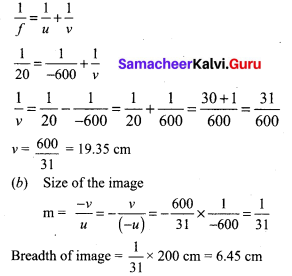
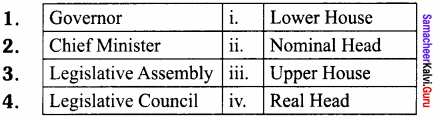
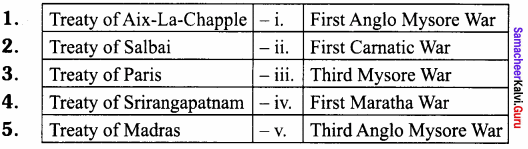
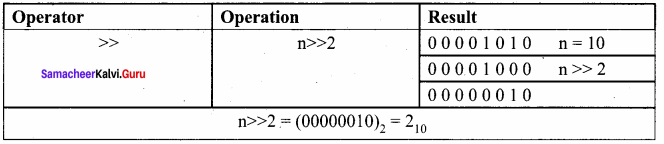
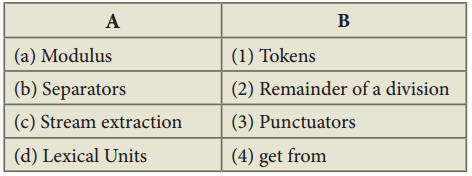
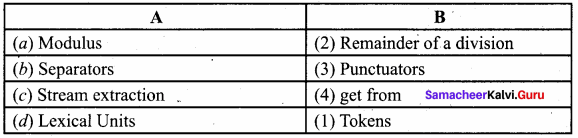
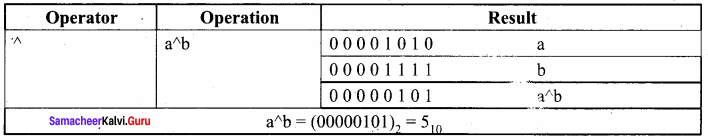
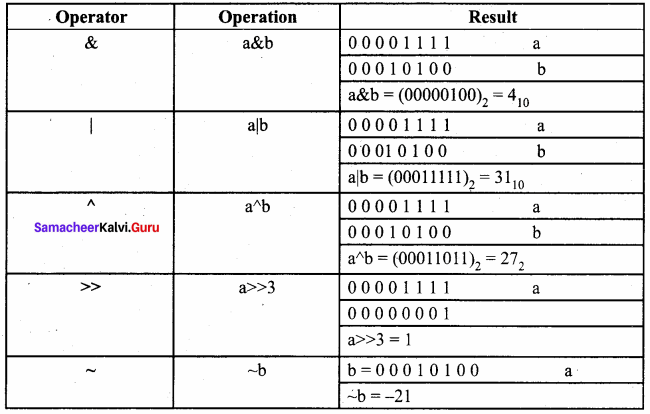
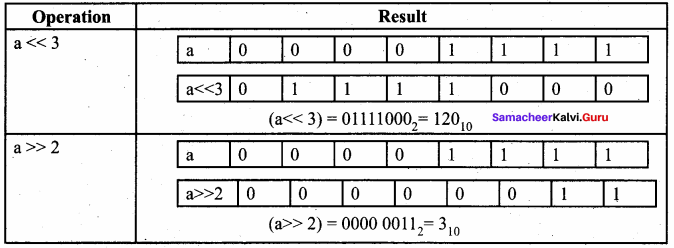
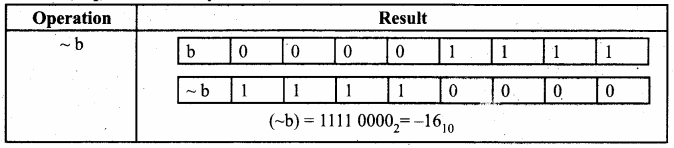
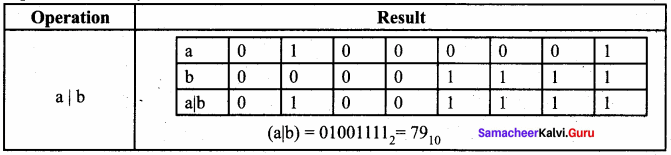
Students can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Paper 4 Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamil Nadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Model Question Paper 4
நேரம்: 3,00 மணி
மதிப்பெண்கள் : 100
(குறிப்புகள்:
- இவ்வினாத்தாள் ஐந்து பகுதிகளைக் கொண்டது. அனைத்து பகுதிகளுக்கும் விடையளிக்க – வேண்டும். தேவையான இடங்களில் உள் தேர்வு வினாக்கள் கொடுக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது. காக
- பகுதி I, II, III, IV மற்றும் Vல் உள்ள அனைத்து வினாக்களுக்குத் தனித்தனியே விடையளிக்க வேண்டும்.
- வினா எண். 1 முதல் 15 வரை பகுதி-1ல் தேர்வு செய்யும் வினாக்கள் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன. ஒவ்வொரு வினாவிற்கும் ஒரு மதிப்பெண். சரியான விடையைத் தேர்ந்தெடுத்து குறியீட்டுடன் எழுதவும்.
- வினா எண் 16 முதல் 28 வரை பகுதி-IIல் இரண்டு மதிப்பெண் வினாக்கள் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன: ஏதேனும் 9 வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் விடையளிக்கவும்.
- வினா எண் 29 முதல் 37 வரை பகுதி-IIIல் மூன்று மதிப்பெண் வினாக்கள் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன. –
ஏதேனும் 6 வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் விடையளிக்கவும். - வினா எண் 38 முதல் 42 வரை பகுதி-IVல் ஐந்து மதிப்பெண் வினாக்கள் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன. ஏதேனும் 5 வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் விடையளிக்கவும்.
- வினா எண் 43 முதல் 45 வரை பகுதி-Vல் எட்டு மதிப்பெண் வினாக்கள் தரப்பட்டுள்ளன. அனைத்து வினாவிற்கும் விடையளிக்கவும்.
பகுதி – 1 (மதிப்பெண்கள்: 15)
(i) அனைத்து வினாக்களுக்கும் விடையளிக்கவும்.
(ii) கொடுக்கப்பட்ட நான்கு விடைகளில் சரியான விடையினைத் தேர்ந்தெடுத்துக் குறியீட்டுடன் விடையினையும் சேர்த்து எழுதுக. [15 x 1 = 15]
(குறிப்பு: விடைகள் தடித்த எழுத்தில் உள்ளன)
Question 1.
”அன்னை மொழியே” என்ற தலைப்பில் அமைந்த கவிதையில் குறிப்பிடாத நூல் ………..
(அ) திருக்குறள்
(ஆ) பத்துப்பாட்டு
(இ) எட்டுத்தொகை
(ஈ) தொல்காப்பியம்
Answer:
(ஈ) தொல்காப்பியம்
Question 2.
செய்தி 1 – ஒவ்வோர் ஆண்டும் ஜுன் 15 ஐ உலகக் காற்று நாளாகக் கொண்டாடி வருகிறோம்.
செய்தி 2 – காற்றாலை உற்பத்தியில் இந்தியாவில் தமிழகம் இரண்டாமிடம் என்பது எனக்குப் பெருமையே.
செய்தி 3 – காற்றின் ஆற்றலைப் பயன்படுத்திக் கடல் கடந்து வணிகம் செய்து வெற்றி கண்டவர்கள் தமிழர்கள்.
(அ) செய்தி மட்டும் சரி
(ஆ) செய்தி 1, 2 ஆகியன சரி
(இ) செய்தி 1, 2, 3 சரி –
(ஈ) செய்தி 1, 3 ஆகியன சரி
Answer:
(இ) செய்தி 1, 2, 3 சரி –
Question 3.
சார்பெழுத்துக்களின் வகைகள்………
(அ) எட்டு
(ஆ) ஒன்பது
(இ) பத்து
(ஈ) ஏழு
Answer:
(இ) பத்து
Question 4.
பாரத ஸ்டேட் வங்கியின் உரையாடு மென்பொருள் எது?
அ) துலா
(ஆ) சீலா
(இ) குலா
(ஈ) இலா
Answer:
(ஈ) இலா
Question 5.
‘மூலித் தீர் தேன் வழிந்து ஒழுகு தாரானைக் கண்டு’ என்னும் தொடரில் தாரணை என்பது யாரைக் குறிக்கிறது?
(அ) சிவபெருமான்
(ஆ) கபிலர்
(இ பாண்டியன்
(ஈ) இடைக்காடனார்
Answer:
(இ பாண்டியன்
Question 6.
சரியான விடை வரிசையைத் தேர்ந்தெடு.
1) கரகாட்டம் – உறுமி எனப்படும் தேவதுந்துபி
2) மயிலாட்டம் – தோலால் கட்டப்பட்ட குடம், சிங்கி, டோலாக், தப்பு
3) ஒயிலாட்டம் – நையாண்டி மேள இசை
4) தேவராட்டம் – நையாண்டி மேள இசை, நாகசுரம், தவில், பம்பை
(அ) 4, 3, 2, 1 (ஆ) 1, 2, 3, 4- (இ) 3, 4, 1, 2 (ஈ) 2, 1, 4, 3
Answer:
1) கரகாட்டம் – உறுமி எனப்படும் தேவதுந்துபி
Question 7.
‘நசை’ என்ற சொல்லின் பொருள் …..
(அ) விருப்பம்
(ஆ) அவமானம்
(இ) வசை
(ஈ) இசை
Answer:
(அ) விருப்பம்
Question 8.
காலக்கணிதம் கவிதையில் இடம்பெற்ற தொடர்….
(அ) இகழ்ந்தால் என்மனம் இறந்துவிடாது
(ஆ) என் மனம் இகழ்ந்தால் இறந்துவிடாது
(இ) இகழ்ந்தால் இறந்துவிடாது என் மனம்
(ஈ) என் மனம் இறந்துவிடாது இகழ்ந்தால்
Answer:
(அ) இகழ்ந்தால் என்மனம் இறந்துவிடாது
Question 9.
உயிரளபெடைகளின் வகைகள்
(அ) ஒன்று
(ஆ) இரண்டு
(இ) மூன்று
(ஈ) நான்கு
Answer:
(இ) மூன்று
Question 10.
செந்தீ – இலக்கணக் குறிப்பு
(அ) பண்புத்தொகை
(ஆ) வினைத்தொகை
(இ) வேற்றுமைத் தொகை
(ஈ) சொல்லிசை அளபெடை
Answer:
(அ) பண்புத்தொகை
Question 11.
சந்தக் கவிமணி எனப்படுபவர்…..
(அ) தமிழழகனார்
(ஆ) பெருஞ்சித்திரனார்
(இ) வெள்ளி வீதியார்
(ஈ) அம்மூவனார் பாடலைப்
Answer:
(அ) தமிழழகனார்
படித்துப் பின்வரும் வினாக்களுக்கு (12, 13, 14, 15) விடை தருக.
செந்தீச் சுடரிய ஊழியும், பனியொடு
தண்பெயல் தலைஇய ஊழியும், அவையிற்று
உள்முறை வெள்ளம் மூழ்கி ஆர்தருபு,
மீண்டும் பீடு உயர்பு ஈண்டி, அவற்றிற்கும்
உள்ளீடு ஆகிய இருநிலத்து ஊழியும்…..
Question 12.
பாடலிலுள்ள எதுகைச் சொற்கள்………
(அ) உள் முறை – உள்ளீடு
(ஆ) வெள்ளம் – மூழ்கி
(இ) தண்பெயல் – தலைஇய
(ஈ) செந்நீர் – தண்பெயல்
Answer:
(அ) உள் முறை – உள்ளீடு
Question 13.
மேற்கண்ட பாடலடிகள் இடம் பெற்ற நூல் ……..
அ) பத்துப்பாட்டு
(ஆ) சங்க இலக்கியங்கள்
(இ) பரிபாடல்
(ஈ) எட்டுத்தொகை
Answer:
(இ) பரிபாடல்
Question 14.
பாடலின் ஆசிரியர் …
(அ) நக்கீரர்
(ஆ) கீரந்தையார்
(இ) பெருங்கௌசிகனார்
(ஈ) குலசேகராழ்வார்
Answer:
(ஆ) கீரந்தையார்
Question 15.
தண்பெயல் என்பதன் பொருள்……..
(அ) குளிர்ந்த மழை
(ஆ) காற்று
(இ) வானம்
Answer:
(அ) குளிர்ந்த மழை
பகுதி – II (மதிப்பெண்க ள்: 18)
பிரிவு – 1
எவையேனும் நான்கு வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் குறுகிய விடையளிக்க.
21 ஆவது வினாவிற்குக் கட்டாயமாக விடையளிக்க வேண்டும். [4 x 2 = 8]
Question 16.
விடைக்கேற்ற வினாக்கள் அமைக்க.
(அ) இயல், இசை, நாடகம் ஆகியன முத்தமிழ் எனப்படும்.
(ஆ) முதற்சங்கம், இடைச்சங்கம், கடைச்சங்கம் விடை:
Answer:
(அ) முத்தமிழ்’ தொகைச் சொல்லை விரித்து எழுதுக.
ஆ) முச்சங்கம்’ தொகைச் சொல்லை விரித்து எழுதுக.
Question 17.
“கழிந்த பெரும் கேள்வியினான் எனக் கேட்டு முழுது உணர்ந்த கபிலன் தன் பால் பொழிந்த பெரும் காதல் மிகு கேண்மையினான் இடைக்காட்டுப் புலவன் தென் சொல்” – இவ்வடிகளில் கழிந்த பெரும் கேள்வியினான் யார்? காதல்மிகு கேண்மையினான் யார்?
Answer:
இவ்வடியில் கழிந்த பெரும் கேள்வியினான்: குசேல பாண்டியன் காதல்மிகு கேண்மையினான். இடைக்காடனார்.
Question 18.
ஆண்பாற் பிள்ளை தமிழ், பெண்பாற் பிள்ளை தமிழ் விளக்குக.
Answer:
ஆண்பாற் பிள்ளைத்தமிழ் (கடைசி மூன்று பருவம்) – சிற்றில், சிறுபறை, சிறுதேர் பெண்பாற் பிள்ளைத்தமிழ் (கடைசி மூன்று பருவம்) – கழங்கு, அம்மானை, ஊசல் இருபாலருக்கும் பொதுவான பருவங்கள் – காப்பு, செங்கீரை, தால், சப்பாணி, முத்தம், வருகை, அம்புலி
Question 19.
பாசவர், வாசவர், பல்நிண விலைஞர், உமணர் – சிலப்பதிகாரம் காட்டும் இவ்வணிகர்கள் யாவர்?
Answer:
வெற்றிலை விற்பவர் – பாசவர் என்றும், ஏலம் முதலான ஐந்து நறுமணப்பொருள் விற்பவர் – வாசவர் என்றும், பல வகையான இறைச்சிகள் விற்பவர் – பல் நிண விலைஞர் என்றும், வெண்மையான உப்பு விற்பவர் – உமணர் என்றும் சிலப்பதிகாரம் காட்டுகிறது.
Question 20.
தானியம் ஏதும் இல்லாத நிலையில் விதைக்காக வைத்திருந்த தினையை உரலில் இட்டுக் குற்றியெடுத்து விருந்தினருக்கு விருந்தளித்தாள் தலைவி’ என்பது இலக்கியச் செய்தி. விருந்தோம்பலுக்குச் செல்வம் மட்டுமே இன்றியமையாத ஒன்றா? உங்கள் கருத்தைக் குறிப்பிடுக.
Answer:
விருந்தளிக்க செல்வம் மட்டும் இருந்தால் போதாது விருந்து கொடுக்க வேண்டும் என்ற எண்ணமும் வேண்டும். பணம் இல்லை என்றாலும் எண்ணம் இருந்தால் தன்னிடம் இல்லை என்றாலும் பிறரிடம் கடன் பெற்றாவது விருந்து அளிக்கப்படும் அதற்குப் பணம் முக்கியம் இல்லை எண்ணம்தான் முக்கியம்.
Question 21.
‘பொருள்’ என முடியும் குறள் எழுதுக.
Answer:
பொருளல் லவரைப் பொருளாகச் செய்யும் பொருளல்ல தில்லை பொருள்.
பிரிவு – 2
எவையேனும் ஐந்து வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் குறுகிய விடையளிக்க. [5 x 2 = 10]
Question 22.
நேற்று என்னைச் சந்தித்தார். அவர் என் நண்பர். (வினைமுற்றை, வினையாலணையும் பெயராக மாற்றுக.)
Answer:
நேற்று என்னைச் சந்தித்தவர் என் நண்பர்.
Question 23.
கீழ்க்காணும் தொடரில் கோடிட்ட சொற்களுக்கு ஏற்ற அதே பொருளுடைய வேறு சொல் அமைத்து எழுதுக. (துணைவியும், முகில், மஞ்சை, களி)
Answer:
நளனும் அவனது துணைவியும் நிடதநாட்டுக்கு வந்ததைக் கண்டு, அந்நாட்டு மக்கள் மழைமுகில் கண்ட மஞ்ஞை போலக் களி கொண்டனர். நளனும் அவனது மனைவியும் நிடதநாட்டுக்கு வந்ததைக் கண்டு, அந்நாட்டு மக்கள் மழைமேகம் கண்ட மயில் போல மகிழ்ச்சி கொண்டனர்.
Question 24.
இரு சொற்களையும் ஒரே தொடரில் அமைத்து எழுதுக.
Answer:
தொடு – தோடு
காதை தொடு, தோடு இருக்கும்.
Question 25.
கலைச்சொற்கள் தருக.
Answer:
(அ) Homograph – ஒப்பெழுத்து
(ஆ) Conversation – உரையாடல்
Question 26.
வா – வேர்ச்சொல்லைக் கொண்டு எழுவாய் தொடர், வினையெச்சத் தொடர் ஆகியவை எழுதுக.
Answer:

Question 27.
பொருத்தமான நிறுத்தற் குறிகளை இடுக.
தமிழை அதன் வழிமொழிகளாகிய தெலுங்கு கன்னட மலையாள துளுவங்களோடு அடங்கி உண்ணாட்டு மொழிகள் என வகைப்படுத்தினர் சிலர்.
Answer:
விடை: தமிழை அதன் வழிமொழிகளாகிய தெலுங்கு, கன்னட, மலையாள, துளுவங்களோடு அடங்கி ‘உண்ணாட்டு மொழிகள்’ என வகைப்படுத்தினர் சிலர்.
Question 28.
பொறித்த – பகுபத உறுப்பிலக்கணம் தருக
Answer:
பொறித்த = பொறி + த் + த் + அ
பொறி – பகுதி
த் – சந்தி
த் – இறந்தகால இடைநிலை
அ – பெயரெச்ச விகுதி பகுதி
III (மதிப்பெண்கள்: 18)
பிரிவு – 1
எவையேனும் இரண்டு வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் சுருக்கமாக விடையளிக்க. [2 x 3 = 6]
Question 29.
தோற்பாவைக் கூத்து பற்றி விளக்குக.
Answer:
- தோலில் செய்த வெட்டு வரைபடங்களை, விளக்கின் ஒளி ஊடுருவும் திரைச்சீலையில் பொருத்தி, கதைக்கேற்ப மேலும் கீழும் பக்கவாட்டிலும் அசைத்துக்காட்டி, உரையாடியும் பாடியும் காட்டுவது தோற்பாவைக் கூத்து.
- தோலால் ஆன பாவையைக் கொண்டு நிகழ்த்தும் கலையாதலால் தோற்பாவை என்னும் பெயர் பெற்றது.
- இசை , ஓவியம், நடனம், நாடகம், பலகுரலில் பேசுதல் ஆகியவை இதில் இணைந்துள்ளன. கூத்து நிகழ்த்தும் திரைச்சீலையின் நீளம்.
- அகலம் ஆகியன பாவையின் அமைப்பையும் எண்ணிக்கையையும் பொறுத்து வேறுபடுகின்றன.
- இந்நிகழ்ச்சியில் பாவையின் அசைவு, உரையாடல், இசை ஆகியனவற்றோடு ஒளியும் முதன்மை பெறுகின்றது.
Question 30.
ஜெயகாந்தன் குறிப்பு வரைக.
Answer:
- கருத்தாழமும் வாசகச் சுவைப்பும் கலந்து இலக்கியங்கள் படைத்தவர் ஜெயகாந்தன்.
- சமகாலக் கருத்துகளையும் நிகழ்வுகளையும் சமகால மொழியில் சமகால உணர்வில் தந்தவர்.
- மனிதம் தோய்ந்த எழுத்தாளுமை மிக்கவர் ஜெயகாந்தன்.
- காந்தத் தன்மையுடைய எழுத்தை நினைவூட்டும் வகையில் அவரது படைப்புப் புதையலிலிருந்து சில.
- மணிகளைத் தொடுத்து ஜெயகாந்தம் என்னும் நினைவு இதழ் உருவாக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது.
- குறும்புதினங்களையும், புதினங்களையும், கட்டுரைகளையும், கவிதைகளையும் படைத்துள்ளார்.
- தன் கதைகளைத் திரைப்படமாக இயக்கியிருக்கிறார்; தலைசிறந்த உரத்த சிந்தனைப் பேச்சாளராகவும் திகழ்ந்தார்.
- சாகித்திய அகாதெமி விருதையும் ஞானபீட விருதையும் பெற்ற இவருடைய கதைகள் பிறமொழிகளில் மொழிபெயர்க்கப்பட்டுள்ளன.
- அவருடைய படைப்புகள் உணர்ச்சி சார்ந்த எதிர்வினைகளாக இருக்கின்றன.
இதுவே அவருக்குச் “சிறுகதை மன்னன்” என்ற பட்டத்தைத் தேடித்தந்தது
Question 31.
உரைப்பத்தியைப் படித்து வினாக்களுக்கு விடை தருக.
Answer:
ஒரு மொழி பொதுமக்களாலும் அதன் இலக்கியம், புல மக்களாலும் அமையப்பெறும். தமிழ்ப் பொதுமக்கள் உயர்ந்த பகுத்தறிவுடையர். எத்துணையோ ஆராய்ச்சி நடந்துவரும் இக்காலத்திலும் எத்துணையோ மொழிகளினின்று கடன் கொண்ட ஆங்கில மொழியிலும் நூலிலும் இலையைக் குறிக்க Leaf (லீஃப் என ஒரே சொல் உள்ளது.
ஆங்கில நூல்களிலும் வேறு பல வகைகளில் இலைகளைப் பாகுபாடு செய்தனரேயன்றி, தமிழ்ப்பொதுமக்களைப் போல வன்மை மென்மை பற்றித் தாள், இலை, தோகை, ஓலை எனப் பாகுபாடு செய்தாரில்லை. இத்தகைய பாகுபாடு ஏனைய உறுப்புகளுக்குள்ளும் செய்யப்பட்டது முன்னர்க் காட்டப்பெற்றது.
(அ) தமிழ்ப் பொதுமக்கள் எத்தகைய தன்மையுடையவர்?
Answer:
தமிழ்ப் பொதுமக்கள் உயர்ந்த பகுத்தறிவுடையவர்.
(ஆ) ஆங்கில மொழியிலும், நூலிலும் இலையைக் குறிக்கப் பயன்படும் ஒரே சொல் என்ன?
Answer:
Leaf (லீஃப்)
(இ) இலையைக் குறிக்கும் மற்ற சொற்கள் யாவை?
Answer:
தோகை, ஓலை
பிரிவு – 2
எவையேனும் இரண்டு வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் சுருக்கமாக விடையளிக்க.
34 ஆவது வினாவிற்குக் கட்டாயமாக விடையளிக்க வேண்டும். [233 = 6]
Question 32.
தமிழன்னையை வாழ்த்துவதற்கான காரணங்களாகப் பாவலரேறு சுட்டுவன யாவை?
Answer:
- அன்னைத் தமிழ்மொழியே! அழகாய் அமைந்த செந்தமிழே! பழமைக்கும் பழமையாய்த் தோன்றிய நறுங்கனி நீயே!
- கடல் கொண்ட குமரிக் கண்டத்தில் அரசாண்ட மண்ணுலகப் பேரரசே! பாண்டிய மன்னனின் மகளே!
- திருக்குறளின் பெரும் பெருமைக்குரியவளே, இனிமையான பத்துப்பாட்டே, எட்டுத்தொகையே பதினெண்கீழ்க்கணக்கே நிலைத்த சிலப்பதிகாரமே.
- அழகான மணிமேகலையே ! விளங்கும் உன்னைத் தலைபணிந்து வாழ்த்துகின்றோம்.
- பழமைக்கும் பழமையாய்த் தோன்றியது.
- கடல் கொண்ட குமரிக்கண்டத்தில் அரசாண்ட மண்ணுலகப் பேரரசாகத் திகழ்வது.
- பாண்டிய மன்னனின் மகளாகத் தோன்றியது. திருக்குறளைப் பெற்ற பெருமைக்குரியது.
- பத்துப்பாட்டு, எட்டுத்தொகை, பதினெண்கீழ்க்கணக்கு போன்ற நூல்களையும் சிலப்பதிகாரம்.
- மணிமேகலை போன்ற காப்பியங்களையும் பெற்ற பெருமைக்குரியது.
Question 33.
முல்லை நிலத்து முதற்பொருள் கரும்பொருள் உரிப்பொருள் ஆகியவற்றை விரித்து எழுதுக.
Answer:
- முதற்பொருள் நிலம் – காடும் காடு சார்ந்த இடமும்
- பொழுது – பெரும்பொழுது கார்காலம் ஆவணி, புரட்டாசி
- சிறுபொழுது – மாலை கருப்பொருள் – நீர்- குறுஞ்சுனை நீர், காட்டாறு
- மரம் – கொன்றை, காயா, குருந்தம்
- பூ- முல்லை, பிடவம், தோன்றிப்பூ
- உரிப்பொருள் – இருத்தலும் இருத்தல் நிமித்தமும்
Question 34.
அடிபிறழாமல் எழுதுக.
Answer:
”தண்டலை மயில்களாட” எனத் தொடங்கும் கம்பராமாயணப் பாடல்.
தண்டலை மயில்களாட தாமரை விளக்கந் தாங்க,
கொண்டல்கள் முழவினேங்க குவளைகண் விழித்து நோக்க,
தெண்டிரை யெழினி காட்ட தேம்பிழி மகரயாழின்
வண்டுகளி னிதுபாட மருதம் வீற்றிருக்கும்மாதோ – கம்பர்
(அல்லது)
“தூசும் துகிரும்” எனத் தொடங்கும் சிலப்பதிகாரப் பாடல்.
தூசும் துகிரும் ஆரமும் அகிலும்
மாசு அறு முத்தும் மணியும் பொன்னும்
அருங்கல வெறுக்கையோடு அளந்துகடை அறியா
வளம் தலை மயங்கிய நனந்தலை மறுகும்;
பால்வகை தெரிந்த பகுதிப் பண்டமொடு
கூலம் குவித்த கூல வீதியும்; – இளங்கோவடிகள்.
பிரிவு – 3
எவையேனும் இரண்டு வினாக்களுக்கு மட்டும் சுருக்கமாக விடையளிக்க. [2 x 3 = 6]
Question 35.
தொழிற்பெயருக்கும், வினையாலணையும் பெயருக்கும் உள்ள வேறுபாட்டை எழுதுக.
Answer:
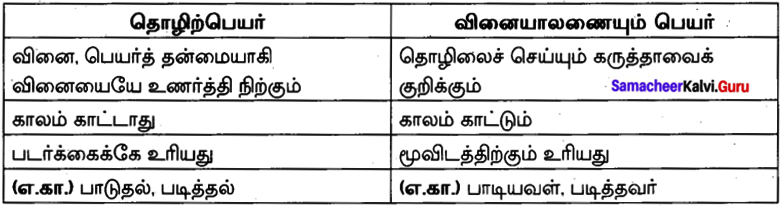
Question 36.
நன்றிக்கு வித்தாகும் நல்லொழுக்கம் தீயொழுக்கம் என்றும் இடும்பை தரும். இக்குறட்பாவினை அலகிட் பாடு தருக.
Answer:
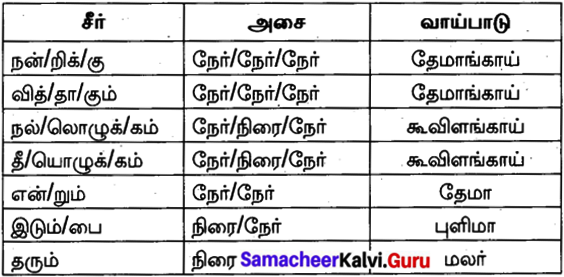
Question 37.
நிரல்நிறை அணி என்றால் என்ன? சான்றுடன் விளக்குக.
Answer:
நிரல் = வரிசை ; நிறை = நிறுத்துதல் சொல்லையும் பொருளையும் வரிசையாக நிறுத்தி அவ்வரிசைப்படியே இணைத்துப் பொருள் கொள்வது நிரல்நிறை அணி எனப்படும்.
(எ.கா.) அன்பும் அறனும் உடைத்தாயின் இல்வாழ்க்கை
பண்பும் பயனும் அது.
பாடலின் பொருள் : இல்வாழ்க்கை அன்பும், அறமும் உடையதாக விளங்குமானால், அந்த வாழ்க்கையின் பண்பும் பயனும் அதுவே ஆகும்.
அணிப்பொருத்தம்: இக்குறளில் அன்பும் அறனும் என்ற சொற்களை வரிசையாக நிறுத்தி, பண்பும் பயனும் என்ற சொற்களை முறைப்படக் கூறியுள்ளமையால் இது நிரல் நிறை அணி ஆகும்.
பகுதி – IV (மதிப்பெண்கள்: 25)
அனைத்து வினாக்களுக்கும் விடையளிக்க. [5 x 5 = 25]
Question 38.
(அ) ஆற்றுப்படுத்தல் என்பது அன்றைக்குப் புலவர்களையும் கலைஞர்களையும்
வள்ளல்களை நோக்கி நெறிப்படுத்துவதாக இருந்தது. அது இன்றைய நிலையில் ஒரு வழிகாட்டுதலாக மாறியிருப்பதை விளக்குக.
Answer:
- ஆற்றுப்படுத்துதல் என்பது வள்ளலை நாடி எதிர்வருபவர்களை அழைத்து யாம் இவ்விடத்தே சென்று இன்னவெல்லாம் பெற்று வருகின்றோம்.
- நீயும் அந்த வள்ளலிடம் சென்று வளம் பெற்று வாழ்வாயாக என்று கூறுதல் ஆற்றுப்படை ஆகும்.
- ஆற்றுப்படுத்துதல் என்பது இன்றைய நிலையில் ஒரு வழிகாட்டுதலாக இருக்கிறது.
- தன்னிடம் இல்லை என்றோ அல்லது தெரியாது என்றோ கூறாமல் யார் வந்தாலும்.
- அவர்களுக்கு வழிகாட்டுதலாகவும் இருக்கிறது.
- அவர்களுக்கு அறிவுரை கூறி அவர்களை வழிகாட்டுகின்றனர்.
- அன்றைய ஆற்றுப்படுத்துதல் இன்றைய வழிகாட்டுதலாக மாறியுள்ளது.
- இது ஒவ்வொரு நிலையிலும் மாற்றம் அடைந்துள்ளது. உதவி தேவைப்படுபவர்களுக்கு பெரும் உதவியாக இருந்து வருகிறது.
- இதுவே இன்றைய ஆற்றுப்படுத்துதல் ஆகும். பாகானை
(அல்லது)
(ஆ) காலக்கணிதம் கவிதையில் பொதிந்துள்ள நயங்களைப் பாராட்டி எழுதுக.
Answer:
கவிஞன் யானோர் காலக் கணிதம்
கருப்படு பொருளை உருப்பட வைப்பேன்!
புவியில் நானோர் புகழுடைத் தெய்வம்
பொன்னினும் விலைமிகு பொருளென் செல்வம்!
இவைசரி யென்றால் இயம்புவதென் தொழில்
இவைதவ றாயின் எதிர்ப்பதென் வேலை!
ஆக்கல் அளித்தல் அழித்தல் இம் மூன்றும்
அவனும் யானுமே அறிந்தவை, அறிக! – கண்ண தாசன்
கருத்து:
நான் தான் காலக்கணிதன் கருப்படும் பொருளை உருப்பட வைப்பேன் ! புவியில் நல்லவர்கள் பலபேர் இருக்கின்றனர். பொன்னும் விலைமிகு பொருளும் இருக்கிறது. அது செல்வம், இது சரி, இது தவறு என்று சொல்வது என் வேலை செய்வது தவறாயின் எதிர்ப்பது என் வேலை சரி என்றால் புகழ்வது என் தொழில் ஆக்கல், காத்தல், அழித்தல் இம்மூன்றும் இறைவனும் நானும் மட்டுமே அறிந்த தொழில்களாகும். எதுகை. செய்யுளின் இரண்டாம் எழுத்து ஒன்றி வரத் தொடுப்பது எதுகை.
கவிஞன், புவியில் மோனை: செய்யுளில் முதல் எழுத்து ஒன்றிவரத் தொடுப்பது மோனை. கவிஞன், காலம், கணிதம், கருப்படு முரண்: சரி X தவறு, ஆக்கல் x அழித்தல் சொல் நயம்: கவிஞன் யானோர் காலக் கணிதம் கருப்படு பொருளை உருப்பட வைப்பேன் என்ற சொற்றொடர்களை அமைத்துப் பாடலுக்குச் சிறப்புச் சேர்த்துள்ளார்.
(எ.கா.) தெய்வம் எனத் தன்னைக் கூறும் கவிஞர் புகழுடைத் தெய்வம் என்ற சொற்றொடரைக் கையாளும் நயம் படித்து இன்புறத்தக்கது.
பொருள் நயம்: ஆக்கல் அளித்தல் அழித்தல் இம்மூன்றும் அவனும் யானுமே அறிந்தவை என்றும் ஆழ்ந்த பொருள் சுவை உடையது (எ.கா.) தன் செல்வம் எது எனக் கூற வந்த கவிஞர், பொன் விலை உயர்ந்தது. அதைக் காட்டிலும் விலை உயர்ந்த கவிதைப்பொருளே என் செல்வம் எனக் கூறியிருக்கும். இக்கவிதையின் பொருள்நயம் போற்றுதற்குரியது.
Question 39.
(அ) உங்கள் பள்ளிக்குத் தேவையான கையேடுகளை அனுப்பித் தருமாறு புத்தக பதிப்பகத்திற்கு கடிதம் வரைக.
Answer:
அனுப்புநர்
கண்ண ன், அரசினர் மேல்நிலைப் பள்ளி, மேலூர்,
திருச்சி – 620 018.
பெறுநர்
உயர்திரு நவீன் அவர்கள்,
சாரதா பதிப்பகம், 10/34,
மகாலட்சுமி தெரு,
தி.நகர்,
சென்னை – 600 017.
ஐயா,
பொருள்: கையேடுகள் சில அனுப்பி வைத்தல் – தொடர்பாக வணக்கம். எம் பள்ளிக்கு சில கையேடுகள் தேவைப்படுகின்றன. அவற்றிற்குரிய தொகையினைப் பணவிடைத்தாள் மூலம் அனுப்பியுள்ளேன். கீழே குறிப்பிட்ட எனது முகவரிக்குப் பதிவஞ்சல் மூலமாகத் தாமதமின்றி கையேடுகளை அனுப்பி வைக்குமாறு. தாழ்மையுடன் வேண்டுகிறேன்.
நன்றி,
இடம்: திருச்சி
தேதி: 10.04.2019
இங்ஙனம்,
தங்கள் உண்மையுள்ள
கண்ண ன்.
தேவையான கையேடுகள்
- தமிழ் பத்தாம் வகுப்புக் கையேடு – 30 பிரதிகள்
- ஆங்கிலம் பத்தாம் வகுப்புக் கையேடு – 15 பிரதிகள்
- கணிதம் பத்தாம் வகுப்புக் கையேடு – 20 பிரதிகள்
- அறிவியல் பத்தாம் வகுப்புக் கையேடு – 10 பிரதிகள்
உறைமேல் முகவரி
பெறுநர்
உயர்திரு நவீன் அவர்கள்,
சாரதா பதிப்பகம்,
10/34, மகாலட்சுமி தெரு, தி. நகர்,
சென்னை – 600017.
(அல்லது)
(ஆ) பள்ளி வளாகத்தில் நடைபெற்ற மரம் நடுவிழாவுக்கு வந்திருந்த சிறப்பு விருந்தினருக்கும் பெற்றோருக்கும் பள்ளியின் பசுமைப் பாதுகாப்புப் படை’ சார்பாக நன்றியுரை எழுதுக.
Answer:
வீட்டுக்கொரு மரம் வளர்ப்போம் என்பது அன்றைய வாசகம். ஆளுக்கொரு மரம் வளர்க்க வேண்டிய தேவை இன்று ஏற்பட்டுள்ளது. மரங்கள் இயற்கையின் கொடை இயற்கை அன்னையின் மடியில் மலர்ந்த முதல் குழந்தை மரம் தானே! அவற்றை நாம் இல்லாமல் செய்யலாமா? இயற்கையின் வழியில் செல்வோம் ! மரங்களையும், பயனுள்ள செடி, கொடிகளையும் வளர்ப்போம் பயன் பெறுவோம் பசுமை பாரதத்தை உருவாக்குவோம் என்ற சிந்தனையை மாணவர்கள் மனதில் விதை ஊன்றிய எம் சிறப்பு விருந்தினருக்கு நன்றிகளை எங்கள் பள்ளியின் சார்பாகத் தெரிவித்துக் கொள்கிறோம். இங்கு வந்திருந்து எங்களைச் சிறப்பித்த பெற்றோருக்கும் நன்றிகளைத் தெரிவித்துக் கொள்கிறோம்.
Question 40.
படம் உணர்த்தும் கருத்தை நயமுற எழுதுக.
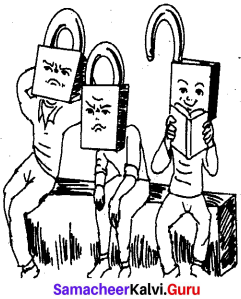
Answer:
விடை மனிதர்களே! தன் மனதிற்கும்
அறிவுக்கும் பூட்டு போட்டுக்கொள்ளாதீர்கள்
திறந்த மனதுடன் தொலைநோக்குடன்
கல்வியைக் கற்க பழகுங்கள் – நம்
எண்ணங்களுக்குப் பூட்டு போட்டுக்
கொண்டால் விழிப்புணர்வும் – அறிவு
முதிர்ச்சியும் இல்லாமல் போகும்.
Question 41.
கீழ்க்காணும் படிவத்தை நிரப்புக.
Answer:
நூலக உறுப்பினர் படிவம் மதுரை மாவட்ட நூலக ஆணைக்குழு மைய கிளை ஊர்ப்புற நூலகம் மைய நூலகம்.
உறுப்பினர் சேர்க்கை அட்டை
அட்டை எண்
உறுப்பினர் எண் 567
- பெயர் – கந்தன்
- தந்தை பெயர் – ஆறுமுகம்
- பிறந்த தேதி – 06.06.2005
- வயது – 14
- படிப்பு – பத்தாம் வகுப்பு
- தொலைபேசி எண் – 98678 64590
- முகவரி – 35 அம்மன் கோயில் தெரு
(அஞ்சல் குறியீட்டு எண்ணுடன்) – 5வது தெரு, மேலவீதி, மதுரை – 625 002
நான் அ. கந்தன் நூலகத்தில் உறுப்பினராகப் பதிவு செய்ய இத்துடன் காப்புத்தொகை ரூ 100 சந்தா தொகை ரூ 100 ஆக மொத்தம் ரூ 200 ரொக்கமாகச் செலுத்துகிறேன். நூலக நடைமுறை மற்றும் விதிகளுக்குக் கட்டுப்படுகிறேன் என உறுதியளிக்கிறேன்.
இடம் : மதுரை
நாள் : 24.5.2019
தங்கள் உண்மையுள்ள
அ. கந்தன்
திரு/திருமதி / செல்வி /செல்வன் அவர்களை எனக்கு நன்கு தெரியும் எனச் சான்று அளிக்கிறேன்.
தீபா அலுவலக முத்திரை
பிணைப்பாளர் கையொப்பம்
(பதவி மற்றும் அலுவலகம்)
மாநில மைய அரசு அதிகாரிகள், கல்லூரி முதல்வர்கள் பேராசிரியர்கள்,
உயர் மேல்நிலைப்பள்ளி தலைமை ஆசிரியர்கள், சட்டமன்ற நாடாளுமன்ற
உறுப்பினர்கள், நகராட்சி/மாநகராட்சி ஒன்றிய பேரூராட்சி உறுப்பினர்கள்
Question 42.
(அ) புயலின் போது – கீழ்க்கண்ட அறிவிப்பைக் கேட்ட நீங்கள், உங்களையும் உங்கள் குடும்பத்தாரையும் காப்பாற்றும் வகையில் செய்யும் செயல்களை வரிசைப்படுத்தி எழுதுக.

Answer:
விடை
- புயலின் போது மின்சாரம் துண்டிக்க நேரிடும் அதனால் மெழுகுவர்த்தி தீப்பெட்டி அருகில் வைத்துக் கொள்ளவும்.
- பிஸ்கெட், பால் பாக்கெட்களை வாங்கி வைத்துக் கொள்ள வேண்டும்.
- வெளியே செல்வதைத் தவிர்க்க வேண்டும்.
- மரங்களின் அருகில் நிற்கக் கூடாது.
- உதவிக்கு அழைக்க அவசர எண்களைத் தெரிந்து வைத்துக் கொள்ள வேண்டும்.
(அல்லது)
(ஆ) மொழிபெயர்க்க.
Respected ladies and gentlemen, I am Ilangovan studying tenth standard. I have come here to say a few words about our Tamil culture. Sangam literature shows that Tamils were best in culture and civilization about two thousand years ago. Tamils who have defined grammar for language have also defined grammar for life. Tamil culture is rooted in the life styles of Tamils throughout India. Srilanka, Malaysia, Singapore, England and Worldwide. Though our culture is very old, it has been updated consistently. We should feel proud about our culture. Thank you one and all.
விடை இங்கு கூடி இருக்கும் அனைவருக்கும் என் மனமார்ந்த வணக்கம். என் பெயர் இளங்கோவன். நான் 10 ஆம் வகுப்பு படிக்கிறேன். தமிழ்க் கலாச்சாரத்தைப் பற்றி சில வார்த்தைகள் கூற வந்துள்ளேன். இரண்டாயிரம் ஆண்டுகளுக்கு முன்னரே தமிழன் கலாச்சாரத்திலும், நாகரிகத்திலும் மேம்பட்டு இருந்தான் என்பதைச் சங்க இலக்கியங்கள் புலப்படுத்துகின்றன தமிழ் மொழிக்கு இலக்கணம் வகுத்த தமிழன் வாழ்க்கை நெறிக்கும் இலக்கணம் வகுத்துள்ளான்.
தமிழ்க் கலாச்சாரம் இலங்கை, சிங்கப்பூர், இங்கிலாந்து மற்றும் உலகளாவிய இந்தியத் தமிழ் மக்களின் வாழ்வாதாரங்களில் வேரூன்றி நிற்கிறது. நம் கலாச்சாரம் பழமை வாய்ந்ததாக இருப்பினும் அது தொடர்ச்சியாகப் புதுப்பித்த வண்ணமே இருக்கின்றன. நாம் நம் கலாச்சாரத்தைப் பற்றி பெருமை கொள்ள வேண்டும். அனைவருக்கும் நன்றி.
பகுதி – V (மதிப்பெண்கள்: 24)
அனைத்து வினாக்களுக்கும் விரிவாக விடையளிக்க. [3 x 8 = 24]
Question 43.
(அ) ஜெயகாந்தன் நினைவுச் சிறப்பிதழை, வார இதழ் ஒன்று வெளியிட இருக்கிறது. அதற்கான ஒரு சுவரொட்டியை வடிவமைத்து அளிக்க
மாவட்ட ஆட்சியர் தலைமையில்
நினைவுச் சிறப்பிதழ் வெளியீட்டு விழா
ஞானபீட விருது பெற்ற காலம் சென்ற
எழுத்துலக வித்தகர். தெய்வத்திரு
ஜெயகாந்தன்
அவர்களின் நினைவுச் சிறப்பிதழ் வெளியீட்டு விழா
நாள் : 14.4.2019
நேரம் : 6.00 மாலை
இடம் : கலையரங்கம்
சென்னை
(அல்லது)
(ஆ) ஒரு குழந்தையைத் தூக்கவும் கீழே விழுந்த ஒரு தேனீர்க் கோப்பையை எடுக்கவும் மென்பொருள் அக்கறை கொள்ளுமா? வெறும் வணிகத்துடன் நின்றுவிடுமா? இக்கருத்துகளை ஒட்டிச் செயற்கை நுண்ணறிவின் எதிர்கால வெளிப்பாடுகள்’ பற்றி ஒரு கட்டுரை எழுதுக.
எதிர்காலத்தில் ரோபோக்கள் :
வேலை வாய்ப்புகளில் கணிசமான மாற்றங்களைச் செயற்கை நுண்ணறிவு கொண்டுவரப்போகிறது. எதிர்காலத்தில் ரோபோ’ விடம் குழந்தையை ஒப்படைத்துவிட்டு நிம்மதியாக அலுவலகம் செல்லும் பெற்றோர்களை நாம் பார்க்கப்போகிறோம். வயதானவர்களுக்கு உதவிகள் செய்தும் அவர்களுக்கு உற்ற தோழனாய்ப் பேச்சுக் கொடுத்தும் பேணும் ரோபோக்களை நாம் பார்க்கப்போகிறோம்! செயற்கை நுண்ணறிவுள்ள ரோபோக்களால், மனிதர் செய்ய இயலாத, அலுப்புத் தட்டக்கூடிய, கடினமான செயல்களைச் செய்ய முடியும்; மனித முயற்சியில் உயிராபத்தை விளைவிக்கக் கூடிய செயல்களைச் செய்யமுடியும்!
புதிய வணிக வாய்ப்புகளைச் செயற்கை நுண்ணறிவு நல்குகிறது. பெருநிறுவனங்கள் தங்கள் பொருள்களை உற்பத்தி செய்யவும் சந்தைப்படுத்தவும் செயற்கை நுண்ணறிவைப் பயன்படுத்துகின்றன. விடுதிகளில், வங்கிகளில், அலுவலகங்களில் தற்போது மனிதர் அளிக்கும் சேவைகளை ரோபோக்கள் அளிக்கும். மேலும், நம்முடன் உரையாடுவது, ஆலோசனை வழங்குவது, பயண ஏற்பாடு செய்துதருவது, தண்ணீர் கொண்டு வந்து தருவது, உடன் வந்திருக்கும் குழந்தைகளுக்கு வேடிக்கை காட்டுவது எனப் பலவற்றைச் செய்யும்.
எதிர்காலத்தில் நாம் பயணிக்கும் ஊர்திகளைச் செயற்கை நுண்ணறிவைக் கொண்டு இயக்கவேண்டியிருக்கும். இத்தகைய ஊர்திகள் ஏற்படுத்தும் விபத்துகள் குறையும்; போக்குவரத்து நெரிசல் இருக்காது. அதன்மூலம் பயண நேரம் குறையும் ; எரிபொருள் மிச்சப்படும். இத்தகைய மென்பொருள்கள் கவிதைகள், கதைகள், விதவிதமான எழுத்து நடைகள் போன்றவற்றைக் கற்றுக்கொண்டு மனிதர்களுடன் போட்டியிட்டாலும் வியப்பதற்கில்லை. கல்வித் துறையில் இத்தொழில் நுட்பத்தைப் பலவிதங்களில் பயன்படுத்தும் சாத்தியக்கூறுகள் இருக்கின்றன.
செயற்கை நுண்ணறிவின் பொதுவான கூறுகள்:
செயற்கை நுண்ணறிவு நமது வாழ்க்கையையும் வணிகத்தையும் நம்மை அறியாமலேயே வளப்படுத்திக் கொண்டிருக்கின்றது. இந்தத் தொழில் நுட்பத்தைக் கண்டு அச்சப்பட்டவர்களின் அலறல்களை நாம் எதிர்கொள்வதே முதல் அறைகூவல். ஒவ்வொரு புதிய கண்டுபிடிப்பு அறிமுகமாகும் போதும் பழைய வேலைவாய்ப்புகள் புதிய வடிவில் மாற்றம் பெறுகின்றன. ஆகவே, செயற்கை நுண்ணறிவுத் தொழில்நுட்பம் அளிக்கும் வியக்கத்தக்க நன்மைகளைப் புரிந்துகொள்ளவும் வரவேற்கவும் நாம் தயாராக வேண்டும்.
மனித இனத்தைத் தீங்குகளிலிருந்து காப்பாற்றவும் உடல் நலத்தைப் பேணவும் கொடிய நோய்களைத் தொடக்க நிலையிலேயே கண்டறியவும் மருத்துவம் செய்யும் முறைகளைப் பட்டறிவு மிக்க மருத்துவரைப் போலப் பரிந்துரை செய்யவும் செயற்கை நுண்ணறிவைப் பயன்படுத்தும் ஆராய்ச்சிகள் மும்முரமாக நடந்து வருகின்றன.
கல்வியில் செயற்கை நுண்ணறிவு :
ஒரு காலத்தில் வாழ்க்கையில் முன்னேறுவதற்கு எழுதப் படிக்கத் தெரிந்த கல்வியறிவே போதுமானதாக இருந்தது. இப்போது கல்வியறிவுடன் மின்னணுக் கல்வியறிவையும் மின்னணுச் சந்தைப்படுத்துதலையும் அறிந்திருப்பது வாழ்க்கையை எளிதாக்கவும் வணிகத்தில் வெற்றியடையவும் உதவுகிறது. ஆனால் எதிர்காலத்தில் செயற்கை நுண்ணறிவு பற்றிய அறிவும் நான்காவது தொழிற்புரட்சியின் தொழில் நுட்பங்களைப் பயன்படுத்தும் அறிவுமே நம்மை வளப்படுத்த உதவும்.
ஆனாலும் முன்னேற்றமே! :
மனிதக் கண்டுபிடிப்புகள் அனைத்திலும் நன்மை, தீமை என்று இரண்டு பக்கங்கள் இருந்தே வந்திருக்கின்றன. அதற்கேற்ப மனிதர்கள் தங்களை மாற்றிக்கொள்வார்கள். இப்போது உலகில் இங்கொன்றும் அங்கொன்றுமாகப் பயன்பாட்டில் இருக்கின்ற செயற்கை நுண்ணறிவுத் தொழில்நுட்பம், எதிர்காலத்தில் உலகின் ஒவ்வொரு துறையிலும் அளவிடற்கரிய முன்னேற்றத்தைத் தரும்.
Question 44.
(அ) குறிப்புகளைக் கொண்டு ஒரு பக்க அளவில் நாடகம் எழுதுக. மாணவன் – கொக்கைப் போல, கோழியைப் போல – உப்பைப் போல – இருக்க வேண்டும் – கொக்கு காத்திருந்து கிடைக்கும் வாய்ப்பைப் பயன்படுத்திக்கொள்ளும் – குப்பையைக் கிளறினாலும் தனது உணவை மட்டுமே எடுத்துக்கொள்ளும் கோழி – கண்ணுக்குத் தெரியாவிட்டாலும் உப்பின் சுவையை உணரமுடியும் – ஆசிரியர் விளக்கம் – மாணவன் மகிழ்ச்சி
Answer:
காட்சி – 1
இடம் : வகுப்பறை
பங்கு பெறுவோர் : தமிழ் ஆசிரியர் மாணவிகள் (செல்வி, மேரி, பர்வினா) (ஆசிரியர் இலக்கிய மன்றப் போட்டிக்கான தலைப்புகளை அறிவித்தல்) பாகை கலை கள்
மாணவர்கள் : வணக்கம் அம்மா ! ஆசிரியரே!)
ஆசிரியர் : வணக்கம் மாணவிகளே அனைவரும் நலம் தானே உங்களுக்கெல்லாம் ஒரு
மகிழ்ச்சியான செய்தி : சொல்லட்டுமா?
செல்வி : அது என்ன செய்தி ஆசிரியரே ஆர்வமாக இருக்கு கொஞ்சம் விளக்கிக் கூறுங்கள்
ஆசிரியர் : வருகின்ற புதன்கிழமையன்று, இலக்கிய மன்ற விழா நடைபெற இருக்கிறது. அதன் சிறப்பு விருந்தினர் நம் பள்ளி முதல்வர். அந்த விழாவில் சொற்பொழிவில் பங்குபெறும் மாணவிகளுக்குச் சிறப்பு பரிசுகளை நம் முதல்வர் கையால் வழங்குவார்.
மேரி : மிக்க மகிழ்ச்சி ஆசிரியரே அதன் தலைப்புகள் என்ன?
ஆசிரியர் : கொக்கு! கோழி ! உப்பு இவற்றின் சிறப்புத் தன்மைகளை விளக்கிக் கூற வேண்டும். இதைப்பற்றிய கூடுதல் தகவல்களை வீட்டில் உள்ளவர்களிடமும் கேட்டு அறிந்து கொண்டு, போட்டியில் பங்கு பெற்று, பரிசு பெற உங்களை வாழ்த்துகிறேன்.
பர்வின் : நன்றி ஆசிரியரே!
ஆசிரியர் : நாளை தான் கடைசி நாள்! போட்டியில் பங்கு பெறுவோர் பெயர் பட்டியலை கொடுக்கவும்.
காட்சி – 2
இடம் : வீடு
பங்கு பெறுவோர் : மேரி, அப்பா, அம்மா, தாத்தா (மாணவிகள் வீட்டுக்கு சென்று போட்டிக்கான விவரங்களை சேகரித்தல்)
அப்பா : மேரி இன்னைக்கு (இன்றைக்கு என்ன ஆச்சு உனக்கு? பள்ளி முடிந்து வீட்டிற்கு வந்ததிலிருந்து ஏதோ யோசிச்சிட்டே
இருக்கிற? : அது அப்பா ! எங்க பள்ளியிலே இலக்கிய மன்ற விழா நடக்க போகிறது. அதில் சொற்பொழிவு நடத்த எங்க தமிழ் ஆசிரியர் மூன்று தலைப்புகளை
கொடுத்திருக்காங்க அது பற்றிதான் ஒரே யோசனையா இருக்கு அப்பா!
அப்பா : அது என்ன தலைப்பு மேரி?
மேரி : கொக்கு, கோழி, உப்பு இவற்றின் சிறப்புகளைக் கூற வேண்டும் அப்பா.
அப்பா : அவ்வளவு தானே உன் சோகத்தை விடு எனக்குத் தெரிந்த கொக்கின் சிறப்புக்களைக் கூறுகிறேன் கேட்டுக்கோ!
மேரி : சரி அப்பா நீங்க சொல்ல சொல்ல நானும் எழுதிக் கொள்கிறேன்.
அப்பா : கொக்கானது தனக்கு ஏற்ற பெரிய மீன் வரும் வரை ஓடையில், வாடிய நிலையில் இருக்கும், தனக்கு ஏற்ற பெரிய மீன் வருவதை அறிந்தவுடன் விரைந்து தன் கூர்மையான அலகுகளால் கொத்தி எடுக்கும். அதுபோல நாமும் எந்தச் செயலைச் செய்தாலும் காலத்தின் இறப்பை உணர்ந்து விரைந்து செயல்பட வேண்டும். காலத்தின் முக்கியத்துவத்தை உணர்ந்ததால் தான் திருவள்ளுவரும், கொக்கொக்கக் கூம்பும் பருவத்து மற்றதன் குத்தொக்க சீர்த்த இடத்து என்று கூறியுள்ளார்.
மேரி : சிறப்பான செய்திகள் அப்பா
அப்பா : அடுத்த தலைப்பான கோழியின் தன்மைகளைத் தாத்தாவிடம் கேட்டுத் தெரிந்துகொள். அப்பாவிற்கு சில முக்கியமான அலுவலக வேலைக் காரணமாக வெளியே செல்ல வேண்டும் சரியா மேரி.
மேரி : சரி அப்பா ! தாத்தா ! தாத்தா! எனக்குக் கொஞ்சம் கோழியின் பண்புகளைச் சொல்வீங்களா!
தாத்தா : சொல்கிறேன் மேரி குட்டி ! கோழி தனக்கு வேண்டிய உணவினைக் குப்பைமேட்டில் தேடித்தான் உட்கொள்ளும். எல்லாக் குப்பைகளையும் உட்கொள்ளாமல், தனக்கு வேண்டிய உணவினை மட்டுமே உண்ணும் அதைப் போல நாமும், நம் முன்னேற்றத்திற்கான நல்ல செய்திகளை மட்டுமே எடுத்துக் கொண்டு வேண்டாதவற்றை விட்டொழிக்க வேண்டும் மேரி.
மேரி : தாத்தா உண்மையிலேயே நீங்க மிக நல்ல தாத்தா.
அம்மா : மேரி கொஞ்சம் சமையலறைக்கு ஓடி வா! (என்று அம்மா அழைக்க சமையலறைக்கு மேரி செல்கிறாள்)
மேரி : என்னம்மா அவசரம்! அம்மா : அண்ணாச்சி கடைக்குச் சென்று உப்பு வாங்கிக் கொண்டு வா !
மேரி : அம்மா உப்பு என்ற உடனேதான் ஞாபகம் வருது? உப்பின் சிறப்புகள் என்னம்மா?
அம்மா : உப்பில்லா பண்டம் குப்பையிலே’ என்ற பழமொழிக்கேற்பே உணவில் நாம் சுவைத்து உண்ண உப்புதான் முதற்காரணம் ! உப்பு சமையலில் சேர்த்த உடனே தான் இரண்டறக் கலந்து தன் சுவையினைக் கொடுக்கும், அதுபோல நீயும் சமூகப் பணிகளில் மக்களோடு மக்களாகக் கலந்து உன்னால் முடிந்த பயனைநாட்டுக்கும், சமுதாயத்திற்கும் செய்து சிறந்த தொண்டாற்றும் சாதனை பெண்ணாக உயர வேண்டும். சரியா மேரி?!
காட்சி-3
இடம் : பள்ளி (இலக்கிய மன்ற விழா)
பங்கு பெறுவோர் : (தலைமையாசிரியர், தமிழ் ஆசிரியர், மேரி மற்றும் சில மாணவர்கள்) (மேரி இலக்கிய மன்ற விழாவில் பங்கேற்றுத் தலைமையாசிரியர் கையால் பரிசு பெறுதல்)
தமிழ் ஆசிரியர் : இவ்விலக்கிய மன்ற விழாவிற்கு வருகை புரிந்துள்ள தலைமை ஆசிரியரையை வரவேற்று பேச்சுப்போட்டியில் முதலில் பேச ஒன்பதாம் வகுப்பு மாணவி மேரியை அழைக்கிறேன்.
மேரி : அனைவருக்கும் வணக்கம்! (என்று கூறி தான் சேகரித்த செய்திகளை எல்லாம் நிரல்பட, சுவைபட அனைவரும் மகிழும் வண்ணம் எடுத்துக் கூறுதல்) [மேரியின் பேச்சுத்திறனைக் கேட்ட அனைவரும் கைகளைத்தட்டி தங்கள் மகிழ்ச்சியினை வெளிப்படுத்துதல்.
தமிழ் ஆசிரியர் : பேச்சுப் போட்டியில் பங்கேற்கப் பெயர்ப் பதிவு செய்துள்ள மாணவிகள் ஒவ்வொருவராக வந்து பேசுங்கள். [போட்டியாளர்கள் அனைவரும் பேசி முடிகின்றனர்)
தலைமையாசிரியர் : இவ்விலக்கிய மன்ற விழாவில் சிறப்பாகப் பேசிய அனைத்து மாணவிகளுக்கும் எனது பாராட்டுகள் ! வாழ்த்துகள்! பரிசு மட்டும் வெற்றியில்லை இம்மேடையில் பேசிய ஒவ்வொருவரும் வெற்றியாளர்களே ! என்றாலும் சிறப்பாகப் பேசி, நம்மை எல்லாம் சிந்திக்கச் செய்த மேரிக்கு இப்பரிசினை அளிப்பதில் நான் மிக்க மகிழ்ச்சியடைகிறேன்.
மேரி : நன்றி ஐயா! [பரிசினைப் பெற்ற பெருமிதத்தில் மேரி வீட்டுக்கு செல்லுதல்]
(அல்லது)
(அ) புயலிலே ஒரு தோணி கதையில் இடம்பெற்றுள்ள வருணனைகளும் அடுக்குத் தொடர்களும் ஒலிக்குறிப்பு சொற்களும் புயலில், தோணி படும் பாட்டை எவ்வாறு விவரிக்கின்றன?
முன்னுரை :
1. இந்தோனேசியாவில் மெயின் நகரில் இருந்தபோது இரண்டாம் உலகப்போர் நிகழ்ந்தது.
2. ஆசிரியரின் நேரடி அனுபவங்களோடு கற்பனையும் கலந்த கதைதான் புயலிலே ஒரு தோணி என்னும் புதினம் கடற்பயணத்தில் கண்ட காட்சிகளும் அதன் தொடர்ச்சியாக நடைபெறும் நிகழ்வுகளும் தான் இக்கதைப்பகுதி.
3. தொங்கான் படும்பாடு கொளுத்திக் கொண்டிருந்த வெயில் இமை நேரத்தில் மறைந்துவிட்டது.
4. புழுங்கிற்று. பாண்டியன் எழுந்து போய் அண்ணாந்து பார்த்தான். மேகப் பொதிகள் பரந்து திரண்டு கும்மிருட்டாய் இறுகி நின்றன. அலைகள் எண்ணெய் பூசியவை போல் மொழுமொழுவென நெளிந்தன.
5. காற்றையே காணோம். ஒரே இறுக்கம். எதிர்க்கோடியில் வானையும், கடலையும் மாறிமாறிப் பார்த்தவாறு தலைமை மாலுமி பரபரப்பாகப் பேசிக் கொண்டிருந்தார். மாலுமிகள் திடுமெனப் பாய்மரத்தை நோக்கி ஓடிச்சென்று கட்டுக் கயிறுகளை இறுக்குகிறார்கள். விவரிக்க இயலாத ஓர் உறுத்தல் ஒவ்வோர் உணர்விலும் பட்டது.
6. எல்லோரும் எழுந்து ஒருவர் முகத்தை ஒருவர் பார்த்து மிரண்டு விழித்தனர். திடுமென அமைதி பாய்ந்து வந்து மிரட்டியது. வானும் கடலும் பிரிந்து தனித்துத் தென்பட்டன. பலகை அடைப்புக்குள்ளிருந்து கப்பித்தான் (கேப்டன்) கத்துகிறான்.
7. “ஓடி வாருங்கள் ! இங்கே ஓடி வாருங்கள்” பாண்டியன் எழுந்தான். எங்கெங்கோ இடுக்குகளில் முடங்கிக் கிடந்த உருவங்கள் தலை தூக்கின. தொங்கான் தள்ளாடுகிறது அலைகள் மலைத்தொடர் போன்ற அலைகள் மோதித் தாக்குகின்றன. தட்டுத் தடுமாறி நடந்தோடினர்.
தொங்கானின் நிலை:
- வானும் கடலும் வளியும் மழையும் மீண்டும் ஒன்றுகூடிக் கொந்தளிக்கின்றன.
- வானம் பிளந்து தீ கக்கியது. மழை வெள்ளம் கொட்டுகிறது. வளி முட்டிப் புரட்டுகிறது.
- கடல் வெறிக் கூத்தாடுகிறது.
- கப்பல் நடுநடுங்கித் தாவித் தாவிக் குதிகுதித்து விழுவிழுந்து நொறுநொறு நொறுங்குகிறது.
- முகத்தில் வெள்ளம் உடலில் வெள்ளம். கால் கையில் வெள்ளம்.
- உடை உடலை இறுக்கியிறுக்கி ரம்பமாய் அறுக்கிறது. மரத்தூண்.
- கல்தூண் இரும்புத்தூண், உயிர்த்தூண் கப்பல் தாவி விழுந்து சுழல்கிறது.
- மூழ்கி நீந்துகிறது, தாவி நீந்துகிறது. இருட்டிருட்டு கும்மிருட்டு, குருட்டிருட்டு.
- சிலுசிலு மரமரப்பு இடி முழக்கச் சீனப் பிசாசுகள் தாவி வீசுகின்றன.
தொங்கான் மிதந்து சென்ற காட்சி:
- • மூடைகள் சிப்பங்கள் நீந்தியோடி மறைகின்றன. தொங்கான் குதித்து விழுந்து நொறுநொறு நொறுங்குகிறது.
- சுழன்று கிறுகிறுத்துக் கூத்தாடுகிறது கலவை அடிக்கிறது.
- என்னயிது சூரிய வெளிச்சம் ! சூரியன் சூரியன் சூரியன் கப்பலில் நீர் நெளிகிறது.
- பாய்மரம் ஒடிந்து கிடக்கிறது. கப்பலின் இருபுறமும் பின்னேயும் தேயிலைப் பெட்டிகளும் புகையிலைச் சிப்பங்களும் மிதந்து வருகின்றன.
- பாண்டியன் நாற்புறமும் கடலைப் பார்த்து மலைத்து நின்றான்.
- கடற்கூத்து எவ்வளவு நேரம் நீடித்ததென்று கணக்கிட முடியவில்லை.
- தொடங்கியபோதோ, முடிந்தபோதோ முடிந்து வெகுநேரம் வரையிலோ யாரும் கடிகாரத்தைப் பார்க்கவில்லை.
- பார்த்தபோது எல்லாக் கடிகாரங்கள் நின்று போயிருந்தன.
- இனிமேல் பயமில்லை இரண்டு நாளில் கரையைப் பார்க்கலாம்.
- அன்றிறவு யாரும் உண்ணவில்லை பேச்சாடவில்லை.
முடிவுரை:
- கடற்கூத்துக்குப் பின் ஐந்தாம் நாள் மாலையில் வானொடு வானாய் கடலோடு கடலை மரப்பச்சை தெரிவது போலிருந்து அடுத்த நாள் முற்பகலால் பினாங்குத் துறைமுகத்தை அணுகினார்கள்.
- தொங்கான் கரையை நெருங்கிப் போய் நின்றது.
Question 45.
(அ) இந்தியாவின் கணினிப் புரட்சி – எனும் தலைப்பில் கட்டுரை ஒன்று எழுதுக.
Answer:
முன்னுரை:
உலக நாடுகளிடையே இந்தியாவும் முன்னேற்ற மடைந்த வளர்ச்சியுற்ற நாடாக வேண்டும். இக்கனவு நனவாகுமா? இதற்குப் பாரதம் பல துறைகளிலும் நன்கு உழைக்க வேண்டும். அவற்றுள் ஒன்றுதான் கணினிப் புரட்சி. உலக நாடுகள் அனைத்தும் கணினித் துறையில் வளர்ந்த அளவிற்கு நாமும் உயர வேண்டும் என்ற எண்ணம் தான் 1984இல் கணினியைக் கொணர்ந்தோம். அன்றைய பிரதமர் திரு. ராஜீவ் காந்தி அவர்கள் கணினிக்கு முக்கியத்துவம் கொடுத்து முதலிடம் அளித்தார்.
பாரதத்தில் கணினியின் வளர்ச்சி :
முதன் முதலாக மும்பையிலுள்ள டாடா ஆய்வு மையம் தான் 1966இல் கணினியை செயல்படத் தொடங்கியது. நம் நாட்டிலுள்ள மின்னியல் கழகம் கணினிகளை வாணிக நோக்குடன் தயாரிக்கத் தொடங்கியது. மின்னியல் துறையில் ஒரு புரட்சி ஏற்பட்டது. அப்போதைய பிரதமர் திரு ராஜீவ் காந்தி அவர்கள் இந்தியாவிற்கு நல்ல எதிர்காலம் நல்கும் என வலியுறுத்தினார். வேலையில்லாத் திண்டாட்டத்திற்கு முற்றுப்புள்ளி வைக்கும் அளவிற்கு மின்னியல் துறையை வளர்த்தார். தற்போது நல்ல அடிப்படையுடன் கணினித் துறை பல துறைகளிலும் நிலைபெற்று விட்டது.
கணினியின் பயன்கள் :
மக்கள் சபையிலும், மாநில சட்ட மன்றங்களிலும் கூட கணினி பயன்படுகிறது. தேர்தல் முடிவுகளை உடனுக்குடன் அறிவிப்பதிலும், வானொலி, தொலைக்காட்சி நிகழ்ச்சிகளைத் தயாரிப்பதிலும் கணினித் தொழில் நுட்பம் அங்கம் வகிக்கிறது. எல்லா மாநிலத் தலைநகரங்களிலும், மாவட்டத் தலைநகரங்களிலும் கணினி மயமாக்கப்பட்டுவிட்டது. போர்க்கால அடிப்படையில் வங்கிகள் யாவும் கணினியை ஏற்றுக்
கொண்டுவிட்டன. தேசிய மயமாக்கப்பட்ட வங்கிகளைக் கணினியைக் கொண்டு கண்காணிக்க உதவுகிறது. தேசிய காப்பீட்டுக் கழகம் பெரிய அளவில் கணினி மயமாக்கப்பட்டு விட்டது.
பிறதுறைகளில் கணினி :
போக்குவரத்துத் துறையான விமான, இரயில் துறைகளில் இருக்கை முன்பதிவு செய்யவும், அவற்றைக் கட்டுப்பாட்டுக்குள் செயல்படவும் கணினி பயன்படுகிறது. குற்றவாளிகளைக் கண்டு பிடிக்கக் கூடிய முறைகள் கையாளப்படுகின்றன. மருத்துவத் துறையில் இரத்தப் பரிசோத ருத்துவத் துறையில் இரத்தப் பரிசோதனை, இருதய ஆய்வு, அறுவைச் சிகிச்சையிலும் கூட குறிப்பிடத்தக்க அளவில் பயன்படுத்தப்படுகிற.
கல்வி நிலையங்களிளும் கணினி :
வணிகம், தொழில், தபால், தந்தி போன்ற பல துறைகளிலும் கணினி புரட்சி ஏற்பட்டு விட்டது. கல்வி நிலையங்களில், பல்கலைக் கழகங்களில் கல்வி மேம்பாட்டுப் பணிகளைச் செய்து விடுகிறது. பலரும் கணினி பற்றிய கல்வி நிலையங்களைத் துவங்கி பட்டம் பட்டமேற்படிப்பு என வகைப்படுத்தி இந்தியாவில் அனைவருமே கணினி பற்றிய கல்வி நிலையங்களைத் துவங்கி பட்டம் பட்ட மேற்படிப்பு என வகைப்படுத்தி இந்தியாவில் அனைவருமே கணினி அறிவு பெற்றுத் திகழ வாய்ப்பினை ஏற்படுத்தி விட்டது. இதன்மூலம் நம் நாட்டு இளைஞர்கள் மேனாடுகளில் சென்று வேலைவாய்ப்பு பெற்று நிரம்பப் பொருளீட்டும் வாய்ப்பும் பெற்றுள்ளனர். கணினித் தொழில் நுட்பம் செய்திகளை அனுப்பவும், தொலை தூர நாடுகளிடையே தொடர்பு ஏற்படுத்தவும் பெரிதும் உதவுகிறது. கல்வி நிலையங்களில் கணினி ஒரு பாடத் திட்டமாக அமைந்துள்ளது. தற்கால இளைஞர்கள் கணினியை விரும்பிக் கற்று புரட்சி ஏற்படுத்துவதில் முனைந்துவிட்டனர்.
முடிவுரை:
கணினித்துறை, நம் நாட்டின் எதிர்காலத்தில் மிக விரைவாகவும், திறமையாகவும் செயல்படும் என்பதில் ஐயமில்லை. பாரதத்தின் தொழில் வளர்ச்சிக்கேற்ப கணினித் துறை பெருமளவில் வளர்ச்சி பெறுவது இயற்கை நியதிகளில் ஒன்றாகிவிடும்.
(அல்லது)
(ஆ) குறிப்புகளைப் பயன்படுத்திக் கட்டுரை ஒன்று வரைக.
முன்னுரை – முறையான ஒப்பந்தம் – நீர் தேவையை சமாளித்தல் – குறைபாடுகள் – திட்டம் – நன்மைகள் – முடிவுரை.
தேசிய நதி நீர் இணைப்புத் திட்டம்
முன்னுரை:
21 ஆம் நூற்றாண்டின் மிகப்பெரிய பிரச்சினையாக உருவெடுப்பது தண்ணீர் பிரச்சினையாகும். இதனைத் தீர்க்க தண்ணீர் பிரச்சினையைச் சமாளிக்க நதிகளை இணைக்க வேண்டும் என்பது பல்லாண்டுகளாகப் பேசப்பட்டு வருவதொன்றாகும். இதற்கு ஓராண்டில் 56 கோடி ரூபாய் செலவாகும் என்று திட்டமிடப்படுகிறது.
முறையான ஒப்பந்தம் :
ஆயிரம் கிலோ மீட்டர் நீளத்திற்குக் கால்வாய்கள் அமைத்து 30 நதிகளை அடுத்த இரண்டு ஆண்டுகளில் ஒன்றாக இணைக்கலாம். 10 ஆயிரம் மெகா வாட் மின்சாரம் எடுக்க முடியும் 11 ஆயிரம் கியூ செக்ஸ் நீர் தேவைப்படும். இதற்கு 400 புதிய நீர்நிலைகள் அமைக்கப்பட்டு நதிநீர் இணைப்புத் திட்டத்தைச் செயல்படுத்த எந்த இடத்தின் வழியாகக் கால்வாய் அமைத்தால் பயனுள்ளதாக அமையும் எனத் திட்டமிட வேண்டும். மகாந்தி, கோதாவரி ஆகிய நதிகளில் நீர் அதிகம் உள்ளது. ஆனால் வல்லுநர்களிடையே விவாதம் நடத்தி முறையான ஒப்பந்தம் ஏற்பட வேண்டும்.
நீர் தேவையை சமாளித்தல் :
மழைக் காலங்களில் வட இந்தியாவில் பாயும் பல நதிகளில் வெள்ள அபாயம் ஏற்படுகிறது. இதைத் தடுக்க வேண்டுமானால், கால்வாய்கள் வெட்டி அந்நீரை ஒருநிலைப்படுத்த வேண்டும். இதற்காக வெட்டப்படும் கால்வாய்கள் மூலம் ஏராளமான தொழிலாளர்களுக்கு வேலை கிடைப்பதுடன் கூடுதல் வருவாயும் கிடைக்கும். அதிகமாகக் கிடைக்கும் மழைநீரைச் சேமித்து வைக்கத் தேவையான திட்டங்கள் நிறைவேற்றப்படவேண்டும். இந்தியாவில் வறட்சி ஏற்படும் பெரும்பாலான பகுதிகளில் நீர் தேவையை எளிதாகச் சமாளிக்க முடியும்.
குறைபாடுகள் :
தமிழகத்தில் வற்றாத ஜீவநதிகள் இல்லாத காரணத்தால் மழைக்காலங்களில் மட்டுமே இத்திட்டத்தின் மூலம் நீர் பெறமுடியும். காவிரி டெல்டா பகுதியிலுள்ள நிலத்தடி நீர்வளம், குடிநீருக்கு ஆதாரமாக உள்ளது. இதனால் இப்பகுதிகளில் தண்ணீருக்காகக் கிணறுகள் தோண்ட வேண்டிய நிலை உள்ளது. இந்நிலையில் வற்றாத ஜீவந்திகளான கிருஷ்ணா, கோதாவரி, மகாந்தி போன்ற தென்னிந்திய நதிகளை தமிழகத்தின் நதிகளோடு இணைத்தால் மட்டுமே ஆண்டு முழுவதும் நீர்வளம் குறையாமல் இருக்கும். இன்றைய நிலையில் பல கடைக்கோடி கிராமங்களில் வசிக்கும் மக்களுக்குச் சராசரி இரண்டு லிட்டர் குடிநீர் கூடக் கிடைப்பதில்லை.
மூன்று நீர்வழித்திட்டம்:
மூன்று நீர்வழிகளைக் கொண்டதாக இத்திட்டம் அமைக்கப்பட்டு ஒன்றன் பின் ஒன்றாக நிறைவேற்றலாம்.
- இமயமலை நீர்வழி. இது கங்கை பிரம்மபுத்திரா நதிகளை இணைக்கும்.
- மத்திய நீர்வழி : கங்கை, மகாந்தி, தபதி ஆகிய நதிகளை இணைக்கிறது.
- தென்னக நீர்வழி: இது கோதாவரி, கிருஷ்ணா, காவிரி மற்றும் கேரள நதிகளை.
இணைக்கும் இந்நீர்நிலைகள் 120 மீட்டர் அகலமும் 10 மீட்டர் ஆழமும் கொண்டதாக இருக்கும். இவை உரிய வழியில் ஒன்றுடன் ஒன்று இணைக்கும். நீர் சேமிப்பு போக்குவரத்து மற்றும் நீரைப் பல்வேறு நதிகளில் பகிர்ந்தளித்தல் போன்ற பல நன்மைகளைக் கொண்டதாக விளங்கும்.
நன்மைகள் :
மழைக்காலங்களில் ஏற்படும் கட்டுப்படுத்த முடியாத வெள்ளத்தை இத்திட்டத்தின் மூலம் கட்டுப்படுத்தலாம். இதனால் அசாம், பீகார், உத்தரப் பிரதேசம், மேற்கு வங்கம் போன்ற மாநிலங்களில் ஏற்படும் அபாய வெள்ள அளவைக் குறைக்கலாம்.
வெள்ளத்தினால் ஏற்படும் பாதிப்பு குறைந்து வெள்ள நிவாரணப் பணிக்கு ஒதுக்கப்படும் தொகையும் வெகுவாகக் குறையும். அனைத்து முக்கிய நகரங்களுக்கும், கிராமங்களுக்கும் போதுமான குடிநீர் வசதியை ஆண்டு முழுவதும் வழங்க முடியும்.
முடிவுரை:
தேவையான அளவு நீர்வள மேலாண்மைத் திட்டங்கள் செயல்படுத்தாத காரணத்தால் கிடைக்கும் மழைநீர் அனைத்தும் கடலில் வீணாகக் கலந்து நாட்டில் நீர்ப் பற்றாக்குறை ஏற்பட்டு உழல்கிறோம். அதனால் தேசிய நதிகளை இணைத்து சிறந்த முறையில் சுற்றுச் சூழலைப் பாதுகாத்து வாழ்வோம்.