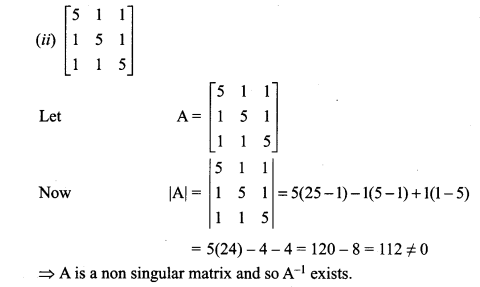
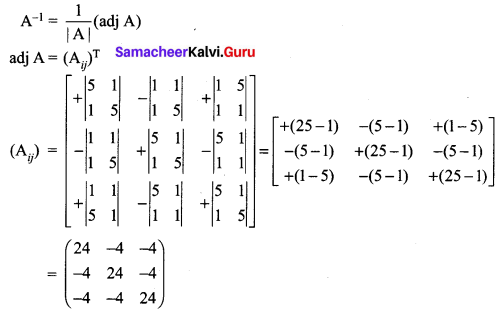
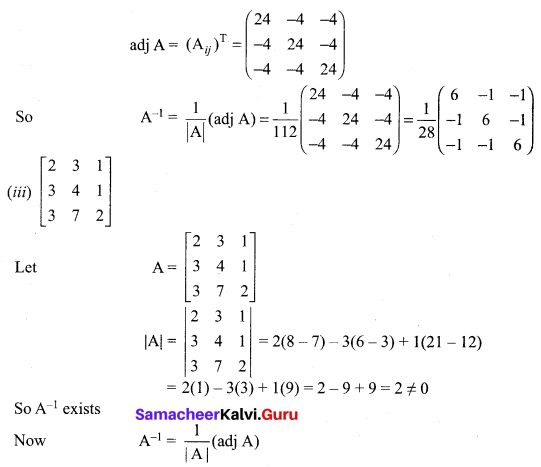
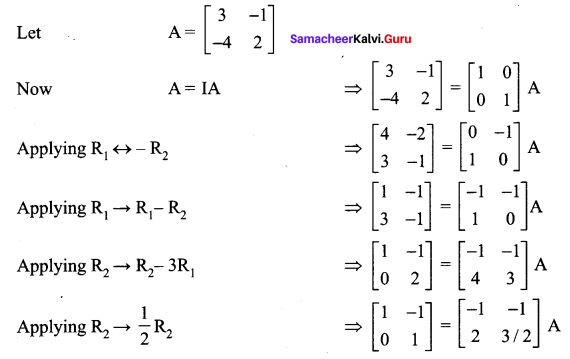
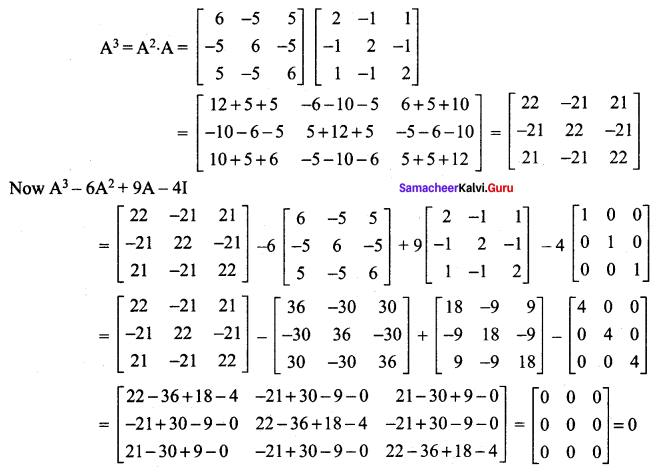
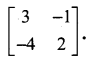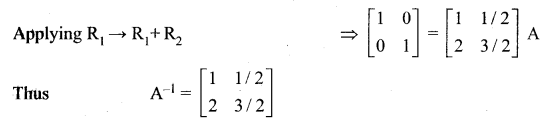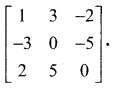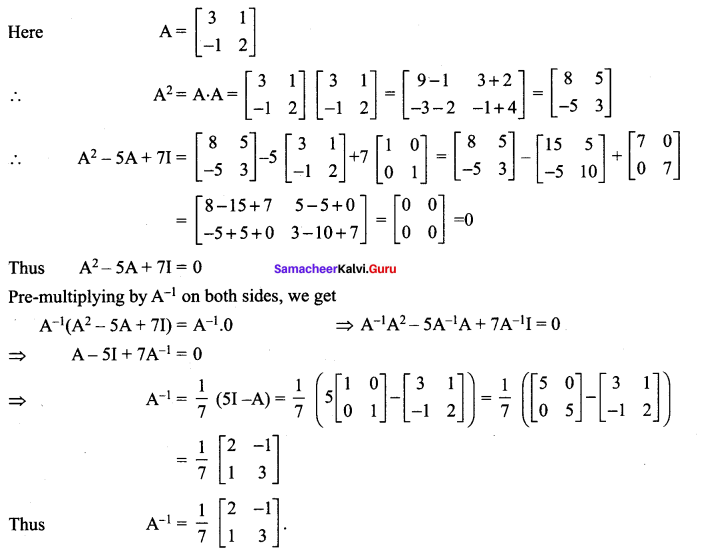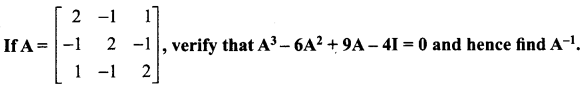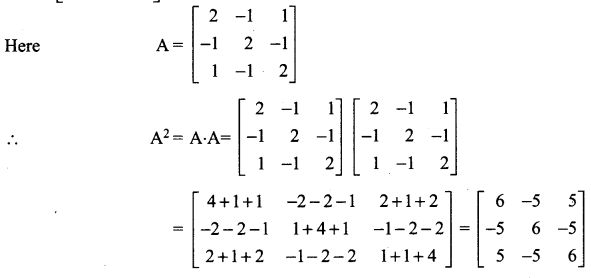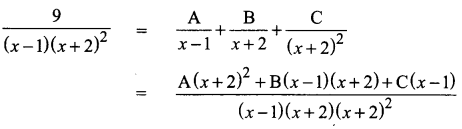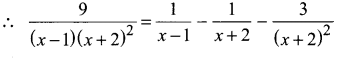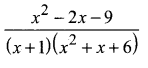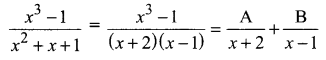Enhance your subject knowledge with Tamilnadu State Board for Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations and learn all the underlying concepts easily. Make sure to Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Book Solutions, Notes Pdf Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations Questions and Answers PDF on a day to day basis and score well in your exams. Are given after enormous research by people having high subject knowledge. You can rely on them and prepare any topic of Chemistry as per your convenience easily.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations
Students looking for Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations Concepts can find them all in one place from our Tamilnadu State Board Solutions. Simply click on the links available to prepare the corresponding topics of Chemistry easily. Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Chapter wise Questions and Answers are given to you after sample research and as per the latest edition textbooks. Clarify all your queries and solve different questions to be familiar with the kind of questions appearing in the exam. Thus, you can increase your speed and accuracy in the final exam.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations Textual Evaluation Solved
I. Choose the Best Answer
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions Question 1.
40 ml of methane is completely burnt using 80 ml of oxygen at room temperature. The volume of gas left after cooling to room temperature is ………..
(a) 40 ml CO2 gas
(b) 40 ml CO2 gas and 80 ml H2O gas
(c) 60 ml CO2 gas and 60 ml H2O gas
(d) 120 ml CO2 gas
Answer:
(a) 40 ml CO2 gas
Solution:
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l)
| Content | CH4 | O2 | CO2 |
| Stoichiometric coefficient | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Volume of reactants allowed to react | 40 mL | 80 mL | – |
| Volume of reactant reacted and product formed | 40 mL | 80 mL | 40 mL |
| Volume of gas after cooling to the room temperature | – | – | – |
Since the product was cooled to room temperature, water exists mostly as liquid. Hence, option (a) is correct
Basic Concepts Of Chemistry And Chemical Calculations Question 2.
An element X has the following isotopic composition 200X = 90 %, 199X = 8 % and 202X = 2 %. The weighted average atomic mass of the element X is closest to …………
(a) 201 u
(b) 202 u
(c) 199 u
(d) 200 u
Answer:
(d) 200 u
= \(\frac {(200 × 90) + (199 × 8) + (202 × 2) }{100}\) = 199.96 = 200 u
Basic Concepts Of Chemistry And Chemical Calculations Book Back Answers Question 3.
Assertion:
Two mole of glucose contains 12.044 × 1023 molecules of glucose.
Reason:
Total number of entities present in one mole of any substance is equal to 6.02 × 1022
(a) both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion
(b) both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
(c) assertion is true but reason is false
(d) both assertion and reason are false
Answer:
(c) assertion is true but reason is false
Correct reason:
Total number of entities present in one mole of any substance is equal to 6.022 x 1023
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 11th Chemistry Question 4.
Carbon forms two oxides, namely carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. The equivalent mass of which element remains constant?
(a) Carbon
(b) Oxygen
(c) Both carbon and oxygen
(d) Neither carbon nor oxygen
Answer:
(b) Oxygen
Reaction 1:
2 C + O2 → 2 CO2
2 × 12 g carbon combines with 32 g of oxygen.
Hence, Equivalent mass of carbon = \(\frac {2 × 12}{32}\) × 8 = 6
Reaction 2:
C + O2 → 2 CO2
12 g carbon combines with 32 g of oxygen.
Hence, Equivalent mass of carbon = \(\frac {12}{32}\) × 8 = 3
11th Chemistry Samacheer Kalvi Question 5.
The equivalent mass of a trivalent metal element is 9 g eq-1 the molar mass of its anhydrous oxide is ………..
(a) 102 g
(b) 27 g
(c) 270 g
(d) 78 g
Answer:
(a) 102 g
Let the trivalent metal be M3+
Equivalent mass = mass of the metal / valance factor
9g eq-1 = mass of the metal / 3 eq
Mass of the metal = 27 g
Oxide formed M2O3
Mass of the oxide = (2 × 27) + (3 × 16) = 102 g
11th Chemistry Lesson 1 Question 6.
The number of water molecules in a drop of water weighing 0.018 g is ………….
(a) 6.022 × 1026
(b) 6.022 × 1023
(c) 6.022 × 1020
(d) 99 × 1022
Answer:
(c) 6.022 × 1020
Weight of the water drop = 0.0 18 g
No. of moles of water in the drop = Mass of water / molar mass = 0.018/18 = 10-3 mole
No of water molecules present ¡n I mole of water = 6.022 × 1023
“No. water molecules in one drop of water (10 mole) = 6.022 × 1023 × 10-3
= 6.022 × 1020
Chemistry Class 11 Samacheer Kalvi Question 7.
1 g of an impure sample of magnesium carbonate (containing no thermally decomposable impurities) on complete thermal decomposition gave 0.44 g of carbon dioxide gas. The percentage of impurity in the sample is ………..
(a) 0 %
(b) 4.4 %
(c) 16 %
(d) 8.4 %
Answer:
(c) 16%
Mg CO3 → MgO + CO2↑
Mg CO3 : (1 × 24) + (1 × 12) + (3 × 16) = 84 g
CO2 : (1 × 12) + (2 × 16) 44g
100% pure 84 g MgCO3 on heating gives 44 g CO2
Given that I g of MgCO3 on heating gives 0.44 g CO2
Therefore, 84 g MgCO3 sample on heating gives 36.96 g CO2 = 100%
Percentage of purity of the sample = \(\frac{100 \%}{44 \mathrm{g} \mathrm{CO}_{2}}\) × 36.96 g CO2 = 84%
Percentage of impurity = 16%
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Question 8.
When 6.3 g of sodium bicarbonate is added to 30 g of acetic acid solution, the residual solution is found to weigh 33 g. The number of moles of carbon dioxide released in the reaction is –
(a) 3
(b) 0.75
(c) 0.075
(a) 0.3
Answer:
(c) 0.075
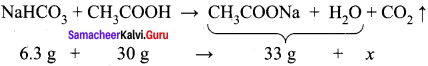
The amount of CO2 released, x = 3.3 g
No. of moles of CO2 released = 3.3 / 44 = 0.075 mol
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Solutions Question 9.
When 22.4 liters of H2 (g) is mixed with 11.2 liters of Cl2 (g), each at 273 K at 1 atm the moles of HCl (g), formed is equal to ………..
(a) 2 moles of HCl (g)
(b) 0.5 moles of HCl (g)
(c) 1.5 moles of HCl (g)
(d) 1 moles of HCl (g)
Answer:
(d) 1 moles of HCl (g)
Solution:
H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2 HCl (g)
| Content | H2(g) | cl2(g) | HCl (g) |
| Stoichiometric coefficient | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| No. of moles of reactants allowed to react at 273 K and 1 atm pressure | 22.4 L (1 mol) | 11.2 L (0.5 mol) | — |
| No. of moles of reactant reacted and product formed | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 |
| A mount of HCl formed 1 mol | |||
11th Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions Question 10.
Hot concentrated sulfuric acid is a moderately strong oxidizing agent. Which of the following reactions does not show oxidizing behavior?
(a) Cu + 2H2SO4 → CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O
(b) C + 2H2SO4 → 4 CO2 + 2SO2 + 2H2O
(c) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4+ 2HCl
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4+ 2HCl
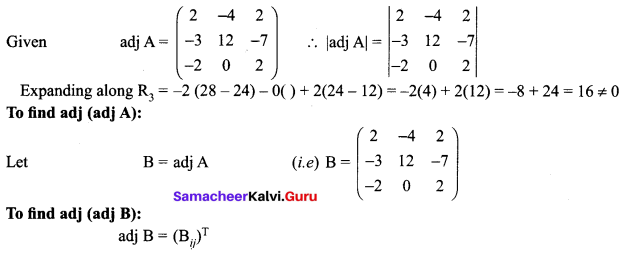
![]()
11th Chemistry Chapter 1 Book Back Answers Question 11.
Choose the disproportional reaction among the following redox reactions.
(a) 3Mg (s) + N2(g) → Mg2N2 (s)
(b) P4 (s) + 3NaOH + 3H2O → PH3(g) + 3NaH2PO2 (aq)
(c) Cl2 (g) + 2Kl (aq) → 2KC1 (aq) + I2
(d) Cr2O3 (s) + 2Al (s) → A2O3 (s) + 2Cr (s)
Answer:
(b) P4 (s) + 3NaOH + 3H2O → PH3(g) + 3NaH2PO2 (aq)
![]()
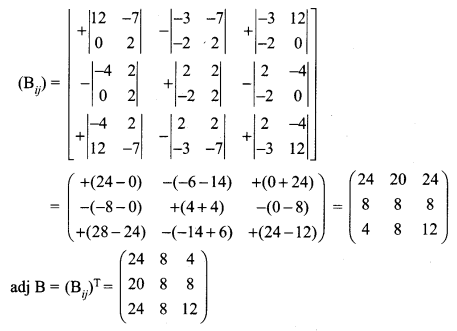
Basic Concepts Of Chemistry And Chemical Calculations Pdf Question 12.
The equivalent mass of potassium permanganate in alkaline medium is
MnO4 + 2H2O + 3e– → MnO2 + 4OH–
(a) 31.6
(b) 52.7
(c) 79
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) 52.7
The reduction reaction of the oxidizing agent(MnO4) involves gain of 3 electrons.
Hence the equivalent mass = (Molar mass of KMnO4) / 3 = 158.1 / 3 = 52.7
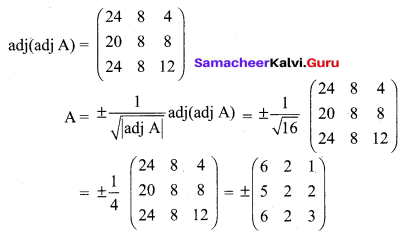
11th Chemistry 1st Chapter Question 13.
Which one of the following represents 180 g of water?
(a) 5 Moles of water
(b) 90 moles of water
(c) \(\frac{6.022 \times 10^{23}}{180}\) Molecules of water
(d) 6.022 × 1024 Molecules of water
Answer:
(d) 6.022 x 1024 Molecules of water
No. of moles of water present in 180 g
= Mass of water / Molar mass of water
= 180 g /18 g mol-1 = 10 moles
One mole of water contains
= 6.022 × 1023 water molecules
10 mole of water contains = 6.022 × 1023 × 10
= 6.022 × 1024 water molecules
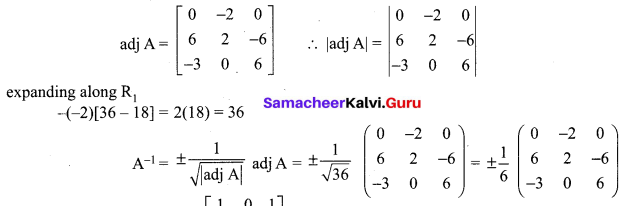
Class 11 Chemistry All Formulas Question 14.
7.5 g of a gas occupies a volume of 5.6 liters at 0°C and 1 atm pressure. The gas is …………
(a) NO
(b) N2O
(c) CO
(d) CO2
Answer:
(a) NO
7.5 g of gas occupies a volume of 5.6 liters at 273 K and 1 atm pressure Therefore, the mass of gas that occupies a volume of 22.4 liters –
\(\frac {7.5 g}{5.6 L}\) × 22. 4 L = 30g
Molar mass of NO (14 + 16) = 30g
11th Chemistry Solutions Samacheer Kalvi Question 15.
Total number of electrons present in 1.7 g of ammonia is ………..
(a) 6.022 × 1023
(b) \(\frac{6.022 \times 10^{22}}{1.7}\)
(c) \(\frac{6.022 \times 10^{24}}{1.7}\)
(d) \(\frac{6.022 \times 10^{23}}{1.7}\)
Answer:
(a) 6.022 × 1023
No. of electrons present in one ammonia (NH3) molecule (7 + 3) = 10
No. of moles of ammonia = \(\frac {Mass}{Molar mass}\)
= \(\frac{1.7 \mathrm{g}}{17 \mathrm{g} \mathrm{mol}^{-1}}\) = 0.1 mol
No. of molecules present in 0ne ammonia
= 0.1 × 6.022 × 1023 = 6.O22 × 1022
No. of electrons present in 0.1 mol of ammonia
10× 6.022 × 1022 = 6.022 × 1023
Samacheer Kalvi Class 11 Chemistry Solutions Question 16.
The correct increasing order of the oxidation state of sulphur in the anions SO42-, SO32-, S2O42-,S2O62- is ………..
(a) SO32- < SO32- < S2O42- < S2O62-
(b) SO42- < S2O42- < S2O62-<SO32-
(c) S2O42- < SO32- < S2O62- < SO42-
(d) S2O62- < S2O42- < SO42- < SO32-
Answer:
(c) S2O42- < SO32- < S2O62- < SO42-
![]()
Class 11 Chemistry Solutions Samacheer Kalvi Question 17.
The equivalent mass of ferrous oxalate is ……….

Answer:
![]()
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 11 Chemistry Solutions Question 18.
If Avogadro number were changed from 6.022 × 1023 to 6.022 × 1020, this would change ………..
(a) the ratio of chemical species to each other in a balanced equation
(b) the ratio of elements to each other in a compound
(c) the definition of mass in units of grams
(d) the mass of one mole of carbon
Answer:
(d) the mass of one mole of carbon
Samacheerkalvi.Guru 11th Chemistry Question 19.
Two 22.4 liter containers A and B contains 8 g of O2 and 8 g of SO2 respectively, at 273 K and 1 atm pressure, then ……….
(a) number of molecules in A and B are same
(b) number of molecules in B is more than that in A
(c) the ratio between the number of molecules in A to the number of molecules in B is 2 : 1
(d) number of molecules in B is three times greater than the number of molecules in A
Answer:
(c) The ratio between the number of molecules in A to number of molecules in B is 2 : 1
Question 20.
What is the mass of precipitate formed when 50 ml of 8.5% solution of Ag NO3 is mixed with 100 ml of 1.865% potassium chloride solution?
(a) 3.59 g
(b) 7 g
(c) 14 g
(d) 28 g
Answer:
(a) 3.59 g
AgNO3 + KCl → KNO3 + AgCl
Solution:
50 mL of 8.5% solution contains 4.25 g of AgNO3
No. of moles of AgNO3 present in 50 mL of 8.5% AgNO3 solution
= Mass / Molar mass = 4.25 / 170 = 0.025 moles
Similarly, No of moles of KCl present in loo mL of 1.865% KCl solution
= 1.865 / 74.5 = 0.025 moles
So total amount of AgCl formed is 0.025 moles (based on the stoichiometry calculator)
Amount of AgCl present in 0.025 moles of AgCl
= no. of moles × molar mass
= 0.025 × 143.5 = 3.59 g
Question 21.
The mass of a gas that occupies a volume of 612.5 ml at room temperature and pressure (25°C and 1 atm pressure) is 1.1g. The molar mass of the gas is ………..
(a) 66.25 g mol-1
(b) 44 g mol-1
(c) 24.5 g mol -1
(d) 662.5 g mol-1
Answer:
(b) 44 g mol-1
Solution:
No. of moles of a gas that occupies a volume of 6 12.5 ml at room temperature and pressure
(25° C and 1 atm pressure)
= 612.5 × 10-3 L/24.5 L mol-1
= 0.02 5 moles
We know that,
Molar mass = Mass / no. of moles
= 1.1 g/0.025 mol = 44 g mol-1
Question 22.
Which of the following contain same number of carbon atoms as in 6 g of carbon -12?
(a) 7.5 g ethane
(b) 8 g methane
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) both (a) and (b)
Solution:
No. of moles of carbon present in 6 g of C – 12 = Mass / Molar mass
= 6/12 = 0.5 moles = 0.5 × 6.022 × 1023 carbon atoms.
No. of moles in 8 g of methane = 8 116 = 0.5 moles
= 0.5 × 6.022 × 1023 carbon atoms.
No. of moles in 7.5 g of ethane = 7.5 / 16 = 0.25 moles
= 2 × 0.25 × 6.022 × 1023 carbon atoms.
Question 23.
Which of the following compound( s) has/have percentage of carbon same as that in ethylene (C2H4)?
(a) propene
(b) ethyne
(c) benzene
(d) ethane
Answer:
(a) propene
Solution:
Molar mass of carbon
Percentage of carbon in ethylene(C2H6) = ![]()
= \(\frac {24}{28}\) × 100 = 85.71%
Percentage of carbon in propene (C3H6) = \(\frac {24}{28}\) × 100 = 85.7 1%
Question 24.
Which of the following is/are true with respect to carbon – 12?
(a) relative atomic mass is 12 u
(b) oxidation number of carbon is +4 in all its compounds.
(c) I mole of carbon -12 contain 6.022 × 1022 carbon atoms.
(d) all of these
Answer:
(a) relative atomic mass is 12 u
Question 25.
Which one of the following is used as a standard for atomic mass?
(a) 6C12
(b) 7C12
(c) 6C13
(d) 6C14
Answer:
(a) 6C12
II. Write brief answer to the following questions
Question 26.
Define relative atomic mass.
On the basis of carbon, the relative atomic mass of element is defined as the ratio of mass of one atom of the element to the mass of l/12th mass of one atom of Carbon – 12.
![]()
Question 27.
What do you understand by the term mole?
Answer:
The mole is defined as the amount of a substance which contains 6.023 x 1023 particles such as atoms, molecules or ions. It is represented by the symbol
Question 28.
Define equivalent mass.
Answer:
The equivalent mass of an element is the number of parts of the mass of an element which combines with or displaces 1.008 parts of hydrogen or 8 parts of oxygen or 35.5 parts of chlorine.
Question 29.
What do you understand by the term oxidation number?
Answer:
Oxidation number refers to the number of charges an atom would have in a molecule or an ionic compound, if electrons were transferred completely. The oxidation numbers reflect the number of electrons “transferred”.
Question 30.
Distinguish between oxidation and reduction.
Answer:
Oxidation:
According to the classical concept, oxidation is a process of addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen.
Removal of hydrogen
2H2S + O2 → H2O + 2S
Addition of oxygen
C + O2 → CO2
According to the electronic concept, loss of electrons is called oxidation reaction.
Ca → Ca2+ + 2e–
During oxidation, oxidation number increases.
Dining oxidation, reducing agent gets oxidised.
Reduction:
Reduction is a process of removal of oxygen or addition of hydrogen.
Addition of hydrogen
Ca + H2 → CaH2
Removal of oxygen
Zn O + C → Zn + CO
According to the electronic concept, gain of electrons is called reduction reaction.
Zn2+ + 2e– → Zn
During reduction, oxidation number decreases.
During reduction, oxidising agent gets reduced.
Question 31.
Calculate the molar mass of the following compounds.
- urea [CO(NH2)2]
- acetone [CH3COCH3]
- boric acid [H3BO3]
- sulphuric acid [H2SO4]
Answer:
1. urea [CO(NH2)2]
Atomic mass of C =12
Atomic mass of O =16
Atomic mass of 2(N) = 28
Atomic mass of 4(H) = 4
∴ Molar mass of Urea = 60
2. Acetone [CH3COCH3]
Atomic mass of 3(C) = 36
Atomic mass of 1(0) = 16
Atomic mass of 6(H) = 6
∴ Molar mass of Acetone = 58
3. Boric acid [H3BO3]
Atomic mass of B = 10
Atomic mass of 3(H) = 3
Atomic mass of 3(O) = 48
∴ Molar mass of Boric acid = 61
4. Sulphuric acid 2[H2SO4]
Atomic mass of 2(H) = 2
Atomic mass of 1(S) = 32
Atomic mass of 4(O) = 64
∴ Molar mass of Sulphuric acid = 98
Question 32.
The density of carbon dioxide is equal to 1.977 kg m-3 at 273 K and 1 atm pressure. Calculate the molar mass of CO2
Answer:
Molecular mass = Density x Molar volume
Molar volume of CO2 = 2.24 x 10-2 m3
Density of CO2 = 1.977 kg m-3
Molecular mass of CO2 = 1.977 x 103 gm-3 x 2.24 x 10-2 m3
= 1.977 × 10-1 × 2.24 = 44 g
Question 33.
Which contains the greatest number of moles of oxygen atoms?
- 1 mol of ethanol
- 1 mol of formic acid
- 1 mol of H2O
Answer:
1. 1 mol of ethanol
C2H5OH (ethanol) – Molar mass = 24 + 6 + 16 = 46
46 g of ethanol contains 1 × 6.023 × 1023 number of oxygen atoms.
2. 1 mol of formic acid.
HCOOH (formic acid) – Molar mass = 2+12 + 32 = 46
46 g of HCOOH contains 2 × 6.023 × 1023 number of oxygen atoms.
3. 1 mol of H2O
H2O (water) – Molar mass = 2 + 16 = 18
18 g of water contains 1 × 6.023 × 1023 number of oxygen atoms.
∴ 1 mole of formic acid contains the greatest number of oxygen atoms.
Question 34.
Calculate the average atomic mass of naturally occurring magnesium using the following data
| Isotope | Isotopic atomic mass | Abundance (%) |
| Mg24 | 23.99 | 78.99 |
| Mg26 | 24.99 | 10 |
| Mg25 | 25.98 | 11.01 |
Answer:
Isotopes of Mg.
Atomic mass = Mg24 = 23.99 x \(\frac {783. 99}{100}\) = 18.95
Atomic mass = Mg26 = 24.99 x \(\frac {10}{100}\) = 2.499
Atomic mass = Mg25 = 25.98 x \(\frac {11.01}{100}\) = 2.860
Average Atomic mass = 24.309
Average atomic mass of Mg = 24.309
Question 35.
In a reaction x + y + z2 → xyz2, identify the limiting reagent if any, in the following reaction mixtures.
(a) 200 atoms of x + 200 atoms of y + 50 molecules of z2
(b) 1 mol of x + 1 mol of y + 3 mol of z2
(c) 50 atoms of x + 25 atoms of y + 50 molecules of z2
(d) 2.5 mol of x + 5 mol of y + 5 mol of z2
Answer:
x + y + z2
(a) 200 atoms of x + 200 atoms of y + 50 molecules of z2 According to the reaction, 1 atom of x reacts with one atom of y and one molecule of z to give product. In the case (a) 200 atoms of x, 200 atoms of y react with 50 molecules of z2 (4 part) i.e. 50 molecules of z2 react with 50 atoms of x and 50 atoms of y. Hence z is the limiting reagent.
(b) 1 mol of x + 1 mol of y + 3 mol of z2
According to the equation 1 mole of z2 only react with one mole of x and one mole of y. If 3 moles of z2 are there, z is limiting reagent.
(c) 50 atoms of x + 25 atoms of y + 50 molecules of z2
25 atoms of y react with 25 atoms of x and 25 molecules of z2. So y is the limiting reagent.
(d) 2.5 mol of x + 5 mol of y + 5 mol of z2
2.5 mol of x react with 2.5 mole of y and 2.5 mole of z2. So x is the limiting reagent.
Question 36.
Mass of one atom of an element is 6.645 × 10-23 g. How many moles of element are there in 0.320 kg?
Answer:
Mass of one atom of an element = 6.645 × 10-23 g = Atomic mass.
Mass of given element = 0.320 kg
Number of moles =
Atomic mass
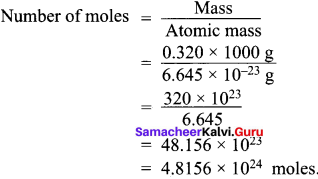
= 48.156 x 10-23
= 4.8156 x 10-24 moles.
Question 37.
What is the difference between molecular mass and molar mass? Calculate the molecular mass and molar mass for carbon monoxide.
Answer:
Molecular mass:
- Relative molecular mass is defined as the ratio of the mass of the molecule to the unified atomic mass unit.
- It can be calculated by adding the relative atomic masses of its constituent atoms.
- For carbon monoxide (CO) Molecular mass = Atomic mass of carbon + Atomic mass of oxygen 12 + 16 = 28 u.
Molar mass:
- It is defined as the mass of one mole of a substance.
- The molar mass of a compound is equal to the sum of the relative atomic masses of its constituent expressed in g mol-1.
- For carbon monoxide (CO) 12 + 16 = 28 g mol-1 Both molecular mass and molar mass are numerically same but the units are different.
Question 38.
What is the empirical formula of the following?
- Fructose (C6H12O6) found in honey
- Caffeine (C8H10N4O2) a substance found in tea and coffee.
Answer:
1. Fructose (C6H12O6)
Empirical formula is the simplest formula. So it is divided by 6 and so empirical formula is CH2O.
2. Caffeine (C8H10N4O2)
Simplified formula = \(\frac {molecular formula}{2}\)
Empirical formula = C4H5N2O.
Question 39.
The reaction between aluminium and ferric oxide can generate temperatures up to 3273 K and is used in welding metals. (Atomic mass of AC = 21 u Atomic mass of 0 = 16 u) 2Al + Fe2O2 → Al2O3 + 2Fe; If, in this process, 324 g of aluminium is allowed to react with 1.12 kg of ferric oxide.
- Calculate the mass of Al2O3 formed.
- How much of the excess reagent is left at the end of the reaction?
Answer:
![]()
1. As per balanced equation 54 g A1 is required for 112 g of iron and 102 g of Al2O3.
54 g of Al gives 102 g of Al2O3.
∴ 324 g of Al will give \(\frac{102}{54}\) x 324 = 612 g of Al2O3.
2. 54 g of Al requires 160 g of Fe2O3 for welding reaction.
∴ 324 g of Al will require \(\frac {160}{54}\) x 324 = 960 g of Fe2O3.
∴ Excess Fe2O3 – Un reacted Fe2O3 = 1120 – 960 = 160 g
160 g of excess reagent is left at the end of the reaction.
Question 40.
How many moles of ethane is required to produce 44 g of CO2 (g) after combustion.
Answer:
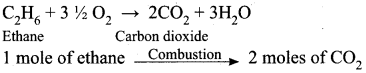
∴ 44g of CO2 = I mole of CO2
2 moles of CO2 is produced by 1 mole of ethane.
∴ 1 mole of CO2 will be produced by = ?
∴ To produce 1 mole of CO2, the required mole of ethane is = \(\frac {1}{2}\) x 1 = 0.5 mole of ethane.
Question 41.
Hydrogen peroxide is an oxidizing agent. It dioxides ferrous ion to ferric ion and reduced itself to water. Write a balanced equation.
Answer:
H2O2 – Oxidizing agent
Fe2+ + H2O2 → Fe3+ + H2O (Acetic medium)
Ferrous ion is oxidized by H2O2 to Ferric ion.
The balanced equation is Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e– x 2

Question 42.
Calculate the empirical and molecular formula of a compound containing 76.6% carbon, 6.38 % hydrogen and rest oxygen its vapour density is 47.
Answer:
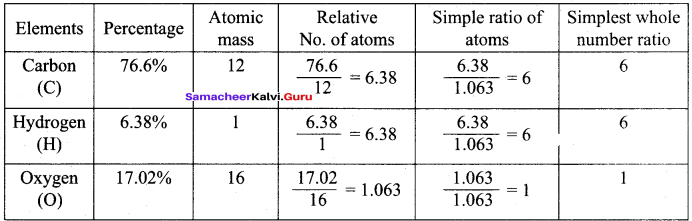
Empirical formula = C6H6O
Va-pour density 47
∴ Molecular mass = 2 x vapor density = 2 x 47 = 94
Molecular formula Empirical formula x n
Molecular mass x n
n = \(\frac { Molecular mass }{ Empirical formula mass }\) = \(\frac {94}{94}\) = 1
∴ Molecular formula = C6H6O
Question 43.
A Compound on analysis gave Na = 14.31% S = 9.97% H = 6.22% and O = 69.5% calculate the molecular formula of the compound if all the hydrogen in the compound is present in combination with oxygen as water of crystallization, (molecular mass of the compound is 322).
Answer:
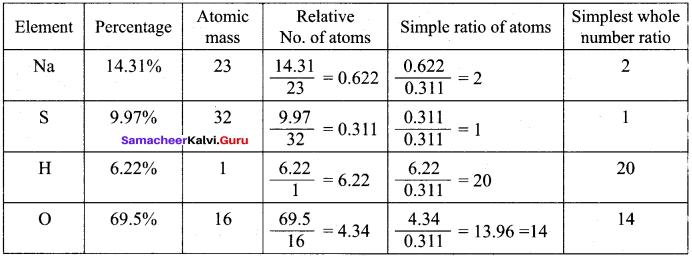
All H combines with 10 oxygen atoms to form as 10H2O.
So the empirical formula is Na2SO4 .10H2 O
Empirical formula mass = (23 x 2) + (32 x 1) + (16 x 4) + (10 x 18)
= 46 + 32 + 64 + 180 = 322
n = \(\frac { Molecular mass }{ Empirical formula mass }\) = \(\frac {322}{322}\) = 1
Molecular formula = Na2SO4. 10H2O
Question 44.
Balance the following equations by oxidation number method
- K2Cr2 O7 + KI + H2SO2 → K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3 + I2 + H2O
- KMnO4 + Na2SO3 → Mn02 + Na2SO4 + KOH
- Cu+ HNO3 → Cu(N03)2 + NO2 + H2O
- H2C2O4 + KMnO4 + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + MnSO4 + CO2 + H2O
Answer:
1. K2Cr2 O7 + KI + H2SO2 → K2SO2 + Cr2(SO4)3 + I2 + H2O
Step – 1.
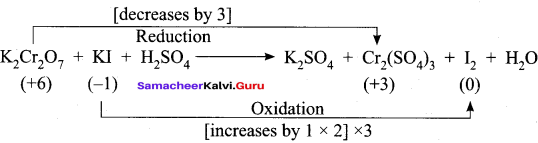
Step – 2
K2Cr2 O7 + 6KI + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3 + 3I2 + H2O
Step – 3
To balance other atoms
K2Cr2 O7 + 6KI + H2SO4 → 4K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3 + 3I2 + H2O
Step – 4
K2Cr2 O7 + 6KI + 7H2SO4 → 4K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3 + 3I2 + 7H2O
2. KMnO4 + Na2SO3 → MnO2 + Na2SO4 + KOH (Alkaline medium)
Step – 1
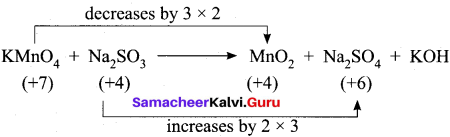
Step – 2
2KMnO4 + 3Na2SO3 → 2MnO2 + 3Na2SO4 + KOH
Step – 3
balancing potassium, KOH is multiplied by 2
2KMnO4 + 3Na2SO3 → 2MnO2 + 3Na2SO4 + KOH
Step – 4
To balance H atom, H20 is added on reactant side.
2KMnO4 + 3Na2SO3 + H2O → 2MnO2 + 3Na2SO4 + KOH
3. Cu + HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + NO2 + H2O
Step – 1
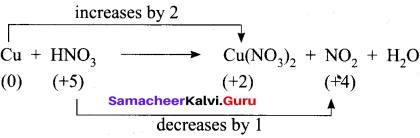
Step – 2
Cu + HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + NO2 + H2O
Step – 3
To balance Nitrogen, 2HNO3 is multiplied by 2 and NO2 is multiplied by 2
Cu + 4HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO2 + H2O
Step 4.
To balance oxygen, H2O is multiplied by 2
Cu + 4HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O
4. H2C2O4 + KMnO4 + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + MnSO4 + CO2 + H2O
Step – 1
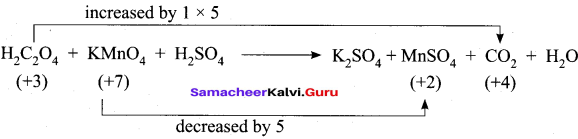
Step – 2
5 H2C2O4 + KMnO4 + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + MnSO4 + 10 CO2 + H2O
Step – 3
To balance K, KMnO4 and MnSO4 are multiplied by 2
5 H2C2O4 + 2KMnO4 + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 10 CO2 + H2O
Step – 4
To balance O and H, H2O and H2SO4 are multiplied by 3 and 6.
5 H2C2O4 + 2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 10 CO2 + 8H2O
Question 45.
Balance the following equations by ion electron method.
- KMnO4 + SnCl2 + HCl → MnCl2 + SnCl4 + H2O + KCl
- C2O42- + Cr2 O7 2- → Cr 3+ + CO2 (in acid medium)
- Na2S2O3 + I2 → Na2S4O6 + NaI (in acid medium)
- Zn + NO3– → Zn2+ + NO
Answer:
1. KMnO4 + SnCl2 + HCl → MnCl3 + SnCl3 +H2O + KCl
Oxidation half reaction: (loss of electrons)
![]()
Reduction half reaction: (gain of electrons)
![]()
Add H2O to balance oxygen atoms.
![]()
Add HCl to balance hydrogen atoms
KMnO4 + 5e– + 8HCl → MnCl2 + 4H2O ………(4)
To equalize the number of electrons equation (1) x 5 and equation (2) x 2
5SnCl2 → 5SnCl4 + 10e–
2KMnO4 + 16HCl + 10e– → 2MnCl2 + 4H2O + 2KCl
2KMnO4 + 5SnCl2 + 16HCl → 5SnCl4 + 2MnCl2 + 4H2O + 2KCl
2. C2O42- + Cr2 O72- → Cr 3+ + CO2 (in acid medium)
Oxidation half reaction:
![]()
Reduction half reaction:
![]()
To balance oxygen atoms, H2O is added on RHS of equation (2)
Cr2O72- + 6e– → 2Cr3+ + 7 H2O ……….(3)
To balance Hydrogen atoms, H+ is added on LHS of equation (1)
C2O42- + 14H+ → 2CO2 + 2e– ……..(4)
To equalize the number of electrons gained and lost, multiply the equation (4) x 3.
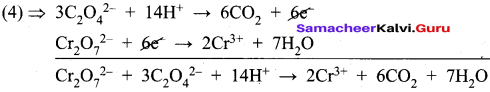
3. Na2S2O3 + I2 → Na2S4O6 + NaI (in acid medium)
Oxidation half reaction: (Loss of electron)
Na2S2O3 → Na2S4O6 + 2e2- ……..(1)
Reduction half reaction: (Gain of electron)
I2 + 2e2-→ 2NaI …………(2)
Adding (1) and (2)
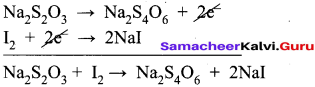
To balance oxygen,
2Na2S2O3 + I2 → Na2S2O2 + 2NaI
In acidic medium
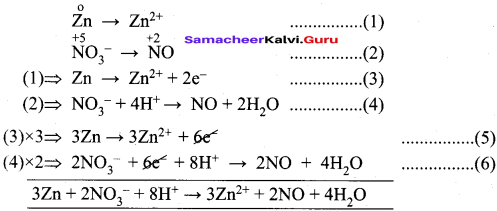
4. Zn + NO3– → Zn2+ + NO
Half reactions are –
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations In Text Questions – Evaluate Yourself
Question 1.
By applying the knowledge of chemical classification, classify each of the following Into elements, compounds or mixtures.
- Sugar
- Sea water
- Distilled water
- Carbon dioxide
- Copper wire
- Table salt
- Silver plate
- Naphthalene balls
Answer:
| Elements | Compounds | Mixtures |
| Copper wire (Cu) Silver plate (Ag) |
Sugar Distilled water Carbon dioxide Naphthalene balls |
Sea water Table salt |
Question 2.
Calculate the molar mass of the following.
- Ethanol (C2H5OH)
- Potassium permanganate (KMnO4)
- Potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7)
- Sucrose (C12H22O11)
Answer:
(1) Ethanol (C2H5OH)
Molar mass = (2 × 12) + (6 × 1) + (1 × 16)
= 24 + 6+16 = 46 g mol-1
(2) Potassium permanganate (KMnO4)
Molar mass = 39 + 55 + (4 × 16)
= 39 + 55 + 64 = 158 g mol-1
(3) Potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7)
Molar mass = (39 × 2) + (2 × 52) + (7 × 16)
= 78 + 104 + 112 = 294 g mol-1
(4) Sucrose (C12H22O11)
Molar mass = (12 × 12) + (22 × 1) + (11 × 16) = 144 + 22 + 176 = 342 g mol-1
Question 3.
(a) Calculate the number of moles present in 9 g of ethane.
Answer:
Mass of ethane = 9 g
Molar mass of ethane C2H6 = 30 g mol-1
No. of moles = \(\frac {Mass}{Molar mass}\) = \(\frac {9}{30}\) = 0.3 mol.
(b) Calculate the number of molecules of oxygen gas that occupies a volume of 224 ml at 273 K and 3 atm pressure.
Answer:
Molar volume of oxygen = 22400 ml.
22400 ml of oxygen contains 6.023 x 1023 molecules.
224 ml of oxygen contain \(\frac{6.023 \times 10^{23}}{22400}\) x 224
\(\frac{6.023 \times 10^{23}}{100}\) = 6.023 × 1021
Question 4.
(a) 0.456 g of a metal gives 0.606 g of its chloride. Calculate the equivalent mass of the metal.
Answer:
Mass of the metal = W1 = 0.456 g.
Mass of the metal chloride = W2 = 0.606 g.
∴Mass of chlorine = W2 – W1 = 0.606 – 0.456 = 0.15 g
0.15 g of chlorine combine with 0.456 g of metal.
∴ 35.46 g of chlorine will combine with \(\frac {0.456}{0.15}\) x 35.46 = 107.79 g eq-1
(b) Calculate the equivalent mass of potassium dichromate. The reduction half – reaction in acid medium is –
Cr2O72- + 14H+ +6e– → 2 Cr3+ + 7H2O
Answer:
Cr2O72- + 14H+ +6e– → 2 Cr3+ + 7H2O
![]()
Molar mass of K2Cr2O7 = 294.18
∴ Equivalent mass of K2Cr2O7 = \(\frac { 294.18}{6}\) = 49.03
Question 5.
A Compound on analysis gave the following percentage composition C = 54.55%, H = 9.09%, O = 36.36%. Determine the empirical formula of the compound.
Answer:
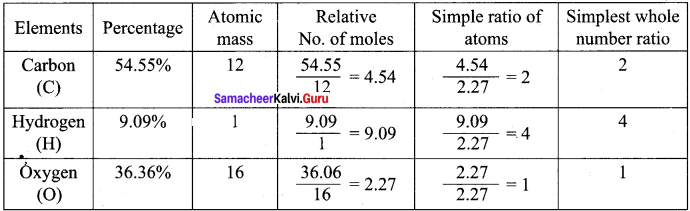
Empirical formula = C2H4O
Question 6.
Experimental analysis of a compound containing the elements x,y,z on analysis gave the following data, x = 32 %, y = 24 %, z = 44 %. The relative number of atoms of x, y and z are 2,1 and 0.5, respectively. (Molecular mass of the compound is 400 g) Find out.
- The atomic masses of the element x,y,z.
- Empirical formula of the compound and
- Molecular formula of the compound.
Answer:
Element x = 32% ; y = 24% ; z = 44%
Relative number of atoms x = 2 ; y = 1 ; z = 0.5
Molar mass of the compound = 400 g.
1. Atomic mass of the element.
Relative number of atoms ![]()
∴ Atomic mass ![]()
Atomic mass x = \(\frac {32}{2}\) = 16
Atomic mass y = \(\frac {24}{1}\) = 24
Atomic mass z = \(\frac {44}{0.5}\) = 88
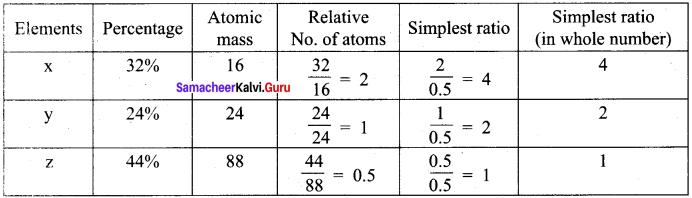
2. Empirical formula of the compound x4 y2 Z1
Molecular mass of the compound = 400
![]() = \(\frac {400}{200}\) = 2
= \(\frac {400}{200}\) = 2
3. Molecular formula of the compound = x8 y4 z2
Question 7.
The balanced equation for a reaction is given below 2x + 3y → 41 + m When 8 moles of x react with 15 moles of y, then –
- Which is the limiting reagent?
- Calculate the amount of products formed.
- Calculate the amount of excess reactant left at the end of the reaction.
Answer:
2 x + 3 y → 41 + m
1. 2x reacts with 3y to give products.
5x reacts with l5y means, y is the excess because 8 moles of x should react withn 4 x 3y = 12y moles of y to give products. In this reaction 15y moles are used. Therefore, 3 moles of y is excess and it is the limiting agent.
2. When 8 moles of x react with 12 moles of y, the product formed will be 4 x 41 i.e. 161 and 4m as product.
8x + 12y → 161 + 4m
3. At the end of the reaction, the excess reactant left in 3 moles of y.
Question 8.
Balance the following equation using oxidation number method
AS2 S3 + HNO3 + H2O → H3ASO4 + H2SO4 + NO
Answer:
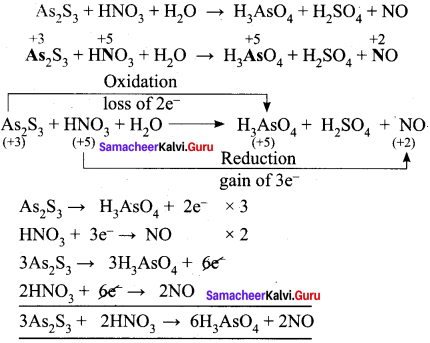
To balance oxygen and sulphur, H2O and H2SO4 are added.
3AS2S3 + 2HNO3 + H2O → 6H3ASO4 + 2NO + H2SO2
3AS2S3 + 28HNO3 + 4H2O → 6H3ASO4 + 28NO + 9H2SO4
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Solutions Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations Textual Calculations based on Stolchlometry Solved
Question 1.
How many moles of hydrogen is required to produce 10 moles of ammonia?
Answer:
The balanced stoichiometric equation fòr the formation of ammonia is
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH2(g)
4s per the stoichiometric equation, to produce 2 moles of ammonia, 3 moles of hydrogen are required.
∴ to produce 10 moles of ammonia,
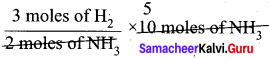
= 15 moles of hydrogen are required.
Question 2.
Calculate the amount of water produced by the combustion of 32 g of methane.
Answer:
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
As per the stoichiometric equation,
Combustion of 1 mole (16 g) CH4 produces 2 moles (2 x 18 = 36 g) of water.
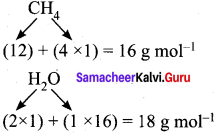
Combustion of 32 g CH4 produces
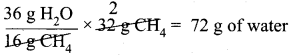
Question 3.
How much volume of carbon dioxide is produced when 50 g of calcium carbonate is heated completely under standard conditions?
Answer:
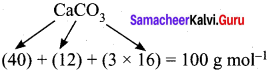
The balanced chemical equation is,
![]()
As per the stoichiometric equation,
1 mole (100g) CaCO3 on heating produces 1 mole CO2
At STP, 1 mole of CO2 occupies a volume of 22.7 litres
At STP, 50 g of CaCO3 on heating produces,
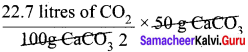
= 11.35 litres of CO2
Question 4.
How much volume of chlorine is required to form 11.2 L of HCl at 273 K and 1 atm pressure ?
Answer:
The balanced equation for the formation of HCl is,
H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2 HCl (g)
As per the stoichiometric equation, under given conditions,
To produce 2 moles of HCl, 1 mole of chlorine gas is required.
To produce 44.8 liters of HCl, 22.4 liters of chlorine gas are required
∴ To produce 11.2 liters of HCl,
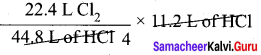
= 5.6 litres of chlorine are required.
Question 5.
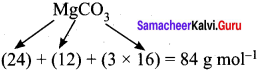
Calculate the percentage composition of the elements present in magnesium carbonate. How many kilogram of CO2 can be obtained by heating 1 kg of 90 % pure magnesium carbonate.
Answer:
The balanced chemical equation is
![]()
Molar mass of MgCO3 is 84 g mol-1.
84 g MgCO3 contain 24 g of Magnesium.
∴ 100 MgCO3 contain
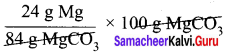
= 28.57 g Mg i.e. percentage of magnesium = 28.57 %.
84 g MgCO3 contain 12 g of carbon
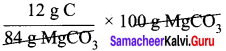
= 14.29 g of carbon
Percentage of carbon = 14.29 %.
84 g MgCO3 contain 48 g of oxygen
∴ 100 g MgCO3 contains
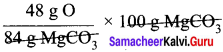
= 57.14 g of oxygen.
∴ Percentage of oxygen = 57.14 %.
As per the stoichiometric equation,
84 g of 100 % pure Mg CO3 on heating gives 44 g of CO2.
∴1000 g of 90 % pure Mg CO3 gives
\(\frac {44 g}{84 g x 100 %}\) x 90 % x 1000 g
= 471.43 g of CO2
= 0. 471 kg of CO2
Question 6.
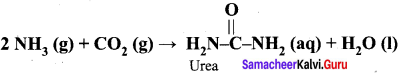
(1) If the entire quantity of all the reactants is not consumed in the reaction which is the limiting reagent ?
(2) Calculate the quantity of urea formed and un reacted quantity of the excess reagent. The balanced equation is
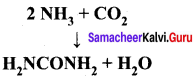
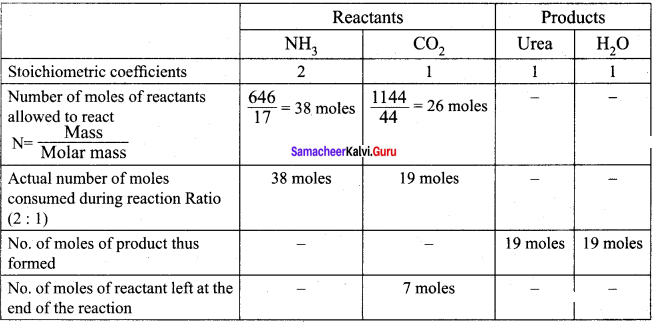
Answer:
(1) The entire quantity of ammonia is consumed in the reaction. So ammonia is the limiting reagent. Some quantity of CO2 remains unreacted, so CO2 is the excess reagent.
(2) Quantity of urea formed = number of moles of urea formed x molar mass of urea
= 19 moles x 60 g mol-1
= 1140 g = 1.14 kg
Excess reagent leftover at the end of the reaction is carbon dioxide. Amount of carbon dioxide leftover = number of moles of CO2 left over x molar mass of CO2
= 7 moles x 44 g mol-1 = 308 g.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Solutions Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations Additional Questions Solved
I. Choose the correct answer from the following
Question 1.
Which one of the following is the standard for atomic mass?
(a) 1H1
(b) 66C12
(c) 6C14
(d) 8O16
Answer:
(b) 66C12
Hint:
Standard element used to determine atomic mass is 6 Cl2
Question 2.
One mole of CO2 contains ………….
(a) 6.023 x 1023 atoms of C
(b) 6.023 x 1023 atoms of O
(c) 18.1 x 1023 molecules of CO2
(d) 3g atoms of CO2
Answer:
(a) 6.023 x 1023 atoms of C
Hint:
One mole of any substance contains Avogadro number of atoms. In this carbon one mole is present and oxygen two atoms are present. So, 6.023 x 1023 atoms of C is correct.
Question 3.
The largest number of molecules is in
(a) 54 g of nitrogen pent oxide
(b) 28 g of carbon dioxide
(c) 36 g of water
(d) 46 g of ethyl alcohol
Answer:
(c) 36 g of water
Hint:(a) 54 g of N2O5
N2O5 = Molecular mass = 28 + 80 = 108
108 g of N2O5 contains 6.023 x 1023 molecules.
∴ 54 g of N2O5 will contain \(\frac{6.023 \times 10^{23}}{108}\) x 54 = 3.0115 x 1023 molecules.
(b) 28 g of CO2
CO2 = Molecular mass = 12 + 32 = 44
44 g of CO2 contains 6.023 x 1023 molecules.
∴ 28 g of CO2 will contain \(\frac{6.023 \times 10^{23}}{44}\) x 28 = 3.832 x 1023 molecules.
(c) 36 g of H2O
H2O = Molecular mass = 2 + 16 = 18
18 g of H2O contains 6.023 x 1023 molecules.
∴ 36 g of H2O will contain \(\frac{6.023 \times 10^{23}}{18}\) x 36 = 12.046 X 1023molecules.
(d) 46 g of C2H5OH
C2H5OH = Molecular mass = 24 + 6 + 16 = 46
46 g of C2H5OH contains 6.023 x 1023 molecules.
So, among the 4, 36 g of water contain the largest number of molecules as 12.046 x 1023.
Question 4.
The number of moles of H2 in 0.224 liter of hydrogen gas at STP is …………..
(a) 1
(b) 0.1
(c) 0.01
(d) 0.001
Answer:
(c) 0.01
22.4 liter of hydrogen gas at STP contains 1 mole.
∴ 0.224 liter of hydrogen gas at STP will contain \(\frac{1}{22.4}\) x 0.224 = 0.01
Question 5.
10 g of hydrogen and 64 g of oxygen were filled in a steel vessel and exploded. The amount of water produced in this reaction will be ………..
(a) 3 mol
(b) 4 mol
(c) 1 mol
(d) 2 mol
Answer:
(b) 4 mol
10 g of H2 + 64 g of O2 → water
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
4 g of hydrogen react with 32 g of oxygen. So 10 g of hydrogen will react with 80 g of oxygen. But we have given amount of oxygen only 64 g. It means, here oxygen is the limiting agent. Now all the oxygen react with 8 g of hydrogen and form 4 moles of water.
Question 6.
6.023 x 1020 molecules of urea are present in 100 ml of its solution. The concentration of the solution is –
(a) 0.02 M
(b) 0.1 M
(c) 0.01 M
(d) 0.001 M
Answer:
(c) 0.01 M
100 ml of solution contain 6.023 x 1020 molecules.
6.023 x 1023 molecules in 1000 ml = 1 M.
∴ 6.023 x 1020 molecules in 1000 ml = 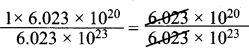
= 1020 x 10-23 = 10-3
10-3 moles present in 100 ml.
∴ In 1000 ml the moles present is = \(\frac{10^{-3}}{100}\) x 1000 = 10-2 moles
Concentration = 0.01 M
Question 7.
Two containers A and 13 of equal volume contain 6 g of O2 and SO2 at 300 K and 1 atm. Then
(a) No. of molecules in A is less than that in B
(b) No. of molecules in A is more than that in B
(c) No. of molecules in A and B are same
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) No, of molecules in A is more than that in B
O2 = Mass = 6 g
Molar mass = 32 g
32 g of O2 contains 6.023 x 1023 molecules.
∴ 6 g of O2 will contain = 6.023 X 1023 x 6 = 1.129 x 1023 molecules.
SO2 = Mass = 6 g
Molar mass = 64 g
64 g of SO2 contains 6.023 x 1023 molecules.
∴ 6 g of SO2 will contain 6.023 x 1023 x 6 = 0.5646 x 1023 molecules.
∴ Number of molecules in A is more than that in B.
Question 8.
The number of molecules in 16 g of methane is ……….
(a) 3.023 x 1023
(b) 6.023 x 1023
(c) 16 / 6.023 x 1023
(d) 6.023 / 3 x 1023
Answer:
(b) 6.023 x 1023
Hint:
Methane: CH4
Molecular mass 12 + 4 = 16
16 g of methane contains Avogadro number of molecules 6.023 x 1023 molecules.
Question 9.
Number of atoms in 4.25 g of ammonia is …………..
(a) 1 x 1023
(b) 2 x 1023
(e) 4 x 1023
(d) 6 x 1023
Answer:
(d) 6 x 1023
Hint:
Ammonia = NH3 (4 atoms)
Molecular mass = 14 + 3 = 17
17 g of Ammonia contains 6.023 X 1023 atoms.
∴ 4.25 g of Ammonia will contain 6.0231; 1023 x 4.25 = 1.5055 x 1023 molecules.
∴ 1.5055 x 1023 molecules will contain 4 x 1.5 x 1023 = 6 x 1023 molecules.
Question 10.
The number of molecules in a drop of water (0.0018 ml) at room temperature is ……….
(a) 6.02 x 1023
(b) 1.084 x 1023
(c) 4.84 x 1023
(d) 6.02 x 1023
Answer:
(a) 6.02 x 1023
Hint:
0.0018 ml – drop of water = 0.0018 g
H2O = molecular mass = 18 g.
Number of molecules in 18 g = 6.023 x 1023
∴ Number of molecules in 0.0018 g 6.023 x 1023 x 0.0018 = 6.023 x 1023 x 105
= 6.023 x l019 molecules.
or
Density of water at 25°C = 997.0479 g / L
Mass of 0.0018 ml (or) 0.00 18 x 10-3 L
= D x V
= 997.05 x 0.0018 x 10-3
= 1.795 x 10-3 g
Molar mass of water = 18 g
Mole = \(\frac{Mass}{Molecular mass}\) = \(\frac{1.795 \times 10^{-3}}{18}\)
= 9.971 x 10-5
∴ Number of molecules in 0.0018 ml = moles x Avogadro number
= 9.971 x 10-5 x 6.023 x 1023
= 6 x 1019 molecules.
Question 11.
7.5 g of a gas occupy 5.6 liters of volume at STP. The gas ……….
(a) NO
(b) N2O
(c) CO
(d) CO2
Answer:
(a) NO
Hint:
22.4 liters = 1 mole
5.6 liters = \(\frac {1}{22.4}\) x 5.6 = 0.25 mole.
NO = molar mass = 14 + 16 = 30 g = 1 mole
N2O = molar mass = 28 + 16 = 44g = 1 mole
CO = molar mass = 12 + 16 = 28 g = 1 mole
CO2=molar mass = 12 + 32 = 44g = 1 mole
Among the four gases, 0.25 mole = 7.5 g is equal to NO gas.
Question 12.
The mass in grams of 0.45 mole of CO2 ions ……….
(a) 1.8
(b) 40
(c) 36
(d) 18
Answer:
(d) 18
Hint:
Ca = Atomic mass = 40
Ca → Ca2+ + 2e–
41 g of Ca = 1 mole (for Ca2+ Atomic mass remains same)
1 mole of Ca2+ = 40 g
∴ 0.45 mole of Ca2+ = \(\frac {40}{1}\) x 0.45 = 18g
Question 13.
The mass of one molecule of HI in grams is ……….
(a) 2.125 x 10-22
(b) 128
(c) 127
(d) 6.02 x 10-23
Answer:
(b) 128
Hint:
HI = 1 mole = 1 + 127 = 128 g
Question 14.
Avogadro’s number is the number of molecules present in ……….
(a) 1 g of molecule
(b) 1 g atom of molecule
(c) gram molecular mass
(d) I lit of molecule
Answer:
(c) gram molecular mass
by definition (c) is correct
Question 15.
Which of the following contains same number of carbon atoms as are in 6.0 g of carbon (C-12)?
(a) 6.0 g ethane
(b) 8.0 g methane
(c) 21.0 g Propane
(d) 28.0 g CO
Answer:
(b) 8.0 g methane
Hint:
(a) 6.0 g of ethane (C2H6)
C2H6 = molar mass = 24 + 6 = 30 g
30 g of ethane contains 2 x 6.023 x 1023 Carbon atoms.
(b) 8.0 g of methane (CH4)
CH4 molar mass = 12 + 4 = 16g
16 g of methane contains 6.023 x 1023 Carbon atoms.
(c) 21.0 g of propane (C3H8)
C3H8 = molar mass = 36 + 8 = 44 g
44 g of propane contains 3 x 6.023 x 1023 Carbon atoms.
(d) 28.0 g of Carbon monoxide (CO)
CO = molar mass = 12+ 16 = 28 g
28 g of Carbon monoxide contains 6.023 x 1023 Carbon atoms.
6.0 g of Carbon contains = 6.023 x 10 x 6 = 3.0115 x 1023 Carbon atoms.
Among the (a), (b), (c), (d) – 8 g of CH4 contains x 8 = 3.0115 x 1023 Carbon atoms.
Question 16.
Equivalent mass of KMnO4 when it is converted to MnSO4 is equal to molar mass divided by ………..
(a) 6
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 2
Answer:
(c) 5
Hint:
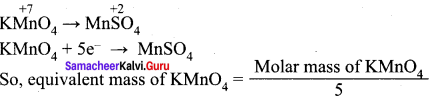
Question 17.
How many equivalents of Sodium sulphate is formed when Sulphuric acid is completelyn neutralized with a base NaOH?
(a) 0.2
(b) 2
(e) 0.1
(d) 1
Answer:
(d) 1
Hint:
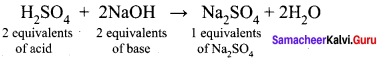
Question 18.
Cl2 changes to Cl– and ClO– in cold NaOH. Equivalent mass of Cl2 will be ………..
(a) Molar mass / 2
(b) Molar mass / 1
(c) Molar mass / 3
(d) 2 x Molar mass / 2
Answer:
(a) Molar mass / 2

Question 19.
Equivalent mass of KMnO4 in acidic medium, concentrated alkaline medium and dilute basic medium respectively are M, M, M. Reduced products can be ……………
(a) MnO2, MnO22-, Mn2+
(b) MnO2, Mn2+, MnO42-
(c) Mn2+, MnO2, MnO42-
(d) Mn2+, MnO42-, MnO2
Answer:
(c) Mn2+, MnO2, MnO42-
Hint:
MnO4– + 8H+ + 5e– → Mn2+ + 4H2O (acidic medium)
MnO4 + 4H+ + 3e– → MnO2 + 2H2O (concentrated basic medium)
MnO4 + e– → MnO42- (dilute basic medium)
Question 20.
The empirical formula of hydrogen peroxide is
(a) HO
(b) H2O
(e) H3O
(d) H2O2
Answer:
(a) HO
Hint:
Molecular formula of hydrogen peroxide = H2O2
H2O2 ÷ 2 = HO = Empirical formula.
Question 21.
Molecular mass =
(a) Vapour Density × 2
(b) Vapour Density ÷ 2
(c) Vapour Density × 3
(d) Vapour Density
Answer:
(a) Vapour Density × 2
Question 22.
20.0 g of a magnesium carbonate sample decomposes on heating to give carbon dioxide and 8.0 g magnesium oxide. What will be the percentage of purity of magnesium carbonate in the sample?
(a) 60
(b) 84
(e) 75
(d) 96
Answer:
(b) 84
Hint:
![]()
84 g of MgCO3 gives 40 g of MgO. (100% purity)
20 g of MgCO3 will give = \(\frac{40 \times 20}{84}\) = 9.52 g
9.52 g of MgO is given by 100% pure MgCO3.
8.0 g of MgO will be given by = \(\frac{100 \times 8}{9.52}\) = 84.03%
Question 23.
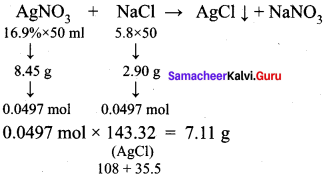
What is the mass of the precipitate formed when the preparation of alkyl halides 50 ml of 16.9 % solution of AgNO3 is mixed with 50 ml of 5.8 % NaCl solution?
(a) 7 g
(b) 14 g
(c) 28 g
(d) 35 g
Answer:
(a) 7 g
Hint:
Question 24.
When 22 L of hydrogen gas is mixed with 11.2 L of chlorine gas, each at STP, the moles of HCl gas formed is equal to ……….
(a) 2
(b) 0.5
(c) 1.5
(d) 1
Answer:
(d) 1
Hint:
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
22 liters + 11.2 litres
1 mole + \(\frac {1}{2}\) mole = 1 mole of HCl and \(\frac {1}{2}\) mole of H2 is remained.
Question 25.
5.6 L of a gas at STP are found to have mass of 11 g. The molecular mass of the gas is
(a) 36
(b) 48
(c) 40
(d) 44
Answer:
(d)44
Hint:
5.6 L of gas has the mass of 11 g.
∴ 22.4 L of gas will have the mass \(\frac {11}{5.6}\) x 22.4 = 44
Question 26.
Oxidation number f Fluorine in all compounds is ……….
(a) + 1
(b) -1
(c) 0
(d) – 2
Answer:
(b) – 1
Question 27.
In redox reaction which of the following is true?
(a) Number of electrons lost is more than number of electrons gained
(b) Number of electrons lost is less than number of electrons gained
(c) Number of electrons lost s equal number of electrons gained
(d) No transfer and gain of electrons during the reaction.
Answer:
(c) Number of electrons lost is equal number of electrons gained
Question 28.
Which of the following is a mono-atomic molecule?
(a) Hydrogen
(b) Oxygen
(c) Sodium
(d) Ozone
Answer:
(c) Sodium
Question 29.
Which one of the following is a diatomic molecule?
(a) Ozone
(b) Copper
(c) Hydrogen
(d) Gold
Answer:
(c) Hydrogen
Question 30.
The value of Avogadro Number N is equal to ……….
(a) 2.24 x 10-2L
(b) 22400 cm3
(c) 6.023 x 10-23
(d) 6.023 x 1023
Answer:
(d) 6.023 x 1023
Question 31.
46 g of ethanol contains ……….
(a) 2 x 6.023 x 1023 C atoms
(b) 3 x 6.023 x 1023 atoms
(c) 9 x 6.023 x 1023 H atoms
(d) 6.023 x 1023 Carbon atoms
Answer:
(a) 2 x 6.023 x 1023 C atoms
Hint:
C2H5OH = Molecular mass = (12 x 2) + (1 x 6) + (1 x 16)
=24 + 6 + 16 = 46
2 Carbon atoms are present.
∴ 2 x 6.023 x 1023 C atoms is correct.
Question 32.
The mass of one mole of CaCl2 is ……….
(a) 55.5 g mol-1
(b) 111 g mol-1
(c) 222 g mol -1
(d) 77.5 g mol-1
Answer:
(b) 111 g mol-1
Hint:
CaCl2 = Mass = 40 + 71 = 111 g mol-1
Question 33.
22 g of CO2 contains molecules of CO2
(a) 6.023 x 1023
(b) 6.023 x 1023
(c) 3.0115 x 1023
(d) 3.0115 x 1023
Answer:
(c) 3.0115 x 1023
Hint:
44 g of CO2 contains 6.023 x 1023 molecules.
∴ 22 g of CO2 will contain = \(\frac{6.023 \times 10^{23}}{44}\) x 22 = 3.0115 x 1023
Question 34.
The formula weight of ethanol (C2H5OH) is ……….
(a) 56.5 amu
(b) 16 amu
(c) 60 amu
(d) 46 amu
Answer:
(d) 46 amu
Hint:
Formula weight of C2H5OH = (12 x 2) + (6 x 1) + (1 x 16)
= 24 + 6 + 16 = 46 amu
Question 35.
The number of moles of ethane in 60 g is ……….
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 0.5
(d) 1
Answer:
(a) 2
Hint:
C2H6 – Ethane – molar mass = 24 + 6 = 30 g
30 g of C2H6 contains = 1 mole.
∴ 60 g of C2H6 will contains = x 1 = 2 moles.
Question 36.
Which of the following method is used to prevent rusting of iron?
(a) Galvanization
(b) Painting
(c) Chrome plating
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 37.
Which of the following is not a redox reaction?
(a) H2 + F2 → 2HF
(b) Cu + 4HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O
(c) 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
(d) AgCl + NH3 → [Ag(NH3)2]Cl
Answer:
(d) AgCl + NH3 → [Ag(NH3)2]Cl
Question 38.
How many H2O molecules are there in a snowflake weighing 1 mg?
(a) 3.35 x 1019
(b) 6.023 x 1023
(c) 335 x 10-19
(d) 100
Answer:
(a) 3.35 x 1019
Hint:
1 mg of H2O
Molar mass of H2O = 2 + 16 = 18 g
1 Mole contains 6.023 x 1023 water molecules
18 g contains 6.023 x 1023 water molecules
l mg contains \(\frac{6.023 \times 10^{23}}{18}\) x 1g /1000 mg = 3.35 x 10-19 H2O molecule.
Question 39.
The volume of HCl gas weighing 73 g at STP is ……….
(a) 2.24 x 10-2 m3
(b) 4.48 x 10-2 m3
(c) 4.48 x 102m3
(d) 2.24 x 102m3
Answer:
(b) 4.48 x 10-2 m3
Hint:
HCl = Molar mass = 1 + 35.5 = 36.5 g
36.5 g of HCl occupies 2.24 x 10-2m3
∴ 73 g of HCl at STP will occupy \(\frac{2.24 \times 10^{-2}}{36.5}\) x 73 = 4.48 x 10-2m3
Question 40.
The molar volume of 22 g of CO2 is ……….
(a)2.24 x 10-2m3
(b)4.48 x 10-2m3
(c) 1.12 x 10-2m3
(d)2.24 x 10-2m3
Answer:
(c) 1.12 x 10-2m3
Hint:
CO2 = Molar’mass of 12 + 32 = 44 g
44 g of CO2 occupies molar volume = 2.24 x 10-2m3
∴ 2g of CO2 will occupy = \(\frac{2.24 \times 10^{-2}}{44}\) x 2= 1.12 x 10-2 L
Question 41.
The equivalent mass of Aluminium is ……….
(a) 27
(b) 13.5
(c) 54
(d) 9
Answer:
(d) 9
Question 42.
The equivalent mass of HSO4 is ……….
(a) 98
(b) 97
(c) 48
(d) 96
Answer:
(a) 98
Hint:
HSO4 = Molar mass= 1 + 32 + 64 + 1 = 98
Equivalent mass = Molar mass / 1 = 98
Question 43.
The equivalent mass of NaCl is ……….
(a) 40
(b) 58.5
(c) 35.5
(d) 23
Answer:
(b) 58.5
Hint:
NaCl = Salt Molar mass 23 + 35.5 = 58.5
Equivalent mass of Salt = Molar mass of Salt.
Question 44.
Match the List-I and List-lI using the correct code given below the list.
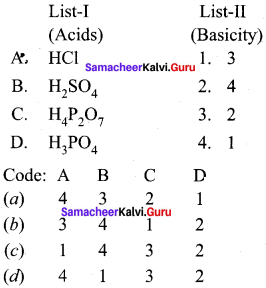
Answer:
![]()
Question 45.
Match the List-I and List-Il using the correct code given below the list.
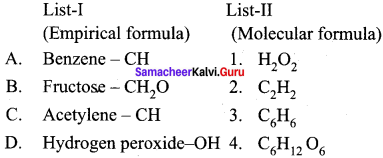

Answer:
![]()
Question 46.
Consider the following statements ……….
(i) Empirical formula shows the actual number of atoms of different elements in one molecule of the compound.
(ii) Ozone is a diatomic molecule.
(iii) Gases are easily compressible.
Which of the above statement is/are not correct?
(a) (i), (ii), (iii)
(b) (i) & (ii)
(c) (ii) & (iii)
(d) (iii) only
Answer:
(b) (i) & (ii)
Question 47.
How many molecules of hydrogen is required to produce 4 moles of ammonia?
(a) 15 moles
(b) 20 moles
(c) 6 moles
(d) 4 moles
Answer:
(c) 6 moles
Hint:
3H2 + N2 → 2NH3
To get 2 moles of ammonia, 3 mole of H2 is required.
To get 4 moles of ammonia = \(\frac {3}{2}\), x 4
= 6 moles of H2 is required.
Question 48.
The number of moles of oxygen required to prepare 1 mole of water is …………..
(a) I mole
(b) 0.5 mole
(c) 2 moles
(d) 0.4 mole
Answer:
(b) 0.5 mole
Hint:
![]()
0.5 mole of oxygen is required to prepare 1 mole of H2O.
Question 49.
How much volume of CO2 is produced when 50 g of CaCO3 is heated strongly?
(a) 2.24 x 10-2 m3
(b) 22.4
(c) 11.2 L
(d) 22400 cm3
Answer:
(c) 11.2 L
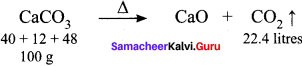
100 g of CaCO3 produces 22.4 litres of CO2.
50 g of CaCO3 will produce = \(\frac{22.4}{100} \times 50\) = 11.2 litres
Question 50.
Which one of the following is not a redox reaction?
(a) Rusting of iron
(b) Extraction of metal Na
(c) Electroplating
(d) Aluminothermic process
Answer:
(a) Rusting of Iron
Question 51.
In the reaction 2 AuCl3 + 3 SnCl2 → 2 Au + 3 SnCl4 which is an oxidising agent?
(a) AuCl3
(b) Au
(c) SnCl2
(d) Both AuCl3 and SnCl2
Answer:
(a) AuCl3
Hint:
AuCl3 undergoes reduction. So, it is an oxidising agent.
Question 52.
Identify the compound formed during the rusting of iron.
(a) Fe2O3
(b) Fe2O3. x H2O
(c) FeO. x H2O
(d) FeO
Answer:
(b) Fe2O3. x H2O – Hydrated iron oxide is rust.
Question 53.
The oxidation state of a substance in its elementary state is equal to ………..
(a) -1
(b) -2
(c) zero
(d) charge of the ion
Answer:
(c) zero
Question 54.
The oxidation number of fluorine in all its compounds is equal to ………….
(a) -1
(b) +1
(c) – 2
(d) +2
Answer:
(a) -1
Question 55.
Consider the following statements.
(i) The sum of the oxidation number of all the atoms in neutral molecule is equal to zero.
(ii) Fluorine has an oxidation number +1 in all its compounds. .
(iii) The oxidation number of a substance in its elementary state is equal to zero.
Which of the above statement is/are not correct?
(a) (i), (ii) & (iii)
(b) (ii) & (iii)
(c) (i) only
(d) (ii) only
Answer:
(d) (ii) only
Question 56.
The oxidation number of Cr in K2Cr2O7 is ………….
(a) +4
(b) + 6
(c) O
(d) + 7
Answer:
(b) + 6
K2Cr2O2
2 + 2x – 140
2x – 12 = 0
2x = + 12
x = + 6
Question 57.
The oxidation number of N in NH4 ion is ……….
(a) +4
(b) + 3
(c) – 3
(d) – 4
Answer:
(c) – 3
NH2+
x + 4 = + 1
x = + 1 – 4
x = – 3
Question 58.
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s). In this reaction, which gets oxidised?
(a) Cu2+
(b) Zn2+
(c) Zn
(d) Zn, Cu2+
Answer:
(c) Zn
Hint:
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e– (loss of electron = oxidation)
Zn gets oxidised
Question 59.
Which one of the following is an example for disproportionation reaction?
(a) CuSO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + Cu
(b) 2KClO3 → 2KCI + 3O2
(c) PCl5 → PCl3 + Cl2
(d) 4H3PO3 → 3H3PO4 + PH3
Answer:
(d) 4H3PO3 → 3H3PO4 + PH3 (Auto oxidation and reduction reaction)
Question 60.
The number of molecules in 40 g of sodium hydroxide is ……….
(a) 6.023 x 1023
(b) 3.0115 x 1023
(c) 6.023 x 1023
(d) 2 x 6.023 x 1023
Answer:
(c) 6.023 x 1023
Sodium hydroxide = NaOH = 23 + 16+ 1 =40 g
40g = 1 mole = 6.023 1023
Question 61.
The mass of one molecule of AgCl in grams is ……….
(a) 108 g
(b) 143.5 g
(c) 35.5 g
(d) 243.5 g
Answer:
(b) 143.5 g
Hint:
Mass of AgCl = 108 + 35.5 = 143.5 g.
Question 62.
The empirical formula of Alkene is ……….
(a) CH
(b) CH2
(c) CH3
(d) CH3O
Answer:
(b) CH2
Hint:
Alkene CnH2n Molecular formula
E.F. = M.F./2
∴ Empirical formula = CH2
Question 63.
22 g of a gas occupies 11.2 litres of volume at STP. The gas is ……….
(a) CH4
(b) NO
(c) CO
(d) CO2
Answer:
(d) CO2
Hint:
22 g of a gas occupies 11.2 litres.
11.2 liters is occupied by 22 g of a gas.
∴ Molar volume 22.4 liter will be occupied by \(\frac {22}{11.2}\) x 22.4 = 44 g
∴ The gas is CO2.
Question 64.
The number of moles of H2 in 2.24 liter of hydrogen gas at STP is ……….
(a) 1
(b) 0.1
(c) 0.01
(d) 0.001
Answer:
(b) 0.1
Hint:
22.4 liter = 1 molar volume = 1 mole.
∴ 2.24 liter = \(\frac {1}{22.4}\) x 2.24 = 01 mole
Question 65.
How many molecules are present in 32 g of methane?
(a) 2 x 6.023 x 1023
(b) 6.023 x 1023
(c) 6.023 x 1023
(d) 3.011 x 1023
Answer:
(a) 2 x 6.023 x 1023
Hint:
Methane (CH4) – Molar mass = 12 + 4 = 16g.
16 g contains 6.023 x 1023 molecules.
∴ 32 g of methane will contain = \(\frac{6.023 \times 10^{23}}{16} \times 32^{2}\) = 2 x 6.023 x 1023
Question 66.
The empirical formula of glucose is ……….
(a) CH
(b) CH2O
(c) CH2O2
(d) CHO
Answer:
(b) CH2O
Hint:
Glucose = Molecular formula = C6H12O6
Empirical formula = \(\frac { Molecular formula}{6}\) = \(\\frac{\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_{6}}{6}\) = CH2O
Question 67.
How many moles of water is present in I L of water?
(a) 1
(b) 18
(c) 55.55
(d) 5.555
Answer:
(c) 55.55
Hint:
1 Liter of water = 1000 g.
Molar mass of water 18 g
Number of moles = \(\frac {Mass}{Molar mass}\) = \(\frac {1000}{18}\) = 55.55 moles
Question 68.
How many moles of Hydrogen atoms are present in 1 mole of C2 H6 ?
(a) 18 moles
(b) 6 moles
(c) 3 moles
(d) 1 mole
Answer:
(b) 6 moles
Hint:
C2H6 contains 6H atoms. 6 moles.
Question 69.
The molar mass of Na2SO4 is ……….
(a).129
(b) 142
(c) 110
(d) 70
Answer:
(b) 142
Hint:
Na2 SO4 = Molar mass
= (23 x 2) + (32 x 1) + (16 x 4)
= 46 + 32 + 64 = 142
Question 70.
Match the List-I with List-Il using the correct code given below the list.
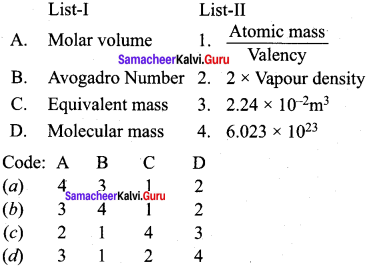
Answer:
![]()
Question 71.
Ore mole of CO2 contains ………….
(a) 6.02 x 1023 atoms of C
(b) 3 g of CO2
(c) 6.02 1023 atoms of O
(d) 18.1 x 1023 molecules of CO2
Answer:
(a) 6.02 x 1023 atoms of C
Question 72.
5.6 liters of oxygen at STP is equivalent to ……….
(a) 1 mole
(b) 1/4 mole
(c) 1/8 mole
(d) 1/2 mole
Answer:
(b) 1/4 mole
Hint:
22.4 litres of O2 = 1 mole
∴ 5.6 litres of O2 = \(\frac {1}{22.4}\) x 5.6 = 0.25 mole = 1/4 mole.
Question 73.
How many grams are contained in 1 gram atom of Na?
(a) 13 g
(b) 1 g
(c) 23 g
(d) 1/23 g
Answer:
(c) 23 g
Hint:
1 gram atom of Na
Na = Atomic mass 23 g (or) 23 amu
1 gram atom of Na = 1 mole = 23 g.
Question 74.
12 g of Mg will react completely with an acid to give ……….
(a) 1 mole of O2
(b) 1/2 mole of H2
(c) I mole of H2
(d) 2 mole of H2
Answer:
(b) 1/2 mole of H2
Hint:
![]()
∴ 12 g of Mg \(\frac {1}{2}\) mole of H2O
Question 75.
which of the following has the highest mass?
(a) I g atom of C
(b) 1/2 mole of CH4
(c) 10 ml of water
(d) 3.011 x 1023 atoms of oxygen
Answer:
(a) I g atom of C
(a) 1 g atom of C = 12 g
(b) 1/2 mole of CH4 = \(\frac {12 + 4}{2}\) = 8 g.
(c) 10 ml of water (H2O) = 1 x 10 = 10 g
(d) 3.011 x 1023 atoms of oxygen = 0.5 mole of oxygen = 8 g
Question 76.
The empirical formula of sucrose is ……….
(a) CH2O
(b) CHO
(c) C12H22O11
(d) C(H2O)2
Answer:
(a) CH2O
Hint:
Sucrose Molecular formula = C12H22O11
E.F.= \(\frac{\mathrm{C}_{12} \mathrm{H}_{22} \mathrm{O}_{11}}{12}\) = CH2O
Question 77.
The number of grams of oxygen in 0.10 mol of Na2CO3. 10H2O is ………..
(a) 20.8 g
(b) 18 g
(c) 108 g
(d) 13 g
Answer:
(a) 20.8 g
Hint:
Na2CO2.10H2O = 1 mole
1 mole of Na2CO3. 10H2O contains 13 oxygen atoms.
Mass of 13 oxygen atoms = 13 x 16 = 208
1 mole of Na2CO3.10H2O contains 208 g of oxygen.
∴ 0.10 mole of Na2CO3.10H2O contains \(\frac {208}{1}\) x 0.12 = 08 g.
Question 78.
The mass of an atom of nitrogen is ……….
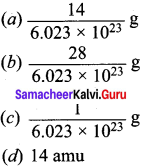
Answer:
![]()
![]()
Question 79.
Which of the following halogens do not exhibit positive oxidation number in its compounds?
(a) Fluorine
(b) Chlorine
(c) Iodine
(d) Bromine
Answer:
(a) Fluorine
Question 80.
Which of the following is the most powerful oxidising agent?
(a) KMnO4
(b) K2Cr2O7
(c) O3
(d) H2O2
Answer:
(a) KMnO4
Question 81.
On the reaction 2Ag + H2SO4 → Ag2SO4 + 2H2O + SO2. Sulphuric acid acts as ……………
(a) oxidising agent
(b) reducing agent
(c) a catalyst
(d) an acid as well as an oxidant
Answer:
(d) an acid as well as an oxidant
Question 82.
The oxidation number of carboxylic carbon atom in CH3COOH is ……….
(a) + 2
(b) + 4
(c) + 1
(d) + 3
Answer:
(d) + 3
CH3COOH
-3 + 3 + x – 4 + 1
x – 3 = 0
x = + 3
Carboxylic carbon oxidation number = + 3
Question 83.
When methane is burnt in oxygen to produce CO2 and H2O, the oxidation number of carbon changes by ……….
(a) – 8
(b) + 4
(c) zero
(d) + 8
Answer:
(b) + 4
![]()
Question 84.
The oxidation number of carbon is zero in ……….
(a) HCHO
(b) C12H22O11
(c) C6H12O6
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 85.
The oxidation number of Fe in Fe2(SO4)3 is ……….
(a) + 2
(b) + 3
(c) + 2, + 3
(d) O
Answer:
(b) + 3
Fe2(SO4)3
2x – 6 = 0
x = + 3
Question 86.
Among the following molecules in which Chlorine shows maximum oxidation state?
(a) Cl21
(b) KCl
(c) KClO3
(d) Cl2O7
Answer:
(d) Cl2O7
Cl2O7
2x – 14 = 0
2x = + 14
x = + 7
Question 87.
The oxidation number of carbon in CH3 → CH2OH is ………….
(a) + 2
(b) – 2
(e) O
(d) + 4
Answer:
(b) – 2
C2H5OH
2x +6 – 2 = O
2x + 4 = 0
2x = -4
x = -2
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations 2 – Mark Questions
I. Write brief answer to the following questions:
Question 1.
State Avogadro’s Hypothesis.
Answer:
It states that ‘Equal volume of all gases under the same conditions of temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules’.
Question 2.
What is molar volume?
Answer:
Molar volume is the volume occupied by one mole of a substance in the gaseous state at STP. It is equal to 2.24 x 10-2m3 (22.4 L).
Question 3.
The approximate production of Na2CO3 per month is 424 x 106 g while that of methyl alcohol is 320 x 106 g. Which is produced more in terms of moles?
Answer:
Na2CO3 mass = 424 x 106g
Molecular mass of Na2CO3 = (23 x 2) + 12 + (16 x 3)
= 46+ 12 +48
= 106 g
No. of moles of Na2CO3 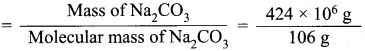
= 4 x 106 moles
Methyl alcohol mass = 320 x 106 g
Molecular mass of CH3OH = 12 + (1 x 4)+ 16 = 32 g
= 12 + 4 + 16 = 32 g
No. of moles of Methyl alcohol ![]()
= 10 x 106 moles.
∴ Methyl alcohol is more produced in terms of moles.
Question 4.
Calculate number of moles of carbon atoms ¡n three moles of ethane.
Answer:
Ethane – Molecular formula = C2H6
1 mole of ethane contains 2 atoms of carbon (6.023 x 1023 C)
∴ 3 moles of ethane contains 6 atoms of Carbon.
∴ No. of moles of Carbon atoms = 3 x 6.023 x 1023 Carbon atoms.
= 18.069 x 1023 Carbon atoms.
Question 5.
Find the molecular mass of FeSO4.7H2O
Answer:
Sum of Atomic mass of all elements = Molecular mass
Atomic mass of Fe = 56.0
Atomic mass of S = 32.0
Atomic mass of 4[O] = 64.0
Atomic mass of 14[H] = 14.0
Atomic mass of 7[O] = 112.0 = 278.0
Molecular mass of FeSO4.7H2O = 278 g.
Question 6.
Mass of one atom of an element ¡s 6.66 x 1023 g. How many moles of element are there in 0.320 kg?
Answer:
Mass of one atom of an element = 6.66 x 1023g
No. of moles = \(\frac {Mass}{Molecular mass}\) 3
Molecular mass = Mass of 1 atom x Avogadro number
6.66 x 1023 x 6.023 x 1023
= 6.66 x 6.023 = 40.11318
Number of moles = \(\frac {Mass}{Molecular mass}\) = \(\frac{0.320 \mathrm{kg} \times 10^{3}}{40}\) = 8 moles.
Question 7.
How many moles of glucose are present in 720 g of glucose?
Answer:
Glucose = C6H4O4
Molecular mass of Glucose = (12 x 6) + (1 x 12) + (16 x 6)
= 72 + 12 + 96 = 180
\(\frac {720}{180}\) = 4 moles.
Question 8.
Calculate the weight of 0.2 mole of sodium carbonate.
Answer:
Sodium carbonate = Na2CO3
Molecular mass of Na2CO3 = (23 x 2)+(12 x 1)+(16 x 3)
= 46 + 12 + 48 = 106 g
Mass of 1 mole of Na2CO3 = \(\frac{106 \times 0.2}{1}\) = 21.2 g
Question 9.
What do you understand by the terms acidity and basicity?
Answer:
Acidity:
The number of hydroxyl ions present in one mole of a base is known as the acidity of the base.
Basicity:
The number of replaceable hydrogen atoms present in a molecule of the acid is referred to as its basicity.
Question 10.
Calculate the equivalent mass of bicarbonate ion.
Answer:
Bicarbonate ion = HCO3
![]()
Formula mass of HCO3 = 1 + 12 + 48 = 61
Equivalent mass of HCO3 = \(\frac {61}{1}\) = 61
Question 11.
Calculate the equivalent mass of barium hydroxide.
Barium hydroxide = Ba(OH)2
Molecular mass of Ba(OH)2 = 137 + (16 x 2) + (1 x 2)
= 171.0 g / mol.
Acidity = 2
Equivalent mass of Ba(OH)2 =
= \(\frac {17 1.0}{2}\) = 85.5
Question 12.
Calculate the equivalent mass of hydrated sodium carbonate.
Answer:
Hydrated sodium carbonate = Na2CO3. 10H2O
Molecular mass of Na2CO3. 10H2O = (23 x 2) + (2 x 1) + (16 x 13) + (1 x 20)
= 46 + 12 + 208 + 20 = 286
Equivalent mass of Na2CO3. 10H2O = \(\frac {Molecular mass}{Acidity}\)
= \(\frac {286}{2}\) = 143
Question 13.
What do you understand by the terms empirical formula and molecular formula?
Answer:
Empirical Formula:
- It is the simplest formula.
- It shows the ratio of number of atoms of different elements in one molecule of the compound.
Molecular Formula:
- It is the actual formula.
- It shows the actual number of different types of atoms present in one molecule of the compound.
Question 14.
Boric acid, H3BO3 is a mild antiseptic and is often used as an eye wash. A sample contains 0.543 mol H3BO3. What is the mass of boric acid in the sample?
Answer:
Molecular mass of H3BO3 = (1 x 3) + (11 x 1) + (16 x 3) = 62
Boric acid sample contains 0.543 mole.
Mass of 0.543 mole of Boric acid = Molecular mass x mole
= 62 x 0.543
= 33.66 g
Question 15.
A compound contains 50% of X (atomic mass 10) and 50% Y (atomic mass 20). Give its molecular formula
Answer:
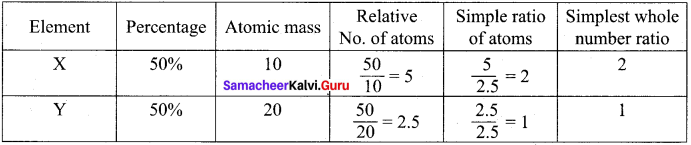
∴ The Empirical Formula is X3Y
Empirical Formula mass = 20 + 20 = 40
Molecular mass = Sum of atomic mass = 40
n = 1, Molecular formula = (Empirical Formula )n = (X2Y)1 = X2Y.
Question 16.
Calculate the mass of sodium (in kg) present in 95 kg of a crude sample of sodium nitrate whose percentage purity is 70%.
Answer:
Sodium Nitrate = NaNO3
Molecular mass of Sodium Nitrate = 23 + 14 + 48 = 85
100% pure 85 g of NaNO3 contains 23 g of Sodium.
100% pure 95 x 103 g of NaNO3 will contains \(\frac {23}{85}\) x 95 x 103
= 25.70 x 103 g of Sodium.
100% pure NaNO3 contains 25.70 x 103 g of Sodium.
∴ 70% pure NaNO3 will contains = img
= 17990 g (or) 17.99 Kg of Na.
Question 17.
Define matter. What are the types of matter?
Answer:
- A matter is anything which has mass and occupies space.
- Matters exist in all three states such as solid, liquid and gas.
Question 18.
Prove that states of matter are inter convertible.
Answer:
States of matter are inter convertible by changing temperature and pressure.
![]()
Question 19.
What is meant by Plasma state? Give an example.
Answer:
Gaseous state of matter at very high temperature containing gaseous ions and free electron is referred to as the Plasma state. e.g. Lightning.
Question 20.
Differentiate an element and an atom.
Answer:
- An atom is the ultimate smallest electrically neutral, being made up of fundamental particles such as proton, neutron and electron.
- An element consists of only one type of atoms. Elements are further divided into metals, non-metals, and metaloids.
Question 21.
Distinguish between a molecule and a compound
Answer:
Molecule:
- A molecule is the smallest particle made up of one or more than one atom in a definite ratio having stable and independent existence.
- e.g. Na – Mono atomic molecule O2 – Diatomic molecule P4 – Poly atomic molecule
Compound:
- A molecule which contains two or more atoms of different elements are called a compound molecule.
- e.g. CO2 – Carbon dioxide CH4 – Methane H2O – Water
Question 22.
Chlorine has fractional average atomic mass. Justify this statement.
Answer:
Chlorine molecule has two isotopes as in 17Cl35 , 17 Cl37 in the ratio of 77 : 23, so when we are calculating the average atomic mass, it becomes fractional.
The average relative atomic mass of Chlorine = \(\frac {(35 x 77) + (37 x 23)}{100}\) = 35.46 amu
Question 23.
Define molecular mass of a substance.
Answer:
Molecular mass of a substance (element or compound) represents the number of times the molecule of that substance is heavier than 1 / 12th of the mass of an atom of C-12 isotope. Molecular mass = 2 x Vapour density
Question 24.
Calculate the molecular mass of Sulphuric acid (H2SO4). Element
Answer:
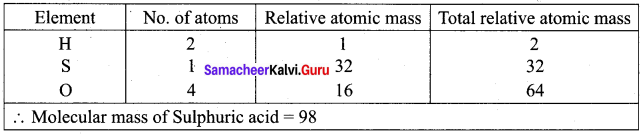
Question 25.
Define Avogadro Number.
Answer:
Avogadro number is the number of atoms present in one mole of an element or number of molecules present in one mole of a compound. The value of Avogadro number (N) = 6.023 x 1023
Question 26.
Calculate the number of moles present in 60 g of ethane.
Answer:
No. of moles =![]() = \(\frac {W}{M}\)
= \(\frac {W}{M}\)
Molar Mass of ethane (C2H6) = 24 + 6 = 30
Number of moles in 60 g of ethane = \(\frac {60}{30}\) = 2 moles.
Question 27.
Calculate the equivalent mass of Copper. (Atomic mass of copper = 63.5)
Answer:
Equivalent mass = \(\frac {Atomic mass}{Valency}\)
Equivalent mass of Copper = \(\frac {63.5}{2}\) = 31.75 g eq-1.
Question 28.
Calculate the equivalent mass of (i) Sulphate ion (ii) Phosphate ion.
Answer:
(i) Sulphate ion (SO42-).
Equivalent mass of Sulphate = ![]() = \(\frac {32 + 64}{2}\) = \(\frac {96}{2}\) = 48 g eq-1
= \(\frac {32 + 64}{2}\) = \(\frac {96}{2}\) = 48 g eq-1
(ii) Phosphate ion (P043-)
Molar mass of Phosphate ion = ![]() = \(\frac {31 + 64}{3}\) = \(\frac {95}{2}\) = 31.6 = 31.6g eq-1
= \(\frac {31 + 64}{3}\) = \(\frac {95}{2}\) = 31.6 = 31.6g eq-1
Question 29.
Calculate the equivalent mass of sulphuric acid.
Answer:
Sulphuric acid = H2SO4
Molar mass of Sulphuric acid = 2 + 32 + 64 = 96
Basicity of Sulphuric acid = 2
Equivalent mass of acid = ![]() = \(\frac {96}{2}\) = 49g eq-1
= \(\frac {96}{2}\) = 49g eq-1
Question 30.
How many moles of hydrogen is required to produce 20 moles of ammonia?
Answer:
3H2 + N2 → 2NH3
A per stoichiometric equation,
No. of moles of hydrogen required for 2 moles of ammonia 3 moles
No. of moles of hydrogen required for 20 moles of ammonia = \(\frac {3}{2}\) x 20 = 30 moles.
Question 31.
Calculate the amount of water produced by the combustion of 32 g of methane.
Answer:

As per stoichiometric equation,
16 g of methane produces 36 g of H2O
∴ 32 g of methane will produce = \(\frac {36}{16}\) x 32 = 72 g of water.
Question 32.
How much volume of Carbon dioxide is produced when 25 g of calcium carbonate is heated completely under standard conditions?
Answer:

100 g of CaCO3 produces 22.4 L of CO2.
∴ 25 g of CaCO3 will produce = \(\frac {22.4}{100}\) x 25 = 5.6 L of CO2.
Question 33.
How much volume of chlorine is required to prepare 89.6 L of HCl gas at STP?
Answer:
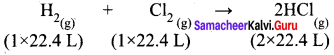
2 x 22.4 L of HCl is produced by 22.4 L of Cl2.
∴ 89.6 L of HCl will be produced by = img = 89.6 L = 44.8 L of chlorine.
Question 34.
What is meant by limiting reagent?
Answer:
A large excess of one reactant is supplied to ensure the more expensive reactant is completely converted to the desired product. The reactant used up first in a reaction is called the limiting reagent.
Question 35.
On the formation of SF6 by the direct combination of S and F2, which is the limiting reagent? Prove it.
Answer:
SF6 is formed by burning Sulphur in an atmosphere of Fluorine. Suppose 3 moles of S is allowed to react with 12 moles of Fluorine.
S(l) +3F2(g) → SF6(g)
As per the stoichiometric reaction, one mole of S reacts with 3 moles of fluorine to complete the reaction. Similarly, 3 moles of S requires only 9 moles of fluorine.
∴ It is understood that the limiting reagent is Sulphur and the excess reagent is Fluorine.
Question 36.
Mention any 4 redox reaction that takes place in our daily life.
Answer:
- Burning of cooking gas, wood
- Rusting of iron articles
- Electroplating
- Galvanic and electrolytic cells
Question 37.
Calculate the oxidation number of underlined elements in the following.
- KMnO4
- Cr2O72-
Answer:
1. KMnO4
1(+1) + x + 4 (-2) = 0
x – 7 = 0
∴ x = + 7
Oxidation state of Mn = +7.
2. Cr2O72-
2x + 7(-2) = -2
2x – 14 = – 2
2x = +l2
∴ x = + 6
Oxidation state of Cr = +6.
Question 38.
If 10 volumes of H2 gas react with 5 volumes of O2 gas, how many volumes of water vapour would be produced?
Answer:
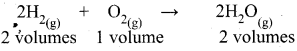
Thus 2 volumes of H2 reacts with 1 volume of O2 to produce 2 volumes of H2O(g).
10 volumes of H2 would react with 5 volumes of O2 to produce 10 volumes of H2O(g)
Thus 10 volumes of H2O will be produced.
Question 39.
Which one of the following will have largest number of atoms?
- 1 g of Au(s)
- 1 g of Na(s)
- 1 g of Li(s)
- 1 g of Cl2 (g)
Answer:
1. Molar mass of Au = 197 g mol-1.
No: of atoms in 1 g of Au = \(\frac {1}{197}\) x 6.023 x 1023
2. Molar mass of Na = 23 g mol-1.
No of atoms in 1 g of Na = \(\frac {1}{23}\) x 6.023 x 1023
3. Molar mass of Li = 7 g mol-1
No. of atoms in 1 g of Li = \(\frac {1}{7}\) x 6.023 x 1023
4. Molar mass of Cl2 = 35.5 g mol-1
No. of atoms in 1 g of Cl2 = \(\frac {1}{35.5}\) x 6.023 x 1023
Comparing the number of atoms, the largest number of atoms will be present in 1 g of Li. Since the mass is same in each case, the element with the lowest molar mass would have the largest number of atoms.
∴ Li with lowest molar mass would have the largest number of atoms.
Question 40.
What will be the mass of one 12C atom in g?
Answer:
Molar mass of 12C = 12.00 g mol-1.
∴ Mass of 6.023 x 1023 carbon atom = 12.0 g
∴ Mass of 1 carbon atom = \(\frac{12}{6.023 \times 10^{23}}\) = 1.992 x 10 g.
Question 41.
Justify the following reaction is a redox reaction.
Answer:
In the above reaction, oxygen is removed from CuO. So CuO gets reduced. Oxygen is added to H2 to form water. So H2 gets oxidised. i.e. In CuO, oxidation number of Cu +2 is reduced to O whereas in H2, oxidation of H2 O is increased to + 1. So the above reaction is a redox reaction.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations 3 – Mark Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish among the different physical states of matter.
Answer:
Differences among three physical states of matter (solid, liquid and gas) are as follows
| S.No. | Properties | Solid | Liquid | Gas |
| 1. | Volume | Definite | Definite | No definite |
| 2. | Shape | Definite | No definite | No definite |
| 3. | Molecular arrangement | Very closely packed | Loosely packed | Very loosely packed |
| 4. | Freedom of movement | Not much freedom | Move around and better than solid | Move easy and fast |
| 5. | Compressibility | Non compressible | Less compressible | Easily compressible |
Question 2.
Define equivalent mass of a salt.
Answer:
Equivalent mass of a salt:
It is defined as the number of parts by mass of the salt that is produced by the neutralization of one equivalent of an acid by a base. Therefore the equivalent mass of the salt is equal to its molar mass.
Question 3.
How much copper can be obtained from 100 g of anhydrous copper sulphate?
Answer:
Anhydrous copper sulphate = CuSO4
Molecular mass of CuSO4 = 63.5 + 32 + (16 x 4)
= 63.5 + 32 + 64
= 159.5 g
159.5 g of CuSO4 contains 63.5 g of copper.
∴ 100 g of CuSO4 contains \(\frac{6.35}{159.5}\) x 100 = 0.39811 x 100 = 39.81 g of Copper.
Question 4.
Calculate the equivalent mass of hydrated ferrous sulphate.
Answer:
Hydrated ferrous sulphate = FeSO4.7H2O
Ferrous sulphate – Reducing agent
Ferrous sulphate reacts with an oxidising agent in acid medium according to the equation.
16 parts by mass of oxygen oxidised 304 g of FeSO4.
8 parts by mass of oxygen will oxidise \(\frac{304}{16}\) x 8 parts by mass of FeSO4.
= 152
Equivalent mass of Ferrous sulphate (Anhydrous) = 152
Equivalent mass of crystalline Ferrous sulphate FeSO4 .7H2O = 152 + 126 = 278
Question 5.
Give difference between empirical and molecular formula
Answer:
Empirical Formula:
- Empirical formula is the simplest formula.
- It shows the ratio of number of atoms of different elements in one molecule of the compound.
- It is calculated from the percentage of composition of the various elements in one molecule.
- For example, Empirical formula of Benzene = CH.
Molecular Formula:
- Molecular Formula is the actual formula.
- It shows the actual number of different types of atoms present in one molecule of the compound.
- It is calculated from the Empirical formula Molecular Formula = (Empirical formula)n
- Molecular formula of Benzene = C6H6.
Question 6.
A sample of hydrated copper sulphate is heated to drive off the water of crystallization, cooled and reweighed 0.869 g of CuSO4 aH2O gave a residue of 0.556 g. Find the molecular formula of hydrated copper sulphate.
Answer:
0.869 g of CuSO4.aH2O gave a residue of 0.556 g of Anhydrous CuSO4.
∴ Weight of a H2O molecule = 0.869 – 0.556 = 0.313 g
Molecular weight of H2O = (1 x 2) + 16 = 2 + 16 = 18
No. of moles of water = \(\frac{Mass}{Molecular mass}\)
CuSO4.5H2O – Molecular mass = 63.5 + 32 + 64 + 90 = 249.5 g
249.5 g of CuSO4.5H2O on heating gives 159.5 g of CuSO4.
0.869 g of CuSO4.aH2O on heating gives = \(\frac{159.5}{249.5}\) x 0.869
= 0.556 g of anhydrous CuSO4 ∴ a = 5
The molecular formula of hydrated copper sulphate = CuSO4.5H2O
Question 7.
Balance by oxidation number method: Mg + HNO3 → Mg(NO3)2 + NO2 + H2O
Step – 1
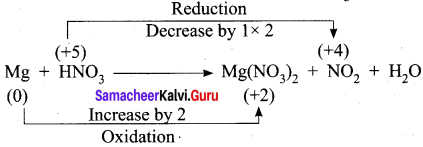
Step – 2
Mg + 2HNO3 -» Mg(NO3)2 + NO2 + H2O
Step – 3
To balance the number of oxygen atoms and hydrogen atoms 2HNO3 is multiplied by 2.
Mg + 4HNO3 → Mg(NO3)2 + 2NO2 + H2O
Step – 4.
To balance the number of hydrogen atoms, the H2O molecule is multiplied by 2.
Mg + 4HNO3 → Mg(NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O
Question 8.
Explain about the classification of matter.
Answer:
Question 9.
Calculate the mass of the following atoms in amu,
(a) Helium (mass of He = 6.641 x 10-24 g)
(b) Silver (mass of Ag = 1.790 x 10-22 g)
1 amu = 1.66056 x 10-24
Answer:
(a) The mass of Helium atom in amu = \(\frac{6.641 \times 10^{-24}}{1.66056 \times 10^{-24}}\) = 3.9992 amu.
(b) The mass of Silver atom in amu = \(\frac{1.790 \times 10^{-22}}{1.66056 \times 10^{-24}}\) = 107.79 amu.
Question 10.
Calculate the number of atoms present in 1 Kg of gold.
Answer:
The atomic mass of Gold = 197 g mol-1.
197 g of gold contains 6.023 x 1023 atoms of gold.
∴ 1000 g of gold will contain = \(\frac{1000 \times 6.023 \times 10^{23}}{197}\)
= 3.055 x 1024 atoms of Gold.
Question 11.
Calculate the molar volume of 146 g of HCl gas and the number of molecules present in it.
Answer:
Molar mass of HCl = 36.5 g
The molar volume of 36.5 g (1 mole) of HCl = 2.24 x 102 m3.
∴ The volume of 146 g (4 moles) of HCl = \(\frac{2.24 \times 10^{-2}}{36.5}\) x 146
= 8.96 x 10 m3
No. of molecules in 146 g of HCl = 4 N
= 4 x Avogadro Number
= 4 x 6.023 x 1023
= 24.092 x 1023
= 2.4092 x 1024 molecules.
Question 12.
Calculate the molar mass of 20 L of gas weighing 23.2 g at STP.
Molar mass =![]()
Molar volume at STP = 2.24 x 10-2 m3 = 22.4 L (or) 22400 cc.
Molar mass of the gas at STP = \(\frac{23.2 x 22.4}{20}\) = 25.984 g.
Question 13.
0.6 g of a metal gives on oxidation 1 g of its oxide. Calculate its equivalent mass.
Answer:
Mass of metal = 0.6
Mass of metal oxide = 1 g
Mass of oxygen = 1 – 0.6 = 0.4 g
0.4 g of oxygen combines with 0.6 g of metal.
∴ 8 g of oxygen will combine with = \(\frac{0.6}{0.4}\) x 8
Equivalent mass of the metal = 12 g eq-1.
Question 14.
How would you calculate the equivalent mass of anhydrous oxalic acid and hydrated oxalic acid.
Answer:
In acid medium,
16 g of oxygen is used for oxidation of 90 g of oxalic acid.
∴ 8 g of oxygen will oxidize = \(\frac{90}{16}\) x 8 = 45 g eq-1.
Equivalent mass of Anhydrous oxalic acid = 45 g eq-1
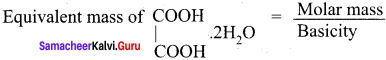
= \(\frac{126}{2}\) = 63 g eq-1.
Question 15.
A compound on decomposition in the laboratory produces 24.5 g of nitrogen and 70 g of oxygen. Calculate the empirical formula of the compound.
Answer:
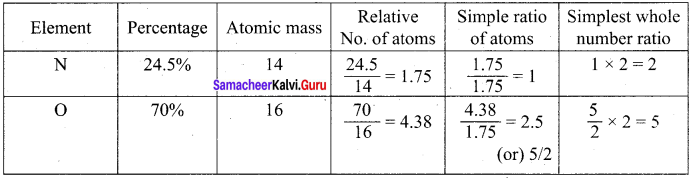
the empirical formula is N2O5
Question 16.
What is the steps involve in the calculation of molecular formula from empirical formula?
Answer:
Molecular mass and empirical formula are used to deduce molecular formula of the compound.
Steps to calculate molecular formula:
- if Empirical formula is found out from the percentage composition of elements
- Empirical formula mass can be found from the empirical formula
- Molecular mass is found out from the given data
- Molecular formula = (Empirical formula)n
- where, n =

![]()
Question 17.
What is combination reaction? Give example.
When two or more substances combine to form a single substance, the reactions are called combination reactions.
A + B → C
Example:
2 Mg + O2 → 2MgO
Question 18.
What is decomposition reaction? Give two examples.
Answer:
Chemical reactions in which a compound splits up into two or more simpler substances are called decomposition reaction.
AB → A + B
Example:
2KCO3 → 2KCl + O2
PCl5 → PCl3 + Cl2
Question 19.
What is displacement reactions? Give its types. Explain with example.
Answer:
The reactions in which one ion or atom in a compound is replaced (or substituted) by an ion or atom of the other element are called displacement reactions.
AB + C → AC + B
Example:
Metal displacement
CuSO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + Cu
Example:
Non-metal displacement
2KBr + Cl2 → 2KCl + Br2
Question 20.
What is disproportionation reactions? Give example.
Answer:
The reactions in which an element undergoes simultaneously both oxidation and reduction are called as disproportionation reactions.
Example:
P4 + 3NaOH + 3H2O → PH3 + 3NaH2PO2
2HCHO + H2O → CH3OH + HCOOH
Question 21.
What are competitive electron transfer reaction? Give example.
Answer:
These are the reactions in which redox reactions take place in different vessels and it is an indirect redox reaction. There is a competition for the release of electrons among different metals.
Example:
Zn releases electrons to Cu and Cu releases electrons to Silver and so on.
Zn(s) + Cu2+ → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) (Here Zn – oxidised; Cu2+ – reduced)
Cu(s) + 2Ag+ → Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s) (Here Cu – oxidised; Ag+ – reduced)
Question 22.
Balance the following equation using oxidation number method.
Answer:
1. S + HNO3 → H2SO4 + NO2 + H2O
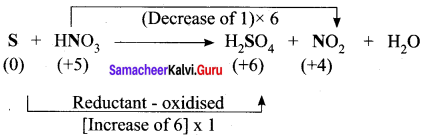
2. S + 6HNO3 → H2SO4 + NO2 + H2O
3. Balance the equation (except O and H)
S + 6HNO3 → H2SO4 + 6NO2 + H2O
4. Balance O atoms by adding 2H2O
5 + 6HNO3 → H2SO4 + 6NO2 + 2H2O
Question 23.
Determine the empirical formula of an oxide of iron which has 69.9% iron and 30.1% oxygen by mass.
Answer:
the empirical formula is Fe2O3
Question 24.
In three moles of ethane (C2H6) calculate the following:
- Number of moles of carbon atoms.
- Number of moles of hydrogen atoms.
- Number of molecules of ethane.
Answer:
(1) 1 mole of C2H6 contains 2 moles of Carbon atoms.
∴ 3 moles of C2H6 will have 6 moles of Carbon atoms.
(2) 1 mole of C2H6 contains 6 moles of Hydrogen atoms.
∴ 3 moles of C2H6 will have 18 moles of Hydrogen atoms.
(3) 1 mole of C2H6 contains 6.023 x 1023 number of molecules.
∴ 3 moles of C2H6 will contain 3 x 6.023 x 1023molecules.
Question 25.
Chlorine is prepared in the laboratory by treating manganese dioxide (MnO2) with aqueous hydrochloric acid according to the reaction.
4HCl(aq) + MnO2(s) → 2H2O(l) + MnCl2(aq) + Cl2(aq)
How many grams of HCl react with 5.0 g of manganese dioxide? (Atomic mass of Mn = 55 g).
Answer:
1 mole of MnO2 = 55 + 32 = 87 g.
87 g of MnO2 reacts with 4 moles of HCl. i.e. = 4 x 36.5 = 146 g of HCl.
∴ 5 g of MnO2 will react with \(\frac{146}{87}\) x 5.0 = 8.40 g.
Question 26.
The density of water at room temperature is 1.0 g/ml. How many molecules are there in a drop of water if its volume is 0.05 ml?
Answer:
Volume of drop of water = 0.05 ml
Mass of a drop of water = Volume x Density
= 0.05 ml x 1.0 g / ml.
= 0.05 g
Molar mass of water (H2O) = 18 g
18 g of water = 1 mole
0. 05 g of water = \(\frac{1}{18}\) x 0.05 = 0.0028 mol.
No. of molecules present in one mole of water = 6.023 x 1023
No. of molecules present in 0.0028 mole of water = \(\frac{6.023 \times 10^{23} \times 0.0028}{1}\) = 1.68 x 1021 water molecules
Question 27.
Balance the following equation by oxidation number method. MnO4– + Fe2+ → Mn 2+ + Fe3+ (Acidic medium)
Answer:
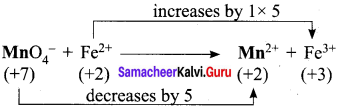
MnO4– + 5e– → Mn2+ ……….(1)
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e– ……….(2)
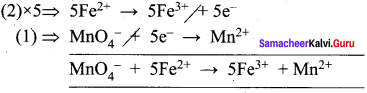
to balance O and H atoms H2O and H+ are added.
MnO4– + 5Fe2+ + 8H+ → 5Fe3+ + Mn2+ + 4H2O
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Chemistry Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations 5-Mark Questions
I. Answer the following questions in detail
Question 1.
Define the following (a) equivalent mass of an acid (b) equivalent mass of a base (c) equivalent mass of an oxidising agent (cl) equivalent mass of a reducing agent.
Answer:
(a) Equivalent mass of an acid:
Equivalent mass of an acid is the number of parts by mass of the acid which contains 1.008 part by mass of replaceable hydrogen atom.
Equivalent mass of an acid = ![]()
(b) Equivalent mass of a base:
It is defined as the number of parts by mass of the base which contains one replaceable hydroxyl ion or which completely neutralizes one gram equivalent of an acid.
Equivalent mass of a base = ![]()
(c) Equivalent mass of an oxidising agent:
It is defined as the number of parts by mass of an oxidising agent which can furnish 8 parts by mass of oxygen for oxidation.
(d) Equivalent mass of a reducing agent:
It is defined as the number of parts by mass of the reducing agent which is completely oxidised by 8 parts by mass of oxygen or with one equivalent of any oxidising agent.
Question 2.
Calculate the percentage composition of the elements present in lead nitrate. How many Kg of 02 can be obtained from 50 kg of 70% pure lead nitrate?
Answer:
Lead nitrate = Pb (NO3)2
Molecular mass of lead nitrate = 207 + (14 x 2) + (16 x 6)
= 207 + 28 + 96 = 331 g / mol.
331 g of lead nitrate contains 96 g of oxygen.
∴ 50 x 103 g of lead nitrate will contain \(\frac {96}{331}\) x 50 x 103
= 14501.5 g
= 14.501 Kg of oxygen.
100 % pure lead nitrate contains 14.501 Kg of oxygen.
70 % pure lead nitrate will contain = \(\frac {14.501}{100}\) x 70 = 10.15 Kg of oxygen.
.’. 70 % pure lead nitrate will contain 10.15 Kg of oxygen.
Question 3.
Determine the empirical formula of a compound containing K = 24.15%, Mn = 34.77% and rest is oxygen.
Answer:
empirical formula of a compound = KMnO4
Question 4.
Write the steps to be followed for writing empirical formula.
Answer:
Empirical formula shows the ratio of number of atoms of different elements in one molecule of the compound.
Steps for finding the Empirical formula:
The percentage of the elements in the compound is determined by suitable methods and from the data collected; the empirical formula is determined by the following steps.
- Divide the percentage of each element by its atomic mass. This will give the relative number of atoms of various elements present in the compound.
- Divide the atom value obtained in the above step by the smallest of them so as to get a simple ratio of atoms of various elements.
- Multiply the figures so obtained, by a suitable integer if necessary in order to obtain whole number ratio.
- Finally write down the symbols of the various elements side by side and put the above numbers as the subscripts to the lower right hand of each symbol. This will represent the empirical formula of the compound.
- Percentage of Oxygen = 100 – Sum of the percentage masses of all the given elements.
Question 5.
An organic compound was found to contain carbon = 40.65%, hydrogen = 8.55% and Nitrogen = 23.7%. Its vapour density was found to be 29.5. What is the molecular formula of the compound?
Answer:
Empirical formula = C2H5NO
Molecular mass = 2 x vapour density = 2 x 29.5 = 59.0
Empirical formula mass of C4H5NO = 24 + 5 + 14 + 16 = 59
n = ![]() = \(\frac {59}{59}\) = 1
= \(\frac {59}{59}\) = 1
Empirical formula mass 59
.’. Molecular formula = (Empirical formula)n
= (C2H5NO)1
Molecular formula = C2H5NO
Question 6.
Calculate the empirical and molecular formula of a compound containing 32% carbon, 4% hydrogen and rest oxygen. Its vapour density is 75.
Answer:
Empirical formula = C2H3O3
Empirical formula mass = 24 + 3 + 48 = 75
Molecular mass = 2 x Vapour density = 2 x 75 = 150
n = ![]() = \(\frac {150}{75}\) = 2
= \(\frac {150}{75}\) = 2
Molecular formula = (Empirical formula)n
Molecular formula = C2H3O3 x 2
Molecular formula = C4H6O6
Question 7.
Explain the different types of redox reactions with example.
Answer:
Redox reactions are classified into the following types:
(1) Combination reactions:
When two or more substances combine to form a single substance, the reactions are called combination reactions.
Example:
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
(2) Decomposition reactions:
Chemical reactions in which a compound splits up into two or more simpler substances are called decomposition reaction.
Example:
2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2
(3) Displacement reactions:
The reactions in which one ion or atom in a compound is replaced by an ion or atom of the other element are called displacement reactions.
Example:
CuSO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + Cu
(4) Disproportionation reactions:
The reactions in which an element undergoes simultaneously both oxidation and reduction are called as disproportionation reactions.
Example:
2HCHO + H2O → CH3OH + HCOOH
(5) Competitive Electron transfer reactions:
These are the reactions in which redox reactions take place in different vessels and it is an indirect redox reaction. There is a competition for the release of electrons among different metals.
Example:
Zn(s) + Cu2+ → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) Here Zn – oxidised; Cu2+ reduced
Question 8.
Write the steps to be followed while balancing redox equation by oxidation number method.
Answer:
Oxidation number method:
This method is based on the fact that
Number of electrons lost by atoms = Number of electrons gained by atoms
Steps to be followed while balancing Redox reactions by Oxidation Number method:
- Write skeleton equation representing redox reaction
- Write the oxidation number of atoms undergoing oxidation and reduction.
- Calculate the increase or decrease in oxidation numbers per atom.
- Make increase in oxidation number equal to decrease in oxidation number by multiplying the formula of oxidant and reductant by suitable numbers.
- Balance the equation atomically on both sides except O and H atoms.
- Balance oxygen atoms by adding required number of water molecules to the side deficient
in oxygen atoms. - Add required number of H+ ions to the side deficient in hydrogen atom if the reaction is in acidic medium.
- For reactions in basic medium, add H2O molecules to the side deficient in hydrogen atoms and simultaneously add equal number of OH ions on the other side of the equation.
- Finally balance the equation by cancelling common species present on both sides of the equation.
Question 9.
Balance the following equation by oxidation number method:
Answer:
K2Cr2O7 + KCl + H2SO4 → KHSO4 + CrO2Cl 2 + H2O
Step – 1
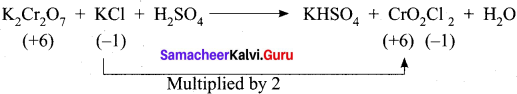
Step – 2
K2Cr2O7 + KCl + H2SO4 → KHSO4 + 2CrO2C2 + H2O
Step 3.
To balance Cl atom, KC1 is multiplied by 4
K2Cr2O7 + 4KCl + H2SO4 → 2CrO2Cl2 + KHSO2 + H2O
Step 4.
To balance K atom, KHSO4 is multiplied by 6.
K2Cr2O7 + 4KCl + H2SO4 → 2CrO2Cl2 + 6KHSO4+ H2O
Step 5.
To balance O and H atoms, HSO4 is multiplied by 6, H20 is multiplied by 3.
Answer:
K2Cr2O7 + 4KCl + 6H2SO4 → 2CrO2Cl2 + 6KHSO4 + 3H2O
(2) P + HNO3 → H3PO4 + NO2 + H2O
Step – 1
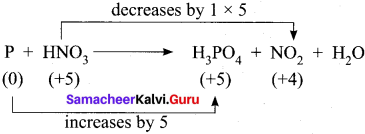
Step 2.
P + 5HNO3 → H3PO4 + 5NO2 + H2O
(3) CuO + NH3 → Cu + N2 + H2O
Step 1.
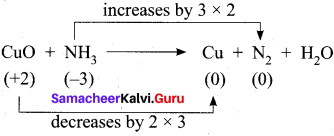
Step 2.
3CuO + 2NH3 → 3Cu + N2 + H2O
Step 3.
To balance O and N, water is multiplied by 3.
3CuO + 2NH3 → 3Cu + N2 + 3H2O
(4) Zn + HNO3 →Zn(N03)2 + NH4NO3 + H2O
Step – 1.

Step 2.
4Zn + HNO3 → 4Zn(NO3)3 + NH4NO2 + H2O
Step 3.
To balance N, HNO3 is multiplied by 10
4Zn + 10HNO3 → 4Zn(NO3)2 + NH4NO3 + H3O
Step 4.
To balance oxygen, H2O is multiplied by 3
4Zn + 10HNO3 → 4Zn(NO3)2 + NH4NO3 + 3H3O
Question 10.
Balance the following equation by ion-electron method In acidic medium.
Answer:
(i) S2O32- + I2 → S2O42- + SO2 + I–
Oxidation half reaction:
![]()
Reduction half reaction:
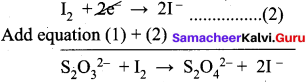
To balance, SO2 is added on RHS of the equation.
S2O32- + I2 → S2O42- + 2I– + SO2
To balance oxygen atom, S2O32- and SO2 is multiplied by 2.
2S2O32- + I2 → S2O42- + 2I – + 2SO2
(2) Sb3+ + MnO4 → Sb5+ + Mn2+
Oxidation half reaction:
Sb3+ → Sb5+ + 2e – ……….(1)
Reduction half reaction:
![]()
In equation (2), H2O is added on L.HS to balance oxygen atom.
MnO2 + 5e– → Mn2+ + 4H2O ………(3)
To balance Hydrogen atoms, H’ is added on RHS.
MnO4– + 5e– + 8H+ → Mn2+ + 4H2O ………(4)
Equation (4) is multiplied by 2 and equation (I) is multiplied by 5 to equalise the electrons gained and electrons lost.

(3) MnO4– + I– → MnO2 + I2
Oxidation half reaction:
2I– + 2e– → I– ………..(1)
Reduction half reaction:
MnO4– → MnO2 + e– ………..(2)
Equation (1)is multiplied by 3
![]()
Equation (2)is multiplied by 2.
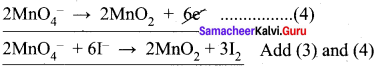
To balance oxygen and hydrogen atoms, H+ is added on RHS and H2O is added on LHS.
2MnO4 + 6I– + 4H+ → 2MnO2 + 2I2 + 2H2O
In acidic medium
(4) MnO4– + Fe2+ → Mn2+ + Fe3+
Oxidation half reaction:
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e– ……..(1)
Reduction half reaction:

To balance oxygen, H+ is added on RHS and H2O is added on LHS.
MnO4– + 5Fe2+ + 8H+ → Mn2+ + 5Fe3+ + 4H2O
(5) Cr(OH)4– + H2O2 → CrO4–
Oxidation half reaction:
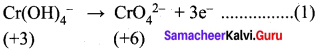
Reduction half reaction:
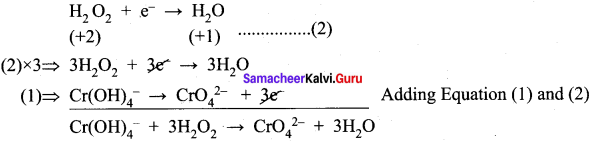
To balance oxygen and hydrogen atoms, OH and H2O are added.
2Cr(OH)4 + 3H2O2 + 20H– → 2CrO2– + 8H2O
Question 11.
(a) Define equivalent mass of an oxidising agent.
(b) How would you calculate the equivalent mass of potassium permanganate?
(a) The equivalent mass of an oxidizing agent is the number of parts by mass which can furnish 8 parts by mass of oxygen for oxidation.
(b) Potassium permanganate is an oxidizing agent.

80 parts by mass of oxygen are given by 316 g of KMnO4.
.’. 8 parts by mass of oxygen will be furnished by \(\frac {316}{80}\) x 8 = 31.6
Equivalent mass of KMnO4 = 31.6 g eq-1.
Question 12.
(a) Define equivalent mass of an reducing agent.
(b) How would you determine the equivalent mass of Ferrous sulphate?
Answer:
(a) The equivalent mass of a reducing agent is the number of parts by mass of the reducing agent which is completely oxidised by 8 parts by mass of oxygen or one equivalent of any oxidising agent.
(b) Ferrous sulphate is a reducing agent.
![]()
16 parts by mass of oxygen oxidised 304 parts by mass of FeSO4.
∴ 8 parts by mass of oxygen will oxidise \(\frac {316}{80}\) x 8 parts by mass of ferrous sulphate = 152 .
The equivalent mass of ferrous sulphate (anhydrous) = 152.
The equivalent mass of crystalline ferrous sulphate is (FeSO4.7H2O) = 152 + 126 = 278
The equivalent mass of crystalline ferrous sulphate = 278.
Question 13.
A compound on analysis gave the following percentage composition: C = 24.47%, H = 4.07 %, Cl = 7 1.65%. Find out its empirical formula.
Answer:
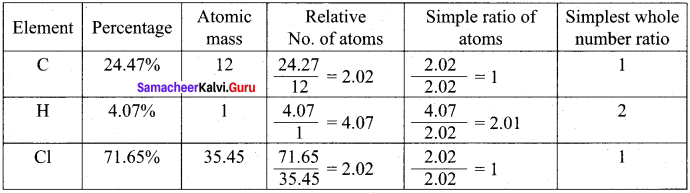
the empirical formula is CH2Cl.
Question 14.
A laboratory analysis of an organic compound gives the following mass percentage composition: C = 60%, H = 4.48% and remaining oxygen.
Answer:
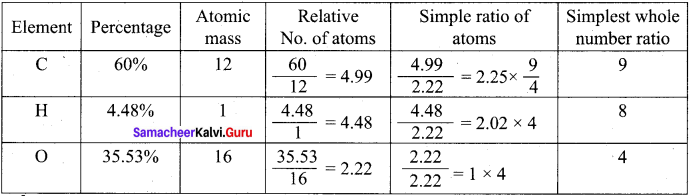
∴ the empirical formula is C9H8O4.
Question 15.
An insecticide has the following percentage composition by mass: 47.5% C, 2.54% H, and 50.0% Cl. Determine its empirical formula and molecular formulae. Molar mass of the substance is 354.5 g mol-1
Answer:
The empirical formula is C14H9C15.
Calculation of Molecular formula:
The empirical formula mass (C14H9C15) = (14 X 12) + (9 X 1) + (5 X 35.5)
n = ![]() = \(\frac {354.5}{354.5}\) = 1
= \(\frac {354.5}{354.5}\) = 1
Empirical formula mass 354.5
Molecular formula = (Empirical formu1a)n
= (C14H9Cl5)1
∴ Molecular formula = C14H9Cl5
Question 16.
An organic fruit smelling compound on analysis has the following composition by mass: C = 54.54%, H = 9.09%, O = 36.36%. Find out the molecular formula of the compound. The vapour density of the compound was found to be 44.
Answer:
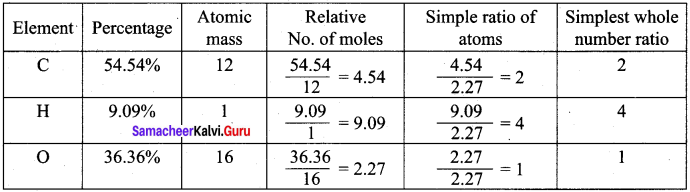
∴ The empirical formula is C2H4O
Theempirical formula mass(C2H4O) = (12 x 2)+(1 x 4)+(16 x 1) = 44
Molecular mass = 2 x Vapour density = 2 x 44 = 88
n = ![]() = \(\frac {88}{44}\) = 2
= \(\frac {88}{44}\) = 2
Molecular formula = (Empirical formula)n
= (C2H4O)2
∴ Molecular formula = C2H4O2
Question 17.
Calculate the percentage composition of the elements present in magnesium carbonate. How many Kg of CO2 can be obtained from 100 Kg of is 90% pure magnesium carbonate.
Molar mass of MgCO3 = 84.32 g mol-1
Percentage of Mg = \(\frac {24}{84.32}\) x 100 = 28.46%
Percentage of C = \(\frac {12}{84.32}\) x 100 = 14.23%
Percentage of O3 = \(\frac {48}{84.32}\) x 100 = 57.0%
![]()
84.32 g of 100% pure MgCO3 gives 44g of CO2
∴ 100 x 103g of 100% pure MgCO3 gives = \(\frac {44}{84.32}\) x 100 x 103
= 52.182 x 103 g CO2
100% pure MgCO3 gives 52.182 x 103 g CO2
∴ 90% pure MgCO3 will give \(\frac{52.182 \times 10^{3}}{100}\) x 90 = 46963.8 g CO2
Question 18.
Urea is prepared by the reaction between ammonia and carbon dioxide.
![]()
In one process, 637.2 g of NH3 are allowed to react with 1142 g of CO2.
(a) Which of the two reactants is the limiting reagent?
(b) Calculate the mass of(NH4)2CO formed.
(c) how much of the excess reagent in grams is left at the end of the reaction?
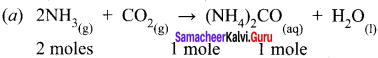
No. of moles of ammonia = \(\frac{637.2}{17}\) = 37.45 mole
No. of moles of CO2 = \(\frac{1142}{44}\) = 25.95 moles
As per the balanced equation, one mole of CO2 requires 2 moles of ammonia.
∴ No. of moles of NH3 required to react with 25.95 moles of CO2 is = \(\frac {2}{1}\) x 25.95 = 51.90 moles.
∴ 37.45 moles of NH3 is not enough to completely react with CO2 (25.95 moles).
Hence, NH3 must be the limiting reagent, and CO2 is excess reagent.
(b) 2 moles of ammonia produce 1 mole of urea.
∴ Limiting reagent 37.45 moles of NH3 can produce \(\frac {1}{2}\) x 37.45 moles of urea.
= 18.725 moles of urea.
∴ The mass of 18.725 moles of urea = No. of moles x Molar mass
= 18.725 x 60
= 1123.5 g of urea.
(c) 2 moles of ammonia requires 1 mole of CO2.
∴ Limiting reagent 37.45 moles of NH3 will require x 37.45 moles of CO2.
= 18.725 moles of CO2.
∴ No. of moles of the excess reagent (CO2) left = 25.95 – 18.725 = 7.225
The mass of the excess reagent (CO2) left = 7.225 x 44 = 317.9 g CO2.
Question 19.
(a) Define oxidation number.
(b) What are the rules used to assign oxidation number?
Answer:
(a) Oxidation number refers to the number of charges an atom would have in a molecule or an ionic compound, if electrons were transferred completely.
(b) Rules to assign oxidation number:
- Oxidation number of a substance in its elementary state is equal to zero (H2, Br2, Na)
- Oxidation number of a mono-atomtic ion is equal to the charge on the Ton (Na4 =+ 1,
- Oxidation number of hydrogen in a compound is +1 (except hydrides).
- Oxidation number of hydrogen in metal hydrides is -1 (NaH, CaH2).
- Oxidation number of oxygen in a compound is -2 (except OF2 and peroxides).
- Oxidation number of oxygen in peroxides is -1 (He,, Na»,) = I.
- Oxidation number of oxygen in fluorinated compounds is either +1 or +2.(OF2 = +2, O,F2 + 1).
- Fluorine has an oxidation number -1 in all ìts compounds.
- The sum of the oxidation number of all the atoms in neutral molecules is equal to Zero.
- For all ions, the sum of the oxidation number of all atoms is equal to the charge of the ion.
Question 20.
Balance the following equation by oxidation number method.
C6H6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O
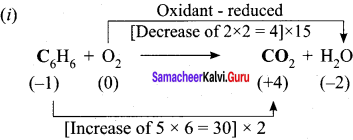
(ii) Balance the changes in O.N. by multiplying the oxidant and reductant by suitable numbers
2 C6H6 + 15 O2 → CO2 + H2O
(iii) Balance the equation atomically (except O and H).
2C6H6 + 15 O2 → 12 CO2 + H2O
(iv) Balance O atoms by adding one HzO molecule to the RHS for making the number of molecules of H2O to be 6.
2C6H6 + 15 O2 → 12 CO2 + 6H2O
Question 21.
Balance the following equation by oxidation number method.
KMnO4 + HCl → KCl + MnCl2 + H2O + Cl2
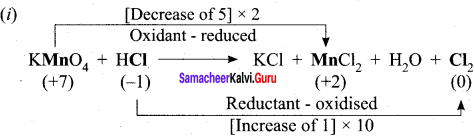
(ii) 2KMnO4 + 1OHCl → KCl + MnCl2 + H2O + Cl2
(iii) Balance the equation atomically (except O and H).
2KMnO4 + 1OHCl → 2KCl + 2MnCl2, + H2O + Cl2
(iv) Balance chlorine atoms by adding HC1 and multiplying Cl2 by 5.
2KMnO4 + 16HCl → 2KCl + 2MnCl2 + H2O + 5Cl2
(v) To balance O and H, H2O is multiplied by 8.
2KMnO4 + I6HCl → 2KCl + 2MnCl4 + 8H2O + 5Cl2
Question 22.
Balance the following equation by oxidation number method.
KMnO4 + FeSO4 + H2S04 → K2SO4 + MnSO4 + Fe2(S04)3 + H2O
Answer:
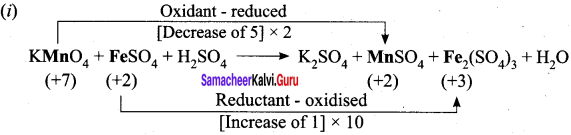
(ii) 2KMnO4 + 10FeSO4 + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + MnSO4 + Fe2(SO4)3+ H2O
(iii) Balance the equation atomically (except O and H) and sulphate ions.
2KMnO4 + 1OFeSO4 + 8H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 5Fe4(SO4)3 + H2O
(iv) Balance O atoms by multiplying H2O by 8.
2KMnO4 + 1OFeSO4 + 8H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 5Fe2(SO4)3 + 8H2O
Question 23.
Balancing of molecular equation in alkaline medium.
MnO2 + O2 + KOH → K2MnO4 + H2O
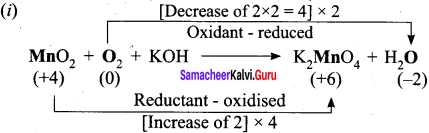
(ii) Balance the changes in O, N, by multiplying the oxidant and reductant by suitable numbers.
4MnO2 + 2O2+ KOH → K2MnO4 + H2O
(iii) Balance the equation atomically (except O and H).
4MnO2 + 2O2 + KOH → K2 MnO4 + H2O
(iv) Balance oxygen and hydrogen atoms by multiplying H20 by 4.
4MnO2 + 2O2 + 8KOH → 4K2MnO4 + 4H2O
Question 24.
Explain the steps involved in ion-electron method for balancing redox reaction.
Answer:
Ion electron method makes use of the Half reactions. Steps involved in this method are,
- Write the equation in the net ionic form without attempting to balance it.
- Write and locate the oxidation number of atoms undergoing oxidation and reduction from the knowledge of calculation of oxidation number.
- Write two half reactions showing oxidation and reduction separately.
- Balance oxygen atoms by adding required number of water molecules to the side deficient in oxygen atoms.
- Add required number of H+ ions to the side deficient in hydrogen atom if the reaction is in acidic medium
- Add electrons to whichever side is necessary to make up the difference in oxidation number.
- Add the two half reactions. The resulting equation is a net balanced equation.
- For reactions in basic medium, add H2O and hydrogen ion to balance H and O.
- Finally balance the equation by cancelling common species present on both sides of the equation.
Question 25.
Write balanced equation for the oxidation of Ferrous ions to Ferric ions by permanganate ions in acid solution. The permanganate ion forms Mn2+ ions under these conditions.
Answer:
Net ionic reaction:
MnO4– + Fe2+ + H+ → Mn2+ + Fe3+
Oxidation half reaction:
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e– ……….(1)
Reduction half reaction:
MnO4– + 5e– → Mn2+ ……….(2)
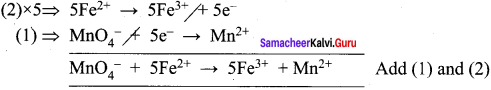
To balance O and H, H+ and H2O are added.
MnO4– + 5Fe2+ + 8H+ → Mn2+ + 5Fe3+ +4H2O
Question 26.
A flask A contains 0.5 mole of oxygen gas. Another flask B contains 0.4 mole of ozone gas. Which of the two flasks contains greater number of oxygen atoms.
Answer:
Flask A:
1 mole of oxygen gas = 6.023 x 1023 molecules
∴ 0.5 mole of oxygen gas = 6.023 x 1023 x 0.5 molecules
The number of atoms in flask A = 6.023 x 1023 x 0.5 x 2 = 6.023 x 1023 atoms.
Flask B:
1 mole of ozone gas = 6.023 x 1023 molecules
0. 4 mole of ozone gas = 6.023 x 1023 x 0.4 molecules
The number of atoms in flask B = 6.023 x 1023 x 0.4 x 3 = 7.227 x 1023 atoms.
∴ Flask B contains a great number of oxygen atoms as compared to flask A.
Question 27.
(a) Formulate possible compounds of ‘Cl’ in its oxidation state is:
0, – 1, + l, + 3,+ 5, + 7
(b) H2O2 act as an oxidising agent as well as reducing agent where as O3 act as only oxidizing agent. Prove it.
(a) (1) Cl oxidation number O in Cl2.
(2) Cl oxidation number -1 in HCl.
(3) Cl oxidation number +3 in HCl O2.
(4) Cl oxidation number +5 in KClO3.
(5) Cl oxidation number +7 in C12O7.
(b) In H2O2, oxidation number of oxygen is -1 and it can vary from O to -2 (+ 2 is possible in OF2). The oxidation number can decrease or increase, because of this H2O2 can act both oxidising and reducing agent. Ozone (O3 ) only acts as oxidising agent since it decomposes to give nascent oxygen.
Question 28.
The Mn3+ ion is unstable in solution and undergoes disproportionation to give Mn2+, MnO2 and H ion. Write a balanced ionic equation for the reaction.
The skeletal equation is:
Mn3+(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + MnO2(aq) + H+(aq)
Oxidation half equation:
![]()
Balance O.N. by adding electrons,
Mn3+(aq) → MnO2(s) + e–
Balance charge by adding 4H ions,
Mn3+(aq) → MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + e–
Balance O atoms by adding 2H2O
Mn3+(aq) + 22H2O(l) → MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + e– ……….(1)
Reduction half equation:
![]()
Balance ON. by adding electrons:
Mn3+(aq) + e– → Mn2+(aq) …………(2)
Adding Equation (1) and (2), the balanced equation for the disproportionation reaction is
2MH3+(aq) + 2H2O(l) → MnO2(s) + Mn2+(aq) + H+(aq)
Question 29.
Chlorine is used to purify drinking water. Excess of chlorine is harmful. The excess chlorine is removed by treating with sulphur dioxide. Present a balanced equation for the reaction for this redox change taking place in water.
The skeletal equation is:
Cl2(aq) + SO2(aq) + H2O(l) → Cl–(aq) + SO42-(aq)
Reduction half equation:
Cl2(aq) → Cl2-(aq)
Balance Cl atoms,
![]()
Balance O.N. by adding electrons
Cl2(aq) + 2e– → 2Cl + 2e–
Oxidation half equation:
![]()
Balance O,N. by adding electrons
SO2(aq) → SO42-(aq) + 2e–
Balance charge by adding 4H+ ions:
SO2(aq) → SO42-(aq) + 4H+(aq) + 2e–
Balance O atoms by adding 2H2O
SO2(aq) + 2H2O(l) → SO42-(aq) + 4H+(aq) + 2e–
Adding equation (1) and (2), we have,
Cl2(aq) + SO2(aq) + 2H2O(l) → Cl–2(aq) + SO42-(aq) + 4H+(aq)
This represents the balanced redox reaction.
We as a team believe the information prevailing regarding the Samacheer Kalvi Solutions for 11th Chemistry Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations has been helpful in clearing your doubts to the fullest. For any other help do leave us your suggestions and we will look into them. Stay in touch to get the latest updates on Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for different subjects in the blink of an eye.