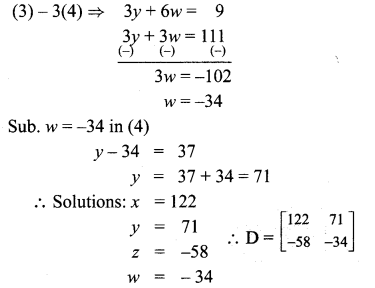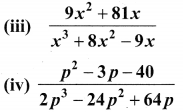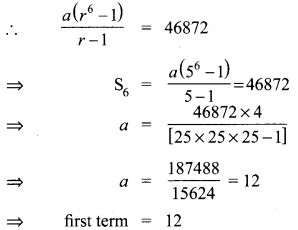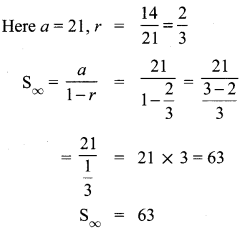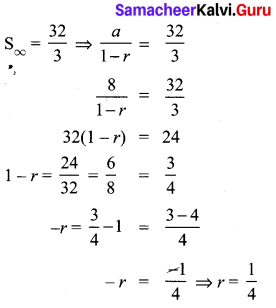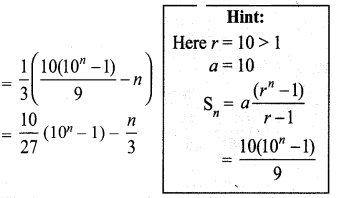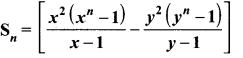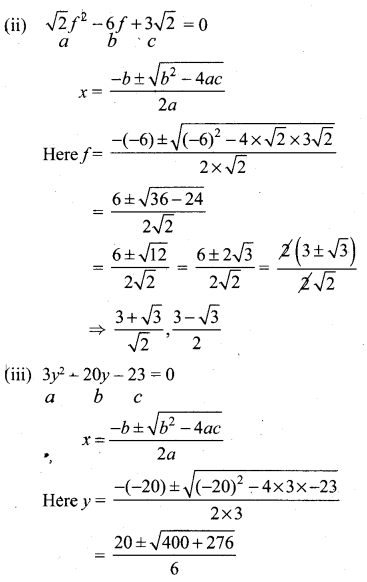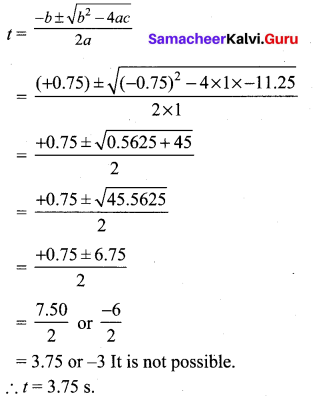You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Unit Exercise 3
10th Maths Unit Exercise 3 Question 1.
Solve \(\frac{1}{3}\) (x + y – 5) = y – z = 2x – 11 = 9 – (x + 2 z).
Solution:
Given

3z = 3 ⇒ z = 1
(3) becomes, 3x + 2 = 20 ⇒ 3x = 20 – 2 = 18
x = \(\frac{18}{3}\) = 6
(1) becomes, 6 – 2y + 3(1) = 5 ⇒ 9 – 2y = 5
⇒ 9 – 5 = 2y ⇒ 2y = 4
∴ y = \(\frac{4}{2}\) = 2
∴ Solution set is {6, 2, 1}
Unit Exercise 3 Question 2.
One hundred and fifty students are admitted to a school. They are distributed over three sections A, B and C. If 6 students are shifted from section A to section C, the sections will have equal number of students. If 4 times of students of section C exceeds the number of students of section A by the number of students in section B, find the number of students in the three sections.
Solution:
Let the students in section A, B, C be a, b, c, respectively.

Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Exercise 3.1 Question 3.
In a three-digit number, when the tens and the hundreds digit are interchanged the new number is 54 more than three times the original number. If 198 is added to the number, the digits are reversed. The tens digit exceeds the hundreds digit by twice as that of the tens digit exceeds the unit digit. Find the original number.
Solution:
Let the three digits numbers be 100a +10b + c.
100b + 10a + c = 3(100a + 10b + c) + 54 ………. (1)
100a + 106 + c + 198 = 100c + 106 + a ……… (2)
(b – a) = 2(b – c) ……… (3)
(1) ⇒ 100b + 10a + c = 300a + 30b + 3c + 54
⇒ 290a – 70b + 2c = -54
(2) ⇒ 99a – 99c = -198 ⇒ a – c = -2
⇒ a = c – 2
(3) ⇒ a + b – 2c = 0 ⇒ a + b = 2c
⇒ b = 2c – c + 2
⇒ b = c + 2
Substituting a, b in (1)
290(c – 2) – 70 (c + 2) + 2c = -54
290c – 580 – 70c – 140 + 2c = -54
222c = 666 ⇒ c = 3
a = 1, 6 = 5
∴ The number is 153.
10th Maths Unit Exercise 2 Question 4.
Find the least common multiple of
xy (k2 + 1) + k(x2 + y2) and
xy(k2 – 1) + k (x2 – y2)
Answer:
xy (k2 + 1) + k(x2 + y2) = k2xy + xy + kx2 + ky2
= (k2xy + kx2) + (ky2 + xy)
= kx(ky + x) + y (ky + x)
= (ky + x) (kx + y)
xy (k2 – 1) + k(x2 – y2) = k2xy – xy + kx2 – ky2
= (k2xy + kx2) – xy – ky2
= kx(ky + x) -y (ky + x)
= (ky + x) (kx – y)
L.C.M. = (ky + x) (kx + y) (kx – y)
= (ky + x)(k2x2 – y2)
The least common multiple is
(ky + x) (k2x2 – y2)
Unit Exercise Question 5.
Find the GCD of the following by division algorithm 2x4 + 13.x3 + 21 x2 + 23x + 7, x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1, x2 + 2x + 1.
Solution:
2x4 + 13x3 + 27x2 + 23x + 7,
x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1, x2 + 2x + 1.
By division algorithm, first divide
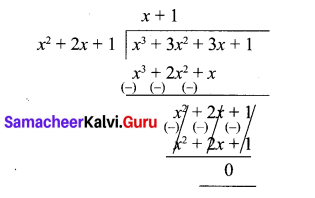
∴ (x + 1)2 is G.C.D of x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1 and x2 + 2x + 1.
Next let us divide
2x4 + 13x3 + 27x2 + 23x + 7 by x2 + 2x + 1
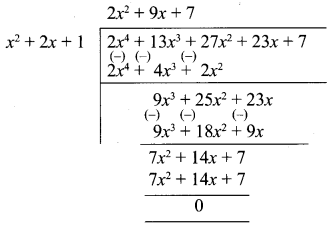
∴ G.C.D of 2x4 + 13x3 + 21 x2 + 23x + 7, x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1, x2 + 2x + 1 is (x + 1)2.
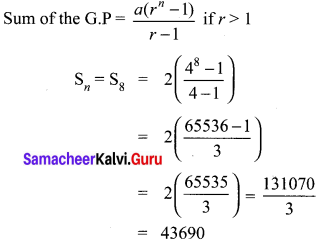
10th Maths Example Sums Question 6.
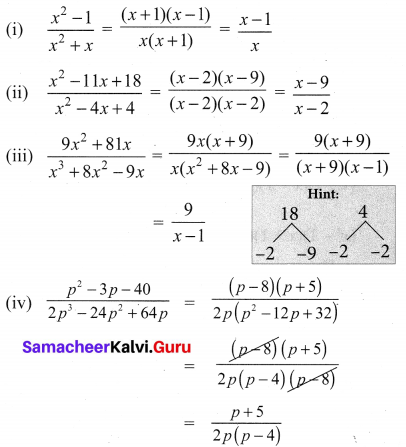
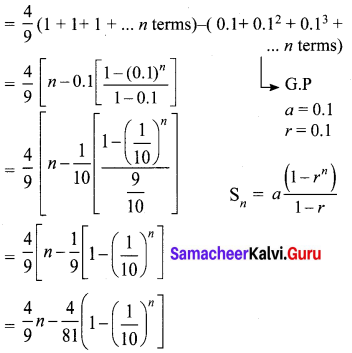
Reduce the given Rational expressions to its lowest form
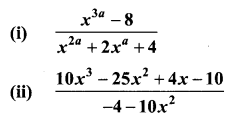
Solution:

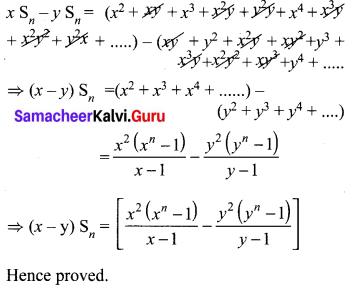
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solution Question 7.
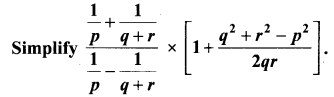
Solution:
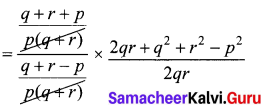
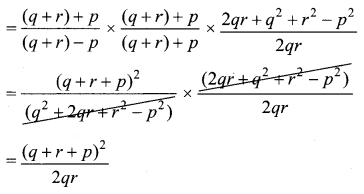
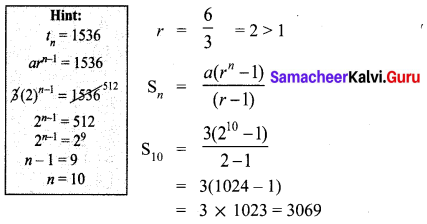
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Answers Question 8.
Arul, Ravi and Ram working together can clean a store in 6 hours. Working alone, Ravi takes twice as long to clean the store as Arul does. Ram needs three times as long as Arul does. How long would it take each if they are working alone?
Solution:
Let Aral’s speed of working be x
Let Ravi’s speed of working be y
Let Ram’s speed of working be z
given that they are working together. ,
Let V be the quantum of work, x + y + z = \(\frac{w}{6}\) …………. (1)
Also given that Ravi takes twice the time as Aral for finishing the work.
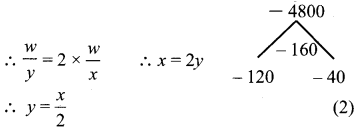
Also Ram takes 3 times the time as Aral for finishing the work.
∴ \(\frac{w}{z}\) = 3 × \(\frac{w}{x}\)
∴ x = 3z ∴ z = \(\frac{x}{3}\)
Substitute (2) and (3) in (1),
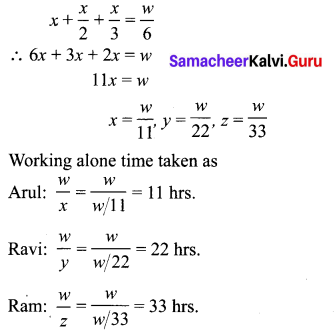
Exercise 1.6 Class 10 Maths Samacheer Question 9.
Find the square root of 289x4 – 612x3 + 970x2 – 684x + 361
Solution:
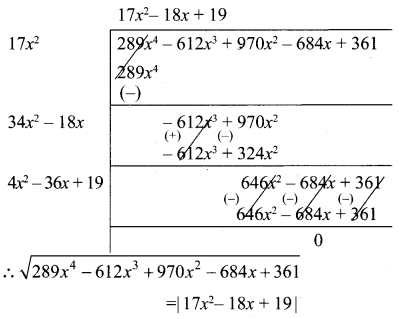
10th Maths Exercise 1.6 Answers Question 10.
Solve \(\sqrt{y+1}+\sqrt{2 y-5}\) = 3.
Solution:
Squaring both sides
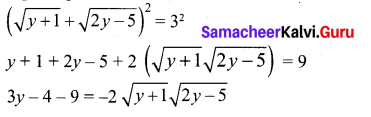
9y2 – 78y + 169 = 4 (y + 1)(2y – 5)
9y2 – 78y + 169 = 4 (2y2 + 2y – 5y – 5)
9y2 – 78y + 169 = 8y2 + 8y – 20y – 20
9y2 – 78y + 169 – 8y2 + 12y + 20 = 0
y2 – 66y + 189 = 0
y2 – 63y – 3y + 189 = 0
y(y – 63) – 3(y – 63) = 0
(y – 63)(y – 3) = 0
y = 63, 3
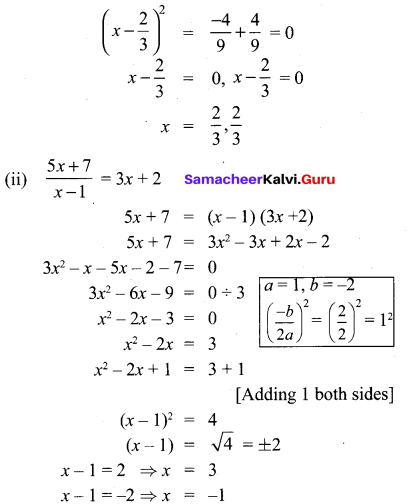
10th Maths Book Example Sums Question 11.
A boat takes 1.6 hours longer to go 36 kms up a river than down the river. If the speed of the water current is 4 km per hr, what is the speed of the boat in still water?
Solution:
Let the speed of boat in still water be ‘v’
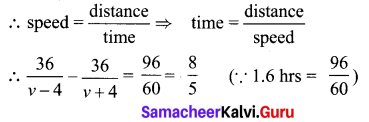
⇒ 36(v + 4) – 36(v – 4) = \(\frac{8}{5}\) (v – 4) (v + 4)
⇒ 36v + 144 – 36v + 144 = \(\frac{8}{5}\) (v2 – 4v + 4v – 16)
⇒ 288 = \(\frac{8}{5}\) v2 – \(\frac{128}{5}\) ⇒ 8v2 – 128 = 1440
⇒ 8v2 = 1568 ⇒ v2 = 196 v = ±14
∴ Speed of the boat = 14 km/hr. (∵ speed cannot be -ve)
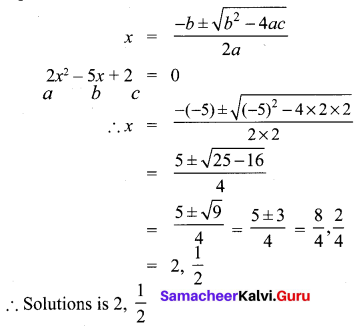
10th Algebra Solutions Question 12.
Is it possible to design a rectangular park of perimeter 320 m and area 4800 m2? If so find its length and breadth.
Solution:
Let the length and breadth of the rectangle be lm and bm
Given 2(1 + b)
⇒ l + b = 160 ………. (1)
Also l b = 4800
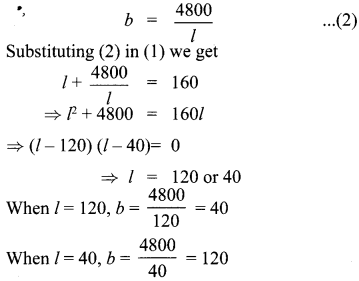
∴ Length and breadth of the rectangular park is 120m and 40 m
10th Maths Samacheer Question 13.
At t minutes past 2 pm, the time needed to 3 pm is 3 minutes less than \(\frac{t^{2}}{4}\) Find t.
Solution:
60 – t = \(\frac{t^{2}}{4}\) – 3
⇒ t2 – 12 = 240 – 4t
⇒ t2 + 4t – 252 = 0
⇒ t2 + 18t – 14t – 252 = 0
⇒ t(t + 18) – 14(t + 18) = 0
⇒ (t + 18) (t – 14) = 0
∴ t = 14 or t = -18 is not possible.
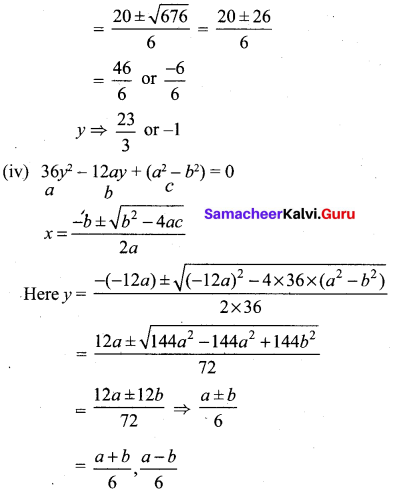
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Solutions Question 14.
The number of seats in a row is equal to the total number of rows in a hall. The total number of seats in the hall will increase by 375 if the number of rows is doubled and the number of seats in each row is reduced by 5. Find the number of rows in the hall at the beginning.
Solution:
Let the no of seats in each row be x
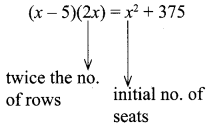
⇒ 2x2 – 10x = x2 + 375
⇒ x2 – 10x – 375 = 0
⇒ x2 – 25x + 15x – 375 = 0
⇒ x (x – 25) + 15 (x – 25) = 0
⇒ (x – 25) (x + 15) = 0
⇒ x = 25, x = -15, x > 0
∴ 25 rows are in the hall.
3rd Standard Samacheer Maths Book Solutions Question 15.
If a and b are the roots of the polynomial f(x) = x2 – 2x + 3, find the polynomial whose roots are
(i) α + 2, β + 2
(ii) \(\frac{\alpha-1}{\alpha+1}, \frac{\beta-1}{\beta+1}\)
Solution:
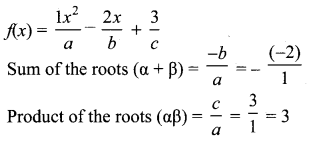
(i) α + 2, β + 2 are the roots (given)
Sum of the roots = α + 2 + β + 2
= α + β + 4
= 2 + 4 = 6
Product of the roots = (α + 2) (β + 2)
= αβ + 2α + 2β + 4
= αβ + 2(α + β) + 4
= 3 + 2 × 2 + 4
= 3 + 4 + 4 = 11
∴ The required equation = x2 – 6x + 11 = 0.
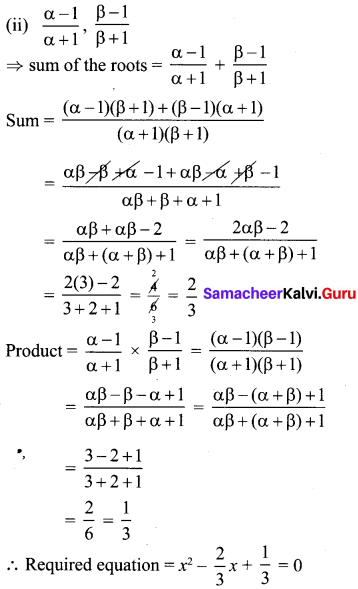
⇒ 3x2 – 2x + 1 = 0
Class 3 Samacheer Kalvi Solutions Question 16.
If -4 is a root of the equation
x2 + px – 4 = 0 and if the equation
x2 + px + q = 0 has equal roots, find the values of p and q.
Answer:
Let p(x) = x2 + px – 4
– 4 is the root of the equation
P(-4) = 0
16 – 4p – 4 = 0
-4p + 12 = 0
-4p = -12
p = \(\frac { 12 }{ 4 } \) = 3
The equation x2 + px + q = 0 has equal roots
x2 + 3 x + q = 0
Here a = 1, b = 3, c = q
since the roots are real and equal
b2 – 4 ac = 0
32 – 4(1)(q) = 0
9 – 4q = 0
9 = 4q
q = \(\frac { 9 }{ 4 } \)
The value of p = 3 and q = \(\frac { 9 }{ 4 } \)
10thmaths Question 17.
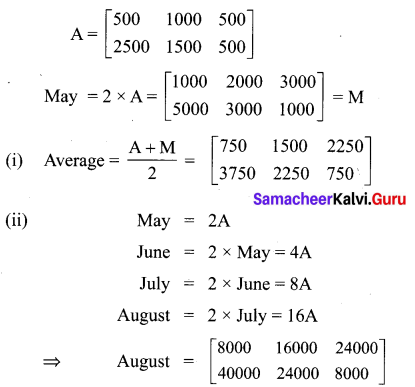
Two farmers Senthil and Ravi cultivates three varieties of grains namely rice, wheat and ragi. If the sale (in ₹) of three varieties of grains by both the farmers in the month of April is given by the matrix.

May month sale (in ₹) is exactly twice as that of the April month sale for each variety.
(i) What is the average sales of the months April and May.
(ii) If the sales continues to increase in the same way in the successive months, what will be sales in the month of August?
Solution:
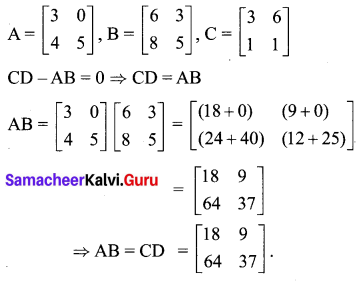
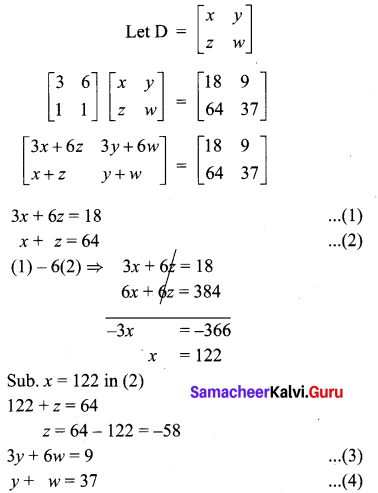
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Answers Question 18.
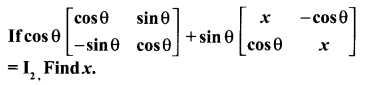
Solution:
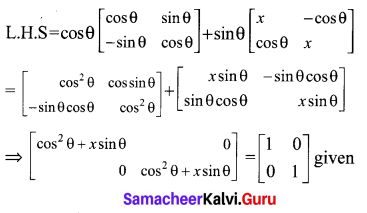
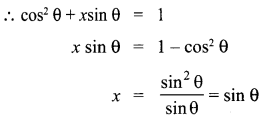
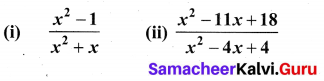
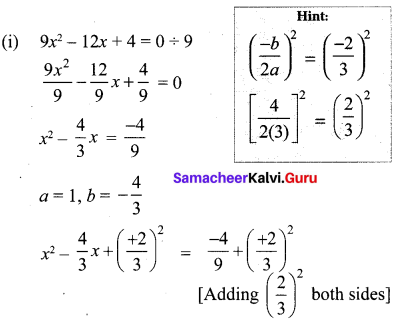
10th Maths Question 19.
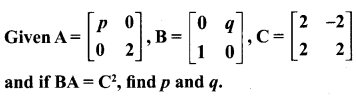
Solution:
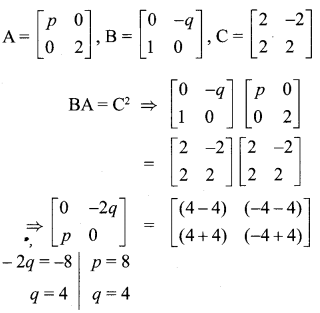
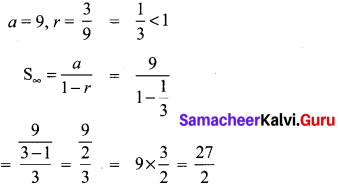
10th Algebra Chapter 3 Question 20.
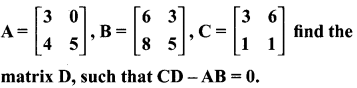
Solution: