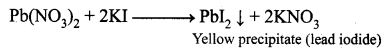
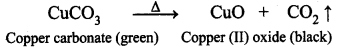
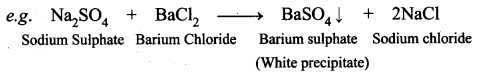
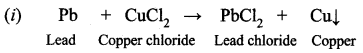Guys who are planning to learn and understand the topics of 10th Social Science History can grab this Tamilnadu State board solutions for Chapter 7 Anti-Colonial Movements and the British of Nationalism Questions and Answers from this page for free of cost. Make sure you use them as reference material at the time of preparation & score good grades in the final exams.
Students who feel tough to learn concepts can take help from this Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, all the Questions and Answers can easily refer in the exams. Go to the below sections and get 10th Social Science History Chapter 7 Anti-Colonial Movements and the British of Nationalism Tamilnadu State Board Solutions PDF.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science History Solutions Chapter 7 Anti-Colonial Movements and the British of Nationalism
Do you feel scoring more marks in the 10th Social Science History Grammar sections and passage sections are so difficult? Then, you have the simplest way to understand the question from each concept & answer it in the examination. This can be only possible by reading the passages and topics involved in the 10th Social Science History Board solutions for Chapter 7 Anti-Colonial Movements and the British of Nationalism Questions and Answers. All the Solutions are covered as per the latest syllabus guidelines. Check out the links available here and download 10th Social Science History Chapter 7 textbook solutions for Tamilnadu State Board.
Anti-Colonial Movements and the British of Nationalism Textual Exercise
I. Choose the correct answer.
Anti Colonial Movements And The Birth Of Nationalism Question 1.
Which one of the following was launched by Haji Shariatullah in 1818 in East Bengal?
(a) Wahhabi Rebellion
(b) Farazi Movement
(c) Tribal uprising
(d) Kol Revolt
Answer:
(b) Farazi Movement
Question 2.
Who declared that “Land belongs to God” and collecting rent or tax on it was against divine law?
(a) Titu Mir
(b) Sidhu
(c) Dudu Mian
(d) Shariatullah
Answer:
(c) Dudu Mian
Question 3.
Who were driven out of their homeland during the process of creation of Zamins under Permanent Settlement?
(a) Santhals
(b) Titu Mir
(c) Munda
(d) Kol
Answer:
(a) Santhals
Question 4.
Find out the militant nationalist from the following.
(a) Dadabhai Naoroji
(b) Justice Govind Ranade
(c) Bipin Chandra pal
(d) Romesh Chandra
Answer:
(c) Bipin Chandra pal
Question 5.
When did the Partition of Bengal come into effect?
(a) 19 June 1905
(b) 18 July 1906
(c) 19 August 1907
(d) 16 October 1905
Answer:
(d) 16 October 1905
Question 6.
What was the context in which the Chota Nagpur Tenancy Act was passed?
(a) Kol Revolt
(b) Indigo Revolt
(c) Munda Rebellion
(d) Deccan Riots
Answer:
(c) Munda Rebellion
Question 7.
Who set up the first Home Rule League in April 1916?
(a) Annie Basant
(b) Bipin Chandra Pal
(c) Lala Lajpat Rai
(d) Tilak
Answer:
(d) Tilak
Question 8.
Who drew the attention of the British to the suffering of Indigo cultivation through his play Nil darpan?
(a) Dina Bandhu Mitra
(b) Romesh Chandra Dutt
(c) Dadabhai Naoroji
(d) Birsa Munda
Answer:
(a) Dina Bandhu Mitra
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. In 1757, Robert Clive was financially supported by…………….., the moneylenders of Bengal.
2. …………….. was an anti-imperial and anti-landlord movement originated in and around 1827.
3. The major tribal revolt took place in Cbotanagpur region was ……………….
4. The ………….. Act, restricted the entry of non-tribal people into the tribal land.
5. Around 1854 activities of social banditry were led by ………………
6. The British Commander of Kanpur killed by the rebels during the 1857 Rebellion was ……………..
7. Chota Nagpur Act was passed in the year ……………..
8. W.C. Bannerjee was elected the president of Indian National Congress in the year …………..
Answers:
1. Jagat Seths
2. Wahhabi rebellion
3. Kol revolt
4. Chotanagpur Tenancy Act
5. Bir Singh
6. Major General High Wheelor
7. 1908
8. 1885
III. Choose the correct statement.
Question 1.
(i) The company received ₹ 22.5 million from Mir Jafar and invested it to propel the industrial revolution in Britain.
(ii) Kols organized an insurrection in 1831-1832, which was directed against Government officers and money lenders.
(iii) In 1855, two Santhal brothers Sidhu and Kanu led the Santhal Rebellion.
(iv) In 1879, an Act was passed to regulate the territories occupied by the Santhals.
(a) (i) (ii) and (iii) are correct
(b) (ii) and (iii) are correct
(c) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (i) and (iv) are correct
Answer:
(a) (i) (ii) and (iii) are correct
Question 2.
(i) Dudu Mian laid emphasis on the egalitarian nature of Islam and declared that “Land belongs to God” .
(ii) According to the Doctrine of Lapse, new territories under the corrupt Indian rulers were to be annexed.
(iii) The British officials after the suppression of 1857 Revolt were given power to judge and take the lives of Indians without due process of law.
(iv) One of the causes of the failure of the Revolt of 1857 was many of the Indian princes and zamindars remained loyal to the British.
(a) (ii) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(b) (i) (ii) and (iv) are correct
(c) (i) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct.
Answer:
(c) (i) (iii) and (iv) are correct
Question 3.
(i) One of the most significant contributions of the early Indian Nationalists was the formulation of an economic critique of colonialism.
(ii) The early Congress leaders stated that the religious exploitation in India was the primary reason for the growing poverty.
(iii) One of the goals of the moderate Congress leaders w as to achieve Swaraj or self-rule.
(iv) The objective of partition was to curtail the Bengali influence and weaken the nationalist movement.
(a) (i) and (iii) are correct
(b) (i) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(c) (ii) and (iii) are correct
(d) (iii) and (iv) are correct
Answer:
(b) (i) (iii) and (iv) are correct
Question 4.
Assertion (A): Under colonial rule, for the first time in Indian history, Government claimed a direct proprietary right over forests.
Reason (R): Planters used intimidation and violence to compel farmers to grow indigo.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are wrong
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(d) (A) is wrong and (R) is correct
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Question 5.
Assertion (A): The Revolt of 1857 was brutally suppressed by the British army.
Reason (R): The failure of the rebellion was due to the absence of Central authority.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are wrong
(b) (A) is wrong and (R) is correct
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(d) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Answer:
(b) (A) is wrong and (R) is correct
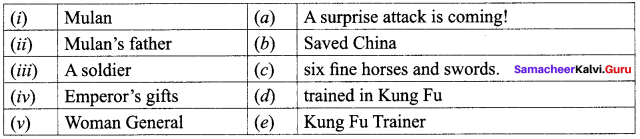
IV. Match the following.

Answer:
1. (e)
2. (d)
3. (a)
4. (e)
5. (b)
V. Answer the following questions briefly.
Question 1.
How are the peasant uprisings in British India classified?
Answer:
The peasants uprising in British India are classified in to four categories:
- Restorative Rebellions – To attempt to restore old order and old social relations.
- Religious movements – Led by religions leaders to liberate the locals by restructuring society on certain religious principles.
- Social banditry – Looked upon by their people as heroes or champions of their cause.
- Mass Insurrection – Leaderless and spontaneous uprisings.
Question 2.
Write about the Kanpur Massacre of 1857.
Answer:
The Siege of Cawnpur was a key episode in the Indian rebellion of 1857. The besieged Company forces and civilians in Cawnpur (now Kanpur) were unprepared for an extended siege and surrendered to rebel forces under Nana Sahib, in return for a safe passage to Allahabad. However under ambiguous circumstances, their evacuation from Cawnpur turned into a massacre, and most of the men were killed.
Question 3.
Name the territories annexed by the British under the Doctrine of Lapse.
Answer:
Satara, Sambalpur, parts of Punjab, Jhansi, and Nagpur were the territories annexed under the Doctrine of Lapse.
Question 4.
What do you mean by drain of wealth?
Answer:
The colonial economy was a continuous transfer of resources from India to Britain without any favourable returns back to India. This is called the drain to wealth.
Question 5.
Explain the concept of constructive Swadeshi.
Answer:
Constructive Swadeshi: It largely stress upon self – help.
- It focused on building alternative-institutions of self governance that would operate free of British control.
- It also laid emphasis on the need of self strengthening of the people.
- In turn it would help them in creating a worthy citizen for political agitation.
- Swadeshi shops spread all over the place selling textiles, handlooms, soaps, earthenwares match and leather goods.
Question 6.
Highlight the objectives of Home Rule Movement.
Answer:
The following were the objectives of the Home Rule Movements in India –
- To attain self-government within the British Empire by rising constitutional means.
- To obtain the status of dominion, apolitical position accorded later to Australia, Canada, South Africa and New Zealand.
- To use non-violent constitutional methods to achieve goals.
Question 7.
Summarise the essence of Lucknow Pact.
Answer:
Lucknow Pact was signed in the year 1916. Under the provision of this pact.
- Congress and Muslim League agreed to work together to attain self Government in India.
- A separate electorate for Muslim was accepted by the Congress leadership.
VI. Answer all the questions under each caption.
Question 1.
Deccan Riots
(а) When and where did the first recorded incident of rioting against the moneylenders in the Deccan appear?
Answer:
The first recorded incident of rioting against the moneylenders in the Deccan appeared in May 1875, in Supa, a village near Poona.
(b What was the right given to moneylenders under a new law of the British?
Answer:
Under a new law, the British moneylenders were allowed to attach the mortgaged land of the defaulters and auction it off.
(c) What did it result in?
Answer:
It resulted in transfer of lands from the cultivators to the non-cultivating classes.
(d) Against whom was the violence directed in the Deccan riots.
Answer:
The violence was directed mostly at the Gujarat moneylenders.
Question 2.
The Revolt of 1857.
(a) Who assaulted his officer, an incident that led to the outbreak of 1857 Revolt?
Answer:
Mangal Pandey assaulted his officer, this was an incident that led to the outbreak of 1857 Revolt.
(b) Who was proclaimed the Sahhensha – e- Hindustan in Delhi?
Answer:
Bahadhur Shah – II was proclaimed as Shahensha – e – Hindustan in Delhi.
(c) Who was the correspondent of London Times who reported on the brutality of the 1857 revolt?
Answer:
William Howard Russell was the correspondent of London Times who reported on the brutality of the 1857 Revolt.
(d) What did the Queen’s proclamation say on matters relating to religion?
Answer:
The Queen’s proclamation said that the British would not interfere in traditional institutions and religious matters.
Question 3.
Indian National Congress
(a) What were the techniques adopted by the Congress to get its grievances redressed?
Answer:
The techniques adopted by the Congress to get its grievances redressed included appeals, petition and delegation to Britain.
(b) What do you know of Lal-Bal-Pal triumvirate?
Answer:
Lala Lajpat Rai of Punjab, Bal Gangadhar Tilak of Maharashtra and Bipin Chandra Pal of Bengal were three prominent leaders during the Swadeshi period. They are often referred to as Lal-Bal-Pal triumvirate.
(c) Where was the first session of Indian National Congress held?
Answer:
The first session of Indian National Congress was held at Bombay.
(d) How did the British respond to the Swadeshi Movement?
Answer:
The British brutally crushed the Swadeshi movement by arresting prominent leaders and putting them into the prison.
VII. Answer the following in detail.
Question 1.
Discuss the causes and consequences of the Revolt of 1857.
Answer:
Political Cause: The annexation policy of British India: Two major policies were followed to bring more territories under British rule.
(a) Doctrine of Paramountcy:
(i) New territories were annexed on the grounds that the native rulers were corrupt and inefficient.
(ii) British claimed themselves as paramount, supreme authority.
(b) Doctrine of Lapse:
(i) If a native ruler does not have biological male heir of their own to the throne after his death the territory would ‘lapse’ in to British India.
(ii) Sambalpur, Satara, Jhansi, parts of Punjab and Nagpur were annexed by the British through Doctrine of Lapse.
Religious Cause:
(i) Indian Sepoys were prohibited from wearing religious marks on their forehead.
(ii) To render their services overseas. Crossing sea meant the loss of their caste. So Sepoys at Barrackpore refused to go to Burma by sea.
Economic Cause: Discrimination in salary and promotion. They felt humiliated by racial abusement.
Immediate Cause:
- Introduction of cartridges to the new Enfield Rifles.
- There was a strong suspicion that the new cartridge was greased with cow and pig fat
- The cartridge had to be bitten off before loading (pork is forbidden to the Muslims and cow is sacred to the Hindus) so the Sepoys refused to use it.
- In 29th March a Sepoy named Mangal Pandey assaulted his European officer Along with some other Sepoys and Mangal Pandey were court martialled and hanged.
This fuelled the anger among the Sepoys and started revolt.
Consequences of the Revolt: The Revolt was suppressed: Army had been restored to British control under Martial law.
- The British officers were given power to judge and take the life of Indians without dae process of law.
- Bahadhur shah II was captured and sent to Burma.
- The British parliament passed a law proclaiming the transfer of power from the East India Company to the British Crown.
- The structure of the Indian army was revised army was reduced and Indians were restrained from holding important ranks and positions.
- Queen Victoria proclaimed that the British would not interfere in traditional institutions and religious matters of Indians.
- It was promised that more Indians would be absorbed in Government services.
- Secretary of state was appointed to review the Indian affairs.
Question 2.
How did the people of Bengal respond to the partition of Bengal (1905)?
Answer:
- The partition of Bengal that took place in 1905, resulted in widespread protests all across India. It started a new phase of the Indian national movement.
- The partition instead of dividing the Bengali people along the religious line united the leaders of both the groups – extremist and moderate.
- The people of Bengal adopted new techniques of protest. The boycott of British goods was one such method.
- The day Bengal was officially partitioned was declared as a day of mourning. Thousand’s of people took bath in River Ganga and marched on the streets of Calcutta singing Vande Mataram.
- The people of Bengal were outraged at what they saw as a ‘divide and rule’ policy of the British government.
Question 3.
Attempt a narrative account of how Tilak and Annie Besant by launching Home Rule Movement sustained the Indian freedom struggle after 1916?
Answer:
The Indian National Movement was revived and also radicalised during the Home Rule Movement (1916- 1918), led by Lokamanya Tilak and Annie Besant.
- It emerged as a mass movement against the British betrayal to the Indian cause of self Government after the I World War in return for the support rendered.
- Tilak first set up the Home Rule League in April 1916.
- In September 1916 Annie Besant by the demand of her followers started the Home Rule Movement in Madras (Adyar) without the support of the congress.
- Both the leagues worked independently.
- They succeeded in enrolling young people in large numbers and extending the movement to the areas,
- The Home Rule league was utilised to carry propaganda through press, speeches, public meetings, lectures, discussions and touring in favour of self Government.
- Both declared their strong view of self Government as right based on the national principle of self determination.
- The Home Rule Movement led to the reunion of moderate and the extremists leaders of Congress at the Lucknow session.
- Opened the fresh talks with the leaders of the Muslim League and decided to work together for self Government.
- The demand for Swaraj was raised by Tilak and Annie Besant gained popularity.
- This strong hold of both the leaders made the British parliament to announce Montagau – Chelmsford reforms which promised gradual progress of India towards self Government.
VIII. Activity
Question 1.
Identify the Acts passed in British India from 1858 to 1919, with a brief note on each. The Government of India Act, 1858.
Answer:
- The Government of India Act 1858, marked the beginning of new chapter in the constitutional history of India.
- Liquidation of East India Company, and the powers of government, territories and revenues ‘ were transfer to the British Crown.
The Indian Council Act, 1861
- It enabled the Governor-General to associate the people of the land with work of legislation.
- However, the legislative councils were merely talk shops with no power to criticize the administration or ask for some information. Their scope was fixed in legislation purpose alone; they had no right to move some kind of vote of no confidence.
The Indian Council Act, 1892
- This act marks the beginning of representative form of Government in India.
- Indian National Congress had adopted some resolutions in its sessions in 1885 and 1889 and put its demand. The major demands placed were as follows:
- A simultaneous examination of ICS to be held in England and India
- Reforms of the legislative council and adoption of the principle of election in place of nomination
- Opposition to the annexation of Upper Burma
- Reduction in the Military expenditure.
The Indian Councils Act, 1909 (The Morely-Minto Reforms)
(i) The British viceroy of India (1905-10)—was able to introduce several important innovations into the legislative and administrative machinery of the British Indian government.
(ii) The act also increased the maximum additional membership of the Imperial Legislative Council from 16 to 60.
The Government of India Act, 1919 (The Montague-Chelmsford Reforms)
(i) Subjects of administration were divided into two categories – ‘Central’ and ‘Provincial’. All important subjects (like Railways and Finance) were brought under the category of Central, while matters relating to the administration of the Provinces were classified as Provincial.
(ii) The provincial subjects were divided into two groups viz. reserved and transferred.
- The reserved subjects were kept with the Governor and transferred subjects were kept with the Indian Ministers.
- This division of subjects was basically what they meant by introducing the Diarchy.
- The reserved subjects were the essential areas of law enforcement such as justice, police, and revenue. The transferred subjects were such as public health, public works, education etc.
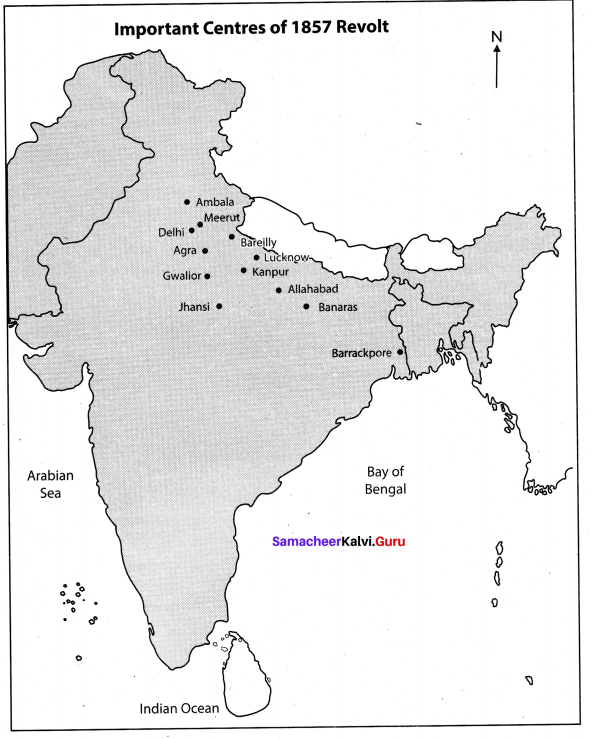
Question 2.
Mark the important Centres of 1857 Revolt in an outline map.
Answer:
Question 3.
Prepare album with pictures of frontline leaders of all the ant-colonial Struggles launched against the British.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Anti-Colonial Movements and the British of Nationalism Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
The British historians call the Revolt of 1857 as ……………….
(a) Military revolt
(b) The great revolt
(c) Freedom struggle
Answer:
(a) Military revolt
Question 2.
The battle of plassey was orchestrated by:
(a) Robert Clive
(b) Hugh Rose
(c) Birsa Munda
(d) Major Munro
Answer:
(a) Robert Clive
Question 3.
During the great revolt of 1857 the Governor General of India was ……………….
(a) Lord Lytton
(b) Lord Ripon
(c) Lord Canning
Answer:
(c) Lord Canning
Question 4.
The British favoured the ……………….. to suppress the peasant uprising.
(a) religious leaders
(b) tribal leaders
(c) local population
(d) zamindars
Answer:
(d) zamindars
Question 5.
The first sign of unrest appeared at ………………
(a) Meerut
(b) Bareilly
(c) Barrackpore
Answer:
(c) Barrackpore
Question 6.
In ……………….. the sepoys at Barrackpur near Calcutta refused to go to Burma by sea, as it meant the loss of their caste.
(a) 1814
(b) 1824
(c) 1815
(d) 1826
Answer:
(b) 1824
Question 7.
The wife of Nawab of Oudh was ……………..
(a) Mumtaj Mahal
(b) Fathima Begum
(c) Begum Hazrat Mahal
Answer:
(c) Begum Hazrat Mahal
Question 8.
After the sepoy revolt, the first civil rebellion broke out in parts of:
(a) North-Western Provinces and Oudh
(b) Bengal and Bihar
(c) North-Eastern Provinces
(d) Central Provinces
Answer:
(a) North-Western Provinces and Oudh
Question 9.
Viceroy means ………………
(a) The representative of the crown
(b) General of an army
(c) Religious leader
Answer:
(a) The representative of the crown
Question 10.
The British Parliament adopted the ……………….. in November 1858.
(a) Lucknow Pact
(b) Swadeshi Movement
(c) Indian Government Act
(d) Rowlatt Act
Answer:
(c) Indian Government Act
Question 11.
The last Emperor of the Mughals …………..
(a) Babur
(b) Akbar
(c) Bahadur Shah – II
Answer:
(c) Bahadur Shah – II
Question 12.
The second half of the ……………….. saw the emergence of national political consciousness.
(a) 16th Century
(b) 17th Century
(c) 18th Century
(d) 19th Century
Answer:
(d) 19th Century
Question 13.
Queen Victoria’s proclamation of 1858 was described as ……………
(a) Human Rights
(b) Magna Carta
(c) citizenship
Answer:
(b) Magna Carta
Question 14.
Partition of Bengal was introduced by:
(a) Lord Lytton
(b) Lord Dalhousie
(c) Lord Rippon
(d) Lord Curzon
Answer:
(d) Lord Curzon
Question 15.
The Nawab of Bengal after Alivardi Khan was ……………..
(a) Tipu Sultan
(b) Siraj-ud-daulah
(c) Mir Questionaim
Answer:
(b) Siraj-ud-daulah
Question 16.
The British who lead the company’s army against Siraj-ud-daulah at plassey was …………..
(a) Robert Clive
(b) Lord Hastings
(c) Edmund Burke
Answer:
(a) Robert Clive
Question 17.
One-third of the population was wiped out from Bengal because ……………
(a) a terrible famine occurred there
(b) a civil war broke out
(c) an epidemic broke out
Answer:
(a) a terrible famine occurred there
Question 18.
The riots were ……………….
(a) cultivators
(b) zamindars
(c) traders
Answer:
(a) cultivators
Question 19.
The Indigo Commission was set up to enquire into the system of indigo production. Whom did the commission hold guilty?
(a) The riots
(b) The government
(c) The planters
Answer:
(c) The planters
Question 20.
After the indigo production collapsed in Bengal, the planters shifted their operation to ……………….
(a) Gujarat
(b) Bihar
(c) Odissa
Answer:
(b) Bihar
Question 21.
At which battle was the Nawab of Bengal Siraj-ud-daulah defeated by the East India Company?
(a) Battle of Plassey
(b) Battle of Buxar
(c) Battle of Panipat
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Battle of Plassey
Question 22.
Who led the Farazi Movement after the death of Dudu Mian?
(a) Titu Mir
(b) Birsa Munda
(c) Sidhu
(d) Noah Mian
Answer:
(d) Noah Mian
Question 23.
Who provided leadership of the 1857 revolt in Bareilly?
(a) Begum Hazrat Mahal
(b) Khan Bahadur
(c) Nana Saheb
(d) Rani Lakshmi Bai
Answer:
(b) Khan Bahadur
Question 24.
The Indigo Revolt began in the year ……………
(a) 1857
(b) 1858
(c) 1859
(d) 1875
Answer:
(c) 1859
Question 25.
Who among the following was not an extremist leader?
(a) Lala Lajpat Rai
(b) Vallabhbhai Patel
(c) Bipin Chandra Pal
(d) Bai Gangadhar Tilak
Answer:
(b) Vallabhbhai Patel
II. Fill in the blanks :
1. The British territories were broadly divided into administrative units called …………..
2. The Royal charter could not prevent other European powers from entering the ………….. Markets.
3. The Bengal Nawabs asserted their power and autonomy after the death of …………..
4. ………….. was made the Nawab of Bengal after the defeat of Siraj-ud-daulah at Plassey.
5. The first Anglo-Maratha war ended with the treaty of …………..
6. Indigo cultivation was done under two main systems known as …………… and …………..
7. By the terms of the Permanent Settlement, the rajas and taluqdars were recognized as …………………
8. ……………… developed Ryotwari System which gradually extended all over South India.
9. The indigo villages were usually around indigo factories owned by ……………….
10. The planters at times pressurised the village between to sign the …………… on behalf of the ryots.
11. The British described the tribal people as …………….
12. Tribals went to work in the ………….. and the ………….. in Bihar.
13. The new law passed in 1850 made …………… into ………….. easier.
14. The Revolt of 1857 began from …………….
15. Mangal Pandey a young soldier was hanged to death for ………….. his officer in ……………
16. The Mughal Emperor Bahadur Shah Zafar died in the …………… jail.
17. In the countryside peasants and zamindars resented the …………….. and the rigid methods of ……………. collection.
18. Nana Saheb, the adopted son of the late Peshwa Baji Rao, gathered armed forces and expelled the……………….. from the city.
19. …………… fought a guerrilla war against the British with the support of several tribal and peasant leaders.
20. The section of Indian nationalists who had little patience for the non-political constructive programmes was called ……………..
21. After the Battle of Plassey, the British adopted the policy of ……………..
22. Many of the peasant revolts were led by …………….. leaders.
23. The Kol uprising took place in Chotanagpur and Singbhum region of Jharkhand and Orissa, under the leadership of ……………. and …………
24. After the 1857 revolt, the British captured Bahadur Shah and transported him to …………….
Answers:
1. Presidencies
2. Eastern
3. Aurangzeb
4. Mir Jafar
5. Salbai
6. Nij, ryots
7. Zamindars
8. Thomas Munro
9. Planters
10. contract
11. Savage
12. tea plantations, Coal mines
14. Meerut
15. Attacking, Barrackpore
16. Rangoon
17. High takes, revenue
18. British garrison
19. Nana Saheb
20. Militant nationalists
21. territorial expansion
22. religious
23. Bindrai, Singhrai
24. Burma
III. True or false
1. Siraj-ud-daulah got help from his commander Mir Jafar and finally won victory in the Battle of Plassey.
2. Birsa urged his followers to purify themselves, give up drinking liquor and stop believing in witchcraft and sorcery.
3. The British wanted to preserve the tribal way of life.
4. The traders and moneylenders never deceived the tribal people.
5. Many tribal groups did not like the colonial forest laws and therefore revolted.
Answers:
1. False
2. True
3. False
4. False
5. True
IV. Choose the correct statement.
Question 1.
(i) The Munda rebellion prompted the British to formulate a policy on tribal land.
(ii) The early objectives of the Congress were to develop and consolidate sentiments of national unity.
(iii) The Indian princes and zamindars were neither loyal to the British power.
(iv) The leaders of the 1857 revolt were defeated due to lack of weapons, organisation, discipline and betrayal by their aides.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv) are correct
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (iii) and (iv) are correct
Answer:
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv) are correct
Question 2.
(i)The boycott and Swadeshi were liked to each other.
(ii) Pheroze Shah Mehta and Gokhale were the two important extremist leaders.
(iii) The methods of moderate leaders failed to yield any substantive change in the British attitude
(iv) The Poona Sarvajanik Sabha came into existence in 1870.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv) are correct
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (iii) and (iv) are correct
Answer:
(d) (iii) and (iv) are correct
Question 3.
Assertion (A): The plight of the indigo growers war miserable.
Reason (R): They were trapped in debts which were often passed from father to son.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) Both A and R are wrong
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(d) Both A and R are correct but R .is not the correct explanation of A
Answer:
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
V. Match the following.
a.
| 1. | Mangal Pandey | (a) | Kanpur |
| 2. | Bahadur Shah II | (b) | Lucknow |
| 3. | Nana Saheb | (c) | Central India |
| 4. | Begum Hazarat Mahal | (d) | Barrackpore |
| 5. | Rani Lakshmi Bai | (e) | Delhi |
Answer:
1. (d)
2. (e)
3. (a)
4. (b)
5. (c)
b.
| 1. | Rani Lakshmi Bai | (a) | Mughal Emperor |
| 2. | Bahadur Shah II | (b) | Colin Campbell |
| 3. | The Great Revolt | (c) | Jhansi |
| 4. | Lucknow | (d) | Magna Carta |
| 5. | Queen Victoria’s Proclamation | (e) | 1857 |
Answer:
1. (c)
2. (a)
3. (e)
4. (b)
5. (d)
c.
| 1. | Birjis Qadr | (a) | Bihar |
| 2. | Rani lakshmi bai | (b) | Faizabad |
| 3. | Kunwar Singh | (c) | Jhansi |
| 4. | Bakht Khan | (d) | Lucknow |
| 5. | Ahmadullah Shan | (e) | Bareilly |
Answer:
1. (d)
2. (c)
3. (a)
4. (e)
5. (b)
d.
| 1. | Khunt Katti | (a) | Mirror of the Indigo |
| 2. | Bethbehari | (b) | Joint holding |
| 3. | Niladarpan | (c) | Self rule |
| 4. | Swaraj | (d) | Great tumult |
| 5. | Ulugulan rebellion | (e) | Forced labour |
Answer:
1. (b)
2. (e)
3. (a)
4. (c)
5.(d)
VI. Answer briefly:
Question 1.
How did the East India Company restructure the Mughal revenue system?
Answer:
- British – The East India Company introduced land tenures and altered the agrarian relations.
- Zamindars and other who collected the revenue never given the possession right on land.
- No wide spread system of private ownership. In this way East India Company restructured the Mughal revenue system.
Question 2.
What was the main reason for the defeat of Siraj-ud-daulah at Plassey?
Answer:
Mir Jafar, one of Siraj-ud-daulah’s commanders did not fight the battle.
Question 3.
“Tribes” who are they?
Answer:
- Tribes in India were and are very much part of the Indian society.
- Infact they are the Indian peasantry subsisting through shifting cultivation.
- The modem usage of word tribe in India restricts the definition to distinguish them from the rest of the Indian society, a stratified system based on caste.
Question 4.
How did the company purchase Indian goods?
Answer:
It purchased Indian goods with gold and silver imported from Britain.
Question 5.
What were the impacts of the transfer of power from East India Company to the Crown?
Answer:
- After the transfer of power to the Crown.
- De-industrialisation led to massive unemployment workers were forced out of the land.
- Heavy taxation mined agriculture.
- Famine deaths increased.
- Peasants were forced to pay revenue directly to the Government.
- Mortgaged land of the defaulters were auctioned by the moneylenders.
- Peasants were trapped in the vicious-cycle of debt and forced to abandon cultivation.
Question 6.
When was Robert Clive appointed the Governor of Bengal?
Answer:
He was appointed the Governor of Bengal in 1764.
Question 7.
What were the two elements of early Indian response to colonialism?
Answer:
First response: Tribal uprisings and peasant rebellions made an attempts to restore the old order in the late 18th and early 19th century. It was restorative in nature.
Second response: In the second half of 19th-century response was in the ‘ form of Indian Nationalism emphasising on consciousness of unity and National aspiration.
Question 8.
What is indigo?
Answer:
It is a plant that produces rich blue colour used as a dye.
Question 9.
Why did cloth dyers prefer indigo to woad?
Answer:
Cloth dyers preferred indigo as a dye because it produced a rich blue colour whereas the dye from woad was pale and dull.
Question 10.
Mention different types of activities of tribal people.
Answer:
(a) Some practised Jhum cultivation
(b) Some were hunter-gatherers
(c) Some herded animals
(d) Some took to settled cultivation
Question 11.
Who was Birsa?
Answer:
Birsa belonged to a family of Mundas, a tribal group that lived in Chottanagpur.
Question 12.
What did people say about Birsa?
Answer:
People said that he had miraculous powers. He could cure all diseases and multiply grain.
Question 13.
What problems did Birsa set out to resolve?
Answer:
(a) The familiar ways of tribals seemed to be disappearing.
(b) Their livelihoods were under threat.
(c) The religion appeared to be in danger.
Question 14.
On what charges was Birsa convicted?
Answer:
Birsa was convicted on the charges of rioting.
Question 15.
When did Birsa die and how?
Answer:
He died of cholera in 1900 in jail.
Question 16.
Name any two smaller rulers who acknowledged the suzerainty of Bahadur Shah Zafar.
Answer:
Nana Saheb and Birjs Qadar.
Question 17.
Who was Tantia Tope?
Answer:
He was the general of Nana Saheb.
Question 18.
Name the important leaders and centres of the mutiny.
Answer:
Important leaders:
- Rani Lakshmi Bai of Jhansi
- Tantia Tope
- Nana Saheb and Kunwar Singh.
Important centres:
- Kanpur
- Delhi
- Lucknow
Question 19.
Why was not the revolt widespread?
Answer:
- There was no unity among the rebels.
- It did not extend beyond north India.
- South India, Punjab, Sind and Rajasthan kept quiet.
- The rulers of the Indian States who did not support the movement remained neutral.
- A large number of rulers of the Indian States and the big zamindars did not join the movement
- The educated Indians did not support the movement.
Question 20.
The early Indian response to colonial exploitation and the colonial political and economic domination consisted of two elements. Mention them.
Answer:
The two responses:
(i) The first response in the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries was restorative in nature. Both tribal uprising and peasant rebellion made an attempt to restore the older order.
(ii) The second response appeared in the second half of the nineteenth century in the form of Indian nationalism that progressively imagined India as a nation emphasising on a consciousness of unity, and national aspiration.
Question 21.
Mention some of the issues that added to a sense of resentment among the Indian peasants and tribals against the British.
Answer:
Some of the issues are – the concept of private property rights in land, rigorous collection of land revenue, encroachment of tribal land by the non-tribal people, the interference of Christian missionaries in the socio-religious life of the local people.
Question 22.
What is the significance of the peasant rebellion that erupted in the first half of the nineteenth century India?
(OR)
What were the characteristics of the peasant uprisings that began except in India in the first half of the nineteenth century ?
Answer:
(i) The peasant uprisings clearly showed an awareness of the power structure in rural society and a strong will to restructure the authority.
(ii) The rebels were quite familiar with the political source of oppression and demonstrated in their actions against the Zamindar houses, grain stocks, the money lenders, and the merchants.
(iii) At times, the British state machinery, which came forward to protect these local agents of oppression, was also attacked.
Question 23.
Highlight the reasons that make the Great Rebellion of 1857 so significant.
(OR)
Why are the events of 1857- 58 significant?
Answer:
The event of 1857-58 is significant for the following reasons,
- This was the first major revolt of armed forces accompanied by civilian rebellions.
- The revolt witnessed the unprecedented violence, peipetrated by both sides.
- The revolt brought an end to the East India Company and the governance of the Indian subcontinent was taken over by the British Crown.
Question 24.
Mention some of the key demands of the Indian National Congress.
Answer:
Here are some of the key demands made by the Indian National Congress:
- Creation of legislative councils at provincial and central level.
- Increasing the number of elected members in the legislative council.
- Separating judicial and executive functions.
- Reducing military expenditure.
- Reduction of home charges.
VII. Answer all the questions given under each caption:
Question 1.
Farazi – Movement
(a) When and by whom was Farazi movement launched?
Answer:
In 1818 Farazi movement was lunched by Shariatullah.
(b) What did he advocate?
Answer:
He advocated the participants to abstain from un islamic activities.
(c) What was the result of it?
Answer:
This resulted in conflict directly with zamindars and in turn with the British who favoured the zamindars.
(d) Who revived this movement in the 1870?
Answer:
This movement was revived by Noahmian in the 1870s.
Question 2.
Revolt at Kanpur.
(a) Who joined the rebels at Kanpur and with whom?
Answer:
Nana Saheb joined the rebels with his commander Tantia Tope.
(b) What happened to the English?
Answer:
The English surrendered to the rebel force. The English men, women and children were mercilessly massacred.
(c) Who defeated Nana Saheb?
Answer:
Sir Colin Campbell defeated Nana Saheb.
(d) When was Cawnpur brought under British control?
Answer:
Kanpur was brought under the control of the British by the middle November 1857.
Question 3.
State of indian After the Battle of Plassey
(a) What was the policy adopted by the British after Plassey battle?
Answer:
British adopted the policy of territorial expansion.
(b) Name the areas that have undergone changes?
Answer:
Army, police, judicial system, land revenue administration and other institutions of Governance had systematic changes.
(c) What was the early Indians response to?
Answer:
The early Indians response to Colonial exploitation, political and Economic Domination.
(d) What was the nature of the response?
Answer:
The response in the. late 18th and early 19th Century was restorative in nature.
Question 4.
Munda Rebellion.
(a) Mention two reasons that aggravated the miseries of Munda people.
Answer:
- The corrupt police
- Lack of access to justice and the disillusionment with Christian missionaries.
(b) Describe briefly the role of Birsa Munda in this rebellion.
Answer:
Birsa Munda gave an impetus to the movement by declaring himself as the messenger of God. He claimed that he had a prophecy and promised supernatural solution to the problem of Munda people. The Munda leaders utilised the cult of Birsa Munda to recruit more people to their cause. A serious of night meetings were held and subsequently a revolt was planned.
(c) When did the revolt take place? How can you say that it was a violent revolt?
Answer:
The revolt took place on the Christmas day in 1889. The rebels resorted to violence. They burnt down buildings and shot arrows at the Christian missionaries, and Munda Christian converts. They also made attacks on police stations and government officials.
(d) How was resistance crushed?
Answer:
Their resistance was crushed and Birsa Munda was arrested who later died in jail.
VIII. Answer the following in detail.
Question 1.
Discuss the four major trends discerned during the Swadeshi Movement in Bengal.
Answer:
Boycott and Swadeshi were the part of the plan to make India self-sufficient. Four major trends can be discerned during the Swadeshi Movement in Bengal.
The Moderate Trend:
- Had faith in British rule and their sense of justice and democratic practice.
- The moderate leaders were not ready to wrest power from British in one single movement.
- Boycott and Swadeshi Movement was of limited significance to them.
Constructive Swadeshi:
- Focused on self-help through Swadeshi industries national schools arbitration courts and constructive programmes in the villages.
- Rejected the self-defeating modest approach of moderates.
- It remained non-political in nature.
Militiant Nationalism:
- Focused more on a relentless boycott of foreign goods.
- Had little patience for the non – political constructive programmes.
- They ridiculed the idea of self-help.
Revolutionary terrorism:
- A radical response to the British rule with violent methods.
- It marked the shift from the mass – based movement to individual action.
- British officials who were anti – Swadeshi or repressive towards native population were targeted.
Question 2.
Mention the results of the Great Revolt of 1857.
Answer:
- It put an end to the company’s rule in India in 1858. The administration of India was directly taken over by the British Crown.
- By a special Act, both the Board of Control and the Court of Directors were abolished.
- The office of the Secretary of State for India was created. He was assisted by an Indian council of 15 members.
- The Governor General of India was designated as viceroy of India.
- The policy of ruthless conquest in India was given up.
- The Indian princess were given the right of adoption.
Social and religious changes:
- Full religious freedom was guaranteed to Indians.
- Indian were also given assurance that high posts would be given to them without any discrimination.
Military changes:
- The Indian army was thoroughly re-organized.
- The number of the European forces were increased.
- The artillery was put under the charge of the British.
Queen Victoria’s Proclamation of 1858:
- Queen Victoria’s Proclamation was issued in 1858.
- According to Queen Victoria’s Proclamation the English East India. The administration of India was taken over by the British Crown. The revolt paved the way for the rise of the national movement and it served as a source of inspiration in the later struggle for freedom.
Question 3.
What do you know about Militant Nationalism?
Answer:
- The following three were the well known extremist leaders of the Indian National Congress. Lala Lajpat Rai of Punjab, Bala Gangadhar Tilak of Maharashtra and Bipin Chandrapal of Bengal during the period of Swadeshi Movement.
- They were referred to as Lai – Bal – Pal Triumvirate.
- Punjab, Bengal and Maharashtra emerged as the hotbed of militant nationalism during the Swadeshi Movement.
- In south India Tuticorin became the most important location of Swadeshi activity.
- V.O.Chidambaranar launched Swadeshi Navigation Company as a part of it.
- One of the common goals of the extremist leaders was to achieve Swaraj or Self-rule.
- Political murders and individual acts of terrorism were not approved by the Militant leaders.
Question 4.
Describe the circumstances that led to the Indigo Revolt in 1859.
Answer:
(i) Natural Indigo dye was highly valued by cloth makers around the World. Many Europeans sought to make their fortunes by becoming Indigo planters in India. They employed Indian peasants to grow the Indigo which was processed into dye at the planters factories. The dye was then exported to Europe.
(ii) The Indian peasants were not interested in growing Indigo. Instead they wanted to grow food crops. But they were forced to grow indigo. The British planters gave them cash advances to help pay for the rent of the land or other costs. These advances needed to be repaid with interest.
(iii) At the end of the season, the planters paid the cultivators low prices for their indigo. Moreover, the small amount they earned was not enough to pay back the cash advance with interest. So, they fell into debt.
(iv) The peasants would be forced to enter into another contract to grow indigo. And same thing would be repeated once again. Thus, the peasants were never able to clear their debts. Debts were often passed from father to son.
Finally, they revolted against the oppressive system in 1859 which came to be known as the Indigo Revolt. The peasants took a collective decision and refused to grow indigo. The movement quickly spread far and wide.
IMPORTANT EVENTS AND YEARS:
Year – Events
1855 – Birth of Indian National Congress
1856 – The General Services Enlistment Act
1857 – The Great Revolt
1858 – Queen Victoria’s Proclamation
1858 – Darbar at Allahabad
1858 – Vernacular Press Act
1905 – Partition of Bengal, Swadeshi Movement
1906 – Formation of the Muslim league
1907 – Surat Split
1909 – Minto – Morley Reforms Act
We think the data given here clarify all your queries of Chapter 7 and make you feel confident to attempt all questions in the examination. So, practice more & more from Tamilnadu State Board solutions for 10th Social Science History Chapter 7 Anti-Colonial Movements and the British of Nationalism Questions and Answers & score well. Need any information regarding this then ask us through comments & we’ll give the best possible answers very soon.