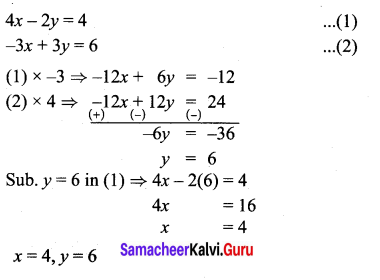
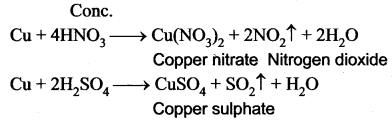
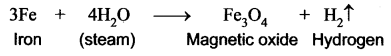
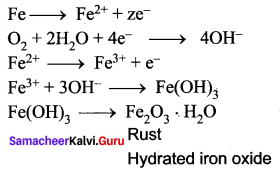
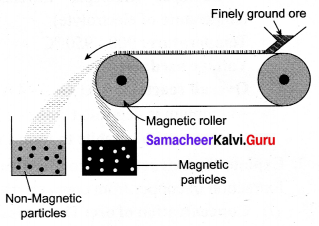
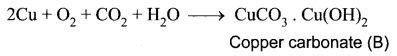
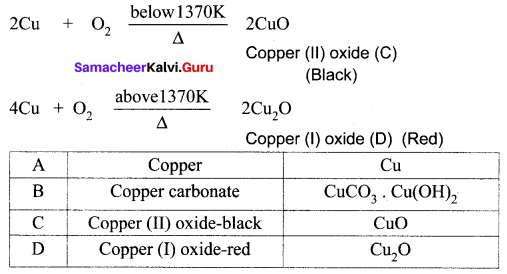
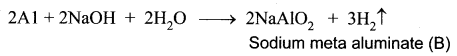
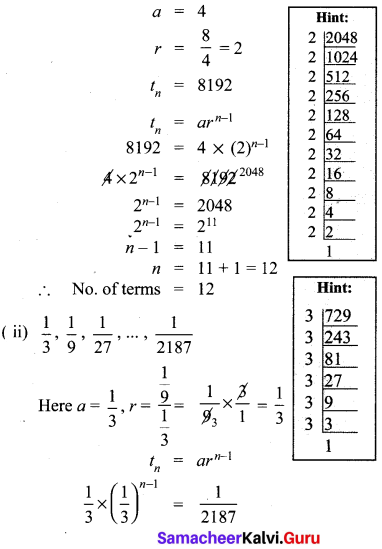
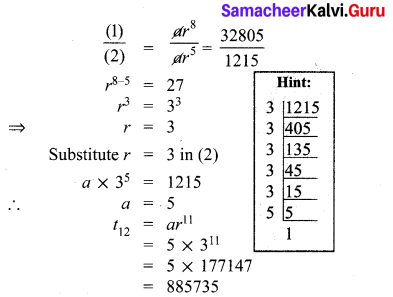
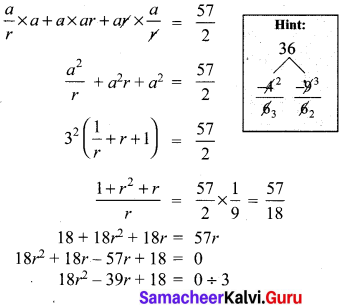
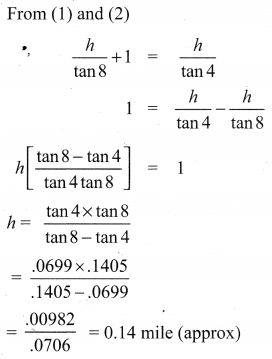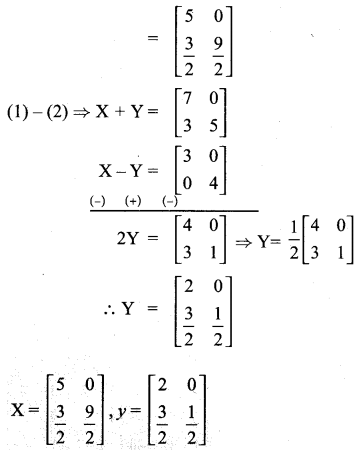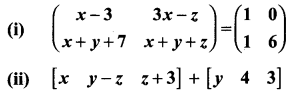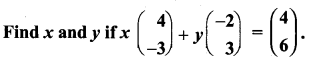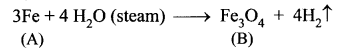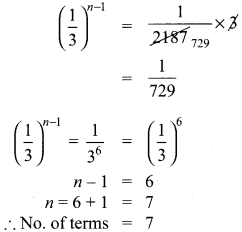You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 6 Trigonometry Ex 6.2
10th Maths Exercise 6.2 Samacheer Kalvi Question 1.
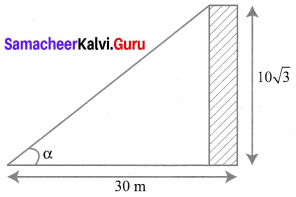
Find the angle of elevation of the top of a tower from a point on the ground, which is 30 m away from the foot of a tower of height 10\(\sqrt{3}\) m.
Solution:
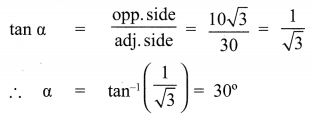
Ex 6.2 Class 10 Samacheer Question 2.
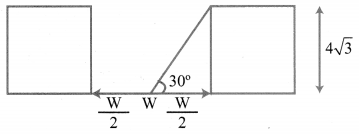
A road is flanked on either side by continuous rows of houses of height 4\(\sqrt{3}\) m with no space in between them. A pedestrian is standing on the median of the road facing a row house. The angle of elevation from the pedestrian to the top of the house is 30°. Find the width of the road.
Solution:
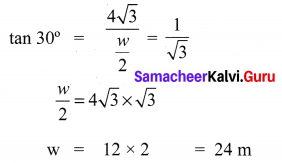
Exercise 6.2 Class 10 Samacheer Kalvi Question 3.
To a man standing outside his house, the angles of elevation of the top and bottom of a window are 60° and 45° respectively. If the height of the man is 180 cm and if he is 5 m away from the wall, what is the height of the window? (\(\sqrt{3}\) = 1.732)
Solution:
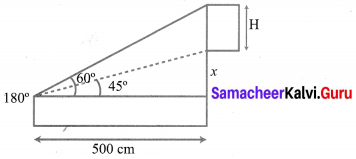
Let ‘H’ be the fit of the window. Given that elevation of top of the window is 60°.
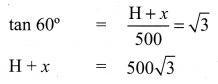
Given that elevation of bottom of the window is 45°.
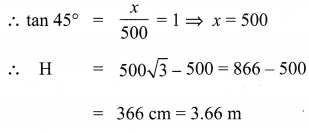
∴ Height of the window = 3.66 m
10th Maths Trigonometry Exercise 6.2 Question 4.
A statue 1.6 m tall stands on the top of a pedestal. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of the statue is 60° and from the same point the angle of elevation of the top of the pedestal is 40°. Find the height of the pedestal. (tan 40° = 0.8391, \(\sqrt{3}\) = 1.732)
Solution:
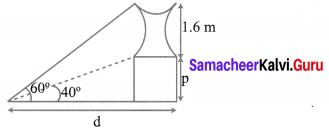
Let ‘p’ be the fit of the pedestal and d be the distance of statue from point of cabs, on the ground.
Given the elevation of top of the statue from pf on ground is 60°.

10th Maths Exercise 6.2 Question 5.
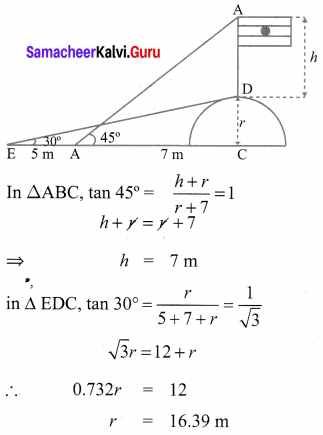
A flag pole ‘h’ metres is on the top of the hemispherical dome of radius V metres. A man is standing 7 m away from the dome. Seeing the top of the pole at an angle 45° and moving 5 m away from the dome and seeing the bottom of the pole at an angle 30°. Find
(i) the height of the pole
(ii) radius of the dome.
Solution:
10th Maths Ex 6.2 Question 6.
The top of a 15 m high tower makes an angle of elevation of 60° with the bottom of an electronic pole and angle of elevation of 30° with the top of the pole. What is the height of the electric pole?
Solution:
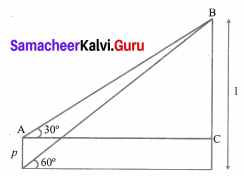
Let BD be tower of height = 15 m
AE be pole of height = ‘p’
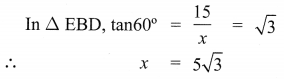
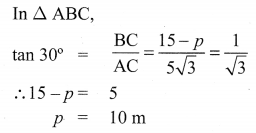
10th Maths 6.2 Question 7.
A vertical pole fixed to the ground is divided in the ratio 1 : 9 by a mark on it with lower part shorter than the upper part. If the two parts subtend equal angles at a place on the ground, 25 m away from the base of the pole, what is the height of the pole?
Solution:
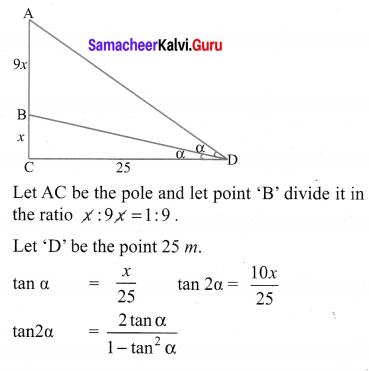
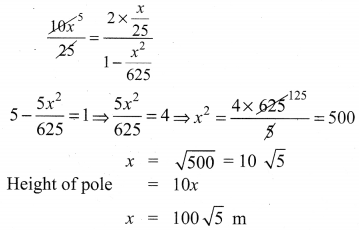
10th Samacheer Kalvi Maths Trigonometry Question 8.
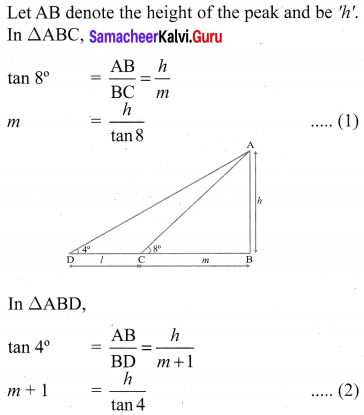
A traveler approaches a mountain on highway. He measures the angle of elevation to the peak at each milestone. At two consecutive milestones the angles measured are 4° and 8°. What is the height of the peak if the distance between consecutive milestones is 1 mile, (tan 4° = 0.0699, tan 8° = 0.1405).
Solution: