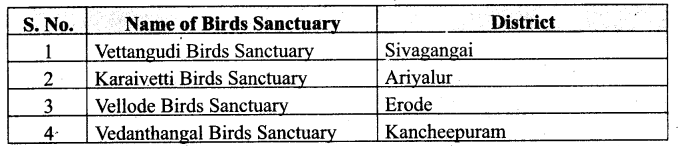
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Civics Solutions Term 1 Chapter 1 Understanding Diversity
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Understanding Diversity Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 6th Social Science Question 1.
India consists of _____ States and’_____Union territories.
(a) 27,9
(b) 29,7
(c) 28,7
(d) 28,9
Answer:
(b) 29, 7
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Question 2.
India is known as a …………….
(a) Continent
(b) Sub continent
(c) Island
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Sub continent
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Guide Question 3.
Mawsynram, the land of highest rainfall is located in
(a) Manipur
(b) Sikkim
(c) Nagaland
(d) Meghalaya
Answer:
(d) Meghalaya
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Book Back Answers Question 4.
Which one of the following religion is not practised in India?
(a) Sikhism
(b) Islam
(c) Zoroastrianism
(d) Confucianism
Answer:
(d) Confucianism
Samacheer Kalvi Social Science 6th Question 5.
Recognised official languages of India, as per VIIIth Schedule of Indian Constitution
(a) 25
(b) 23
(c) 22
(d) 26
Answer:
(c) 22
6th Standard Samacheer Kalvi Social Science Question 6.
Onam festival is celebrated in …………….
(a) Kerala
(b) Tamil Nadu
(c) Punjab
(d) Karnataka
Answer:
(a) Kerala
Class 6 Social Science Samacheer Kalvi Question 7.
Mohiniyattara is a classical dance of
(a) Kerala
(b) Tamil Nadu
(c) Manipur
(d) Karnataka
Answer:
(a) Kerala
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Question 8.
‘Discovery of India’ – a book was written by …………….
(a) Rajaji
(b) V.O.C
(c) Nethaji
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru
Answer:
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru
Samacheer Kalvi 6 Social Science Question 8.
‘Discovery of India’
(a) Rajaji
(b) V.O,C
(c) Nethaji
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru
Answer:
(d) Jawaharlal Nehrul
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Standard Social Science Question 9.
The phrase ‘ Unity in Diversity’ was coined by
(a) Jawaharlal Nehru
(b) Ambedkar
(c) Mahathma Gandhi
(d) Rajaji
Answer:
(a) Jawaharlal Nehru
6th Standard Samacheer Kalvi Social Question 10.
V.A. Smith called India as …………….
(a) Great Democracy
(b) Unique land of diversities
(c) Ethnological museum
(d) Secular nation
Answer:
(c) Ethnological museum
II. Fill in the blanks :
- Geographical features and climatic conditions determine the _________ activities of region
- Jaisalmer, the land of lowest rainfall is located in _________
- Tamil was declared as classical language in the year _________
- Bihu festival is celebrated in _________
Answer:
- economic
- Rajasthan
- 2004
- Assam
III. Match the following
- Negroids – a. Religion
- Coastal areas – b. India
- Zoroastrianism- c. Fishery
- Unity in diversity- d. Indian race
Answer:
- – d
- – c
- – a
- – h
IV. Answer the following questions:
Social Samacheer Kalvi 6th Question 1.
Define diversity.
Answer:
We, the Indians come from different backgrounds, belong to different cultures, worship in different ways. This is known as diversity.
6th Standard Social Samacheer Kalvi Question 2.
What are the types of diversity?
Answer:
The types of diversity are –
- Landforms and Lifestyle diversity
- Social diversity
- Religious diversity
- Linguistic diversity
- Cultural diversity
6th Samacheer Kalvi Social Guide Question 3.
Why is India called a subcontinent?
Answer:
A continent is a very large area of land with various physical features such as mountains, plateaus, plains, rivers and seas and various types of weather patterns. India has all of them. So India is known as a subcontinent.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Guide Question 4.
Write the names of three major festivals celebrated in India.
Answer:
- Pongal, Deepavali – Hindus
- Miladi Nabi, Ramjan – Muslims
- Christmas, Easter – Christians
Social Guide For Class 6 Samacheer Kalvi Question 5.
List out some of the classical dances of India.
Answer:
- Tamil Nadu – Bharatanatyam
- Kerala – Kathakali
- Karnataka – Yakshagana
- Odisha – Odissi
- Andhra Pradesh – Kuchipudi
- Manipur – Manipuri
- Assam – Sattriya
Samacheer Kalvi Social 6th Standard Question 6.
Why is India called the land of unity in diversity?
Answer:
- In India, people who live in different parts of the country differ in their ways of life.
- These differences make us unique as Indians.
- We come from different backgrounds, belong to different cultures, worship different Gods in different ways, yet we live together.
- This is known as unity in diversity.
V. Answer the following in detail:
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 6th Social Guide Question 1.
Explain : Linguistic diversity’ and cultural diversity.
Answer:
Linguistic Diversity :
- According to census of India 2001, India has 122 maj or languages and 1599 other languages.
- Four major Indian language families are Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Austroasiatic and Sino Tibetian. Tamil is the oldest Dravidian language.
- Historically, the Portuguese, the Dutch, the British, the Danish and the French came to India for trade and their occupation of India or some parts of it has left behind a certain impact upon the culture and language of the people.
- In due course, English has emerged as an important language and a medium of instruction in schools and colleges.
- (It is widely used in official communication and daily life.
Cultural Diversity :
- The term ‘culture’ refers to customs and practices of people, their language, their dress code, cuisine, religion, social habits, music, art and architecture.
- The culture of a group of people is reflected in their social behaviour and interactions.
- The group identity fostered by social patterns is unique to a group.
- Art and architecture are an integral part of every community.
- It develops as a part of culture and tradition of a community.
Question 2.
“India is a land of diversity, yet we are all united”. Discuss.
Answer:
- Though diversity is visiable in every aspect of life in India, we are united by the spirit of patriotism.
- Symbols like the National flag and National Anthem remind us of our great nation and the need to stay united.
- Celebration of events like Independence Day , Republic day and Gandhi Jayanthi brings us together and keeps the spirit of one nation alive with us.
- India has a multicultural society.
- India evolved as a single nation through common beliefs, customs and cultural practices.
- The freedom struggle and the drafting of our constitution stands as ample evidence to the spirit of unity of India.
VI. Projects and Activities:
Question 1.
“The occupation of people depends on the landform of a place”. Give some
examples.
Answer:
- The Earth has many landforms such as plains, valleys and mountains.
- Landforms affect where people build houses and communities.
- Many people live on plains because it is easy to travel and to farm on flat land.
- (The low lying regions are suitable for growing crops near clean and fresh water with access to the sea in natural protected harbours.
- People living in the coastal region might prefer finishing. Mountains and hilly regions are cool but transport, farming etc will be difficult here. So the landforms play a major role in the section of occupation.
Question 2.
Read about a state of your choice and make an album to show the culture and tradition of people who live in that state.
Answer:
Tamil Nadu :
- Tamil Nadu is a southern state of India.
- It is supremely rich in culture and heritage.
- Tamil is the official language of the State. Hindus, Jains, Christians and Muslims live here Men wear dhoti and shirt and woman wear sari. Rice, lentils, grains and vegetables form the main cuisine.
- Some Tamilans follow the tradition of eating on banana leaf.
- The Most important form of music is Carnatic music. Bharathanatyam is the
official dance form of Tamil Nadu. - Kolam is drawn at the doors of every house in Tamil Nadu Meenakshi Temple of Madurai and Brihadeeswar
- Temple of Thanjavur display a grand vista of ancient Hindu mythological diversity and Tamil Heritage.
VII. HOTS :
Question 1.
List out the various festivals celebrated in different states.
Answer:
- Andhra Pradesh – Brahmotsavam
- Arunachal Pradesh – Losar festival
- Assam – Bohag Bihu
- Bihar – Chhath Puja
- Chhattisgarh – Bastar Dussehra
- Goa – Carnival
- Gujarat – Janmashtami, Diwali
- Haryana – Baisaki
- Himachal Pradesh – Maha Sivarathiri
- Jammu and Kashmir – Eid-Ul-Fitr and Eid-ul-Azha
- Jharkhand – Holi
- Karnataka – Ugadi
- Kerala – Onam
- Madhya Predesh – Diwali
- Maharastra – Ganesh Chaturthi
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Understanding Diversity Intext Questions
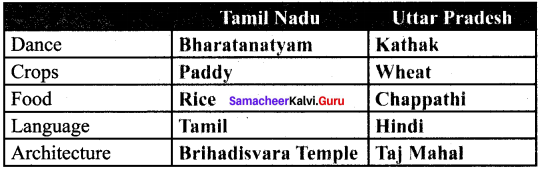
Question 1.
You have read about the diversity that exists in our country. Compare and contrast. Two states in this table.
Answer:
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Understanding Diversity Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Karagattam is a popular folk dance in
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Gujarat
(c) Assam
(d) Kerala
Answer:
(a) Tamil Nadu
Question 2.
The number of recognized official languages …………….
(a) 13
(b) 18
(c) 22
(d) 25
Answer:
(c) 22
Question 3.
India was called an “ethnological museum” by
(a) Rabindranath Tagore
(b) Dr. Ambedkar
(c) V.A. Smith
(d) Adam Smith
Answer:
(c) V.A. Smith
II. Fill in the blanks :
- The migration of people is the reason for India’s rich ___________
- Jaisalmer, located in Rajasthan, is the land of ___________ rainfall.
- The land of the highest rainfall is ___________ in megalaya.
- A ___________ is a place where people live together with a common interest or heritage.
- The fundamental unit of a society are ___________
- In a ___________ nation all religions are treated equally
- ___________ language is widely used in official communication and daily life
- India is known for ___________
- The first Prime Minister of independent India was ___________
Answer:
- diversity
- lowest
- Mawsynram
- community
- families
- secular
- English
- unity in diversity
- Jawarharlal Nehru
III. Match the following
Question 1.
(a) Gujarat -(i) Mohiniattam
(b) Kerala -(ii) Kummi
(c) Rajasthan -(iii) Garba
(d) Tamil Nadu -(iv) Ghoomer
Answer:
(a – iii)
(b – i)
(c – iv)
(d – ii)
Question 2.
(a) Dussehra – (i) Architecture
(b) Zoroastrianism – (ii) Language
(c) Dilwara Temple – (iii) Festival
(d) Malayalam – (iv) Religion
Answer:
(a – iii)
(b – iv)
(e – i)
(d – ii)
IV. Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Who became part of the modern Indian race?
Answer:
The Dravidians, Negroids, Aryans, Alpines and Mongoloids became part of the modem Indian race.
Question 2.
What is meant by community?
Answer:
- A community is a place where people live together with a common interest or heritage.
- Our community is made up of peasants, labourers, artisans, parents, teachers, students and many others.
Question 3.
How is a city formed?
Answer:
- Families live in a harmonious neighbourhood.
- Hundreds of neighbourhoods collectively form a village.
- Thousands of them group together to form a city.
Question 4.
Mention the folk dances of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
- Karagattam
- Oyillattam
- Kummi
- Therukoothu
- Bommalattam
- Puliattam
- Kolattam and Thappattam.
Question 5.
Mention some of the festivals celebrated in India.
Answer:
Festivals like Pongal, Deepavali, Holi, Vijayadhasami, Ayudha puja, Navratri Durga Puja, Ganesh Chaturthi, Onam, Miladi Nabi, Ramzan, Christmas are celebrated in India.
Question 6.
What are the various styles of music practiced in India?
Answer:
The Hindustani music, Kamatic music, Classical music, Folk music, Lavani, Ghazl are some of the musics practiced in India.
Question 7.
What does the term culture refer to?
Answer:
The term culture refers to customs and practices of people, their language, their dress code, cuisine, religion, social habits music, art and architecture.
Question 8.
Mention the importance of dances in India.
Answer:
In ancient times, dance was considered as a way to celebrate worship and also as a gesture of thanks giving and joy. Dances of India reflect its cultural richness.
V. Answer the following questions in detail.
Question 1.
How do land forms affect life style?
Answer:
- India is a sub – continent.
- It has mountains, plateaus, plains, rivers and seas.
- These features influence upon the people who live in different landforms of the country.
- People who live in plains do agriculture.
- Coastal areas take to fishing for their livelihood.
- Diversity in landforms also impacts the flora and fauna of that region.
- As a result food, clothing, occupation and livelihood of the people is closely connected with the regions natural surroundings and climate.













 x 100
x 100
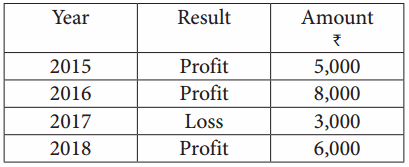
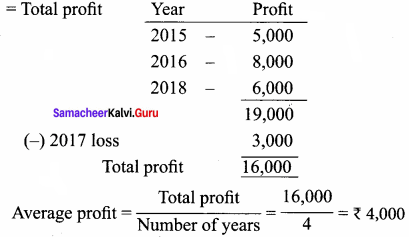
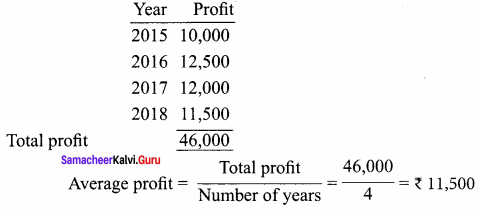
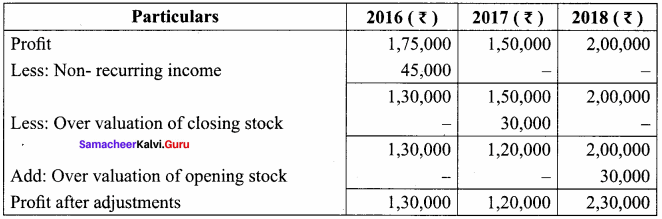
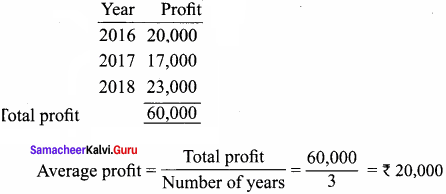
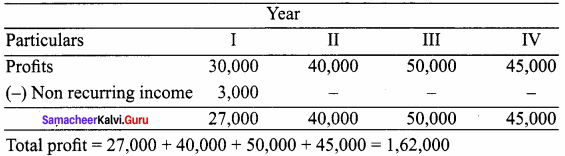
 = \(\frac { 1, 62, 000 }{ 4 }\)
= \(\frac { 1, 62, 000 }{ 4 }\)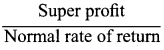 x 100
x 100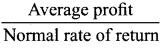 x 100
x 100

 x 100
x 100

 Answer:
Answer:








 Answer:
Answer: