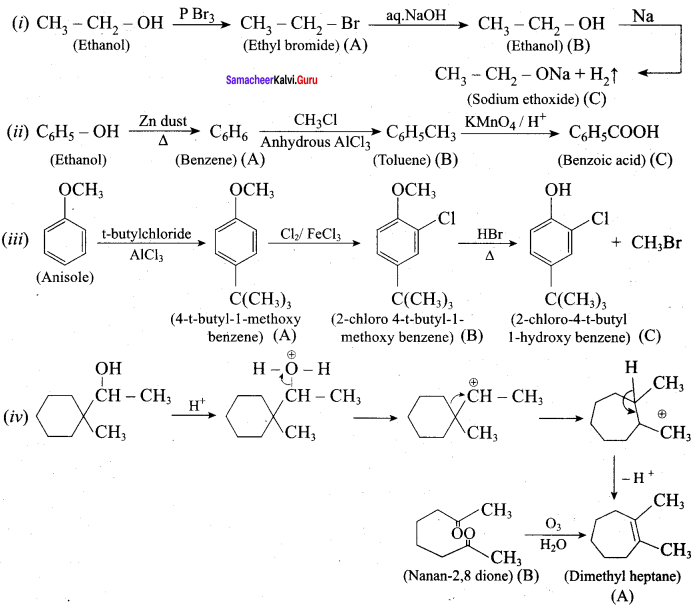
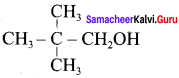
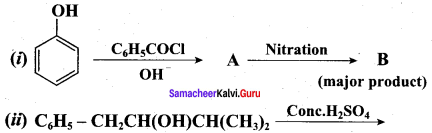
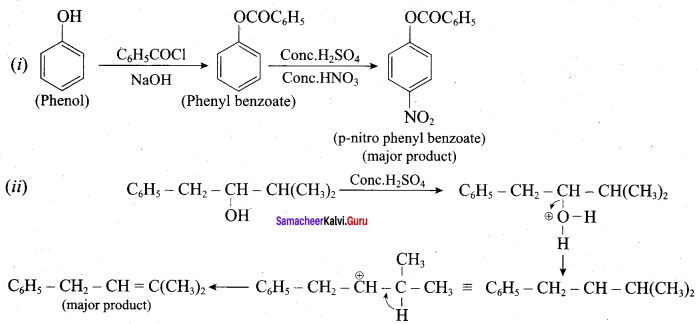
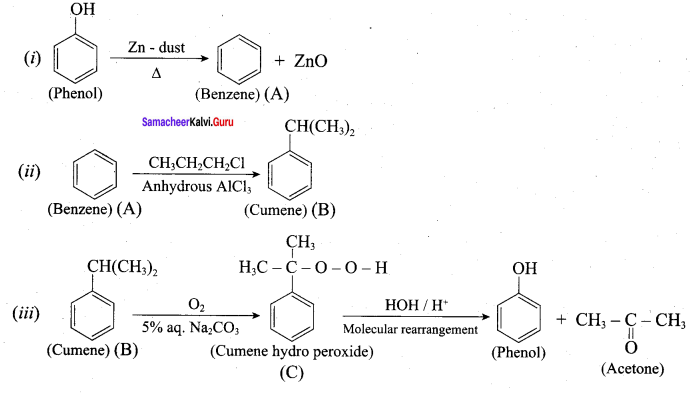
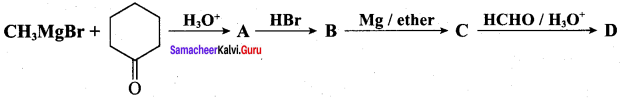
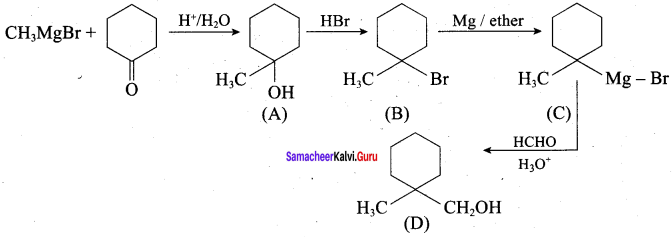
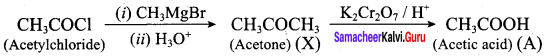
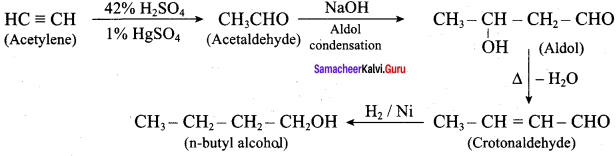
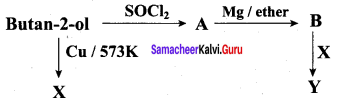
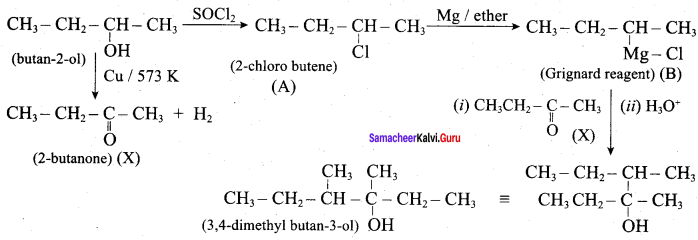
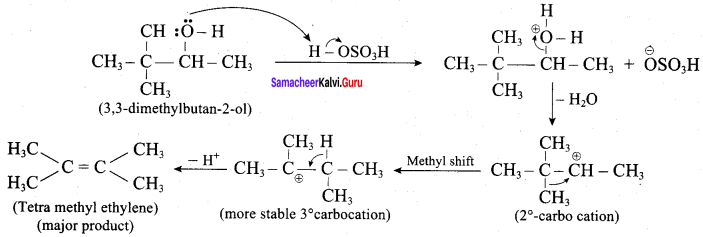
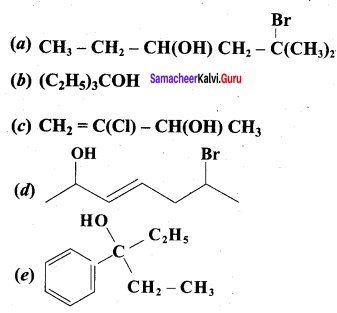
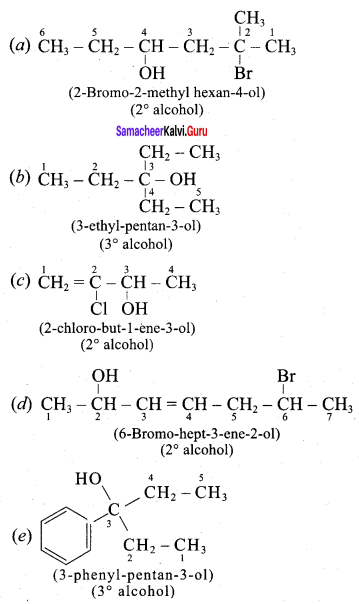
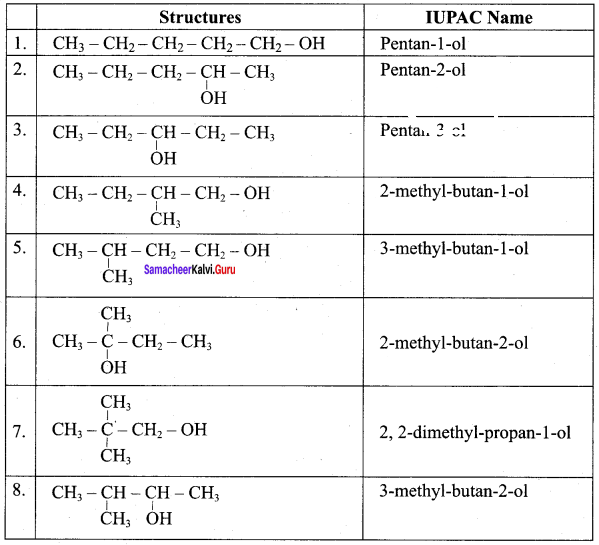
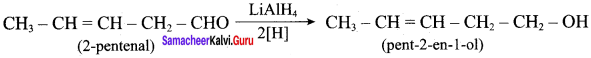
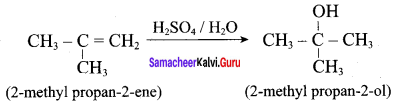
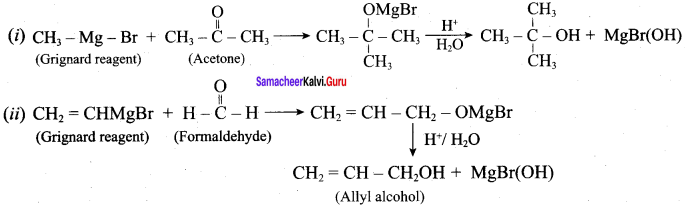
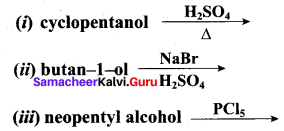
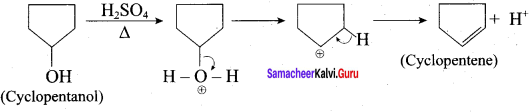
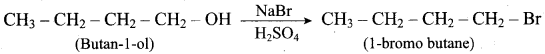
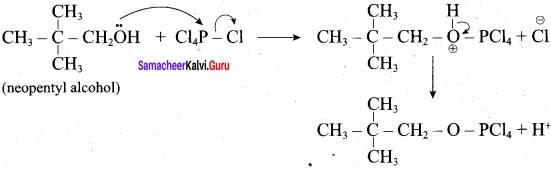
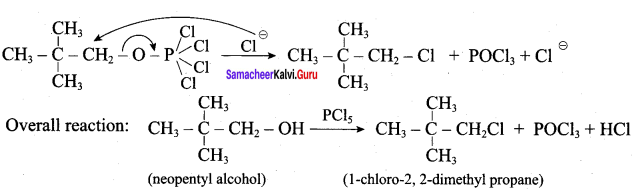
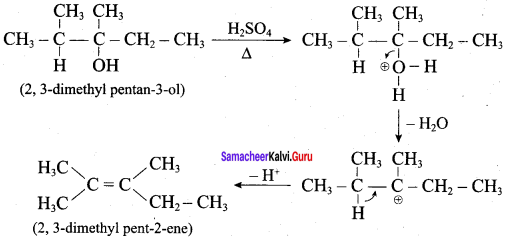
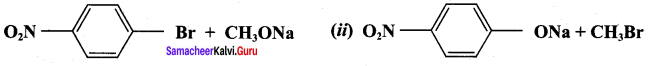
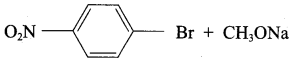
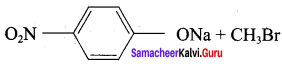
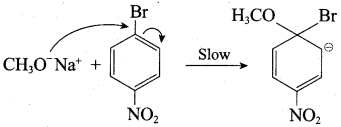
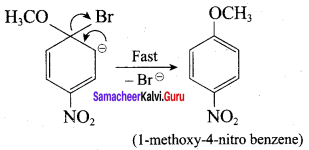
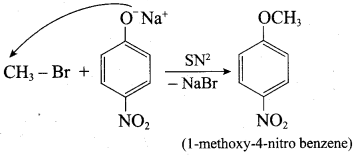
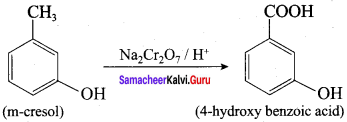
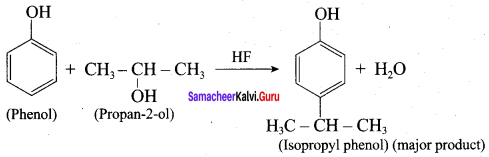
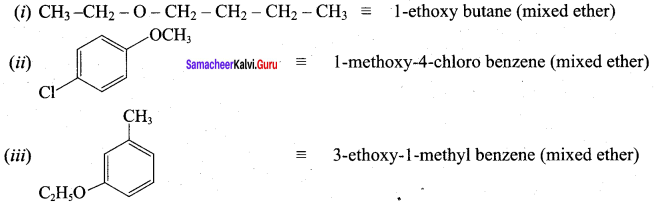
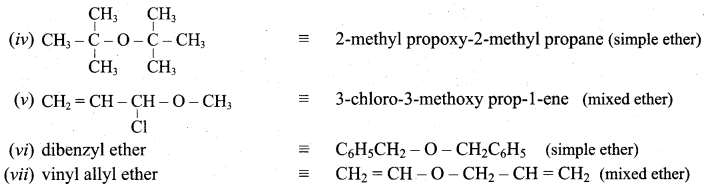
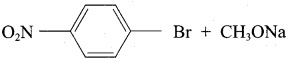
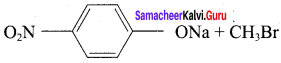
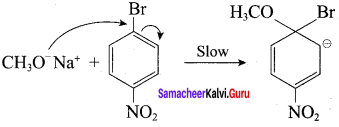
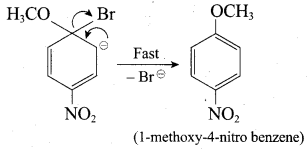
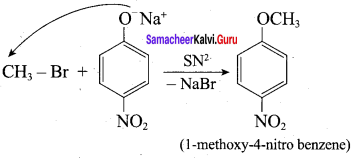
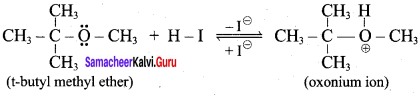
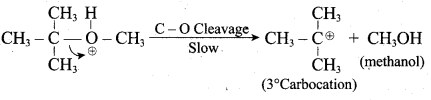

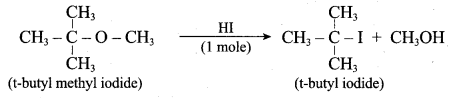
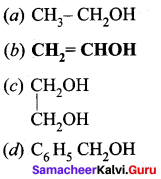
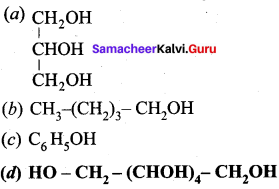
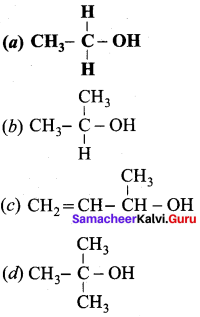
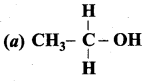
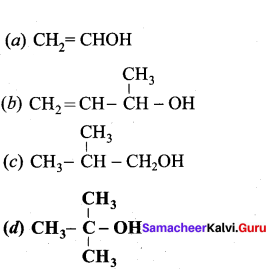
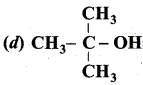
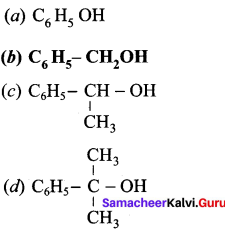


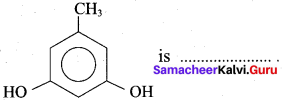
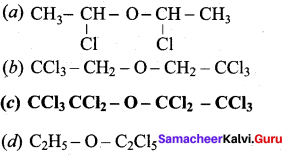
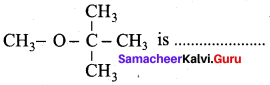
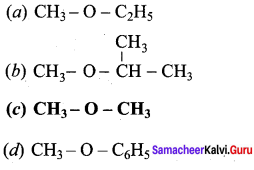
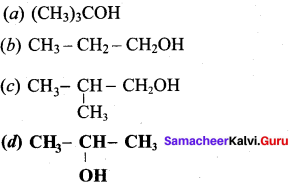
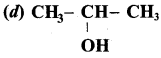
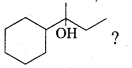
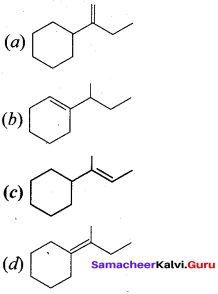
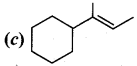

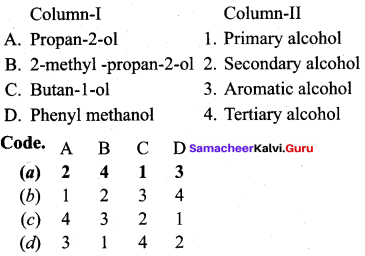
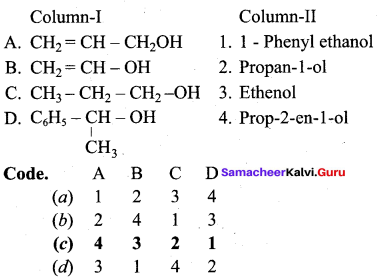

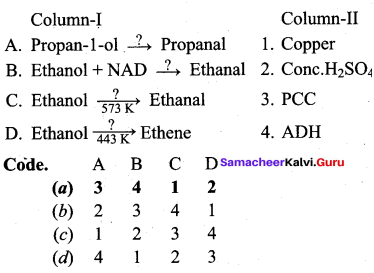
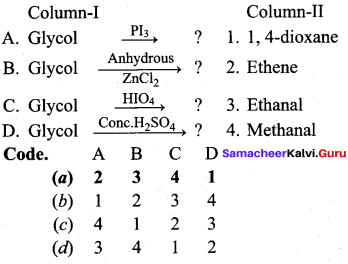
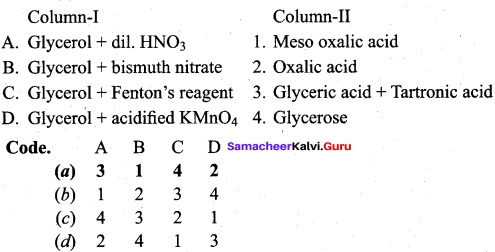


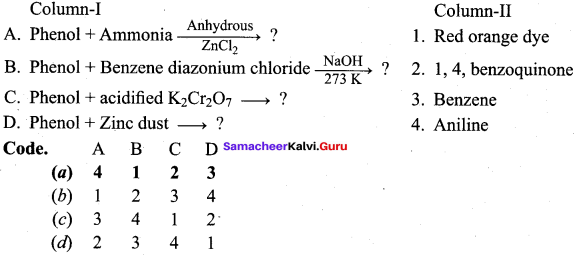
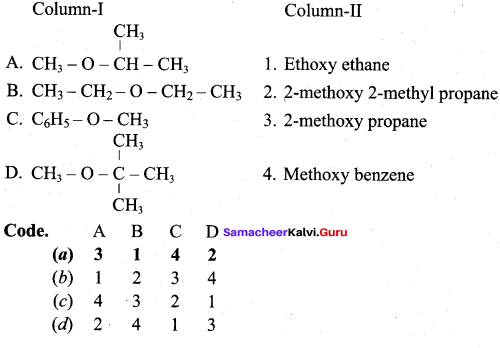
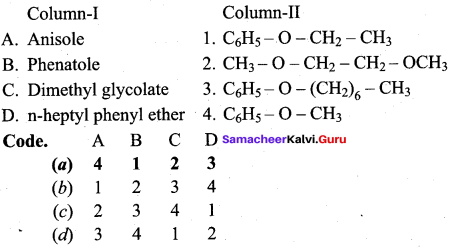
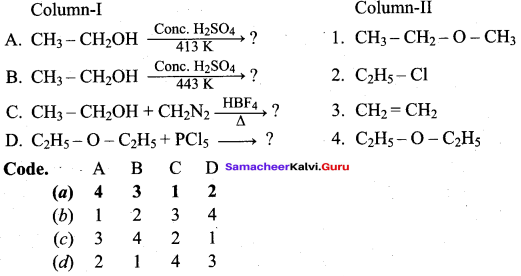
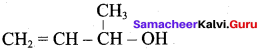
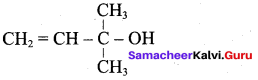
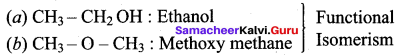
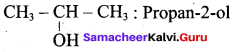
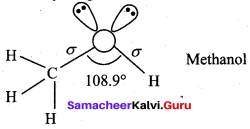
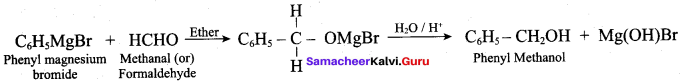
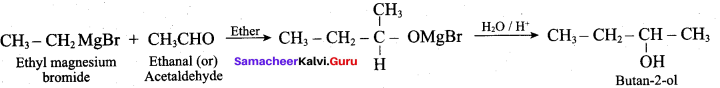
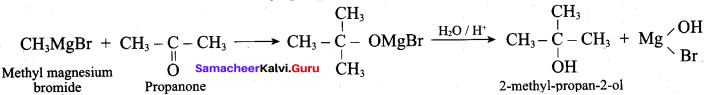
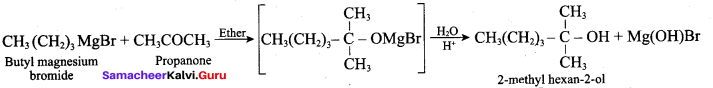
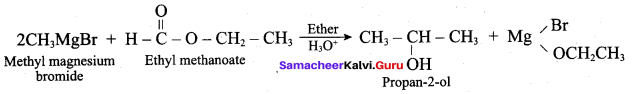
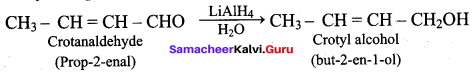
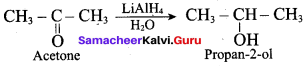
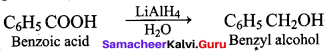
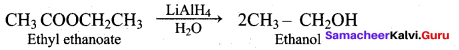
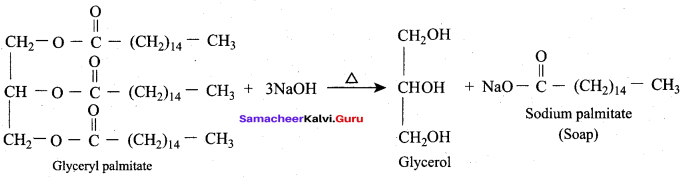
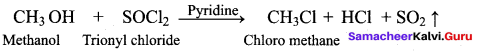
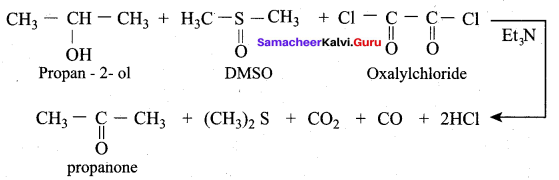
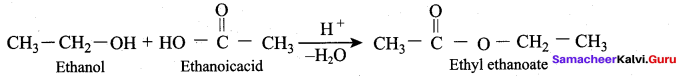
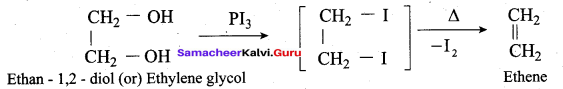
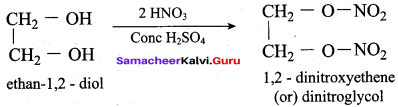
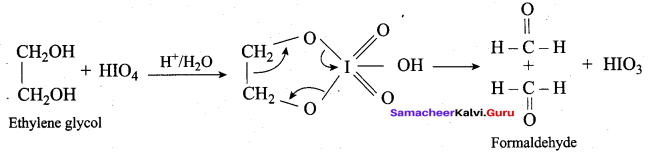
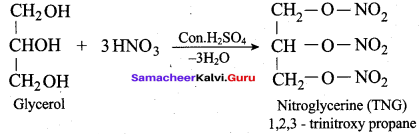
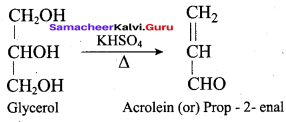
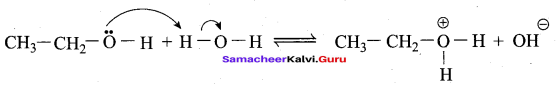
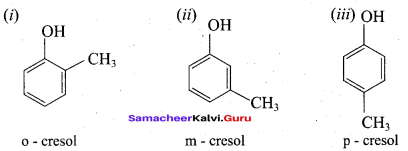
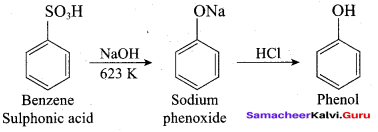
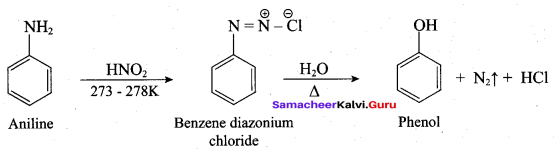
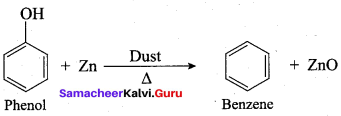
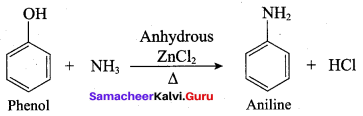
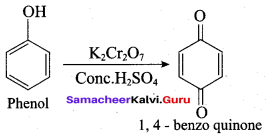
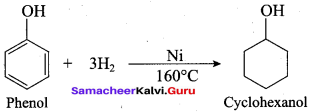
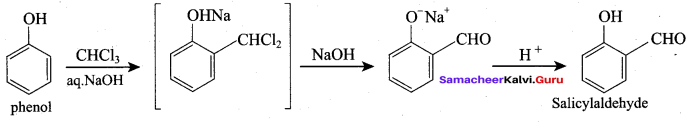
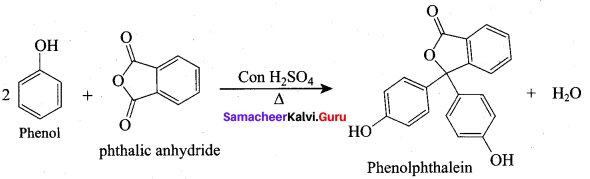
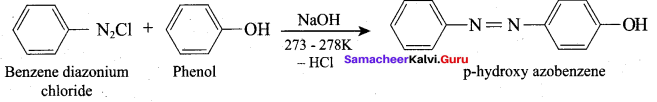
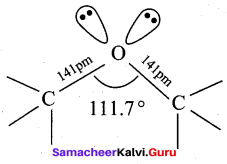


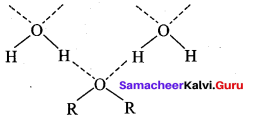
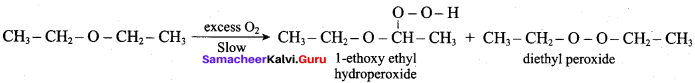
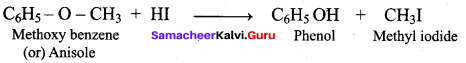
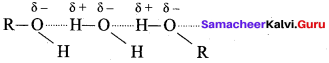
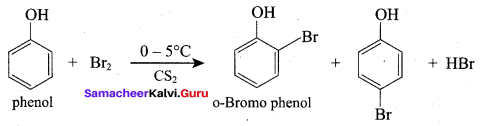
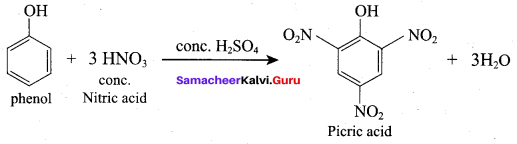
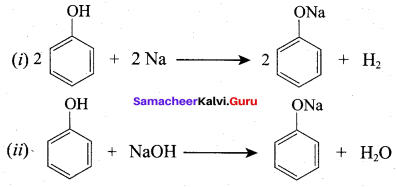
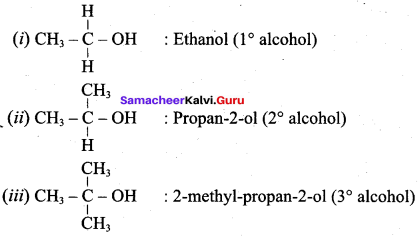
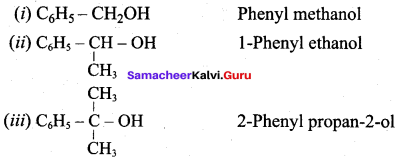
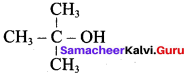
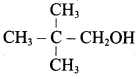
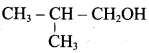
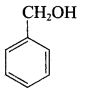
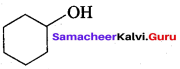
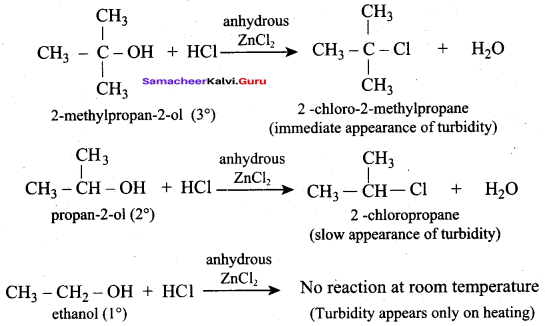
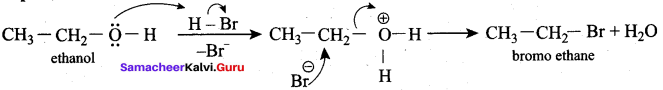
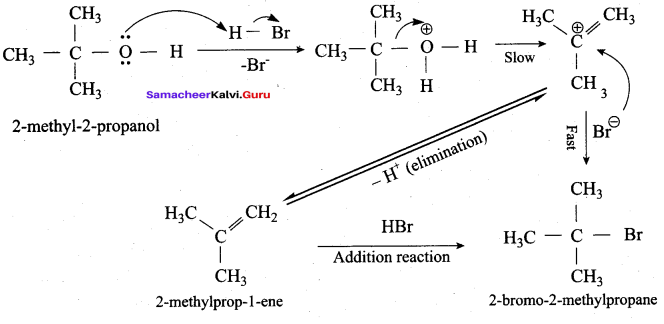
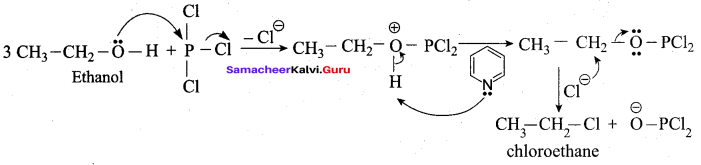
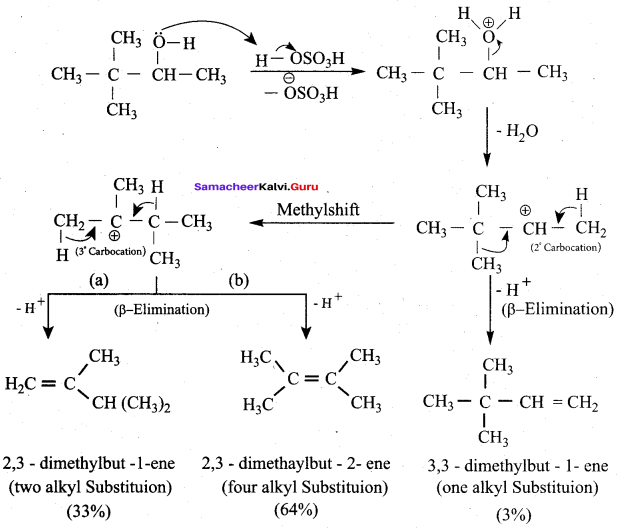
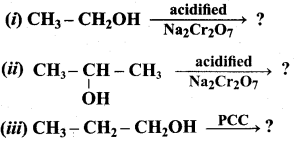
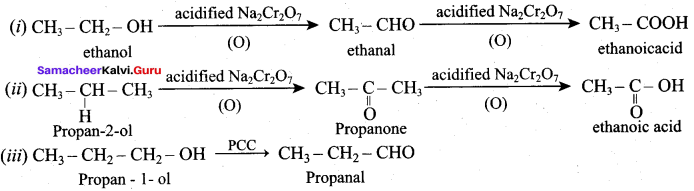
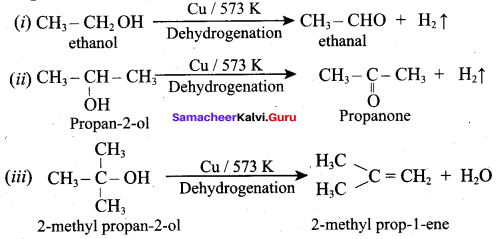
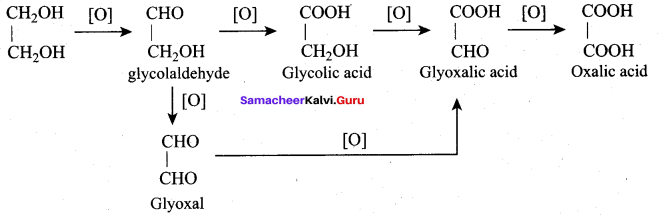
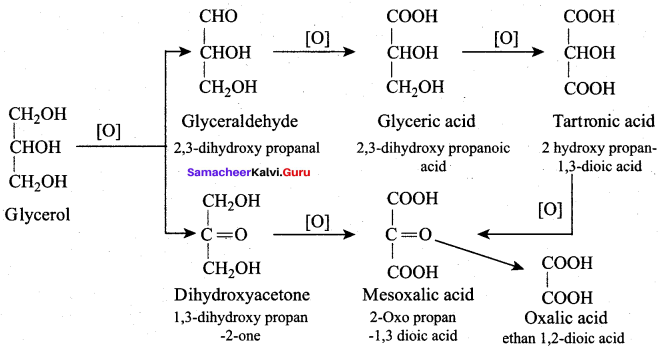
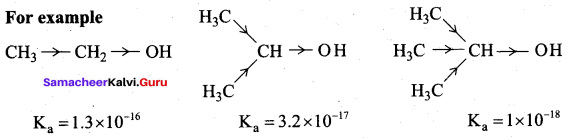
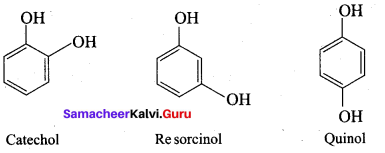
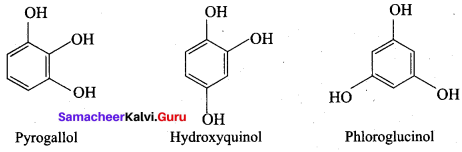
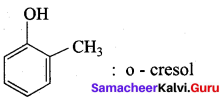
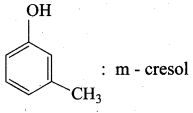
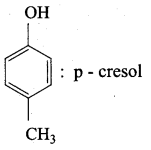
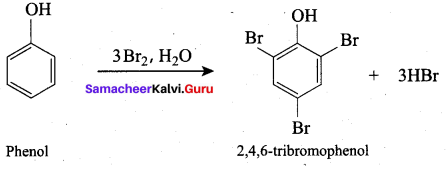
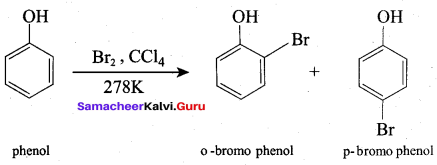
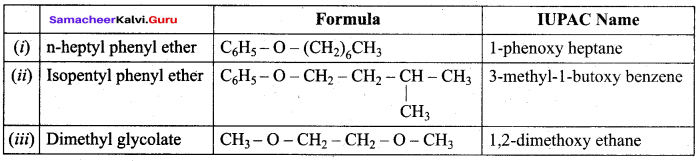
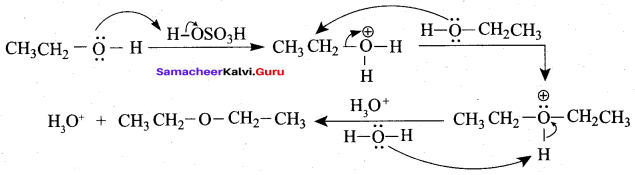
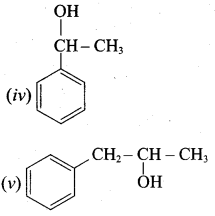
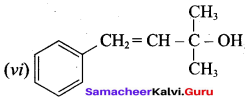
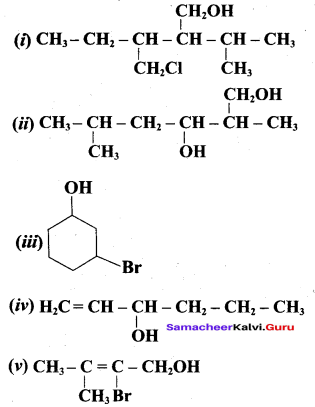
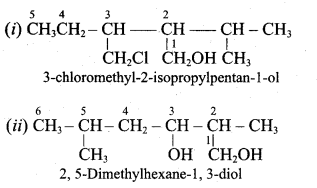
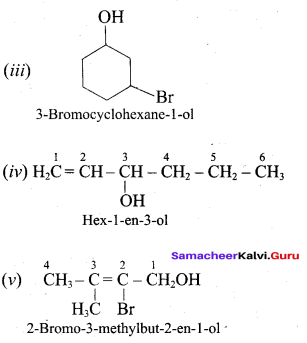

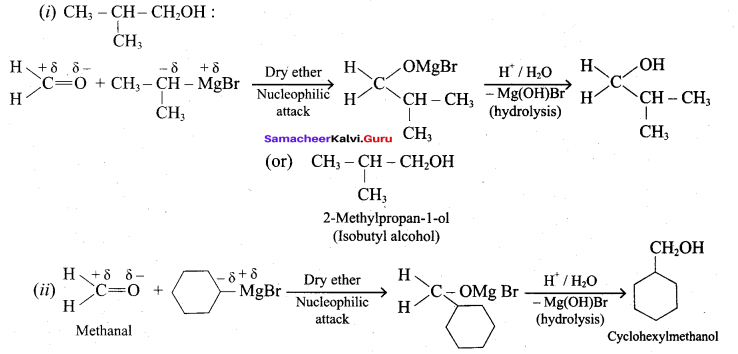
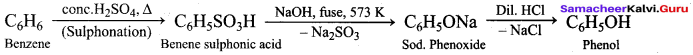
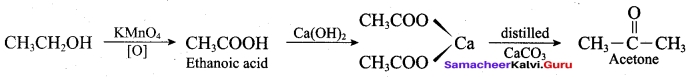
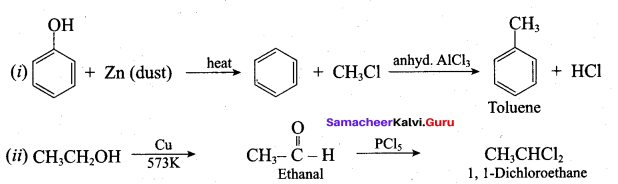
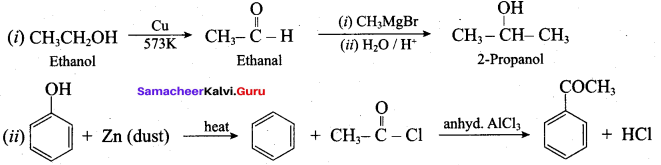

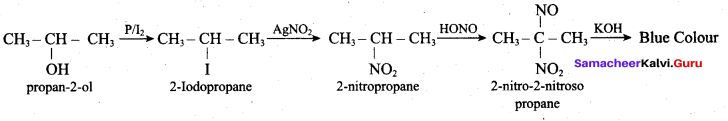
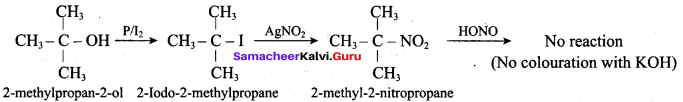
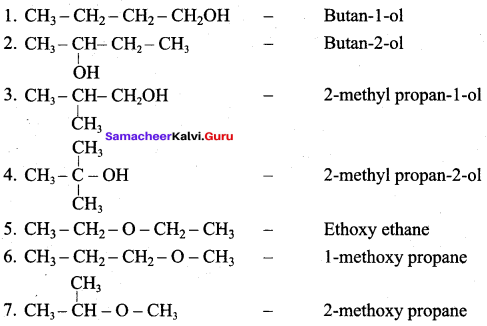
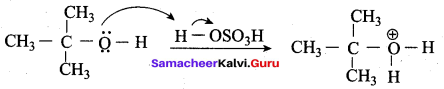
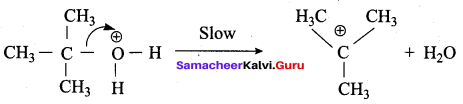
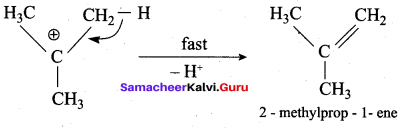
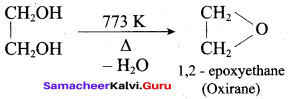
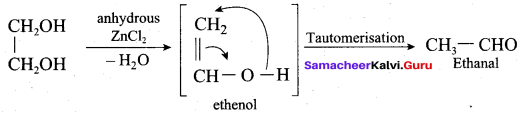
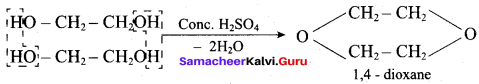
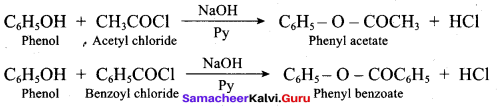
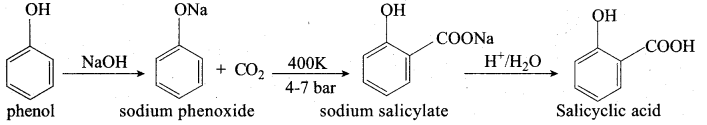
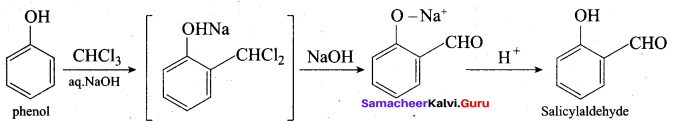
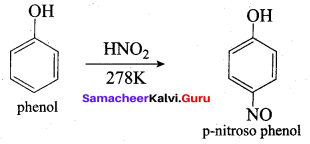
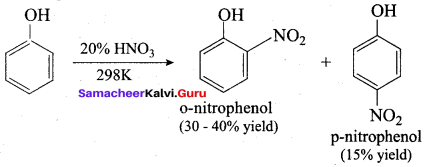
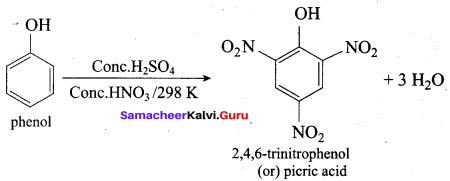
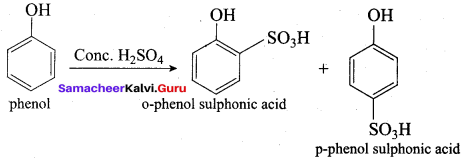
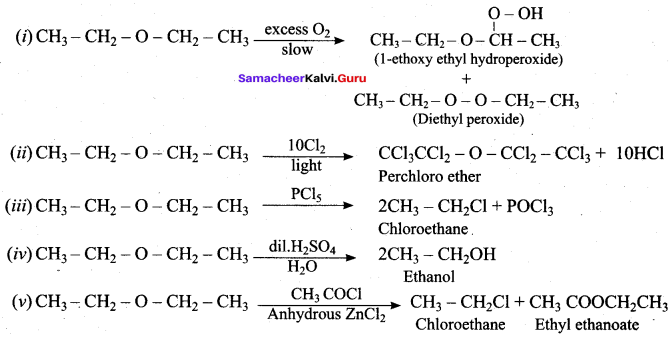
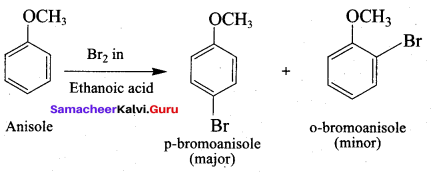
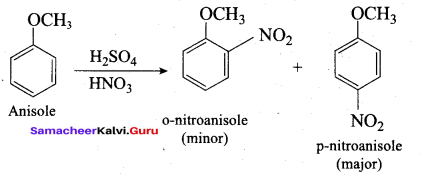
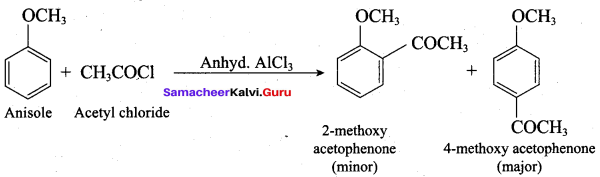
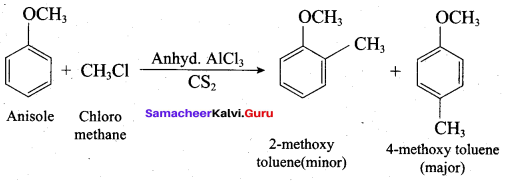
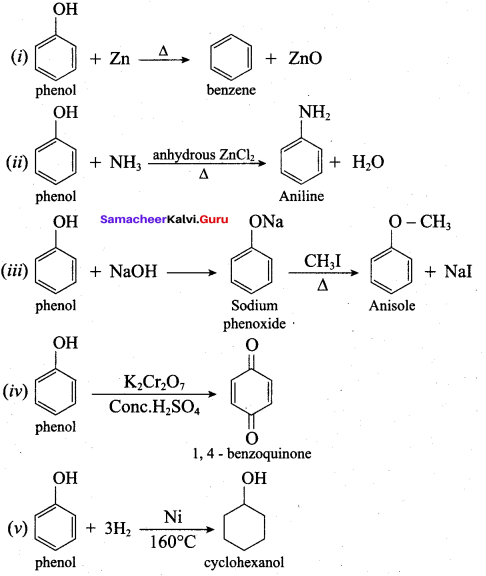
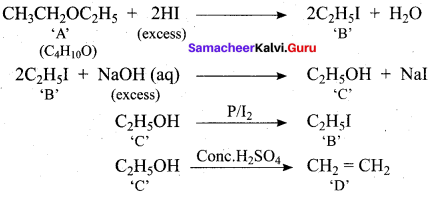
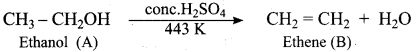
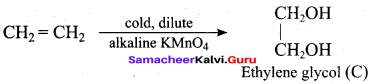
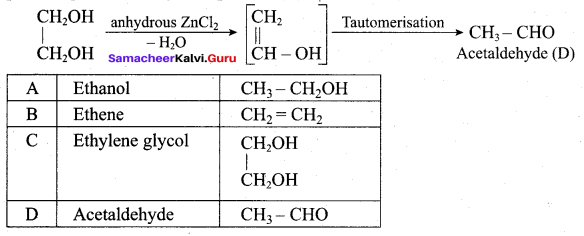

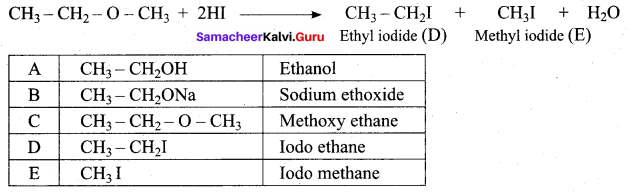
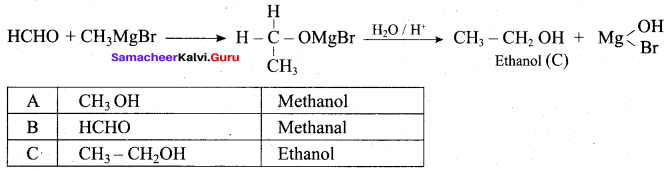

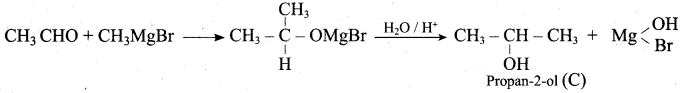
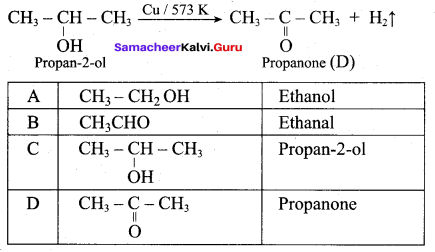
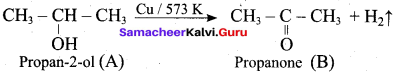
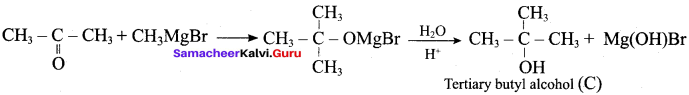
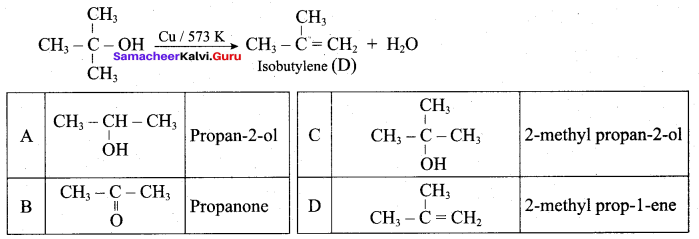
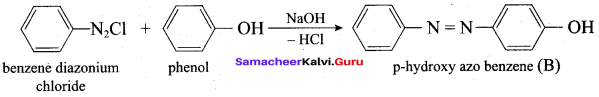
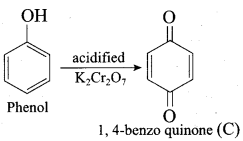
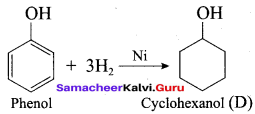
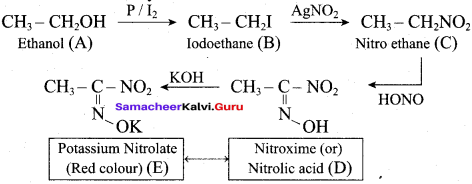
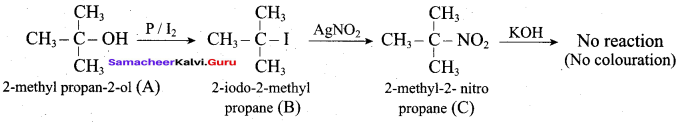
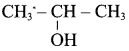 Propan – 2- ol as (B)
Propan – 2- ol as (B)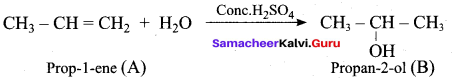
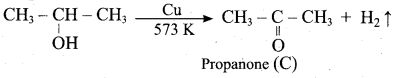
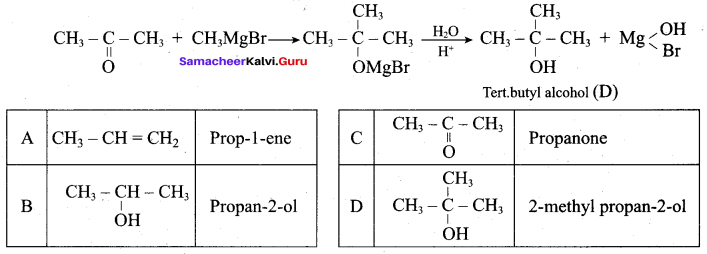

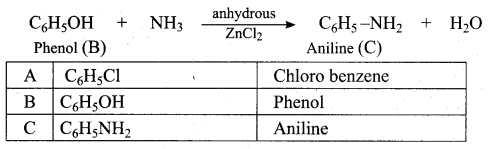
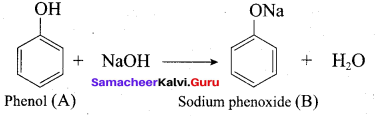
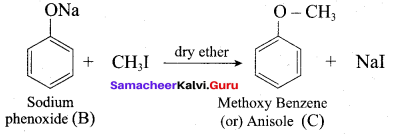
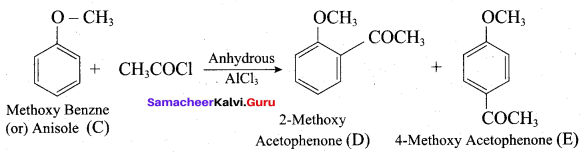
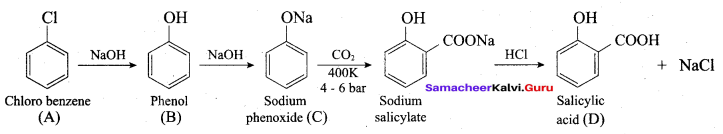
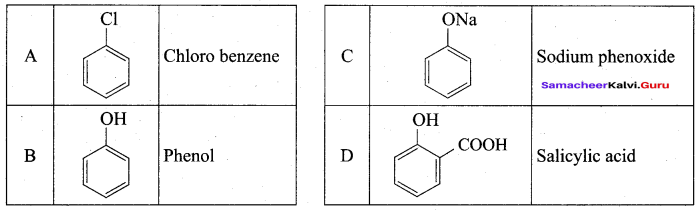
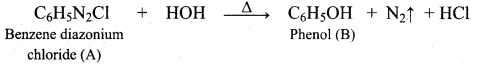
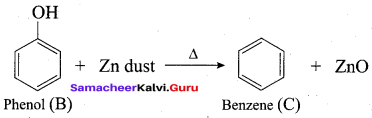
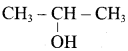 2 – propanol.
2 – propanol.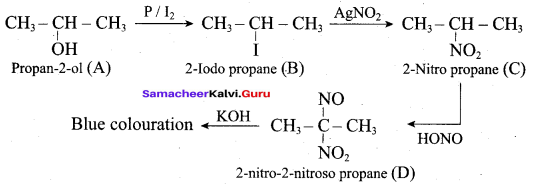
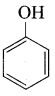
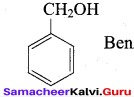
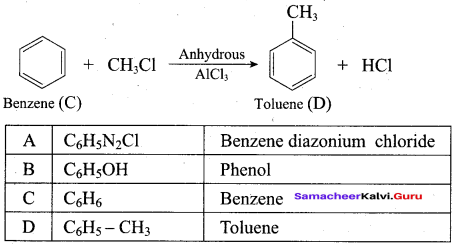
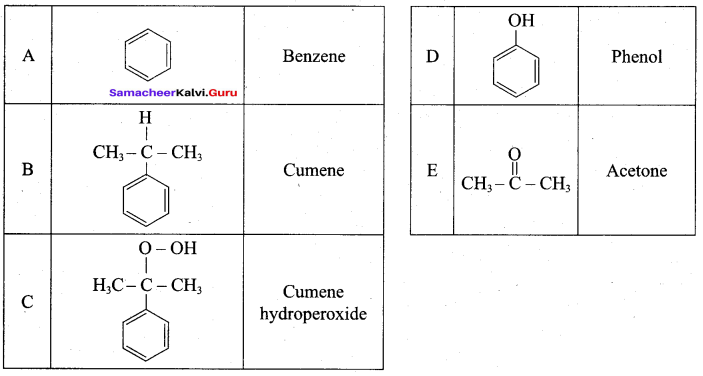
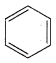 Benzene (C6H6) If you draw the above structure without double bonds, it is cyclo hexane.
Benzene (C6H6) If you draw the above structure without double bonds, it is cyclo hexane. Cyclohexane (C6H12)
Cyclohexane (C6H12)