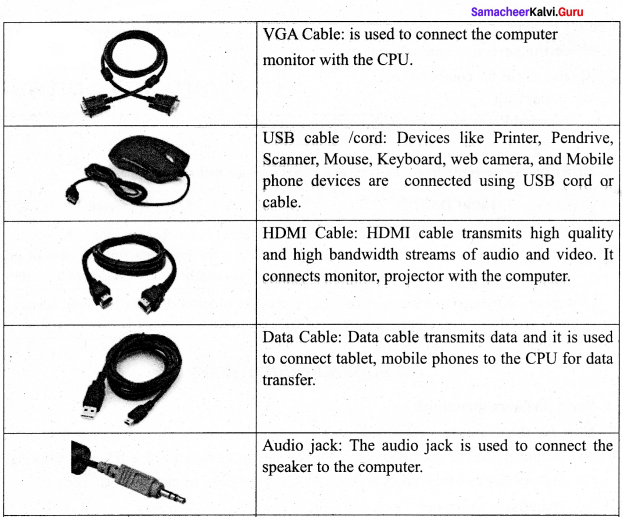
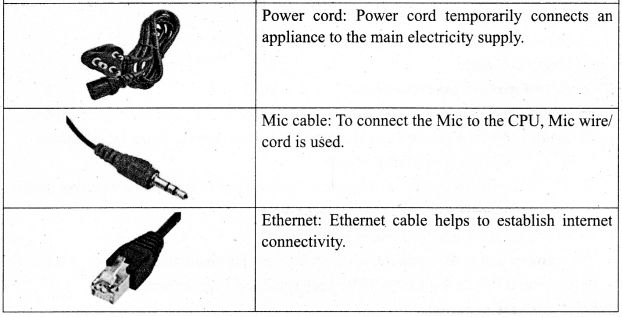
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 27 Hardware and Software
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Hardware and Software Textbook Exercises
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
Find out the part that is not found in CPU?
(a) Mother Board
(b) SMPS
(c) RAM
(d) Mouse
Answer:
(d) Mouse
Question 2.
Which of the following is correct?
(a) Free and Open source
(b) Free and Traditional Software
(c) Passive and Open source
(d) Passive and Traditional source
Answer:
(a) Free and Open source
![]()
Question 3.
LINUX is a ……………..
(a) Paid Software
(b) Licensed Software
(c) Free and Proprietary software
(d) Free and Open source software
Answer:
(d) Free and Open source software
Question 4.
Find out the Paid and Proprietary software from the given list.
(a) Windows
(b) MAC OS
(c) Adobe Photoshop
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 5.
……………….. is an Operating System.
(a) Android
(b) Chrome
(c) Internet
(d) Pendrive
Answer:
(a) Android
II. Match the following.
- MAC OS – (a) Free and Open-source Software
- Software – (b) Paid and Proprietary Software
- Hardware – (c) Input Device
- Keyboard – (d) RAM
- LINUX – (e) Geogebra
Answer:
- (b) Paid and Proprietary Software
- (e) Geogebra
- (d) RAM
- (c) Input Device
- (a) Free and Open-source Software
III. Answer in brief.
Question 1.
What is Hardware and Software?
Answer:
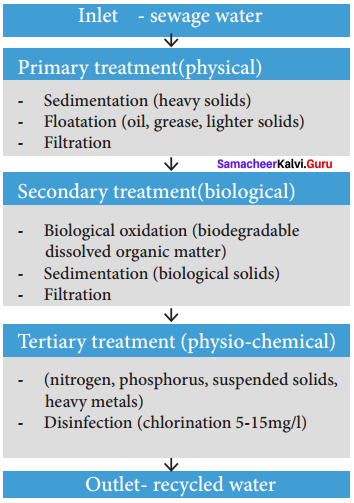
Hardware is the parts of a computer which we can touch and feel. Hardware includes Input and Output devices, Cabinet, Hard Disk, Mother Board, SMPS, CPU, RAM, CD Drive and Graphics Card.
Software are programmed and coded applications to process the input information. The software processes the data by converting the input information into coding or programmed language.
![]()
Question 2.
What do you mean by Operating System? How it Works?
Answer:
Operating system or System software is a software that makes the hardware devices process the data fed by the user and to display the result on the output devices like Monitor. Without the operating system, computer cannot function on its own.
Question 3.
What is Free and Open Source Software? Give any two examples?
Answer:
Free and open software is available at free of cost and can be shared to many end users. Free software is editable and customizable by the user and this leads to updation or development of new software. Examples of Free and Open source software are: LINUX, Open office, Geogebra etc.
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Hardware and Software Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
………………. is a group of programs designed for the benefit of end user to work on computer.
(a) System software
(b) Application software
(c) Paid and Proprietary Software
(d) Free and open source software
Answer:
(b) Application software
Question 2.
…………….. is lifeless without software.
(a) Software
(b) Hardware
(c) System
(d) Application
Answer:
(b) Hardware
![]()
Question 3.
The license of ……………. would not be provided unless it is purchased.
(a) free and open source software
(b) system software
(c) paid and proprietary software
(d) application software
Answer:
(c) paid and proprietary software
II. Match the following.
- Editing software – (a) Paid and Proprietary Software
- Android – (b) Monitor
- Windows – (c) System software
- Output device – (d) Application software
Answer:
- (d) Application software
- (c) System software
- (a) Paid and Proprietary Software
- (b) Monitor
III. Answer in brief.
Question 1.
What do you mean by application software?
Answer:
Application software is a program or a group of programs designed for the benefit of end user to work on computer. The application programs can be installed in the hard disk for the usage on a particular computer. This type of application program completes one or more than one work of the end user. The following are the examples of application program: Video player, Audio player, Word processing software, Drawing tools, Editing software, etc.
Question 2.
What are the types of software?
Answer:
The software is divided into two types based on the process. They are:
- System software (Operating System)
- Application software
![]()
Question 3.
What are the types of system and application software?
Answer:
The operating system and application software are available in two forms. They are:
- Free and Open source Software
- Paid and Proprietary Software
Question 4.
What is Paid and Proprietary Software? Give examples.
Answer:
There are softwares that need a license to use it. They have to be paid for using either permanently or temporarily. The license of the software would not be provided unless it is purchased. Similarly the end users are legally prohibited to steal the software program or to use the pirated version of the Paid and Proprietary Software. Some of the examples of Paid and Proprietary Software are: Windows, Microsoft office, Adobe Photoshop, etc.