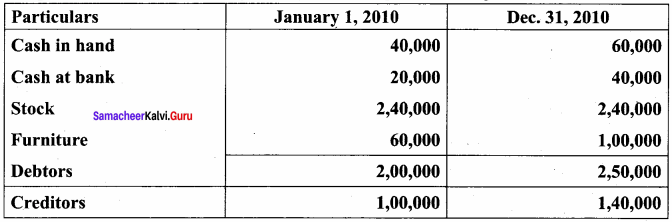
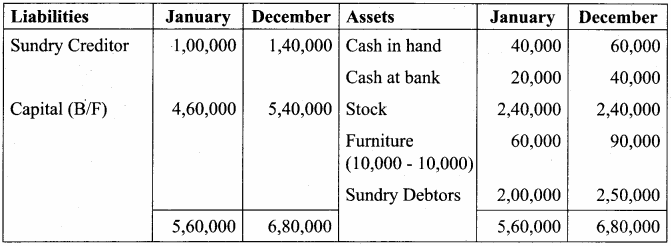
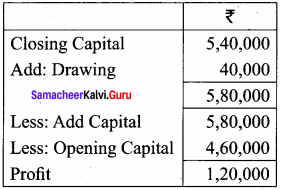
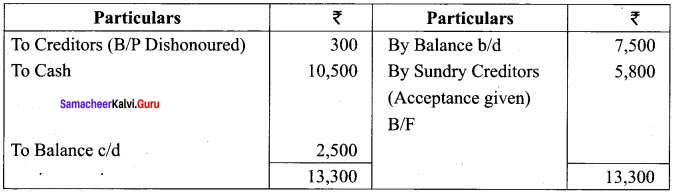
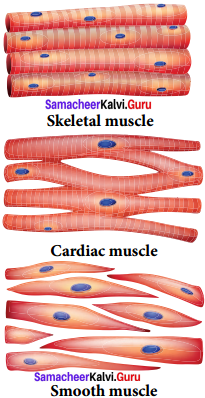
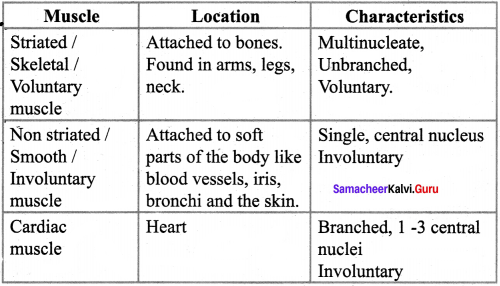
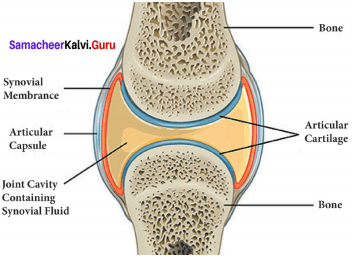
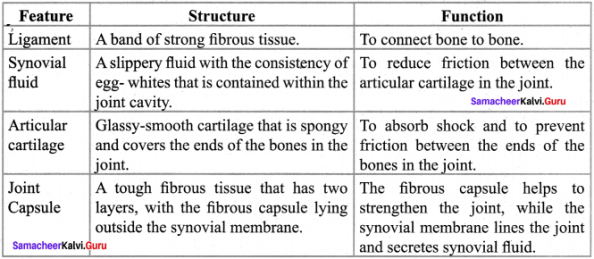
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 13 Chemical Bonding
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Chemical Bonding Textbook Exercises
I. Choose the correct answer.
Chemical Bonding Class 9 Samacheer Kalvi Question 1.
Number of valence electrons in carbon is …………….
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 3
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 4
9th Science Chemical Bonding Question 2.
Sodium having atomic number 11, ready to ………….. electron/ electrons to attain the
nearest Noble gas electronic configuration.
(a) gain one
(b) gain two
(c) lose one
(d) lose two
Answer:
(c) lose one
Chemical Bonding 9th Class Question 3.
The element that would form anion by gaining electrons in a chemical reaction is …………………
(a) Potassium
(b) Calcium
(c) Fluorine
(d) Iron
Answer:
(c) Fluorine
Chemical Bonding Class 9 Question 4.
Bond formed between a metal and non metal atom is usually ……………..
(a) ionic bond
(b) covalent bond
(c) coordinate bond
Answer:
(a) ionic bond
Chapter 13 Chemical Bonding Question 5.
…………….. compounds have high melting and boiling points
(a) Covalent
(b) Coordinate
(c) Ionic
Answer:
(c) Ionic
Chemical Bonding Questions And Answers Class 9 Question 6.
Covalent bond is formed by …………………
Answer:
(a) transfer of electrons
(b) sharing of electrons
(c) sharing a pair of electrons
Answer:
(b) sharing of electrons
Chemical Bonding Class 9 Pdf Question 7.
Oxidising agents are also called as …………….. because they remove electrons from other
substances.
(a) electron donors
(b) electron acceptors
Answer:
(b) electron acceptors
Chemical Bonding Questions And Answers Pdf Class 9 Question 8.
Elements with stable electronic configurations have eight electrons in their valence shell.
They are ………………..
(a) halogens
(b) metals
(c) noble gases
(d) non metals
Answer:
(c) noble gases
II. Answer in brief.
Chemical Bonding Answer Key Question 1.
How do atoms attain Noble gas electronic configuration?
Answer:
Atoms of all elements, other than inert gases, combine to form molecules because they have incomplete valence shell and tend to attain a stable electronic configuration similar to noble gases. Atoms can combine either by transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another or by sharing of valence electrons in order to achieve the stable outer shell of eight electrons.
Chemical Bonding Notes Class 9 Question 2.
NaCl is insoluble in carbon tetrachloride but soluble in water. Give reason.
Answer:
NaCl is an ionic compound that is soluble in polar solvents like water and insoluble in non-polar solvents like benzene (C6H6), carbon tetra chloride (CCl4). Whereas, CCl4 is an organic compound, hence it is insoluble m water
Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Chemical Change And Chemical Bond Question Answer Question 3.
Explain Octet rule with an example.
Answer:
The tendency of atoms to have eight electrons in the valence shell is known as the ‘Octet rule’ or the ‘Rule of eight’.
Example: Sodium with atomic number 11 will readily loose one electron to attain Neon’s stable electronic configuration.
Chemical Bond Class 9 Question 4.
Write a note on different types of bonds.
Answer:
All the elements differ with each other in their valence shell electronic configuration. So the way in which they combine to form compounds also differs. Hence, there are different types of chemical bonding possible between atoms which make the molecules. Depending on the type of bond they show different characteristics or properties. Such types of bonding that are considered to exist in molecules are categorized as the Ionic bond, Covalent bond and Coordinate bond.
Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Question Answer Question 5.
Correct the wrong statements.
- Ionic compounds dissolve in non-polar solvents
- Covalent compounds conduct electricity in molten or solution state
Answer:
- Ionic compounds are soluble in polar solvents like water. They are insoluble in non-polar solvents like benzene (C6H6), carbon tetra chloride (CCl4).
- Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten or solution state.Covalent compounds are non-conductors of electricity.
Class 9 Chemical Bonding Question 6.
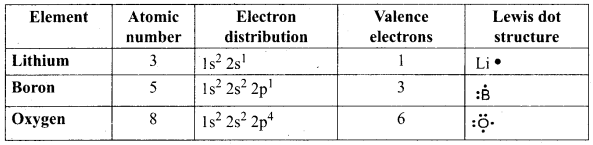
Complete the table given below.
| Element | Atomic number |
Electron distribution |
Valence electrons |
Lewis dot structure |
| Lithium | 3 | |||
| Boron | 5 | |||
| Oxygen | 8 |
Answer:
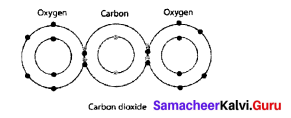
Question 7.
Draw the electron distribution diagram for the formation of Carbon dioxide (CO2) molecule
Answer:
Question 8.
Fill in the following table according to the type of bonds formed in the given molecule CaCl2, H2O, CaO, CO, KBr, HCl, CCl4, HF, C02, Al2Cl6
Answer:
| Ionic bond | Covalent bond | Coordinate covalent bond |
| CaO | H2O, HF | CO |
| CaCl2 | CO2 | |
| KBr | CCl4, Al2Cl6 |
Question 9.
Choose the correct answer from the choices given below.
The property which is characteristics of an Ionic compound is that
- it often exists as gas at room temperature
- it is hard and brittle
- it undergoes molecular reactions
- it has low melting point
- it is hard and brittle
Answer:
2. it is hard and brittle
Question 10.
Identify the following reactions as oxidation or reduction
- Na ➝ Na+ + e–
- Fe3+ + 2 e– ➝ Fe+
Answer:
1. It is an Oxidation reaction.
Oxidation: A chemical reaction which involves addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen or loss of electrons is called oxidation.
2. It is a Reduction reaction.
Reduction: A chemical reaction which involves addition of hydrogen or removal of oxygen or gain of electrons is called reduction.
Question 11.
Identify the compounds as Ionic/Covalent/Coordinate based on the given characteristics.
- Soluble in non-polar solvents
- undergoes faster/instantaneous reactions
- Non-conductors of electricity
- Solids at room temperature
Answer:
- Covalent compounds
- Ionic compounds
- Covalent compounds
- Ionic compounds
Question 12.
An atom X with atomic number 20 combines with atom Y with atomic number 8. Draw the dot structure for the formation of the molecule XY.
Answer:
Atom X is Calcium with atomic number 20 and atom Y is Oxygen with atomic number 8.
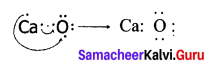
Question 13.
Considering MgCl2 as ionic compound and CH4 as covalent compound give any two differences between these two compounds.
Answer:
| MgCl2 | CH4 |
| Ionic compounds are crystalline solids at room temperature | It occurs in gaseous state |
| It has high melting and boiling point | Have relatively low melting point |
| Soluble in polar solvents and insoluble in non-polar solvent | Soluble in non-polar solvents and insoluble in polar solvents |
Question 14.
Why are Noble gases inert in nature?
Answer:
Noble gases are inert in nature due to the completely filled subshells and thus have stable electronic structures which is very difficult to change. The elements Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon and Radon of group 18 in the periodic table are Noble gases.
III. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
List down the differences between Ionic and Covalent compounds.
Answer:
| Ionic Compound | Covalent Compound |
| Ionic compounds are crystalline solids at room temperature | It occurs in gaseous state |
| They are poor conductors of electricity in solid state. However, in molten state and their aqueous solutions conduct electricity. | They are bad conductors of electricity |
| It has high melting and boiling point | Have relatively low melting point |
| Soluble in polar solvents and insoluble in non-polar solvent | Soluble in non-polar solvents and insoluble in polar solvents |
| They have high density and they are quite hard because of the strong electrostatic force between the ions. But they are highly brittle | They are neither hard nor brittle. But they are soft and waxy |
| Undergoes ionic reactions which are practically rapid and instantaneous | Undergo molecular reactions in solutions and these reactions are slow |
Question 2.
Give an example for each of the following statements.
a. a compound in which two Covalent bonds are formed
b. a compound in which one ionic bond is formed
c. a compound in which two Covalent and one Coordinate bonds are formed
d. a compound in which three covalent bonds are formed
e. a compound in which Coordinate bond is formed
Answer:
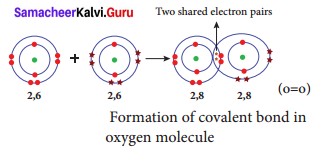
a. Formation of oxygen molecule (O2)
Each oxygen atom has six valence electrons (2, 6). These two atoms achieve a stable electronic configuration (octet) by sharing two pair of electrons. Hence a double bond is formed in between the two atoms.
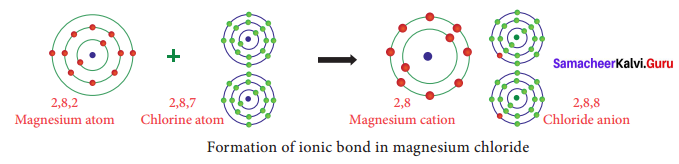
b. Formation of Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2)
Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2) is an ionic compound formed when the magnesium ion loses two electrons to gain the noble state which is accepted by chloride ion.
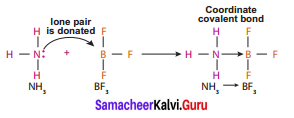
c. Formation of coordinate covalent bond between NH3 ➝ BF3 molecules
Answer:
NH3 ➝ BF3 is a compound formed by coordinate covalent bonding. Here one pair of electrons from ammonia molecule is shared with electron deficit boron trifluoride. This type of bonding is also known as Dative bond.
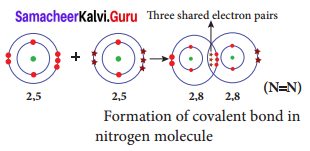
d. Formation of nitrogen molecule (N2)
Nitrogen molecule (N2) is formed by three covalent bonds where three pairs of electrons are shared between the two to achieve a stable configuration.
e. Formation of coordinate covalent bond in ammonium ion (NH4+)
In ammonia molecule the central nitrogen atom has five valence electrons (2,5) among which three electrons are shared with three hydrogen atoms and still it has an unshared lone pair of electrons. This lone pair electrons are donated to a Hydrogen ion and thus a N ➝ H coordinate covalent bond is formed in ammonium ion molecule (NH4+).
Question 3.
Identify the incorrect statement and correct them.
- Like covalent compounds, Coordinate compounds also contain charged particles (ions), so they are good conductors of electricity
- Ionic bond is a weak bond when compared to Hydrogen bond.
- Ionic or electrovalent bonds are formed by mutual sharing of electrons between atoms.
- Loss of electrons is called Oxidation and Gain of electron is called Reduction.
- The electrons which are not involved in bonding are called valence electrons.
Answer:
- Like covalent compounds, coordinate compounds also do not contain charged particles (ions), so they are bad conductors of electricity
- An ionic bond is formed by the electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions. Hence it is stronger than Hydrogen bonding which is formed by electronegativity.
- The ionic bond is formed between two atoms when one or more electrons are transferred from the valence shell of one atom to the valence shell of the other atom. The atom that loses electrons will form a cation (positive ion) and the atom that gains electrons will form an anion (negative ion).
- Loss of electrons is called Oxidation and Gain of electron is called Reduction.
- The electrons which are involved in bonding are called valence electrons.
Question 4.
Discuss in brief about the properties of Coordinate covalent compounds.
Answer:
The compounds containing coordinate covalent bonds are called coordinate covalent compounds.
- Physical state – These compounds exist as gases, liquids or solids.
- Electrical conductivity – Like covalent compounds, coordinate compounds also do not contain charged particles (ions), so they are bad conductors of electricity.
- Melting point – These compounds have melting and boiling points higher than those of purely covalent compounds but lower than those of purely Ionic compounds.
- Solubility – Insoluble in polar solvents like water but are soluble in non-polar solvents like benzene, CCl4, and toluene.
- Reactions – Coordinate covalent compounds undergo molecular reactions which are
slow.
Question 5.
Find the oxidation number of the elements in the following compounds,
- C in CO2
- Mn in MnSO4
- N in HNO3
Answer:
- Oxidation number of C in CO2 is +4
- Oxidation number of Mn in MnSO4 is +2
- Oxidation number of N in HNO3 is +5
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Chemical Bonding In Text Problems
Question 1.
Find the oxidation number of Mn in KMnO4
Solution:
+ 7.
Since manganese atom is attached to four oxygen atoms through three double bonds and one single bond.
Question 2.
Find the oxidation number of Cr in Na2Cr2O7.
Solution:
+ 6.
Question 3.
Find the oxidation number of Cu in CuS04.
Solution:
+ 2
Question 4.
Find the oxidation number of Fe in FeO.
Solution:
+ 2
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Chemical Bonding Additional Questions
I. Short answers questions.
Question 1.
What is an ionic or electrovalent bond?
Answer:
The oppositely charged ions are held together by electrostatic force of attraction which is called Ionic or Electrovalent bond.
Question 2.
What is electrovalency?
Answer:
The number of electrons that an atom of an element loses or gains to form an electrovalent bond is called electrovalency.
Question 3.
Write a short note on oxidizing and reducing agents.
- Substances that have the ability to oxidize other substances are called oxidizing agents. These are also known as electron acceptors as they remove electrons from other substances. Example H202, Mn04, Cr03, Cr20?
- The substances that have the ability to reduce other substances are called reducing agents. These are also called as electron donors as they donate electrons to other substances. Example – NaBEl4, LiAlH2 and metals like palladium and platinum
Question 4.
What is a redox reaction?
Answer:
Generally, the oxidation and reduction occurs in the same reaction (simultaneously). If one reactant gets oxidised, the other gets reduced. Such reactions are called oxidation-reduction ‘ reactions or Redox reactions.
Ex: 2 PbO + C ➝ 2Pb + C02
II. Long answers questions.
Question 1.
Mention some oxidation reactions that occur in daily life.
Answer:
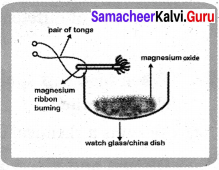
In nature the oxygen present in atmospheric air oxidises many things, starting from metals to living tissues.
- The shining surface of metals tarnishes due to the formation of respective metal oxides on their surfaces. This is called corrosion.
- The freshly cut surfaces of vegetables and fruits turns brown after some time because of the oxidation of organic compounds present in them.
- The oxidation reaction in food materials that were left open for a long period is responsible for spoiling of food. This is called Rancidity.
Question 2.
What is Fajan’s rule? Discuss.
Answer:
As we know, a metal combine with a nonmetal through ionic bond. The compounds so formed are called ionic compounds. A compound is said to be ionic when the charge of the cation and anion are completely separated. But in 1923, Kazimierz Fajans found, through his X-Ray Crystallographic studies, that some of the ionic compounds show covalent character. Based on this, he formulated a set rules to predict whether a chemical bond is ionic or covalent. Fajan’s rules are formulated by considering the charge of the cation and the relative size of the cation and anion.
- When the size of the cation is small and that of anion is large, the bond is of more covalent character.
- Greater the charge of the cation, greater will be the covalent character.
Question 3.
What are the differences between ionic, covalent and coordinate covalent bond?
Answer:
| Ionic Compound | Covalent Compound | Coordinate covalent bond |
| Ionic compounds are crystalline solids at room temperature | It occurs in gaseous state | It can exist as gases, liquids or solids |
| They are poor conductors of electricity in solid state. However, in molten state and their aqueous solutions conduct electricity. | They are bad conductors of electricity | Coordinate compounds also do not contain charged particles (ions), so they are bad conductors of electricity |
| It has high melting and boiling point | Have relatively low melting point | Have melting and boiling points higher than that of purely covalent compounds but lower than those of purely Ionic compounds |
| Soluble in polar solvents and insoluble in non-polar solvent | Soluble in non-polar solvents and insoluble in polar solvents | Soluble in non-polar solvents and insoluble in polar solvents |
| They have high density and they are quite hard because of the strong electrostatic force between the ions.
But they are highly brittle |
They are neither hard nor brittle.
But they are soft and waxy |
|
| Undergoes ionic reactions which are practically rapid and instantaneous | Undergo molecular reactions in solutions and these reactions are slow | Undergoes slow molecular reactions which are slow. |