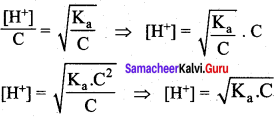
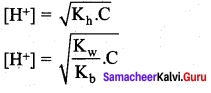
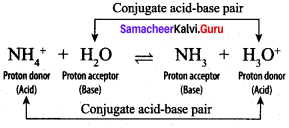
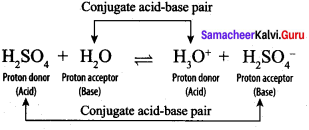
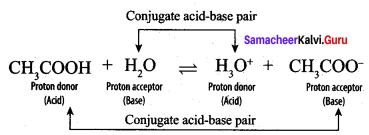
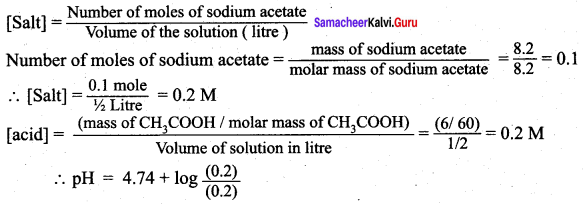
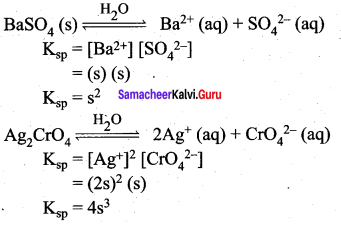
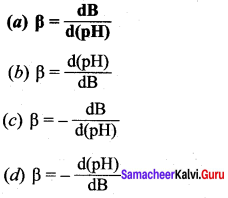
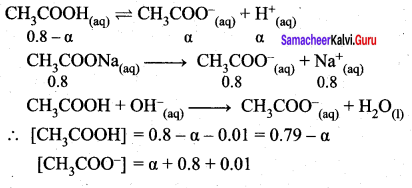
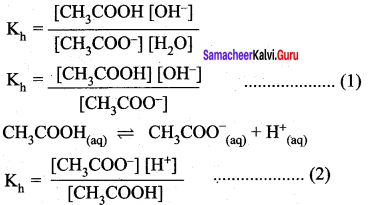
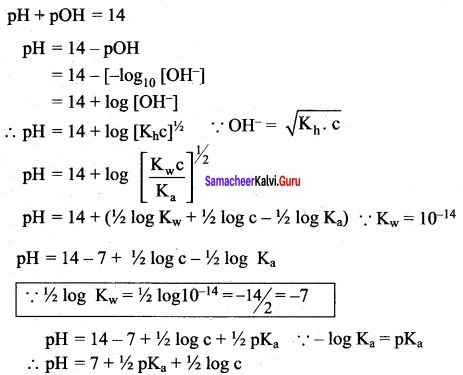
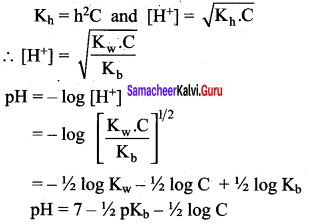
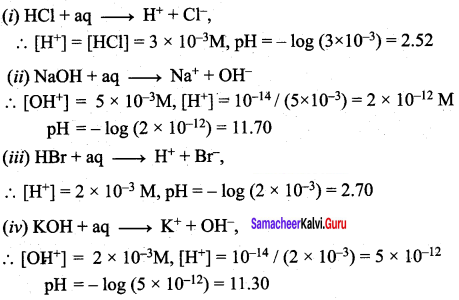
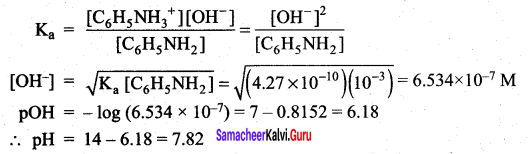
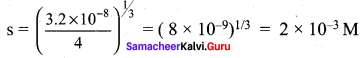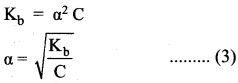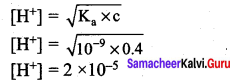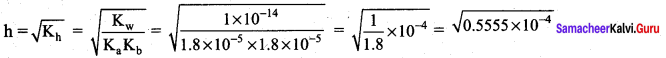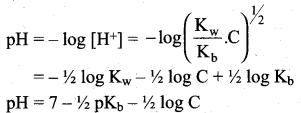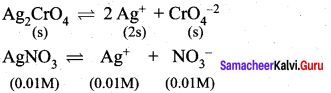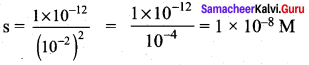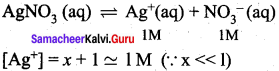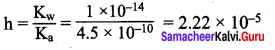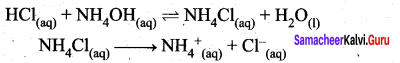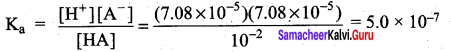Students can Download Science Chapter 3 Polymer Chemistry Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Solutions Term 3 Chapter 3 Polymer Chemistry
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Polymer Chemistry Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answers :
Polymer Chemistry 7th Standard Question 1.
The first man-made fibre is ________
(a) Nylon
(b) Polyester
(c) Rayon
(d) Cotton
Answer:
(c) Rayon
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science 3rd Term Question 2.
Which of the following is the strongest?
(a) Rayon
(b) Nylon
(c) Acrylic
(d) Polyester
Answer:
(b) Nylon
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Term 3 Question 3.
When you place a natural fibre in a flame it ________
(a) melts
(b) burns
(c) gets nothing
(d) explodes
Answer:
(b) burns
Samacheer Kalvi 7th 3rd Term Science Question 4.
A synthetic fibre which has similar properties to wool is ________
(a) Nylon
(b) Polyester
(c) Acrylic
(d) PVC
Answer:
(c) Acrylic
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Books Science Term 3 Question 5.
A good application of plastic is the use of ________
(a) Blood bags
(b) Plastic cutlery
(c) Plastic straws
(d) Plastic carry bag
Answer:
(a) Blood bags
Question 6.
________ is non-biodegradable material.
(a) Paper
(b) A plastic bottle
(c) Cotton cloth
(d) Wool
Answer:
(d) Wool
Question 7.
PET is the acronym for ________
(a) Polyester
(b) Polyester and terylene
(c) Polyethylene terephthalate
(d) Polyetheneterylene
Answer:
(c) Polyethylene terephthalate
II. Fill in the blanks :
- ______ is an example of polyester fabric.
- ______ are used to identify different types of plastics.
- A ______ is a long chain made up of many repeated small units called monomers.
- The fully natural fibreis called ______
- A natural fibre obtained by boiling of cocoons is called ______
Answer:
- Raincoat
- Resin codes
- polymer
- plant fibre
- silk
III. True or False :
Question 1.
A lot of plastic pollutes our environment.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Refuse (avoid) is the best way to manage plastic.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
It is good to wear clothes made of synthetic fibres while cooking.
Answer:
(False)
Correct statement: It is good to wear clothes made of fibres while cooking.
Question 4.
Degradable plastics break down into tiny pieces called microplastics.
Answer:
True.
Question 5.
Cotton is a natural polymer.
Answer:
True.
IV. Match the following :
| A | B |
| 1. Nylon | Thermoplastic |
| 2. PVC | Thermosetting plastic |
| 3. Bakelite | Fibre |
| 4. Teflon | Wood pulp |
| 5. Rayon | Non-stick cookwares |
Answer:
| A | B |
| 1. Nylon | Fibre |
| 2. PVC | Thermoplastic |
| 3. Bakelite | Thermosetting plastic |
| 4. Teflon | Non-stick cookwares |
| 5. Rayon | Wood pulp |
V. Arrange in Correct Sequence:
1. Mix water, starch, vinegar and glycerin in a cooking pot.
2. Let the article cool for 24 hours before we use it.
3. Shape material to form a cup or bowl.
4. Continuously mix on medium heat until the liquid turns clear.
5. When the liquid begins to bubble it is ready to be taken off the stove.
6. Spread the gel onto aluminium foil and cool.
Answer:
1. Mix water, starch, vinegar and glycerin in a cooking pot.
4. Continuously mix on medium heat until the liquid turns clear.
5. When the liquid begins to bubble it is ready to be taken off the stove.
6. Spread the gel onto aluminium foil and cool.
3. Shape material to form a cup or bowl.
2. Let the article cool for 24 hours before we use it.
VI. Analogy :
Question 1.
Cotton: natural:: Polyester: ______
Answer:
Synthetic.
Question 2.
PLA spoon :compostable:: Plastic spoon: ______
Answer:
Disposable.
Question 3.
Nylon :melts on heating:: Silk: ______
Answer:
Burns on heating.
VII. Assertion – Reason type question :
Option:
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c. A is true but R is false.
d. A is false but R is true.
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Vegetable peels buried in the soil disappear within two weeks.
Reason (R) : Vegetable peels are compostable.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : It takes a very long time for nylon clothes to breakdown into microfibers but cotton clothes need only six months to decompose.
Reason (R) : Nylon made out of petrochemicals is non-biodegradable and cotton cloth is biodegradable.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 3.
Assertion (A) : It is good to avoid plastics.
Reason (R) : Plastics end up polluting the environment.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
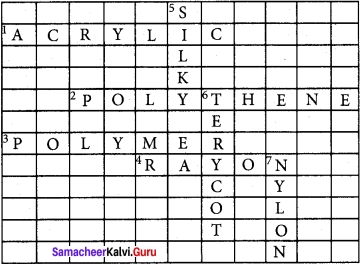
VIII. Crossword
Across
1. Fibre that is used as synthetic wool.
2. A plastic used for making water bottles.
3. A long chain made of small repeating monomers.
4. Another name for this semi-synthetic fibre is artificial silk.
Down:
5. A type of fibre that is naturally obtained from a cocoon.
6. A synthetic fibre classified as polyester.
7. A polymer used for making rope
IX. Very short answer :
Question 1.
What is the chemical name of the polymers that make up cotton?
Answer:
Cellulose.
Question 2.
What gives plastic different qualities and characteristics?
Answer:
Different chemicals (additives) are added to plastic to give them various qualities and characteristics.
Question 3.
It is not advisable to burn plastic and synthetic fabrics. Why?
Answer:
Burning of plastics and synthetic fabrics is not a good solution, as we end up wasting non-renewable resources and produce super toxic chemicals that are difficult to store or dispose safely.
Question 4.
A bucket made of plastic does not rust like a bucket made of iron. Why?
Answer:
- The reason is due to their chemical composition.
- The bucket is made of plastic which does not react with the oxygen and humidity present in air.
- While the iron reacts with the oxygen, air corrodes to form rust.
Question 5.
Why is it better to avoid the use of plastic products?
Answer:
- Plastics do not decompose by natural processes and action of bacteria and are therefore not biodegradable.
- A lot of the plastic produced globally is designed to be used only once and thrown away, creating a large amount of plastic waste.
- Plastic waste ends up being recycled, incinerated, landfilled, dumped or ends up littering our environment.
- So, it is better to avoid the use of plastic products.
Question 6.
Give two examples of thermosetting plastics.
Answer:
Bakelite, Melamine.
Question 7.
What is the 5 R principle?
Answer:
Plastic disposal is the 5 R principle, Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Recover is called as 5 R principle.
X. Short Answer :
Question 1.
What does the term biodegradable mean?
Answer:
A material that gets decomposed through natural processes and action by bacteria is called biodegradable
Question 2.
What kind of fabric is suitable to dress-up and play in summer? Why?
Answer:
- In summer it is better to wear clothing that is made out of cotton materials rather than synthetic.
- This is because most synthetic fibres absorb very little moisture and do not allow air circulation making them hot and uncomfortable to wear.
Question 3.
How do plastics impact animals and the environment?
Answer:
- The increase in the use of plastics, particularly the one-time use and throw away plasticshas serious impacts on the environment, animals and our health.
- We have seen garbage dumps with different plastics. One big problem with plastics is that they do not decompose or biodegrade.
- This leads to large amounts of waste that will not disappear and end up accumulating and polluting the environment.
- Many animals confuse plastic for food and eat it by accident. When leftover food is thrown away it is often packed in plastic. Animals smell the leftover food and eat the plastic by accident.
XI. Long Answer :
Question 1.
List the advantages and disadvantages of synthetic fibres.
Answer:
Advantages-and disadvantages of synthetic fibres.
| Advantages of synthetic fibres | Disadvantages of synthetic fibres | |
| 1. | Do not wrinkle easily and they keep their colour and brightness for a much longer time than natural fibres such as cotton. | synthetic fibres such as polyester is that they are not heat resistant and catch fire easily. |
| 2. | Using synthetic fibres such as nylon, is that they are stronger than many natural fibres such as silk or wool. | Most synthetic fibres absorb very little moisture and do not allow air circulation making them hot and uncomfortable to wear. |
| 3. | These fibres are strong and elastic which gives it the properties to bounce. | Synthetic fibres are made out of petrochemicals and last in the environment for a very long time. It break down into very small pieces called microplastics which cause pollution to soil and water bodies such as rivers, lakes and oceans. |
Question 2.
Suggest safe methods of disposing plastics.
Answer:
Refuse (Avoid):
- The best thing to do is to avoid using plastic products.
- One-time use throw away plastics can often be avoided.
Reduce : Reducing the amount of plastic we use is important.
Reuse : If possible products made of plastics can be used again and again.
Recycle:
- It is better to recycle plastic waste.
- Separating plastic waste (based on the resin code) and making sure it gets recycled is good as it turns waste materials into something new.
- Then it will not be thrown away in landfills, open dumps or ending up as litter in the environment.
Solid waste can be converted into resources such as electricity and compost through thermal and biological means.
XII. HOTS :
Question 1.
The Tamil Nadu Government has banned the use of one-time use throw away plastics. Why
do you think this is important?
Answer:
It is important to reduce the negative consequences of plastics on the environment.
Question 2.
A plastic bag dumped in the soil stays without breaking down for 500years. If a new generation starts in every 30 years, how many generations would it take to see the plastic bag finally broken down?
Answer:
It would take 16 to 17 generations to see the plastic bag finally broken down.
XIII.
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks :
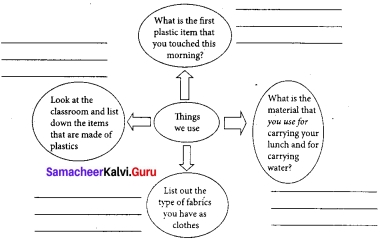
Answer:
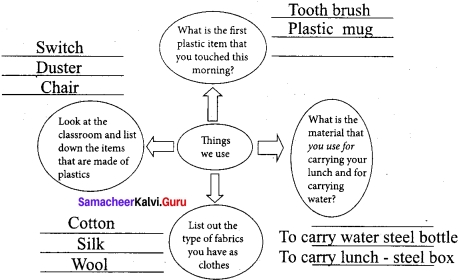
Question 2.
Look at the following picture and explain what is happening

Answer:
A lot of one-time use plastic such as polythene bags and food packaging that are thrown away are responsible for littering the environment and clogging drains. Standing water breeds mosquitoes that can spread diseases such as malaria dengue and chickungunya and also lead to flooding.
Question 3.
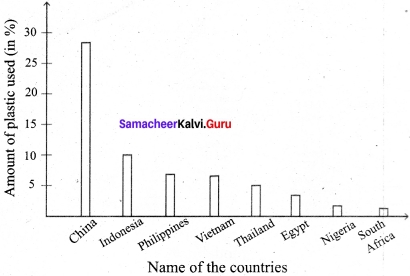
Read the following information and convert them into a graph to compare the countries and the amount of plastic they use.
China contributes the highest share – that is around 28%, of the total plastic used globally. Indonesia uses 10%, both the Philippines and Vietnam use 6% each; Thailand uses 3.2%, Egypt 3%, Nigeria 2.7% and South Africa 2%.
Answer:
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Polymer Chemistry Intext Activity
Activity – 2
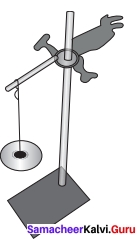
How Strong is Nylon? Take an iron stand with a clamp. Take samples of cotton, wool, nylon and silk threads of about 50cm in length.
First tie cotton thread to the stand so that it hangs freely from it. At the free end, attach a CD as plate so that weights can be placed on it. Add weights starting from 10 grams one by one, until the thread breaks. Note down the total weight required to break the cotton thread. Repeat the same activity with the wool, silk and nylon threads. NOTE: All the varieties of threads should be of same thickness.
Question 1.
Arrange the threads in the order of increasing strength.
Answer:
Cotton, Wool, Silk, Nylon.
Question 2.
What do you infer from the above activity?
Answer:
Nylon thread is the strongest thread.
Question 3.
Which type of fibre is the strongest?
Answer:
Nylon.
Question 4.
Which type of fibre is the weakest?
Answer:
Cotton.
Activity – 4
Question 1.
Synthetic or Natural Fibres : The teacher can give the learner a piece of each and every type of fibre. The learner can feel the fibre and write down the name of the fibre and state whether it is natural or synthetic fibre.
Answer:
| S.No | Name of the fibre | Type of the fibre- Natural /Synthetic |
| 1. | Jute | Natural |
| 2. | Cotton | Natural |
| 3. | Rayon | Synthetic |
| 4. | Wool | Natural |
| 5. | Polyester | Synthetic |
Question 2.
We have done four activities so far. Which activity helped you better to identify the type of fibre?
Answer:
Activity 3, 4
Activity – 5
Question 1.
What do you observe while the cotton cloth burns?
Answer:
The cotton cloth burns completely. Does not melt and has the odour of burning paper.
Question 2.
What do you observe while the polyester cloth burns?
Answer:
Polyester cloth melts on burning and giving off black smoke.
Activity – 6
Question 1.
We use an umbrella on rainy days. What kind of umbrella do we use?
Answer:
Nylon or Polyester
Question 2.
Which of these fabrics allows water to pass through?
Answer:
Cotton cloth allows water to pass through whereas umbrella cloth does not allow water to pass through.
Question 3.
Which of these fabrics dries the fastest? The cotton cloth or the umbrella cloth?
Answer:
Umbrella cloth dries the fastest.
Activity – 7
Question 1.
Right and wrong application of plastics.
Look at the list of eight plastic items. Decide which four plastic items are used for the right application and which four are used for the wrong application by filling in the chart below: Plastic items: straws, helmets, cutlery, thin carry bags, syringes, electrical wires,tea cups and blood bags

Answer:
| Right application | Wrong application |
| Helmets | Straws |
| Syringes | Thin carry bags |
| Electrical wires | Cutlery |
| Blood bags | Tea cups |
Activity – 8
Question 1.
Identify the different types of plastics.
Collect different kinds of plastic products and look carefully for the resin code and/or acronym on them. With the help of the resin code chart, mark the resin code number, acronym, if you think it is a safer, unsafe or questionable (when you cannot find the resin code in the article) type of plastic. What resin codes do you find? Is the resin code safer, un safe or questionable?
Answer:
| Product | Resin code number | Acronym | Category of safety | Use of product |
| Rain coat | 03 | PVC | Unsafe | During rain |
| Pens | 06 | PS | Unsafe | To write |
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Polymer Chemistry Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
Which of these is a natural fibre?
(a) Nylon
(b) Cotton
(c) Rayon
(d) Polyester
Answer:
(b) cotton
Question 2.
Which of these plastics is a polymer?
(a) Bakelite
(b) Polystyrene
(c) Polythene
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 3.
Which of these is not a property of plastics?
(a) Inflammable
(b) Bad conductor of heat
(c) Soluble in water
(d) Bad conductor
Answer:
(c) Soluble in water
Question 4.
Pick the synthetic fibre out of the following.
(a) Jute
(b) Cotton
(c) Nylon
(d) Wool
Question 5.
Which is a thermosetting plastic?
(a) Melamine
(b) Polythene
(c) PVC
(d) Nylon
Answer:
(a) Melamine
Question 6.
Which of the following is non – bio degradable?
(a) Plastic
(b) Paper
(c) Cotton cloth
(d) Wood
Answer:
(a) Plastic
Question 7.
The material similar to silk in appearance is.
(a) nylon
(b) rayon
(c) polyester
(d) terylene
Answer:
(b) rayon
Question 8.
The fibres such as rayon, nylon, polyester are obtained from
(a) natural resources
(b) chemical substances
(c) minerals
(d) plants and animals
Answer:
(b) chemicals substances
Question 9.
Which of the following fibres is considered as the strongest natural fibre?
(a) Cotton
(b) Jute
(c) Silk
(d) Wool
Answer:
(c) Silk
Question 10.
Which of the following is found in sanitary products?
(a) Nylon
(b) Wool
(c) Jute
(d) Rayon
Answer:
(d) Rayon
II. Fill in the Blanks.
- Polymers are very long chains made of repeating smaller molecules called ______
- All the ______ present in your body are polymers.
- ______ is made of sugar molecules and is the main component of cotton used in clothing.
- ______ and ______ are the building block monomers that make up many different types of plastics.
- ______ are long strands of polymers interwoven to form linear, string-like structures.
- Fibres that are made using raw materials from ______ are synthetic fibres.
- The cellulose dissolves in the chemicals added to it and produces syrup called ______
- Nylon is a plastic polymer made of chemical units called ______
- ______ is a synthetic fibre which is strong and elastic that it has the ability to bounce.
- Syringe that is made from a type of plastic called ______
- Edmund Alexander Parkes was the creator of the first plastic called .
- resists fire and can tolerate heat.
- Poly Lactic Acid or polylactide is and , thermoplastic.
Answer:
- monomers
- proteins
- Cellulose
- Ethylene, propylene
- Fibres
- petroleum
- Viscose
- Polyamides
- Trampoline
- polypropylene
- Parkesine
- Melamine
- Compostable, bioactive
III. True or False – if false, give the correct statement.
Question 1.
Polycot is a mixture of polyester and cotton.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Polyamides are made with monomers.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Wool is the first fully processed synthetic fibre.
Answer:
Correct statement: is the first fully processed synthetic fibre.
Question 4.
Rayon is a fibre obtained by the chemical treatment of wood pulp.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Plastics are flexible and waterproof and some are even UV resistant.
Answer:
True
Question 6.
Bakelite and melamine are some examples of thermoplastics
Answer:
False
Correct statement: Bakelite and and melamine are some examples of thermosettingplastic
Question 7.
Polyvinyl chloride has heavy metals such as cadmium and lead which are toxic and harmful to our health.
Answer:
True
Question 8.
Plastics can be found in toothpaste, facewash and bodyscrubs.
Answer:
False
Correct statement : can be found in toothpaste, facewash and bodyscrubs.
Question 9.
Plastics are environment friendly.
Answer:
False
Correct statement: Plastics are not environment friendly.
Question 10.
Artificial fibres are stronger than natural fibres.
Answer:
True
Question 11.
Electric switches, plugs, sockets and handles of cooling utensils are made up of thermoplastics.
Answer:
Correct statement: Electric switches, plugs, sockets and handles of cooling utensils are made up of thermosetting plastic
IV. Match the following :
Question 1.
| 1. | Teflon | (a) | Fabrics do not wrinkle easily |
| 2. | Nylon | (b) | Used to make non-stick cookwares |
| 3. | Polyester | (c) | Prepared by using pulp |
| 4. | Rayon | (d) | Used for making parachutes and stockings |
Answer:
- b
- d
- a
- c
Question 2.
| 1. | Nylon | (a) | Artificial silk |
| 2. | PET | (b) | Artificial wool |
| 3. | Rayon | (c) | Parachute |
| 4. | Acrylic | (d) | Polyester |
Answer:
- c
- d
- a
- b
Question 3.
| 1. | Plastic bags | (a) | Polyvinyl chloride |
| 2. | PVC | (b) | Natural fibre |
| 3. | Melamine | (c) | Non-bio degradable |
| 4. | Wood | (d) | Thermosetting plastic |
Answer:
- c
- a
- d
- b
V. Very short answers:
Question 1.
What is the full form of PVC?
Answer:
Poly Vinyl Chloride.
Question 2.
Name a synthetic fibre which works like wool?
Answer:
Acrylic.
Question 3.
Plastic articles are available in all possible shapes and sizes. Why?
Answer:
Plastic is easily mouldable, so the articles can be made in any shape and size.
Question 4.
Name the unit used in the formation of a polymer.
Answer:
Monomer is the small unit used in the formation of a polymer.
Question 5.
Name the form of polyester which is replacing materials like glass and used for making bottles and jars.
Answer:
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) is a form of polyester.
Question 6.
For making PVC pipes, which type of plastic is used?
Answer:
Thermoplastic.
Question 7.
Name the plastic. Which is coated on the uniform of fireman to make it fire resistant?
Answer:
Melamine is coated in the uniforms of fireman.
Question 8.
Name a natural polymer occuring in plants.
Answer:
Cellulose, Starch, etc.
Question 9.
On burning wool, why we get the small of burning of hair?
Answer:
Since, wool is made from hair of sheep, it gives smell of burning hair.
Question 10
What is polymerization?
Answer:
The process by which monomers are linked together by covalent bonds to form polymers is called polymerization.
VI. Short Answer.
Question 1.
Why is rayon called on artificial silk?
Answer:
- Rayon is a synthetic fibre having properties similar to that of silk.
- It was obtained by chemical treatment of wood pulp.
- That’s why, it is called an artificial silk.
Question 2.
What are the various methods of disposing plastics?
Answer:
- Refuse
- Reduce
- Recycle
- Recover
Question 3.
What is compostable plastic?
Answer:
- Plastics which are derived from renewable resources such as corn, sugar cane, avocado seeds or shrimp cells.
- It can be broken down completely by microbes and turned back into food for plants – COz, methane, water and other natural compounds.
Question 4.
Why do you think some animals eat plastic?
Answer:
- Many animals confuse plastic for food and eat it by accident.
- When leftover food is thrown away it is often packed in plastic.
- Animals smell the leftover food and eat the plastic by accident.
Question 5.
What do you mean by microplastics?
Answer:
- Synthetic fibres are made out of petrochemicals and last in the environment for a very long time.
- It break down into very small pieces called microplastics which cause pollution to soil and water bodies such as rivers, lakes and oceans.
Question 6.
Mention a few household products in which microbeads can found.
Answer:
Microbeads can be found in toothpaste, facewash and bodyscrubs.
Question 7.
What is thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics?
Answer:
Plastics which can be easily softened and bent when heated are known as thermoplastic . There are some plastics which once they are moulded, cannot be softened through heating them. These are called Thermo plastic
Question 8.
Hot foot stuff should not be kept in polythene containers. Why?
Answer:
Hot food stuff should not be kept in polythene containers since polythene is a thermoplastic.
Question 9.
Plastics have completely occupied our life. Why?
Answer:
- Plastics have completely occupied our life because of their characteristic qualities.
- Plastics have many positive qualities such as lightweight, strong and they can be moulded into complex shapes.
- They are also flexible and waterproof and some plastics are even UV resistant.
- Plastics are also cheap and convenient for us to use.
VII. Long Answer
Question 1.
Explain about plastic eating bacteria.
Answer:
- In 2016, scientists from Japan tested different bacteria from a bottle recycling plant and found that Ideonellasakaiens is 201-F6 could digest the plastic used to make single-use drinks bottles that are made of polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
- The bacteria works by secreting an enzyme known as ‘PETase’, that breaks down plastic into smaller molecules.
- These smaller molecules are then absorbed by the bacteria as a food source.
- The scale of the bacteria breaking down plastics is much slower and will therefore not solve the crisis we are facing.
Question 2.
Write a note on manufacturing of glass.
Answer:
- Glass is prepared by heating (SiO) silicondi-oxide until it melts, about 1700°C and Sodium Carbonatfe is added to it.
- Then it is cooled down really fast.
- When SiO2 silicondi-oxide melts, the silicon and oxygen atoms break out of their crystal structure.
- If we cooled it slowly, the atoms would slowly line up back into their crystalline arrangement.
- But if we cool the liquid fast enough, the atoms of the silica will be halted in their tracks, they won’t have time to line up, and they will be stuck in any old arrangement, with no order to the arrangement of the atoms.
- We call materials like this as amorphous.
Question 3.
Write the importance of rayon.
Answer:
- Some types of rayon are made from the short cotton fibres left on cotton seeds after ginning.
- Rayon is cheaper than silk, can be woven like natural silk fibre and can be dyed in a wide variety of colours.
- It can be mixed with cotton to make bed sheets or with wool in the production of carpets and home furnishing products.
- Rayon is also found in sanitary products, diapers, bandages and gauze for dressing
VIII. Complete the following crossword with the help of the clues provided:
Across:
5. First artificially made fibre.
6. Join together to form polymers.
7. Made of ester units.
Down:
1. Terylene and cotton blend.
2. An example of a thermosetting platics.
3. Artificially made fibres.
4. Used to make parachutes.
IX. HOTS:
Question 1.
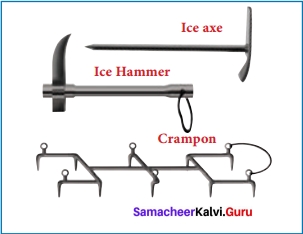
Ram took with him some nylon ropes, when he was going for rock climbing. Can you tell why he selected nylon ropes instead of ropes made up of cotton or jute?
Answer:
- Nylon ropes are strong, elastic and lighter as compared to cotton and jute ropes.
- A nylon thread is actually stronger than a steel wire of similar thickness.
Question 2.
Ramya loves to were the clothes made up of synthetic fibres. When she was working in kitchen, her mother advised her not to wear the synthetic clothes.
- Why Ramya’s mother advised her not to wear synthetic clothes while working in kitchen?
- Why Ramya loves to wear synthetic dress?
Answer:
- Synthetic fibres melt on heating. It the clothes catch fire, it can be disastrous. The fabric melts and sticks to the body of the person wearing it. So, she advised here not to wear synthetic clothes while working in kitchen.
- Ramya loves to wear synthetic dress because these clothes dry up quickly, durable, less expensive, readily available and easy to maintain.
















 ……………….
……………….