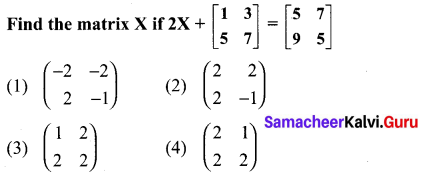
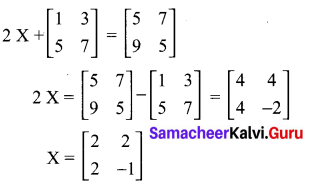
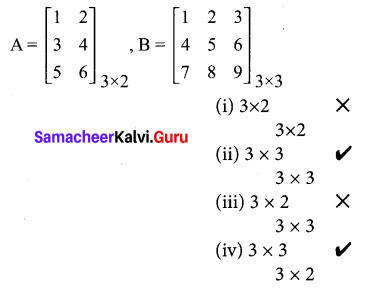
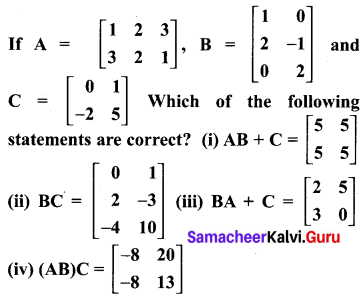
Students who are preparing for the Science exam can download this Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 10th Science Chapter 21 from here for free of cost. These Tamilnadu State Board Textbook Solutions PDF cover all 10th Science Health and Diseases Book Back Questions and Answers.
All these concepts of Chapter 21 Health and Diseases are explained very conceptually by the subject teachers in Tamilnadu State Board Solutions PDF as per the prescribed Syllabus & guidelines. You can download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Book Solutions Chapter 21 Health and Diseases State Board Pdf for free from the available links. Go ahead and get Tamilnadu State Board Class 10th Science Solutions of Chapter 21 Health and Diseases.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Solutions Chapter 21 Health and Diseases
Kickstart your preparation by using this Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 21th Science Chapter 21 Health and Diseases Questions and Answers and get the max score in the exams. You can cover all the topics of Chapter 21 easily after studying the Tamilnadu State Board Class 21th Science Textbook solutions pdf. Download the Tamilnadu State Board Science Chapter 21 Health and Diseases solutions of Class 21th by accessing the links provided here and ace up your preparation.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Health and Diseases Textual Evaluation Solved
I. Choose the Correct Answer.
Samacheerkalvi.Guru Science Question 1.
Tobacco consumption is known to stimulate the secretion of adrenaline. The component causing this could be _______.
(a) Nicotine
(b) Tannic acid
(c) Curcumin
(d) Leptin.
Answer:
(a) Nicotine
10th Science Solution Samacheer Kalvi Question 2.
World ‘No Tobacco Day’ is observed on:
(a) May 31
(b) June 6
(c) April 22
(d) October 2
Answer:
(a) May 31
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 10th Science Book Pdf Download Question 3.
Cancer cells are more easily damaged by radiations than normal cells because they are _______.
(a) Different in structure
(b) Non-dividing
(c) Mutated Cells
(d) Undergoing rapid division.
Answer:
(d) Undergoing rapid division.
10th Science Solutions Samacheer Kalvi Question 4.
Which type of cancer affects lymph nodes and spleen?
(a) Carcinoma
(b) Sarcoma
(c) Leukemia
(d) Lymphoma
Answer:
(c) Leukemia
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 10th Science Book Back Answers Question 5.
Excessive consumption of alcohol leads to _______.
(a) Loss of memory
(b) Cirrhosis of liver
(c) State of hallucination
(d) Suppression of brain function.
Answer:
(b) Cirrhosis of liver
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 10th Science Question 6.
Coronary heart disease is due to:
(a) Streptococci bacteria
(b) Inflammation of pericardium
(c) Weakening of heart valves
(d) Insufficient blood supply to heart muscles
Answer:
(d) Insufficient blood supply to heart muscles
Samacheer Kalvi Guru Science Question 7.
Cancer of the epithelial cells is called _______.
(a) Leukaemia
(b) Sarcoma
(c) Carcinoma
(d) Lipoma.
Answer:
(c) Carcinoma
10th Samacheer Kalvi Science Solutions Question 8.
Metastasis is associated with:
(a) Malignant tumour
(b) Benign tumour
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Crown gall tumour
Answer:
(a) Malignant tumour
Health And Disease Class 10 In Tamil Question 9.
Polyphagia is a condition seen in _______.
(a) Obesity
(b) Diabetes mellitus
(c) Diabetes insipidus
(d) AIDS.
Answer:
(b) Diabetes mellitus
Question 10.
Where does alcohol effect immediately after drinking?
(a) Eyes
(b) Auditory region
(c) Liver
(d) Central Nervous System
Answer:
(d) Central Nervous System
II. State whether True or False. If false, write the correct statement:
Question 1.
AIDS is an epidemic disease.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: AIDS is a viral disease.
Question 2.
Cancer-causing genes are called Oncogenes.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
Obesity is characterized by tumour formation.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Obesity is characterized by an accumulation of excess body fat with an abnormal increase in body weight.
Question 4.
In leukaemia, both WBCs and RBCs increase in number.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Leukemia is characterized by an increase in the formation of white blood cells in the bone marrow and lymph nodes.
Question 5.
Study of the cause of the disease is called aetiology.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Study of a cause of the disease is called Pathology.
Question 6.
AIDS is not transmitted by contact with a patient’s clothes.
Answer:
True.
Question 7.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus results due to insulin deficiency.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: In type 2 diabetes mellitus, Insulin production by the Pancreas is normal, but the target cells do not respond to insulin.
Question 8.
Carcinogens are cancer-causing agents.
Answer:
True.
Question 9.
Nicotine is a narcotic drug.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Nicotine is a stimulant, highly harmful and poisonous substance, in Tobacco.
Question 10.
Cirrhosis is associated with the brain disorder.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Liver damage resulting in Fatty liver which leads to Cirrhosis and formation of fibrous tissues.
III. Expand the following abbreviations:
Question 1.
- IDDM
- HIV
- BMI
- AIDS
- CHD
- NIDDM.
Answer:
- Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
- Human Immunodeficiency Vims
- Body Mass Index
- Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome
- Coronary Heart Disease
- Non – Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus.
IV. Match the following:
Question 1.
| 1. Sarcoma | (a) Stomach cancer |
| 2. Carcinoma | (b) Excessive thirst |
| 3. Polydipsia | (c) Excessive hunger |
| 4. Polyphagia | (d) Lack of blood flow to the heart muscle |
| 5. Myocardial Infarction | (e) Connective tissue cancer |
Answer:
- (e) Connective tissue cancer
- (a) Stomach cancer
- (b) Excessive thirst
- (c) Excessive hunger
- (d) Lack of blood flow to the heart muscle.
V. Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Cirrhosis is caused in the liver due to excessive use of _______.
Answer:
Alcohol.
Question 2.
A highly poisonous chemical derived from tobacco is _______.
Answer:
Nicotine.
Question 3.
Blood cancer is called _______.
Answer:
Leukaemia.
Question 4.
Less response of a drug to a specific dose with repeated use is called _______.
Answer:
Tolerance.
Question 5.
Insulin resistance is a condition in _______ diabetes mellitus.
Answer:
Type – 2.
VI. Analogy Type Questions.
Identify the first words and their relationship and suggest a suitable word for the fourth blank:
Question 1.
Communicable : AIDS :: Non – communicable : _______.
Answer:
Obesity.
Question 2.
Chemotherapy : Chemicals :: Radiation therapy : _______.
Answer:
Radiation.
Question 3.
Hypertension : Hypercholesterolemia :: Glycosuria : _______.
Answer:
Polyphagia.
VII. Answer in a Sentence.
Question 1.
What are psychotropic drugs?
Answer:
The drugs which act on the brain and alter the behaviour, consciousness, power of thinking and perception, are called Psychotropic drags. They are also called Mood altering drugs.
Question 2.
Mention the diseases caused by tobacco smoke.
Answer:
Bronchitis, pulmonary tuberculosis, emphysema hypoxia, lung cancer, hypertension gastric and duodenal ulcer are diseases caused be tobacco smoke.
Question 3.
What are the contributing factors for obesity?
Answer:
Obesity is due to genetic factors, physical inactivity, overeating and endocrine factors.
Question 4.
What is adult onset diabetes?
Answer:
Type-2 Non Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) is called as adult onset diabetes.
Question 5.
What is metastasis?
Answer:
The Cancerous cells migrate to distant parts of the body and affect new tissues and this process is called Metastasis.
Question 6.
How does insulin deficiency occur?
Answer:
Insulin deficiency occur due to the destruction of B – cells of the pancreas, characterized by abnormally elevated blood glucose level resulting from inadequate insulin secretion.
VIII. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the various routes by which transmission of human immunodeficiency virus takes place?
Answer:
HIV is transmitted generally by:
- Sexual contact with infected person
- Use of contaminated needles or syringes especially in case of intravenous drag abusers
- By transfusion of contaminated / infected blood or blood products (iv) From infected mother to her child through placenta.
Question 2.
How is a cancer cell different from a normal cell?
Answer:
Cancer is an abnormal and uncontrolled division of cells that invade and destroy the surrounding tissue, forming a tumour or neoplasm. It is a heterogeneous group of cells, that do not respond to the normal cell division. The cancer cells move to distant parts of bodies such as lungs, bones, liver, skin and brain.
Question 3.
Differentiate between Type-1 and Type-2 diabetes mellitus.
Answer:
| Type-1 Diabetes mellitus | Type-2 Diabetes mellitus |
| 1. People with type – 1 diabetes do not produce insulin in the pancreas. | 1. People with type – 2 diabetes do not respond to insulin. |
| 2. the immune system destroys insulin – producing beta cells in the pancreas. | 2. People with type – 2 diabetes are Insulin Resistant. The body produces insulin but unable to use effectively. |
| 3. Cannot be controlled without taking insulin. | 3. Possible to treat initially without medication or treating with tablets. |
Question 4.
Why is a dietary restriction recommended for an obese individual?
Answer:
Obesity has a positive risk factor in development of hypertension, diabetes, gall bladder disease, coronary heart disease and arthritis. To avoid the dietary restriction is recommended for an obese individual.
Question 5.
What precautions can be taken for preventing heart diseases?
Answer:
Diet Management: Reduction in the intake of calories, low saturated fat and cholesterol – rich food, low carbohydrates and common salt are some of the Dietary modifications. Diet rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids is essential. Increase in the intake of fibre diet, fruits and vegetables, protein, minerals and vitamins are needed.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise, walking and yoga are essential for bodyweight maintenance.
- Avoid Addictive substances: Alcohol consumption, Psychotropic drugs and smoking are to be avoided.
IX. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Suggest measures to overcome the problems of an alcoholic.
Answer:
Education and counselling: Education and proper counselling will help the alcoholics to overcome their problems and stress, to accept failures in their life.
Physical activity : Individuals undergoing rehabilitation should be channelized into healthy activities like reading, music, sports, yoga and meditation.
Seeking help from parents and peer groups : When a problematic situation occurs, the affected individuals should seek help and guidance from parents and peers. This would help them to share their feeling of anxiety, wrong dping and get rid of the habit.
Medical assistance : Individual should seek help from psychologists and psychiatrists to get relieved from this condition and to lead a relaxed and peaceful life.
Alcohol de-addiction and rehabilitation programmes are helpful to the individual so that they could get rid of the problem completely and can lead a normal and healthy life.
Question 2.
Changes in lifestyle is a risk factor for the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases. Can it be modified? If yes, suggest measures for prevention.
Answer:
The lifestyle can be modified to prevent cardiovascular diseases. These are the measures for prevention:
- Do not smoke or use Tobacco.
- Do Exercise for about 30 minutes.
- Eat a heart-healthy diet.
- Reduce the intake of calories, low saturated fat and cholesterol, low carbohydrates and common salt are some of the dietary modifications.
- Diet rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) is essential.
- Increase in the intake of fibre diet, fruits and vegetables, protein, minerals and vitamins are essential.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Get enough quality sleep.
- Manage stress.
- Get regular health screens.
- Control Blood pressure.
- Keep the cholesterol and triglyceride levels under control.
X. Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) Questions
Question 1.
What is the role of fat in the cause of atherosclerosis?
Answer:
The deposition of cholesterol in the blood vessels gradually develops from which form a fatty streak called plaque. This blocks the pathway of blood flow by narrowing the blood vessels leading to atherosclerosis.
Question 2.
Eating junk food and consuming soft drinks results in health problems like obesity, still, children prefer. What are the suggestions you would give to avoid children eating junk food / consumption of soft drinks?
Answer:
Suggestions, to avoid children, eating Junk food / consumption of soft drinks.
- Carry a water bottle and drink water.
- Instead of soft drinks, drink fruit juices, sports drinks or energy drinks.
- Base meals around protein, legumes, chickpeas, kidney beans and nuts, etc.
- Avoid getting extremely hungry.
- Fight stress.
- Practice mindful eating.
- Have a piece of fruit, yoghurt, or some crackers.
Question 3.
Regular physical exercise is advisable for normal functioning of the human body. What are the advantages of practising exercise in daily life?
Answer:
- Physical exercises help us to live longer and prevent many chronic diseases.
- It improves cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness.
- It reduces stress, anxiety and depression and improves our mood.
- Improves sleep quality and overall quality of life.
Question 4.
A leading weekly magazine has recently published a survey analysis which says that a number of AIDS patient in the country is increasing day by day. The report says that the awareness among the people about AIDS is still very poor. You are discussing the magazine report in your class and a team of your class decides to help people to fight against the dreadful disease.
(a) What problem do you face when trying to educate the people in your village near your school?
(b) How do you overcome the problem?
Answer:
(a) The main problem, we face, is as follows:
- AIDS patients find it difficult to accept the news.
- Many people are afraid of telling others because they feel ashamed or they are worried about being rejected.
- AIDS patients are really discouraged with anxiety about their future.
(b)
- Confirm the disease by Western Blot Analysis or ELISA.
- Antiretroviral drugs and immunostimulating therapy can prolong the life of the infected person.
- Do not tell anyone about our friend’s HIV.
- Be there to talk to them.
- Do things together that can reduce stress. Go for a walk. Do something that we enjoy with our AIDS patient friend.
- Advice the patient friend to avoid activities that have bad health effects like smoking.
- Patients with HIV / AIDS should not be isolated from the family and society.
XI. Value-Based Questions
Question 1.
Once a person starts taking drugs or alcohol it is difficult to get rid of the habit. Why?
Answer:
The addictive potential of the drugs pulls the individual into a viscous cycle leading to regular abuse and depending. Moreover, some drugs act in the brain and alter the behaviour, consciousness, power of thinking and perception.
Question 2.
Men addicted to tobacco lead to oxygen deficiency in their body. What could be the possible reason?
Answer:
Carbon monoxide of tobacco smoke binds to the haemoglobin of RBC and decreases its oxygen-carrying capacity causing hypoxia in body tissues.
Question 3.
Name any three foods that are to be avoided and included in the diet of a diabetic patient. Why should it be followed?
Answer:
Refined sugar, carbohydrates rich food and high fat content rich foods should be avoided.
Low carbohydrate and fibre rich diet. Diet comprising whole grains, millet, green leafy vegetables should be included in the diet.
Question 4.
How can informational efforts change people’s HIV knowledge and behaviour?
Answer:
- Find the latest information about viral suppression and Viral Load Monitoring.
- Find the latest prevention and how to talk with patients with HIV about, what it means for them.
- Learn how HIV care providers, can identify and address mental health and substance use disorders to help patients, adhere to HIV treatment and remain in care.
XII. Assertion and Reasoning Questions
In each of the following questions, a statement of Assertion is given and a corresponding statement of Reason is given just below it. Of statements given below mark the correct answer as
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion Mid Reason is true that Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question 1.
Assertion: All drugs act on the brain.
Reason: Drugs disturb the functioning of the body and mind.
Answer:
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
Question 2.
Assertion: Excretion of excess glucose in the urine is observed in a person with diabetes mellitus.
Reason: Pancreas is unable to produce sufficient quantity of insulin.
Answer:
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true that Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
Textbook Activities Solved
Question 1.
Collect pictures of people affected by tobacco chewing and tobacco smoking. Identify which part of the body is affected and the health hazards it can lead to?
Answer:
The students should collect pictures of people affected by Tobacco Chewing and Tobacco smoking.
Health Hazards: Affected part is mouth on Tobacco Chewing. Chewing Tobacco causes mouth cancer, throat cancer, soreness, gum diseases, tooth decay, tooth loss, possible links to other cancer and Cardiovascular diseases.
Tobacco smoking causes Lung diseases causing damaging alveoli, emphysema, chronic bronchitis, cough, cold, wheezing, asthma, pneumonia and lung cancer. It also affects the central nervous system, increases blood pressure and heartbeat. It also damages DNA.
Question 2.
Collect pictures of individuals with normal liver and alcoholic liver, compare and indicate the changes you find in them.
Answer:
- The students should collect pictures of normal liver and alcoholic liver.
- Normal liver: Under normal circumstances, the normal liver is smooth with no irregularities. The enzymes mostly reside within the cells of the liver.
Fatty liver disease occurs as a result of alcohol drinking, which leads to cirrhosis and formation of fibrous tissues, which replaces the normal liver tissue.
Question 3.
Prepare a chart showing the food items which are preferable and which should be avoided to prevent high blood pressure and heart disease. Apart from diet what are the other lifestyle modifications to be followed to manage this condition?
Answer:
- Food items which are preferable: Whole grains, fruits and vegetables, low – fat dairy products, Green tea, Hibiscus tea, Pineapple juice and low carbohydrate food items.
- Food items to be avoided: Salt, Meat, Pickles, Canned Soups, Tomato products, sugar, packaged foods, White bread and packaged snacks, etc.
Other Life Style Modification:
- Exercise for about 30 minutes.
- Eat a heart-healthy diet.
- Do not smoke or use tobacco.
- Get regular health screenings.
- Get enough quality sleep.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Health and Diseases Additional Questions Solved
I. Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
Tobacco is obtained from the Tobacco plant _____ and ______.
Answer:
Nicotiana tobacco and Nicotiana rustica.
Question 2.
The increased urine output, leading to dehydration is termed as ______.
Answer:
Polyuria.
Question 3.
The inflammation of throat and bronchi due to smoke of Tobacco lead to the conditions of _____ and ______.
Answer:
Bronchitis and Pulmonary tuberculosis.
Question 4.
The study of cancer is called ______.
Answer:
Oncology.
Question 5.
The uncontrolled division of cells destroy the surrounding tissue forming a tumour or ______.
Answer:
Neoplasm.
Question 6.
_____ and ______ hydrocarbons present in tobacco smoke is carcinogenic causing Lung cancer.
Answer:
Benzopyrene and Polycyclic.
II. Write ‘True’ or ‘False’ for the following statements. Correct the false statements:
Question 1.
The psychological dependent persons feel that drugs do not help them to reduce stress.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: The psychological dependent persons feel that drugs help them to reduce stress.
Question 2.
Individuals should seek help from psychologists and psychiatrists to get relief from alcohol abuse.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
Tobacco chewing does not cause oral cancer.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Tobacco chewing causes oral cancer.
Question 4.
In Type – 2 Non – Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus, the target cells respond to insulin and allow the movement of glucose into cells.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: In Type – 2 Non – Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus, the target cells do not respond to insulin and does not allow the movement of glucose into cells.
Question 5.
Low Carbohydrate food in the form of starch, complex sugars, and fibre-rich diets are more appropriate for the Dietary management pf Diabetes.
Answer:
True.
III. Expand the following abbreviations:
Question 1.
- CVD
- HDL
- PUFA
- NACO
- NGO
- ELISA
- WHO
- NCPCR
- CPCR
- LOL
- UV rays.
Answer:
- Cardio-vascular Disease
- High-Density Lipoprotein
- Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
- National AIDS Control Organization
- Non-Government Organization
- Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay
- World Health Organization
- National Commission for Protection of Child Rights
- Commission for Protection of Child Rights
- Low-Density Lipoprotein
- Ultra Violet rays.
IV. Match the following:
Question 1.
| 1. Psychotropic drugs | (a) Nicotine |
| 2. Chronic metabolic disorder | (b) Emphysema |
| 3. Addiction to Tobacco | (c) Polyphagia |
| 4. Excess hunger | (d) Polydipsia |
| 5. Inflammation of lung alveoli | (e) Mood Altering drugs |
| 6. Loss of water leads to thirst | (f) Diabetes Mellitus |
Answer:
- (e) Mood Altering drugs
- (f) Diabetes Mellitus
- (a) Nicotine
- (c) Polyphagia
- (b) Emphysema
- (d) Polydipsia.
V. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
When powdered tobacco is taken through the nose, it is called ______.
(a) smoking
(b) stimulant
(c) snuffing
(d) addiction.
Answer:
(c) snuffing
Question 2.
Causative factor of cancer is called:
(a) Oncogenes
(b) Radiogenes
(c) Oestrogenes
(d) Carcinogens
Answer:
(d) Carcinogens
Question 3.
Insulin deficiency due to the destruction of β – cells occur in ______.
(a) IDDM
(b) BMI
(c) NIDDM
(d) CVD.
Answer:
(a) IDDM
Question 4.
Which is not cancer?
(a) Leukaemia
(b) Glaucoma
(c) Sarcoma
(d) Carcinogen
Answer:
(b) Glaucoma
Question 5.
The HIV Virus attack the body’s disease – fighting mechanism and the individual is prone to infectious diseases.
(a) Erythrocytes
(b) Thrombocytes
(c) Lymphocytes
(d) platelets.
Answer:
(c) Lymphocytes
VI. Write the correct dates for the following:
Question 1.
- December 1st
- 4th February
- 7th November
- May 31st
- June 26th.
Answer:
- World AIDS Day
- World Cancer day
- National Cancer awareness day
- No Tobacco Day or World Anti-Tobacco day
- International day against Drug abuse and Illicit Trafficking.
VII. Answer the following briefly:
Question 1.
What are stimulants?
Answer:
Drugs that increase the activities of Central Nervous System.
Question 2.
What is abuse? What does it include?
Answer:
Abuse refers to cruel, violent, harmful or injurious treatment of another human being. It includes physical, emotional or psychological, verbal, child and sexual abuses.
Question 3.
List the instruction to be given to prevent child sexual abuse.
Answer:
- Do not talk to any suspected person or strangers and to maintain a distance.
- Not to be alone with unknown person.
- To be careful while travelling alone in public or private transport:
- Not to receive money, toys, gifts or chocolates from known or unknown person to them without the knowledge of their parents.
- Not to allow known or unknown person to touch them.
Question 4.
What is an addiction? What is the effect of addiction on individuals?
Answer:
The physical and mental dependency on – alcohol, smoking and drugs are called addiction. The addictive potential of these substances pulls an individual into a vicious cycle leading to regular abuse and dependency.
Question 5.
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Answer:
Diabetes mellitus is associated with several metabolic alterations. The most important symptoms are
- Increased blood glucose level (Hyperglycemia).
- Increased urine output (Polyuria) leading to dehydration.
- Loss of water leads to thirst (Polydipsia) resulting in increased fluid intake.
- Excessive glucose excreted in urine (Glycosuria).
- Excess hunger (Polyphagia) due to loss of glucose in urine.
- Fatigue and loss of weight.
Question 6.
Explain the types of cancers on the basis of the tissues from which they are formed?
Answer:
Cancers are classified on the basis of the tissues, from which they are formed:
- Carcinomas arise from epithelial and glandular tissues.
- Sarcomas occur in connective and muscular tissue. They include the cancer of bones, cartilage, tendons, adipose tissue and muscles.
- Leukaemia is characterised by an increase in the formation of white blood cells in the bone marrow and lymph nodes Leukaemia is called blood cancers.
Question 7.
Name the test done to diagnosis Aids.
Answer:
The presence of HIV virus can be confirmed by western Blot analysis or Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Question 8.
What is the treatment of cancer and the preventive measures for cancer?
Answer:
The treatment of cancer involves the following methods:
- Surgery: Tumours are removed by surgery to prevent further spread of cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy: Tumour cells are irradiated by lethal doses of radiation while protecting the surrounding normal cells.
- Chemotherapy: It involves the administration of anticancerous drugs, which prevent cell division and are used to kill cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Biological response modifiers like interferons are used to activate the immune system and help in destroying the tumours.
Preventive measures for cancer:
- Cancer control programmes should focus on primary prevention and early detection.
- To prevent lung cancer, tobacco smoking is to be avoided.
- Protective measures to be taken against exposure to toxic pollutants of industries.
- Excessive exposure to radiation is to be avoided to prevent skin cancer.
Question 9.
Explain the symptoms and treatment of AIDS.
Answer:
- Infected individuals become immunodeficient.
- The person becomes more susceptible to viral, bacterial, protozoan and fungal diseases.
- Swelling of lymph nodes, damage to the brain, loss of memory, lack of appetite and weight loss, fever, chronic diarrhoea, cough, lethargy, pharyngitis, nausea and headache.
1. Diagnosis: The presence of the HIV virus can be detected by Western Blot Analysis or Enzyme – Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay (ELISA).
2. Treatment: Anti – retroviral drugs and immunostimulating therapy can prolong the life of the infected person.
Question 10.
Briefly note down the prevention and control of AIDS.
Answer:
The following steps help in controlling and preventing the spreading of HIV:
- Screening of blood from blood banks for HIV, before transfusion.
- Ensuring the use of disposable needles and syringes in hospitals and clinics.
- Advocating safe sex and the advantages of using condoms.
- Creating an awareness campaign and educating people on the consequences of AIDS.
- Persons with HIV / AIDS should not be isolated from the family and society.
Question 11.
What is obesity and body mass Index?
Answer:
Obesity is the state in which there is an accumulation of excess body fat with an abnormal increase in body weight.
Body Mass Index (BMI) is an estimate of body fat and health risk.
BMI = Weight (kg) / Height (m)2
Question 12.
What are the major causes and contributing factors for heart disease?
Answer:
Hypercholesterolemia (High blood cholesterol) and high blood pressure (Hypertension) are the major causes and contributing factors for heart disease.
- Heredity (family history)
- Diet rich in saturated fat and cholesterol
- Obesity, increasing age
- Cigarette smoking
- Emotional stress
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Excessive alcohol consumption and
- Physical inactivity are some of the causes.
VIII. Identify the first words and their relationship and suggest a suitable word for the fourth blank:
Question 1.
Drug abuse : addictive drug :: Tobacco chewing : ______.
Answer:
Oral cancer or mouth cancer.
Question 2.
Insulin : Diabetes :: Benzopyrene : ______.
Answer:
Lung cancer.
Question 3.
Disease of heart and blood vessels : Cardiovascular disease :: Deposition of cholesterol in the blood vessel : ______.
Answer:
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD).
Question 4.
Deficient blood supply to heart muscle : Ischemia :: Death of the heart muscle tissue : ______.
Answer:
Myocardial Infarction.
Question 5.
HIV Virus : ELISA :: Leukaemia : ______.
Answer:
Blood cancer.
X. Explain the following in detail.
Question 1.
Explain the approaches for protection of an abused child and the prevention of child sexual abuse.
Answer:
- Child helpline: The Child Helpline provides a social worker who can assist the child by providing food, shelter and protection.
- Counselling the child: Psychologists and social workers should provide guidance, counselling and continous support to a victim child.
- Family support: The victimized child should be supported by the family members. They should provide proper care and attention to child to overcome his/her sufferings.
- Medical care: A child victim of sexual offences should receive medical care and treatment from health care professionals to overcome mental stress and depression.
- Legal Counsel: The family or the guardian of the child victim shall be entitled to free assistance of a legal counsel for such offence.
- Rehabilitation: Enrolling in schools and resuming their education is an important step towards the rehabilitation of the child.
- Community – based efforts: Conducting awareness campaign on child abuse and its prevention.
Question 2.
List out the harmful effects of Alcohol to health.
Answer:
Prolonged use of alcohol depresses the nervous system, by acting as a sedative and analgesic substance. Some of the harmful effects are:
- Nerve cell damage resulting in various mental and physical disturbances.
- Lack of co-ordination of body organs.
- Blurred or reduced vision, results in road accidents.
- Dilation of blood vessels which may affect functioning of the heart.
- Liver damage resulting in fatty liver which leads to cirrhosis and formation of fibrous tissues.
- Body loses its control and consciousness eventually leading to health complications and ultimately to death.
Question 3.
Explain in detail the Smoking Hazards and effects of Tobacco. How can it be prevented?
Answer:
When smoke is inhaled, the chemicals get absorbed by the tissues and cause the following harmful effects:
- Benzopyrene and polycyclic hydrocarbons present in Tobacco smoke are carcinogenic causing lung cancer.
- Causes inflammation of throat and bronchi leading to conditions like bronchitis and pulmonary tuberculosis.
- Inflammation of lung alveoli, decrease surface area for gas exchange and cause emphysema.
- Carbon monoxide of Tobacco smoke binds to the haemoglobin of RBC and decreases its oxygen-carrying capacity causing hypoxia in body tissues.
- Increased blood pressure caused by smoking leads to increased risk of heart disease.
- Causes increased gastric secretion which leads to gastric and duodenal ulcers.
- Tobacco chewing causes oral cancer (mouth cancer).
Prevention: Adolescents and old people need to avoid these habits. Proper counselling and medical assistance can help an addict to give up the habit of smoking.
XI. Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) Questions
Question 1.
What do the following symbols represent?
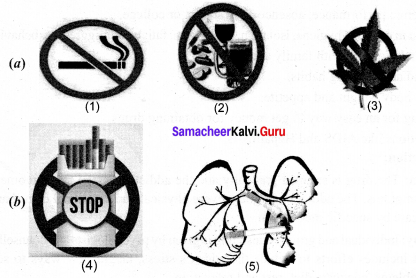
Answer:
(a) 1. No Smoking
2. No Alcohol
3. No Psychotropic drugs
(b) 4. No – International Tobacco day
5. Inflammation of Lung Alveoli and decreased surface area.
Question 2.
Some human diseases are transmitted only through blood in one of such diseases, there is a progressive decrease in the number of lymphocytes of the patient.
(a) Name the disease and its causative agent.
(b) Write any two symptoms of it.
Answer:
(a) Name the disease is the AIDS caused by Human Immuno Deficiency Virus.
(b) Weight loss and lack of appetite are the symptoms of AIDS.
Question 3.
Which is the desirable blood cholesterol level for Indians?
Answer:
200 mg / dl.
Question 4.
Which cholesterol lowers the risk of heart disease and which cholesterol increases the risk of heart diseases?
Answer:
- HDL (High – Density Lipoprotein) or good cholesterol lowers the risk of heart disease.
- LDL (Low – Density Lipoprotein) or bad cholesterol increases the risk of heart diseases.
Question 5.
What are the two types of tumours?
Answer:
- Benign tumours or Non – malignant tumours: Remain confined in the organ affected and do not spread to other parts of the body.
- Malignant tumours: Mass of proliferating cells, which grow very rapidly invading and damaging the surrounding normal tissues.
Question 6.
Name some foods which help to reduce blood sugar levels.
Answer:
Flax seeds containing insoluble fibre, Guava, Tomatoes and spinach are the foods, which helps to reduce blood sugar levels.
Believing that the Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 21th Science Chapter 21 Health and Diseases Questions and Answers learning resource will definitely guide you at the time of preparation. For more details about Tamilnadu State Board Class 21th Science Chapter 21 textbook solutions, ask us in the below comments and we’ll revert back to you asap.