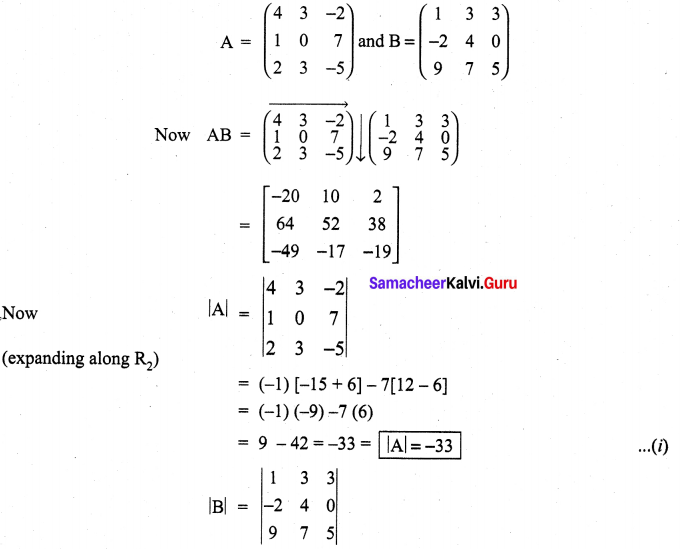
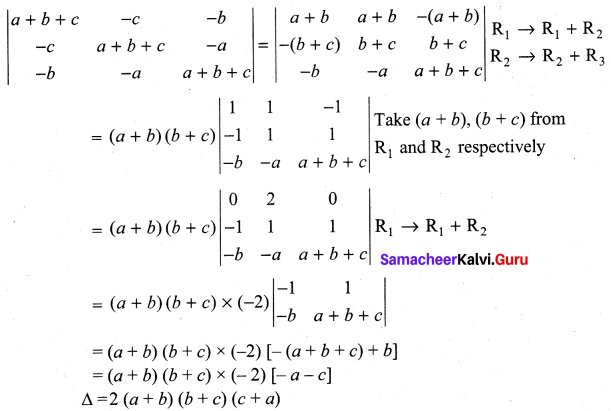
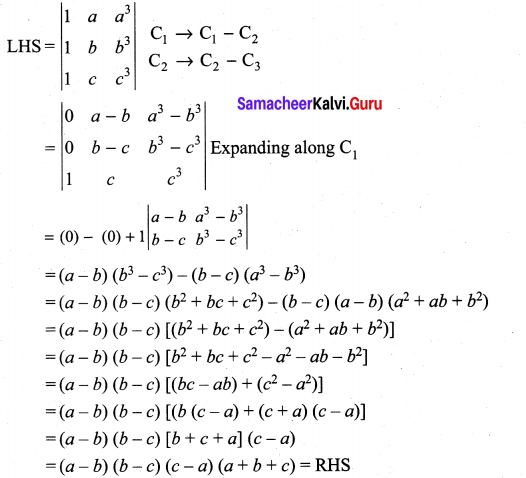
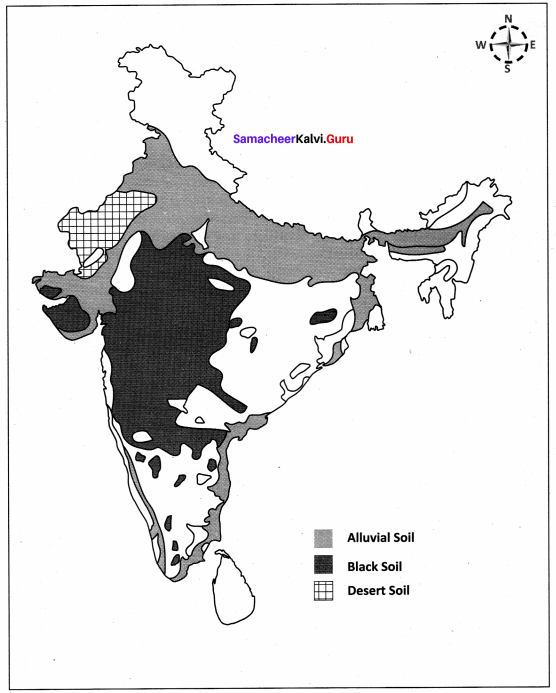
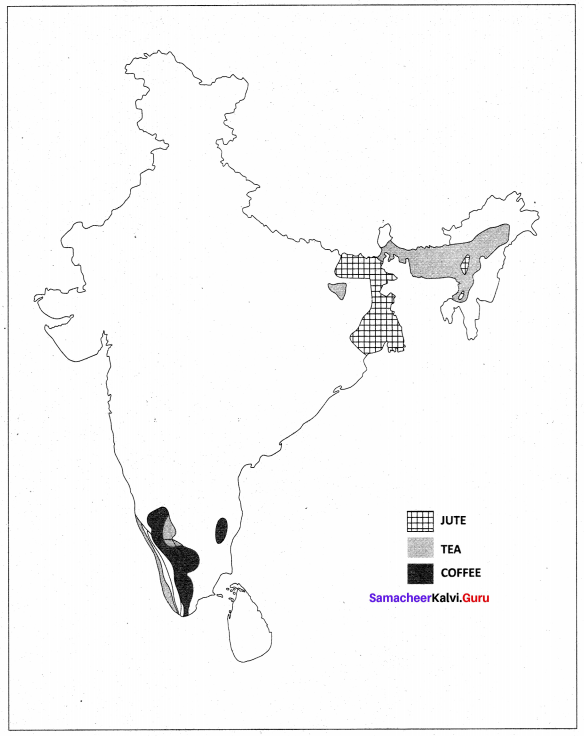
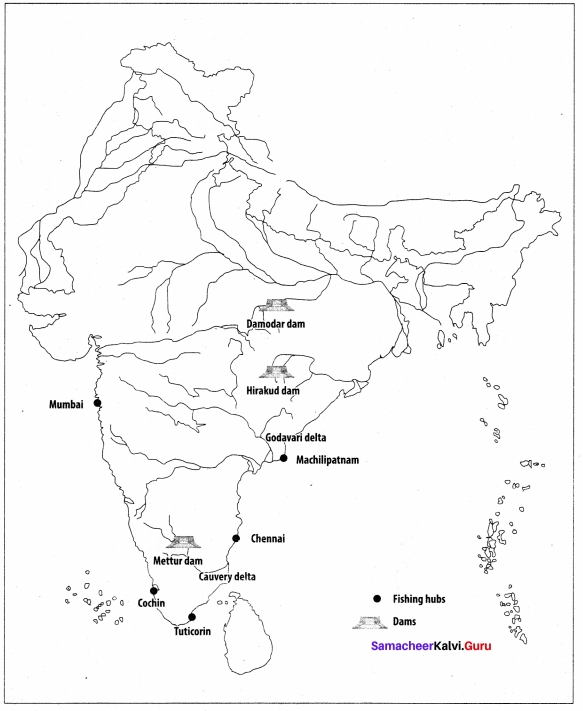
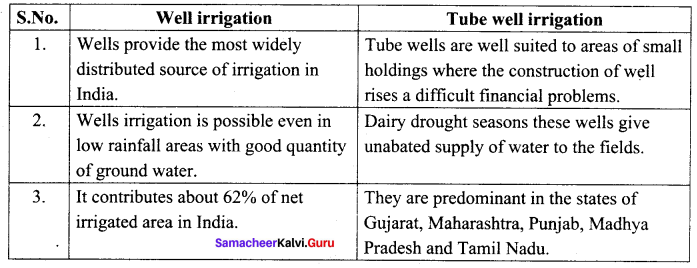
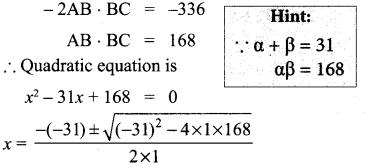
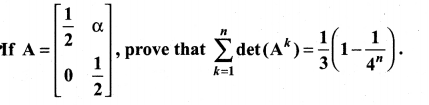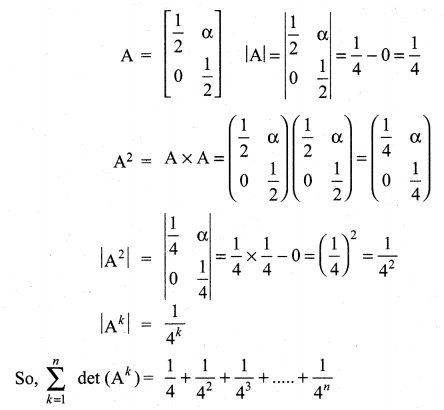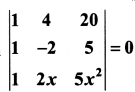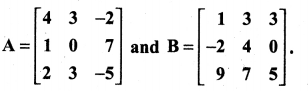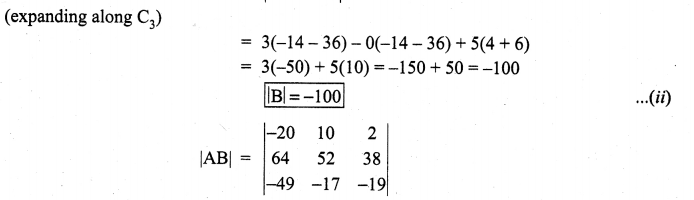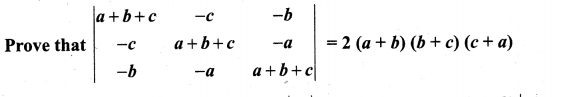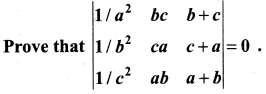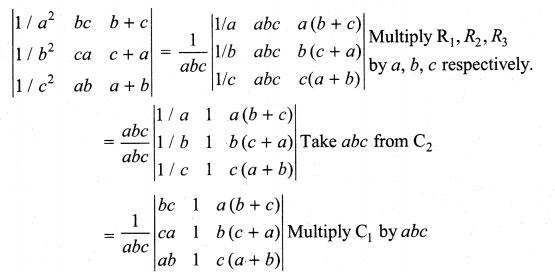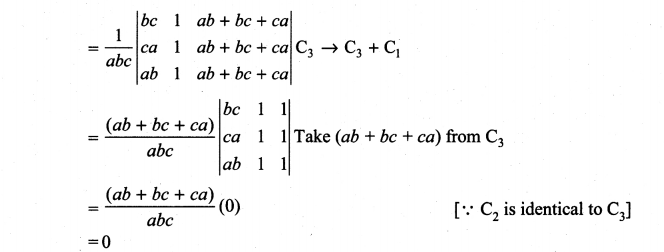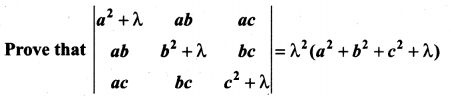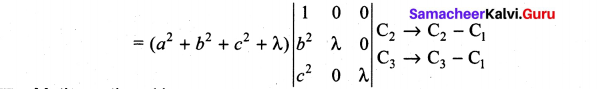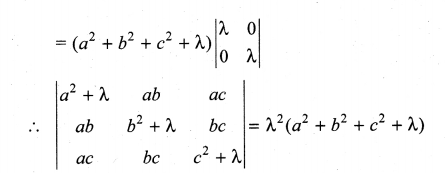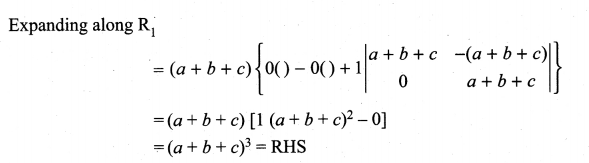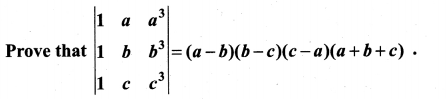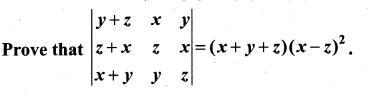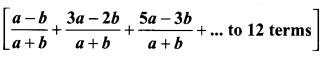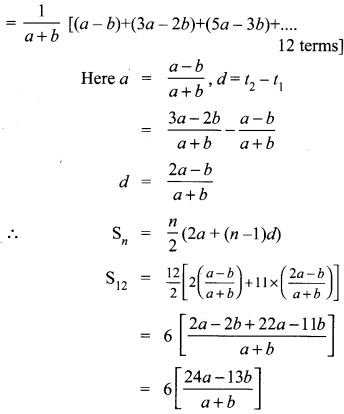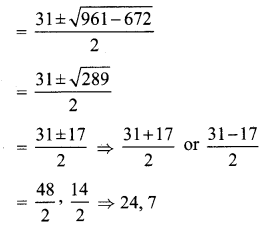You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.3
10th Maths Exercise 3.3 Samacheer Kalvi Question 1.
Find the LCM and GCD for the following and verify that f(x) × g(x) = LCM × GCD.
(i) 21x2y, 35xy2
(ii) (x3 – 1)(x + 1), x3 + 1
(ii) (x3 – 1) (x + 1), (x3 – 1)
(iii) (x2y + xy2), (x2 + xy)
Solution:
(i) f(x) = 21x2y = 3 × 7x2y
g(x) = 35xy2 = 7 × 5xy2
G.C.D. = 7xy
L.C.M. = 7 × 3 × 5 × x2y2 = 105x2 × y2
L.C.M × G.C.D = f(x) × g(x)
105x2y2 × 7xy = 21x2y × 35xy2
735x3y3 = 735x3y3
Hence verified.
(ii) (x3 – 1)(x + 1) = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1)(x + 1)
x3 + 1 = (x + 1) (x2 – x + 1)
G.C.D = (x+ 1)
L.C.M = (x – 1)(x + 1)(x2 + x + 1)(x2 – x + 1)
∴ L.C.M. × G.C.D = f(x) × g(x)
(x – 1)(x + 1)(x2 + x + 1) (x2 – x + 1) = (x – 1)
(x2 + x + 1) × (x + 1) (x2 – x + 1)
(x3 – 1)(x + 1)(x3 + 1) = (x3 – 1)(x + 1)(x3 + 1)
∴ Hence verified.
(iii) f(x) = x2y + xy2 = xy(x + y)
g(x) = x2 + xy = x(x + y)
L.C.M. = x y (x + y)
G.C.D. = x (x + y)
To verify:
L.C.M. × G.C.D. = xy(x + y) × (x + y)
= x2y (x + y)2 ……….. (1)
f(x) × g (x) = (x2y + xy2)(x2 + xy)
= x2y (x + y)2 …………… (2)
∴ L.C.M. × G.C.D = f(x) × g{x).
Hence verified.
Ex 3.3 Class 10 Samacheer Question 2.
Find the LCM of each pair of the following polynomials
(i) a2 + 4a – 12, a2 – 5a + 6 whose GCD is a – 2
(ii) x4 – 27a3x, (x – 3a)2 whose GCD is (x – 3a)
Solution:
(i) f(x) = a2 + 4a – 12 = (a + 6)(a – 2)
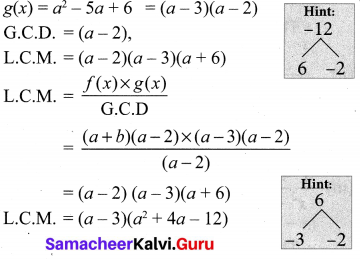
(ii) f(x) = x4 – 27a3x = x(x3 – (3a)3)
g(x) = (x – 3a)2
G.C.D = (x – 3a)
L.C.M. × G.C.D = f(x) × g(x)
L. C.M = \(\frac{x\left(x^{3}-(3 a)^{3}\right) \times(x-3 a)^{2}}{(x-3 a)}\)
L.C.M = x(x3 – (3a)3) . (x – 3a)
= x(x – 3a)2 (x2 + 3ax + 9a2)
10th Maths Exercise 3.3 Question 3.
Find the GCD of each pair of the following polynomials
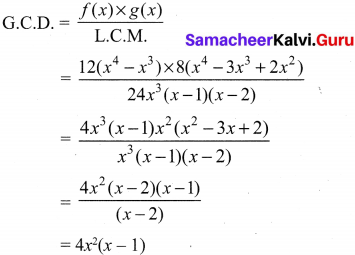
(i) 12(x4 – x3), 8(x4 – 3x3 + 2x2) whose LCM is 24x3 (x – 1)(x – 2)
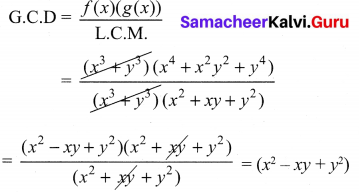
(ii) (x3 + y3), (x4 + x2y2 + y4) whose LCM is (x3 + y3) (x2 + xy + y2)
Solution:
(i) f(x)= 12(x4 – x3)
g(x) = 8(x4 – 3x3 + 2x2)
L.C.M = 24x3 (x – 1)(x – 2)
(ii) (x3 + y3), (x4 + x2y2 + y4)
L.C.M. = (x3 + y3)(x2 + xy + y2)
Exercise 3.3 Class 10 Maths Samacheer Question 4.
Given the LCM and GCD of the two polynomials p(x) and q(x) find the unknown polynomial in the following table
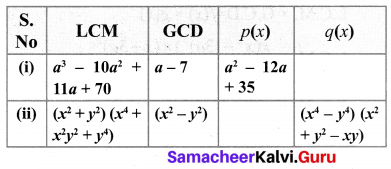
Solution:
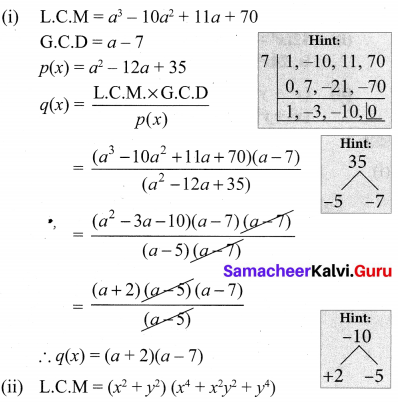
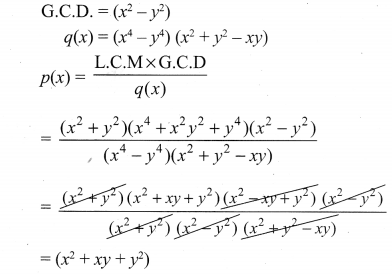


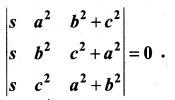
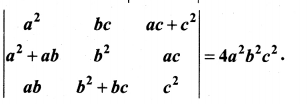

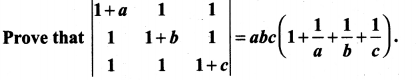
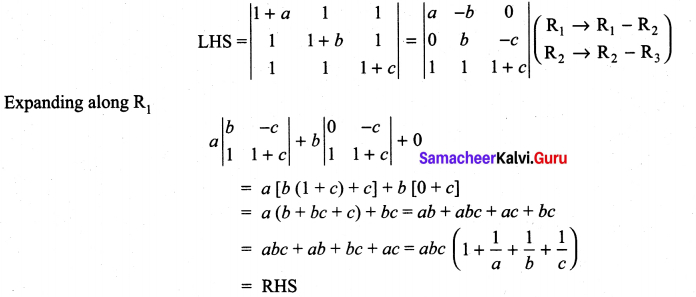
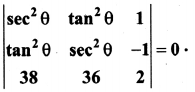
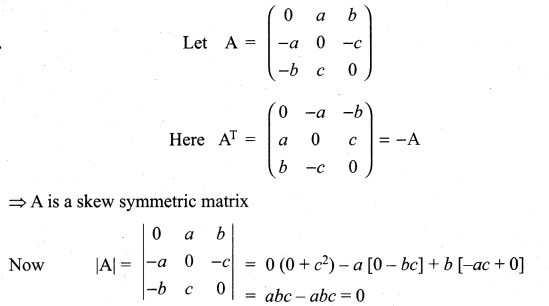
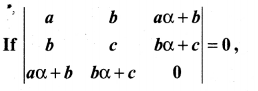
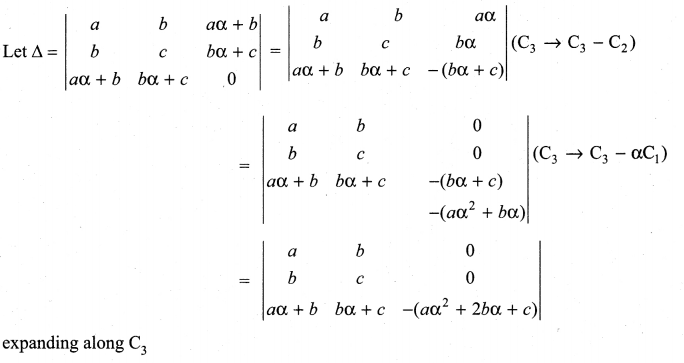
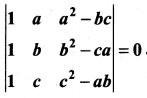
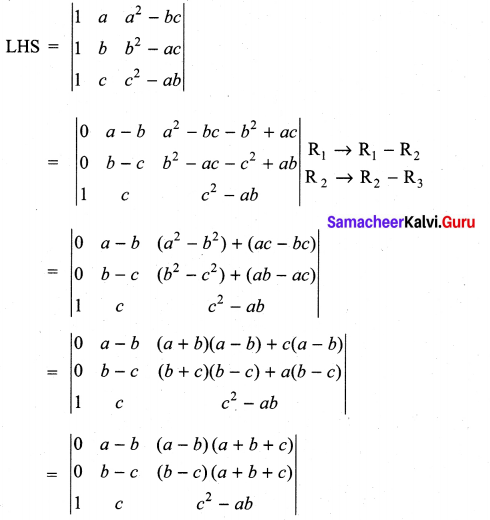
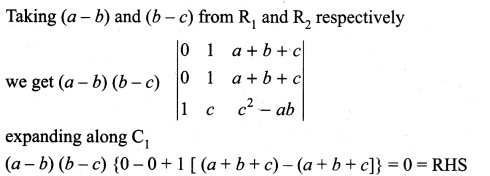
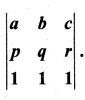
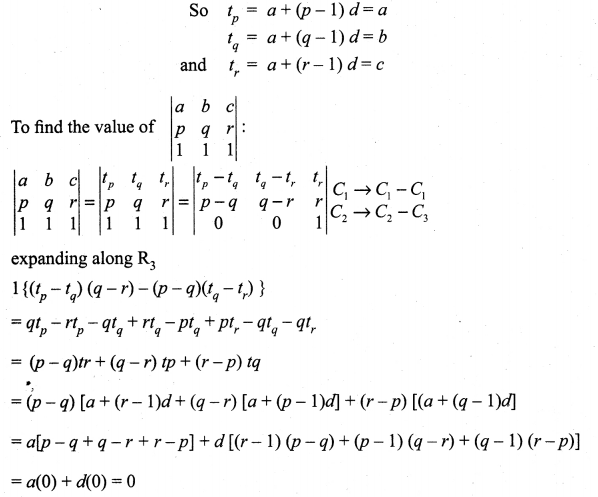
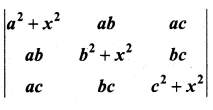 is divisible by x4
is divisible by x4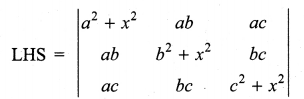
 =
=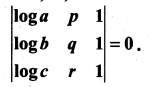

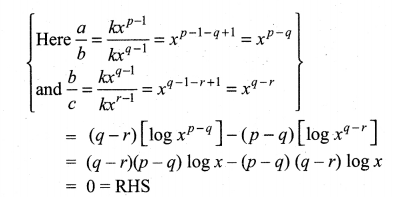
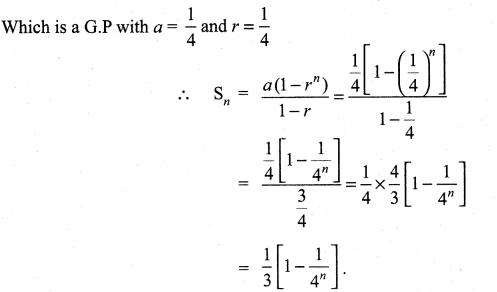
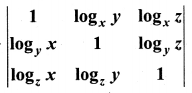 if x, y, z ≠ 1.
if x, y, z ≠ 1.