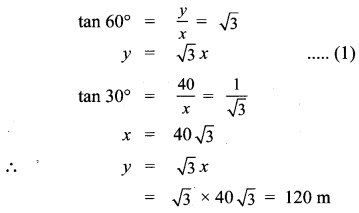You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 7 Mensuration Ex 7.4
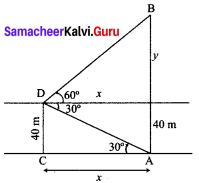
10th Maths Exercise 7.4 Samacheer Kalvi Question 1.
An aluminium sphere of radius 12 cm is melted to make a cylinder of radius 8 cm. Find the height of the cylinder.
Solution:
Sphere – Radius r1 = 12 cm
Cylinder – Radius r2 = 8 cm
h2 = ?
Volume of cylinder = Volume of sphere melted
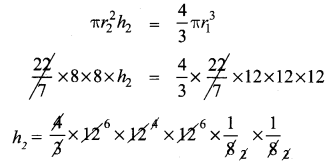
∴ Height of the cylinder made = 36 cm.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Question 2.
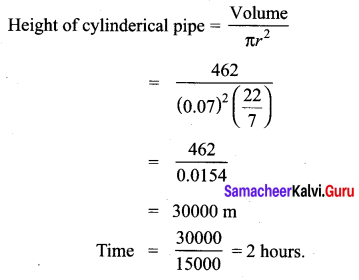
Water is flowing at the rate of 15 km per hour through a pipe of diameter 14 cm into a rectangular tank which is 50 m long and 44 m wide. Find the time in which the level of water in the tanks will rise by 21 cm.
Solution:
In cylinder,
r = 7cm = 0.7m
l = 15 km = 15000 m
In tank
l = 50 m
b = 44 m
h = 0.21 m
Volume of water in tank = lbh
= 50 × 44 × 0.21
= 462 m3
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Mensuration Question 3.
A conical flask is full of water. The flask has base radius r units and height h units, the water poured into a cylindrical flask of base radius xr units. Find the height of water in the cylindrical flask.
Solution:
The volume of water poured = The volume of the water in the conical flask.
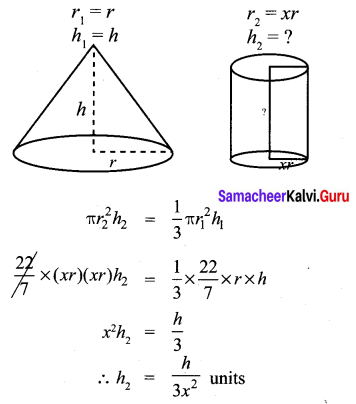
∴ The height of the water in the cylindrical flask = \(\frac{h}{3 x^{2}}\) units.
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 10th Maths Question 4.
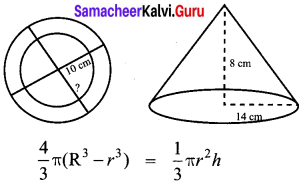
A solid right circular cone of diameter 14 cm and height 8 cm is melted to form a hollow sphere. If the external diameter of the sphere is 10 cm, find the internal diameter.
Solution:
Volume of the hollow sphere made = Volume of the cone melted.

Exercise 7.4 Class 10 Question 5.
Seenu’s house has an overhead tank in the shape of a cylinder. This is filled by pumping water from a sump (underground tank) which is in the shape of a cuboid. The sump has dimensions 2 m × 1.5 m × 1 m. The overhead tank has its radius of 60 cm and height 105 cm. Find the volume of the water left in the sump after the overhead tank has been completely filled with water from the sump which has been full, initially.
Solution:
Volume of water in the sump = lbh
= 2 × 1.5 × l = 200 × 150 × 100 = 3000000 cm3
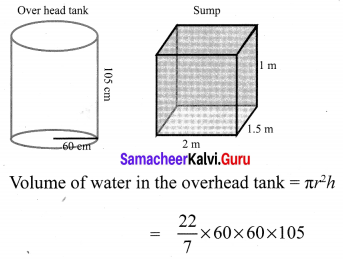
= 1188000 cm3
∴ The volume of water left in the sump = 3000000 – 1188000
= 1812000 cm3
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solution Question 6.
The internal and external diameter of a hollow hemispherical shell are 6 cm and 10 cm respectively. If it is melted and recast into a solid cylinder of diameter 14 cm, then find the height of the cylinder.
Solution:
D = 10 cm,
R = 5 cm
d = 6 cm,
r = 3 cm
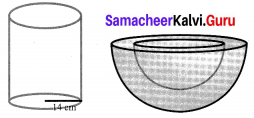
Volume of the cylinder made = Volume of hemisphere melted.
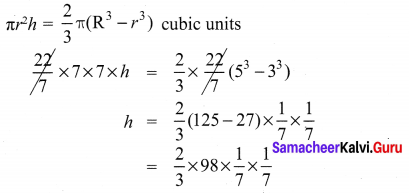
∴ Height of the cylinder made = 1.33 cm.
Ex 7.4 Class 10 Maths Question 7.
A solid sphere of radius 6 cm is melted into a hollow cylinder of uniform thickness. If the external radius of the base of the cylinder is 5 cm and its height is 32 cm, then find the thickness of the cylinder.
Solution:
Volume of the hollow cylinder made = Volume of the sphere melted.
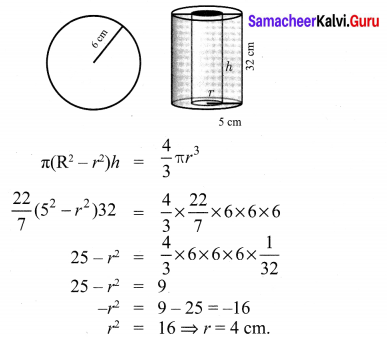
∴ The thickness = External radius – Internal radius
= 5 – 4 = 1
Exercise 7.4 Maths Class 10 Question 8.
A hemispherical bowl is filled to the brim with juice. The juice is poured into a cylindrical vessel whose radius is 50% more than its height. If the diameter is same for both the bowl and the cylinder then find the percentage of juice that can be transferred from the bowl into the cylindrical vessel.
Solution:
Diameter of the bowl = Diameter of the cylinder
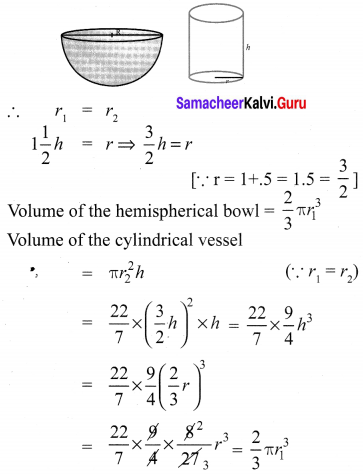
∴ Both volumes are equal.
∴ 100% of juice that can be transferred from the bowl into the cylindrical vessel.