Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 8th Tamil Book Solutions Guide Pdf Chapter 6.3 கொங்குநாட்டு வணிகம் Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Tamil Solutions Chapter 6.3 கொங்குநாட்டு வணிகம்
கற்பவை கற்றபின்
Question 1.
உங்கள் மாவட்டம் பற்றிய செய்திகளைத் திரட்டி எழுதுக.
Answer:
எங்களுடைய மாவட்டம் ஈரோடு மாவட்டம் ஆகும். கணிதமேதை ராமானுஜம், புலவர் குழந்தை, தீரன் சின்னமலை ஆகிய சான்றோர்கள் பிறந்து வளர்ந்த மாவட்டம் ஈரோடு மாவட்டம். அந்தியூர் குருநாதசாமி திருக்கோயில், பாரியூர் அம்மன் கோயில், பண்ணாரி அம்மன் கோயில், கொடுமுடி மகுடேஸ்வரர் கோயில் ஆகிய சிறப்புமிக்க கோயில்கள் அமைந்துள்ளன. பழமையான பிரப் தேவாலயம், மிட்டுமியா பாபா தர்கா, அலாவுதீன் பாட்சா தர்கா ஆகியவை அமைந்துள்ளன. வெள்ளோடு பறவைகள் சரணாலயம் ஈரோட்டில் தான் உள்ளது.
Question 2.
பல்வகைத் தொழில்கள் என்னும் தலைப்பில் படத்தொகுப்பு உருவாக்குக.
Answer:



பாடநூல் வினாக்கள்
சரியான விடையைத் தேர்ந்தெடுத்து எழுதுக.
Question 1.
‘வண்புகழ் மூவர் தண்பொழில் வரைப்பு’ என்று குறிப்பிடும் நூல் …………………………..
அ) தொல்காப்பியம்
ஆ) அகநானூறு
இ) புறநானூறு
ஈ) சிலப்பதிகாரம்
Answer:
அ) தொல்காப்பியம்
Question 2.
சேரர்களின் தலைநகரம் ……………………
அ) காஞ்சி
ஆ) வஞ்சி
இ) தொண்டி
ஈ) முசிறி
Answer:
ஆ) வஞ்சி
Question 3.
பழங்காலத்தில் விலையைக் கணக்கிட அடிப்படையாக அமைந்தது ……………………
அ) புல்
ஆ) நெல்
இ) உப்பு
ஈ) மிளகு
Answer:
ஆ) நெல்
Question 4.
ஆன்பொருநை என்று அழைக்கப்படும் ஆறு ……………….
அ) காவிரி
ஆ) பவானி
இ) நொய்யல்
ஈ) அமராவதி
Answer:
ஈ) அமராவதி
Question 5.
வீட்டு உபயோகப் பொருள்கள் தயாரிக்கும் தொழிற்சாலைகள் நிறைந்த மாவட்டம்
அ) நீலகிரி
ஆ) கரூர்
இ) கோயம்புத்தூர்
ஈ) திண்டுக்கல்
Answer:
இ) கோயம்புத்தூர்
கோடிட்ட இடங்களை நிரப்புக.
1. ‘மாங்கனி நகரம்’ என்று அழைக்கப்படும் நகரம் ………………………..
2. சுங்குடிச் சேலைகளுக்குப் புகழ்பெற்ற ஊர் …………………..
3. சேரர்களின் நாடு ………………….. எனப்பட்டது.
4. பின்னலாடை நகரமாக …………………. விளங்குகிறது.
Answer:
1. சேலம்
2. சின்னாளப்பட்டி (திண்டுக்கல்)
3. குடநாடு
4. திருப்பூர்
குறுவினா
Question 1.
மூவேந்தர்களின் காலம் குறித்து எழுதுக.
Answer:
- மூவேந்தர்களின் காலத்தை வரையறுத்துக் கூறமுடியவில்லை.
- வால்மீகி இராமாயணம், மகாபாரதம், அர்த்தசாத்திரம், அசோகர் கல்வெட்டு ஆகியவற்றில் மூவேந்தர்கள் குறித்த செய்திகள் இடம்பெற்றுள்ளன.
- இதனால் இவர்கள் பல நெடுங்காலத்திற்கு முற்பட்டவர்கள் என்பதை அறியலாம்.
Question 2.
கொங்கு நாட்டில் பாயும் ஆறுகள் யாவை?
Answer:
காவிரி, பவானி, நொய்யல், ஆன்பொருநை (அமராவதி).
Question 3.
‘தமிழ்நாட்டின் ஹாலந்து’ என்று அழைக்கப்படும் ஊர் எது? ஏன்?
Answer:
- ‘தமிழ்நாட்டின் ஹாலந்து’ என்று அழைக்கப்படும் ஊர் திண்டுக்கல்.
- மலர் உற்பத்தியில் முதலிடம் வகிப்பதால், தமிழ்நாட்டின் ஹாலந்து என்று திண்டுக்கல் நகரம் போற்றப்படுகிறது.
சிறுவினா
Question 1.
கொங்கு மண்டலச் சதகம் கூறும் கொங்கு மண்டலத்தின் எல்லைகள் யாவை?
Answer:
வடக்கே பெரும்பாலை தெற்கே பழனி மலை, மேற்கே வெள்ளிமலை, கிழக்கே மதிற்கூரை என இந்நான்கு எல்லைக்கு உட்பட்ட பகுதியாகக் கொங்கு மண்டலம் விளங்கியதாகக் கொங்கு மண்டலச் சதகம் கூறுகிறது.
Question 2.
கரூர் மாவட்டம் பற்றிய செய்திகளைச் சுருக்கி எழுதுக.
Answer:
(i) கரூர் நகரத்திற்கு, வஞ்சிமா நகரம்’ என்ற பெயரும் உண்டு. கிரேக்க அறிஞர் தாலமி கரூரைத் தமிழகத்தின் முதன்மை உள்நாட்டு வணிக மையமாகக் குறிப்பிட்டுள்ளார்.
(ii) நெல், சோளம், கேழ்வரகு, கம்பு, கரும்பு போன்றவை இங்குப் பயிரிடப்படுகின்றன. கல்குவாரித் தொழிற்சாலைகள் இங்கு உள்ளன.
(iii) கைத்தறி நெசவு ஆடைகளுக்குப் பெயர் பெற்ற மாவட்டமாகக் கரூர் விளங்குகிறது.
(iv) தோல் பதனிடுதல், சாயம் ஏற்றுதல், சிற்ப வேலைகள் போன்ற தொழில்களும் நடைபெறுகின்றன.
(v) பேருந்துக் கட்டுமானத் தொழிலின் சிகரமாகக் கரூர் விளங்குகிறது.
நெடுவினா
Question 1.
கொங்கு நாட்டின் உள்நாட்டு, வெளிநாட்டு வணிகம் குறித்து எழுதுக.
Answer:
உள்நாட்டு, வெளிநாட்டு வணிகத்தில் தமிழர்கள் சிறந்து விளங்கி உள்ளனர். கடல் வணிகத்தில் சேர நாடு சிறப்புற்றிருந்தது.
உள்நாட்டு வணிகம் :
சேர நாட்டில் உள்நாட்டு வணிகமும் நன்கு வளர்ச்சியுற்று இருந்தது. மக்கள் தத்தம் பொருள்களைத் தந்து தமக்குத் தேவையான பொருளைப் பெற்றனர். நெல்லின் விலையைக் கணக்கிட அடிப்படையாக இருந்தது என்பர். உப்பும் நெல்லும் ஒரே மதிப்புடையனவாக இருந்தன என்பதை அகநானூற்றின் 390வது பாடல் மூலம் அறியலாம்.
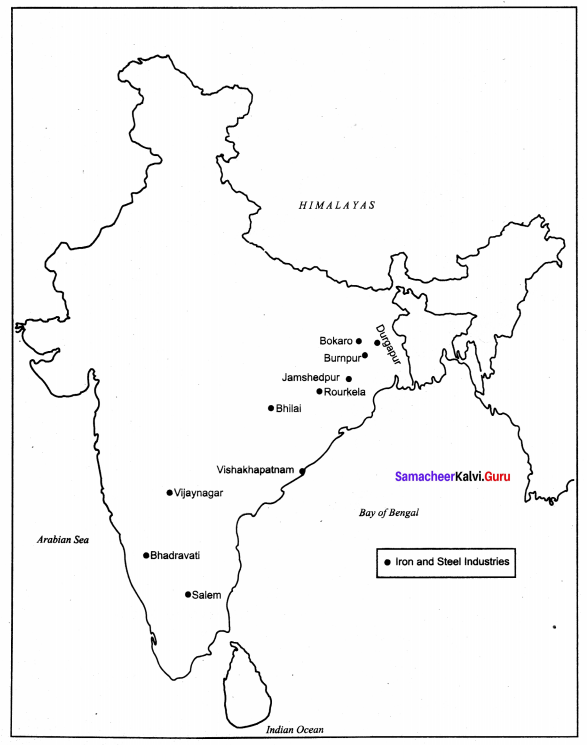
வெளிநாட்டு வணிகம் :
முசிறி சேரர்களின் சிறந்த துறைமுகங்களில் ஒன்றாக விளங்கியது. இங்கிருந்து தான் மற்ற நாடுகளுக்கு மிளகு, முத்து, யானை, தந்தங்கள், மணி போன்றவை ஏற்றுமதி செய்யப்பட்டன. பொன்மணிமிக்க புடவைகள், சித்திர வேலைப்பாடுகள் அமைந்த ஆடைகள், பவளம், செம்பு, கோதுமை ஆகியன இறக்குமதி செய்யப்பட்டன.
சிந்தனை வினா
Question 1.
நாட்டு மக்களின் நாகரிக நல்வாழ்விற்கு வணிகம் தவிர்த்து வேறு எவையெல்லாம் உதவும் என்று நீங்கள் கருதுகிறீர்கள்?
Answer:
நாட்டு மக்களின் நாகரிக நல்வாழ்விற்கு வணிகம் தவிர்த்து கலைகள் பலவும், அறிவியல் கோட்பாடுகளும், பண்டைய தமிழறிஞர்களின் சிந்தனைகளை மீட்டுக் கொணர்வதும், பொதுமைப் பண்பு, புத்தாக்க சிந்தனைகளும், பழைய நாகரிகங்களை வெளிக்கொணரும் அகழாய்வுகளும், பழந்தமிழ் இலக்கியங்களும் உதவும் என்று நான் கருதுகிறேன்.
கூடுதல் வினாக்கள்
சரியான விடையைத் தேர்ந்தெடுத்து எழுதுக.
Question 1.
மூவேந்தர்களில் பழமையானவர்கள் …………………..
அ) சேரர்
ஆ) சோழர்
இ) பாண்டியர்
ஈ) பல்ல வர்
Answer:
அ) சேரர்
Question 2.
சேரர்களின் கொடி ……………..
அ) புலி
ஆ) மீன் இ)வில்
இ) வில்
ஈ) முரசு
Answer:
இ) வில்
Question 3.
சேரனுக்கு உரிய பூ ……………………
அ) பனம்பூ
ஆ) வேப்பம்பூ
இ) அத்திப்பூ
ஈ) தாழம்பூ
Answer:
அ) பனம்பூ
Question 4.
“கொங்கு மண்டலச் சதகம்’ என்னும் நூலை இயற்றியவர் …………………….
அ) காளமேகப்புலவர்
ஆ) கார்மேகக் கவிஞர்
இ) கண்ண தாசன்
ஈ) வாணிதாசன்
Answer:
ஆ) கார்மேகக் கவிஞர்
கோடிட்ட இடங்களை நிரப்புக.
1. கடற்போர் வெற்றிகண்ட சேரன் ……………………..
2. ……………………. என்னும் பெயரே கோயம்புத்தூர் என்று மருவி வழங்கப்பட்டு வருகிறது.
3. பரப்பளவில் தமிழ்நாட்டின் இரண்டாவது பெரிய நகரம் ……………………..
4. தமிழகத்திலேயே மஞ்சள் சந்தை இடம்பெறும் ஒரே ஊர் …………………
5. இந்தியாவின் முதல் ஆயத்த ஆடைப் பூங்கா …………………..
6. ஆயத்த ஆடை பூங்கா அமைந்துள்ள மாவட்டம் ………………………
7. முட்டைக் கோழி வளர்ப்பிலும், முட்டை உற்பத்தியிலும் இந்தியாவிலேயே முதன்மை வகிக்கும் மாவட்டம் ………………………
8. ஏழைகளின் ஊட்டி ………………………
9. கிரேக்க அறிஞர் ……………………..
10. முத்து நகரம் …………………….
11. குட்டி ஜப்பான் ……………………..
12. தூங்கா நகரம் ……………………
13. தீப நகரம் …………….
Answer:
1. கோவன்புத்தூர்
2. செங்குட்டுவன்
3. ஈரோடு
4. ஈரோடு
5. நேதாஜி ஆயத்த ஆடைப் பூங்கா
6. திருப்பூர்
7. நாமக்கல்
8. ஏற்காடு
9. தாலமி
10. தூத்துக்குடி
11. சிவகாசி
12. மதுரை
13. திருவண்ணாமலை
குறுவினா
Question 1.
மூவேந்தர்கள் யாவர்?
Answer:
சேரர், சோழர், பாண்டியர்.
Question 2.
சேர நாட்டின் துறைமுகப்பட்டினங்கள் யாவை?
Answer:
தொண்டி, முசிறி, காந்தளூர்.
Question 3.
கொங்கு நாட்டுப் பகுதிகள் யாவை?
Answer:
சேலம் மற்றும் கோவைப் பகுதிகள் கொங்குநாட்டுப் பகுதிகள் ஆகும்.
Question 4.
ஒரு நாட்டு மக்களின் நாகரிக நல்வாழ்விற்கு அடிப்படை எவை?
Answer:
உழவு, கைத்தொழில் வணிகம்.
Question 5.
நீலகிரி மாவட்டத்தில் பெருமளவு பயிரிடப்படும் பயிர்கள் யாவை?
Answer:
காப்பி, தேயிலை, உருளைக்கிழங்கு, கேரட், முட்டைகோஸ்.
Question 6.
கோவை மாவட்டத்தில் பெருமளவு பயிரிடப்படும் பயிர்கள் யாவை?
Answer:
நெல், வாழை, கரும்பு, காய்கறிகள், பூக்கள்.
Question 7.
திண்டுக்கல்லில் விளைவிக்கப்படும் பயிர் வகைகள் யாவை?
Answer:
நெல், சோளம், தினை வகைகள், வாழைப்பழம், காய்கறிகள், மலர்கள்.
Question 8.
ஈரோட்டில் விளைவிக்கப்படும் பயிர்கள் யாவை?
Answer:
நெல், நிலக்கடலை, மஞ்சள், கரும்பு, பருத்தி.
Question 9.
திருப்பூரில் விளைவிக்கப்படும் முதன்மைப் பயிர்கள் யாவை?
Answer:
நெல், கரும்பு, பருத்தி, வாழை.
Question 10.
நாமக்கல் மாவட்டத்தில் பயிரிடப்படுவது யாவை?
Answer:
நெல், கரும்பு, சோளம், நிலக்கடலை, பருத்தி, திராட்சை, ஆரஞ்சு, காப்பி, பாக்கு, ஏலம்.
Question 11.
சேலம் மாவட்டத்தில் பயிரிடப்படும் பயிர் வகைகள் யாவை?
Answer:
நெல், பருப்புவகைகள், பருத்தி, கரும்பு, மாம்பழம், காப்பி, பாக்கு.
Question 12.
கரூர் மாவட்டத்தில் பயிரிடப்படும் பயிர்கள் யாவை?
Answer:
நெல், சோளம், கேழ்வரகு, கம்பு, கரும்பு.
சிறுவினா
Question 1.
சேரர்களைப் பற்றிய செய்திகளைச் சுருக்கி எழுதுக.
Answer:
- மூவேந்தர்களில் பழமையானவர்கள் சேரர்கள்.
- சேரர்களின் நாடு குடநாடு எனப்பட்டது.
- சேரர்களின் தலைநகரம் வஞ்சி.
- தொண்டி, முசிறி, காந்தளூர் ஆகியன சேரநாட்டின் துறைமுகப் டினங்களாக 10 விளங்கின.
- சேரர்களின் கொடி விற்கொடி ஆகும்.
Question 2
நீலகிரி மாவட்டத்தில் அமைந்துள்ள தொழிற்சாலைகள் யாவை?
Answer:
- தேயிலைத் தொழிற்சாலை
- புகைப்படச் சுருள் தயாரிப்பு தொழிற்சாலை
- துப்பாக்கி வெடிமருந்து தொழிற்சாலை
- தைல மர எண்ணெய் தொழிற்சாலை
Question 3.
கோயம்புத்தூர் மாவட்டத்தில் அமைந்துள்ள தொழிற்சாலைகள் யாவை?
Answer:
- பஞ்சாலைகள்
- நூற்பாலைகள்
- மின்சாரப் பொருட்கள்
- எந்திரங்கள்
- வீட்டு உபயோகப் பொருட்கள் தயாரிக்கும் தொழிற்சாலைகள் ஆகியன கோயம்புத்தூர் மாவட்டத்தில் நிறைந்துள்ளன.
Question 4.
ஈரோடு மாவட்டம் பற்றிய செய்திகளைச் சுருக்கி எழுதுக.
Answer:
- தமிழ்நாட்டின் இரண்டாவது பெரிய நகரம் ஈரோடு.
- இங்கு நெல், நிலக்கடலை, மஞ்சள், கரும்பு, பருத்தி, எள் போன்றவை பயிரிடப்படுகின்றன.
- தமிழகத்திலேயே மஞ்சள் சந்தை உள்ள ஒரே மாவட்டம் ஈரோடு தான்.
- துணி நூற்பாலைகள், எண்ணெய் ஆலைகள், சர்க்கரை ஆலைகள் பெருமளவில் இங்கு உள்ளன.
- நூல் நூற்பு, துணிகளுக்குச் சாயம் ஏற்றுதல், அச்சிடுதல், தோல் பதனிடுதல் முதலான தொழில்களும் ஈரோடு மாவட்டத்தில் நடைபெறுகின்றன.