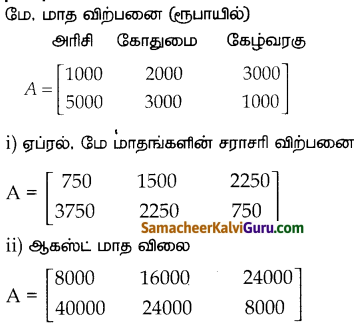
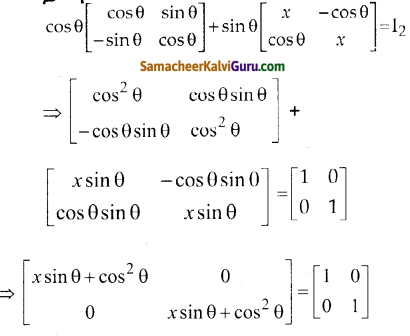
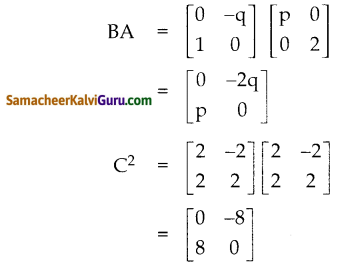
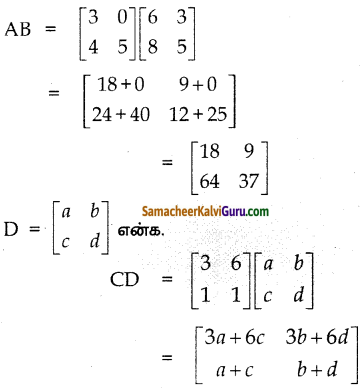
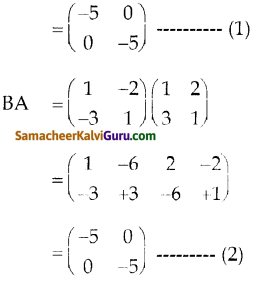
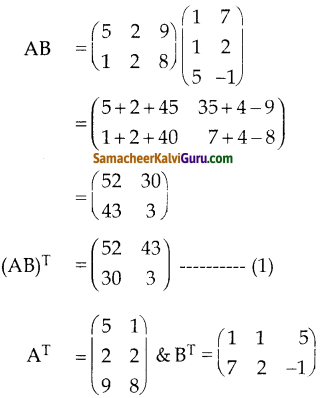
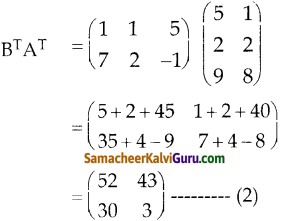
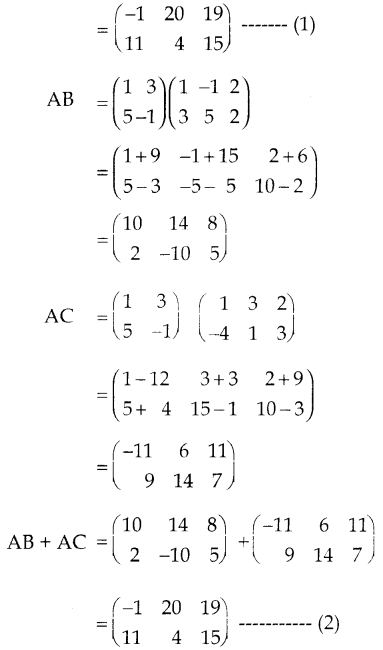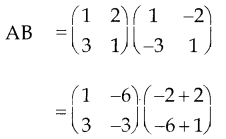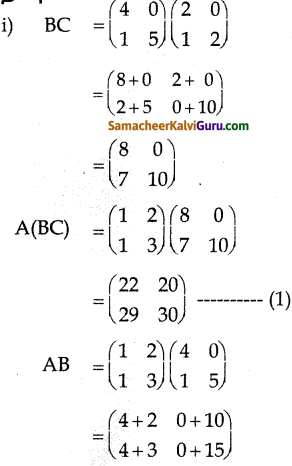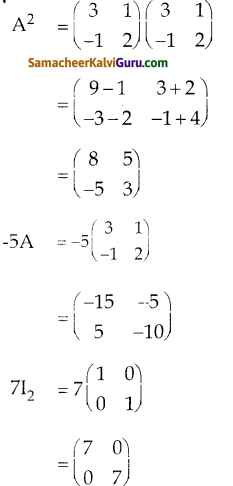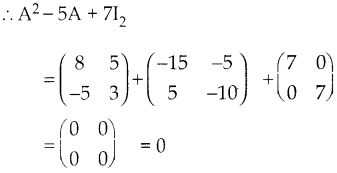You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 5 Magnetism and Electromagnetism
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Magnetism and Electromagnetism Textbook Exercises
I. Choose the correct answer.
9th Science Magnetism And Electromagnetism Question 1.
Which of the following converts electrical energy into mechanical energy?
(a) motor
(b) battery
(c) generator
(d) switch
Answer:
(a) motor
Magnetism And Electromagnetism Samacheer Kalvi Question 2.
The part of the AC generator that passes the current from the armature coil to the external circuit is
(a) field magnet
(b) split rings
(c) slip rings
(d) brushes
Answer:
(d) brushes
Chapter 5 Magnetism And Electromagnetism Question 3.
Transformer works on
(a) AC only
(b) DC only
(c) both AC and DC
(d) AC nor effectively than DC
Answer:
(a) AC only
Magnetism And Electromagnetism Questions And Answers Pdf Question 4.
The unit of magnetic flux density is
(a) Weber
(b) weber/meter
(c) weber/meter2
(d) weber.meter2
Answer:
weber/meter2
II. Fill in the blanks.
- The SI Unit of magnetic field induction is ……………………..
- Devices which is used to convert high alternating current to low alternating current is …………………..
- An electric motor converts …………………..
- A device for producing electric current is ……………………..
Answer:
- Tesla
- Step down transformer
- Electrical energy into mechanical energy
- Generator
III. Match the following.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| 1. Magnetic material | (a) Oersted |
| 2. Non-magnetic material | (b) iron |
| 3. Current and magnetism | (c) induction |
| 4. Electromagnetic induction | (d) wood |
| 5. Electric generator | (e) Faraday |
Answer:
- (b) iron
- (d) wood
- (a) Oersted
- (e) Faraday
- (c) induction
IV. True or False.
- A generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy – True
- Magnetic field lines always repel each other and do not intersect – True
- Fleming’s Left hand rule is also known as Dynamo rule – True
- The speed of rotation of an electric motor can be increased by decreasing the area of the coil – False
Correct Statement: The speed of rotation of coil can be increased by increasing the area of the coil. - A transformer can step up direct current – False
Correct Statement: A transformer can step up alternating current. - In a step down transformer the number of turns in primary coil is greater than that of the number of turns in the secondary coil – True
V. Answer in brief.
Magnetism And Electromagnetism Pdf Question 1.
State Fleming’s Left Hand Rule.
Answer:
It states that while stretching the three fingers of left hand in perpendicular manner with each other, if the direction of the current is denoted by middle finger of the left hand and the second finger is for direction of the magnetic field then the thumb of the left hand denotes the direction of the force or movement of the conductor.
Electromagnetism Exercises And Solutions Pdf Question 2.
Define magnetic flux density.
Answer:
The number of magnetic field lines crossing unit area kept normal to the direction of field lines is called magnetic flux density. Its unit is Wb/m2
9th Class Science Chapter 5 Question Answer Question 3.
List the main parts of an electric motor.
Answer:
Main parts of an electric motor are:
- Shaft,
- Primary and Secondary windings,
- Ball bearings,
- Armature,
- Stator,
- Commutator,
- Brushes,
- Terminals
Magnetism And Electromagnetism Question 4.
Draw and label the diagram of an AC generator.
Answer:
Electromagnetism Exercises Question 5.
State the advantages of AC over DC.
Answer:
Advantages of AC over DC:
- The Voltage of AC can be varied easily using a device called transformer. The AC can be carried over long distances using step up transformers. The loss of energy while distributing current in the form of AC is negligible.
- Direct current cannot be transmitted as such. The AC can be easily converted into DC. Generating AC is easier than DC. The AC can produce electromagnetic induction which is useful in several ways.
Magnetism Notes Class 9 Question 6.
Differentiate step up and step down transformer.
Answer:
| Step up transformer | Step down transformer |
| The transformer used to change a low alternative voltage to a high alternating voltage is called a step up transformer, i.e. (Vs>Vp). | The transformer used to change a high alternating voltage to a low alternating voltage is called a step down transformer (Vs <Vp). |
| In a step up transformer, the number of turns in the secondary coil is more than the number of turns in the primary coil (Ns > Np) | In a step down transformer, the number of turns in the secondary coils are less than the number of turns in the primary coil (Ns < Np) |
Question 7.
A portable radio has a built in transformer so that it can work from the mains instead of batteries. Is this a step up or step down transformer?
Answer:
A step-down transformer is used in a portable radio in order to reduce the voltage.
Question 8.
State Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction.
Answer:
Whenever there is a change in the magnetic flux linked with a closed-circuit an emf is produced and the amount of emf induced varies directly as the rate at which the flux changes. This emf is known as induced emf and the phenomenon of producing an induced emf due to change in the magnetic flux linked with a closed circuit is known as electromagnetic induction.
VI. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
Explain the principle, construction and working of a DC motor.
Answer:
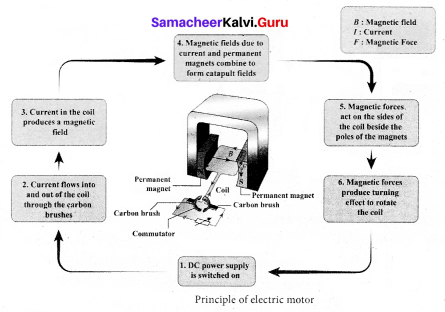
A motor is an electrical machine which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The principle of working of a DC motor according to Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction is that “whenever a current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a mechanical force”. The various parts of a DC motor are; Permanent magnets on both sides of a coil which consists of carbon brush and commutator as shown in
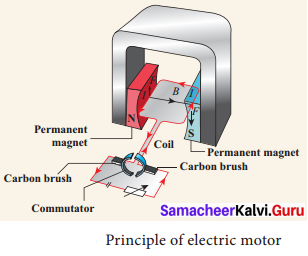
Working of electric motor is primarily dependent upon the interaction between magnetic field and current. The direction of this force is given by Fleming’s left hand rule and it’s magnitude is given by F = BIL. Where, B = magnetic flux density, I = current and L = length of the conductor within the magnetic field.
Question 2.
Explain two types of transformer.
Answer:
Transformer is a device used for converting low voltage into high voltage and high voltage into low voltage. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It consists of primary and secondary coil insulated from each other. Depending upon the number of turns in the primary and secondary coils, the two types of transformers are; step-up or step-down transformers.
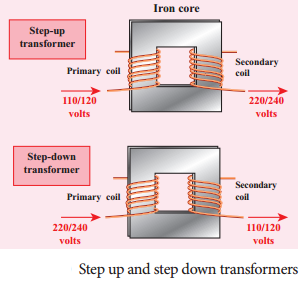
Step up transformer:
The transformer used to change a low alternative voltage to a high alternating voltage is called a step up transformer, ie (Vs > Vp) . In a step up transformer, the number of turns in the secondary coil is more than the number of turns in the primary coil (Ns > Np).
Step down transformer:
The transformer used to change a high alternating voltage to a low alternating voltage is called a step down transformer (Vs < Vp). In a step down transformer, the number of turns in the secondary coils are less than the number of turns in the primary
coil (Ns < Np).
The formulae pertaining to the transformers are given in the following equations.
- The number of primary turns Np / The number of secondary turns Ns = The primary voltage Vp/ The secondary voltage Vs
- The number of secondary turns Ns / The number of primary turns Np – The primary current Ip/ The secondary current Is
Question 3.
Draw a neat diagram of an AC generator and explain its working.
Answer:
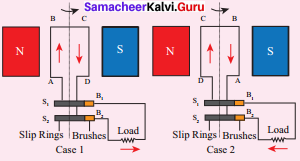
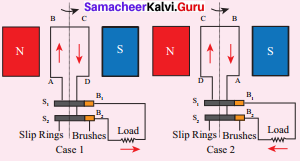
An alternating current (AC) generator, consists of a rotating rectangular coil ABCD called armature placed between the two poles of a permanent magnet. The two ends of this coil are connected to the two slip rings S1 and S2. The inner sides of these rings are insulated. Two conducting stationary brushes B1 and B2 are kept separately on the rings S1 and S2 respectively. The two rings S1 and S2 are internally attached to an axle. The axle may be mechanically rotated from outside to rotate the coil inside the magnetic field. Outer ends of the two brushes are connected to the external circuit.
When the coil is rotated, the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes. This change in magnetic flux will lead to generation of induced current. The direction of the induced current, as given by Fleming’s Right Fland Rule, is along ABCD in the coil and in the outer circuit it flows from B2 to B1. During the second half of rotation, the direction of current is along DCBA in the coil and in the outer circuit it flows from B1 to B7. As the rotation of the coil continues, the induced current in the external circuit is changing its direction for every half a rotation of the coil.
ACTIVITY
Question 1.
Put a magnet on a table and place some paper clips nearby. If you push the magnet slowly towards the paper clips, there will be a point at which the paper clips jump across and stick to the magnet. What do you understand from this?
Answer:
The invisible magnetic field that surrounds the magnet acts at a particular distance. This magnetic field attracts the paper clip which is made of steel.
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Magnetism and Electromagnetism In Text Problems.
Question 1.
A conductor of length 50 cm carrying a current of 5 A is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field of induction 2 × 10– 3 T. Find the force on the conductor.
Solution:
Force on the conductor = ILB
= 5 × 50 × 10– 2 × 2 × 10– 3
= – 5 × 10– 3 N
Question 2.
A current carrying conductor of certain length, kept perpendicular to the magnetic field experiences a force F. What will be the force if the current is increased four times, length is halved and magnetic field is tripled?
Solution:
F = ILB = (4I) × ( L / 2) × (3 B) = 6 F
Therefore, the force increases six times.
Question 3.
The primary coil of a transformer has 800 turns and the secondary coil has 8 turns. It is connected to a 220 V ac supply. What will be the output voltage?
Solution:
In a transformer, Es / Ep = Ns / Np
Es = Ns / Np × Ep
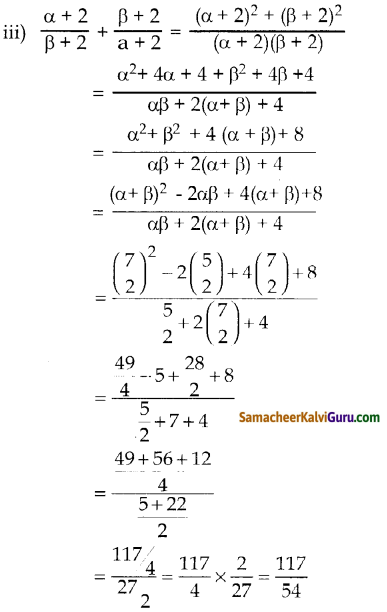
= \(\frac { 8 }{ 800 }\) × 220 = \(\frac { 220 }{ 100 }\) = 2.2 volt
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Magnetism and Electromagnetism Additional Questions
I. Short answers questions.
Question 1.
What are natural magnets?
Answer:
Natural magnets exists in the nature and can be found in rocks and sandy deposits in various parts of the world.
Question 2.
How can the speed of rotation of a coil be increased? Write at least three methods.
Answer:
The speed of rotation of a coil can be increased by;
- increasing the strength of the Current in the coil
- increasing the area of the coil
- increasing the strength of the magnetic field.
Question 3.
What is the connection between electricity and magnetism?
Answer:
Electricity and magnetism are closely related to each other. The current flowing through the wire produces a circular magnetic field outside the wire. The direction of this magnetic field depends on the electric current.
Similarly, a changing magnetic field produces an electric current in a wire or conductor. The relationship between electricity arid magnetism is called electromagnetism.
Question 4.
What are the factors that determine the strength of the magnet?
Answer:
The strength of the magnetic field at a point due to current carrying wire depends on:
- the current in the wire
- distance of the point from the wire
- the orientation of the point from the wire and
- the magnetic nature of the medium.
Question 5.
Name some equipmetns that use electromagnetism for functioning.
Answer:
Many of the medical equipments such as scanners, x-ray equipments and other equipments also use principle of electromagnetism for their functioning.
Question 6.
Explain why the ozone layer is not affected by the solar wind.
Answer:
Magnetic field can penetrate through all kinds of materials. The Earth produces its own magnetic field, which shields the earht’s ozone layer from the solar wind.
Question 7.
Write the properties of magnetic lines of force.
- Magnetic lines of force are closed continuous curves, extending through the body of the magnet.
- Magnetic lines of force start from the North Pole and end at the South Pole.
- Magnetic lines of force never intersect.
- They will be maximum at the poles than at the equator.
- The tangent drawn at any point on the curved line gives the direction of magnetic field.
II. Long answers questions.
Question 1.
What do you know about Michael Faraday?
Answer:
Michael Faraday discovered that a current carrying conductor also gets deflected when it is placed in a magnetic field. Michael Faraday was a British Scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism and electrolysis. Although Faraday received little formal education, he was one of the most influential scientists in history. Faraday was an excellent experimentalist who conveyed his ideas in clear and simple language.
The SI unit of capacitance is named in his honour: the farad. Albert Einstein kept a picture of Faraday on his study wall, alongside pictures of Isaac Newton and James Clerk Maxwell. Faraday is one of the greatest scientific discoverers of all time.
Question 2.
Explain in detail about the application of electromagnets.
Answer:
Applications of electromagnets – Electromagnetism has caused a great impact on various fields such as medicine, industries, space, etc. In our day to day life, it finds application in;
(a) Speakers – In a speaker the electromagnet is placed in front of a permanent magnet. The permanent magnet is fixed whereas the electromagnet is mobile. As pulses of electricity pass through the coil of the electromagnet, the direction of its magnetic field rapidly changes. This causes it to get attached to and repelled from the permanent magnet, thereby causing vibration. The electromagnet is attached to a cone made of plastic or paper which amplifies the sound and the waves reaching our ears.
(b) Maglev – Magnetic levitation trains are suspended with no support other than magnetic fields. In maglev trains two sets of magnets are used. One set to repel and push the train up off the track, and another to move the floating train ahead at a great speed without friction. The train travels along a guideway of magnets which controls the tram’s stability and speed using the basic principles of magnets.
(c) MRI Scanner – Magnetic resonance imaging is a procedure using sophisticated instruments that work on the principle of electromagnetism that can scan minute details of the human body. Other medical equipment such as X-rays etc., also use this principle for their functioning.