You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science History Solutions Term 3 Chapter 1 Society And Culture In Ancient Tamizhagam :The Sangam Age
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science History An Introduction Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer:
6th Standard Social Science Guide Pdf Free Download Question 1.
Pattini cult in Tamil Nadu was introduced by
(a) Pandyan Neducheliyan
(b) Cheran Senguttuvan
(c) Ilango Adigal
(d) Mudathirumaran
Answer:
(b) Cheran Senguttovanj
6th Standard Social Science Guide Pdf Question 2.
Which dynasty was not in power during the Sangam Age?
(a) Pandyas
(b) Cholas
(c) Pallavas
(d) Cheras
Answer:
(c) Pallavas
6th Social Guide Term 3 Question 3.
The rule of Pandyas was followed by
(a) Satavahanas
(b) Cholas
(c) Kalabhras
(d) Pallavas
Answer:
(c) Kalabhras
6th Standard Social Science Guide In English Medium Pdf Download Question 4.
The lowest unit of administration during the Sangam Age was ……………..
(a) Mandalam
(b) Nadu
(c) Ur
(d) Pattinam
Answer:
(c) Ur
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Book Back Answers Question 5.
What was the occupation of the inhabitants of the Kurinji region?
(a) Plundering
(b) Cattle rearing
(c) Hunting and gathering
(d) Agriculture
Answer:
(c) Hunting and gathering
II. Read the Statement and tick the appropriate answer :
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 6th Social Science Question 1.
Assertion (A) :The assembly of the poets was known as Sangam.
Reason (R) :Tamil was the language of Sangam literature,
a. Both A and R are true. R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true. R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
Both A and R is not true.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true. R is not the correct explanation of A
6th Social Science Guide Question 2.
Which of the following statements are not true?
(b) The Pathitrupathu provides information about Chera Kings.
(c) The earliest literature of the Sangam age was written mostly in the form of prose,
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
Answer:
(b) 1 and 3 only
6th Std Social Science Guide Question 3.
The ascending order of the administrative division in the ancient Tamizhagam was
a. Ur < Nadu < Kurram < Mandalam
b. Ur < Kurram < Nadu < Mandalam
c. Ur < Mandalam < Kurram < Nadu
d. Nadu < Kurram < Mandalam < Ur
Answer:
b Ur < Kurram < Nadu < Mandalam
6th Standard Social Guide Question 4.
Match the following dynasties with the Royal Insignia
Chera – 1. Fish
Chola – 2. Tiger
Pandya – 3. Bow and arrow
A. 3 2 1
B. 1 2 3
C. 3 1 2
D. 2 1 3
Answer:
A. 3 2 1
III. Fill in the blanks :
- The battle of Venni was won by ___________
- The earliest Tamil grammar work of the Sangam period was ___________
- ___________ built Kallanai across the river Kaveri.
- The chief of the army was known as ___________
- Land revenue was called ___________
Answer:
- Karikalana
- Tholkappriya
- Karikalana
- Thanithalaivan
- Irai
IV. True or False :
- The singing bards of the Sangam age were called Irular.
- Caste system developed during the Sangam period.
- Kizhar was the village chief.
- Puhar was the general term for city.
- Coastal region was called Marudham
Answer:
- False
- False
- True
- False
- False
V. Match :
- Thennar – i Cheras
- Vanavar – ii Cholas
- Senni – iii Velir
- Adiyaman – iv Pandyas
Answer:
- – iv
- – i
- – ii
- – iii
VI. Answer in one or two sentence
Question 1.
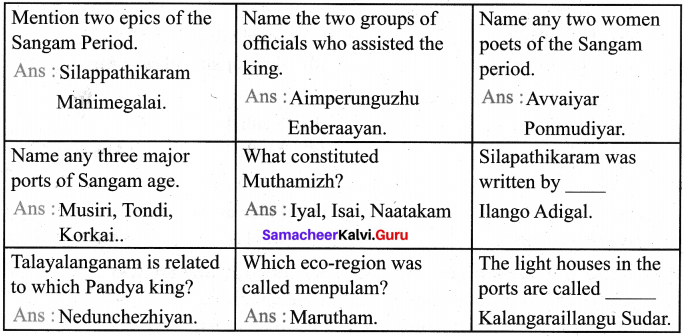
Name any two literacy sources to reconstruct the history of ancient Tamizhagam.
Answer:
Tholkappiyam, Ettuthogai and Patthupattu are some of the literary sources to reconstruct the history of ancient Tamizhagam.
Question 2.
What was Natukkal or Virakkal?
Answer:
In anciant Tamizhagam, the stones erected to commemorate the heroes who died in the battle field are called Natukal (Veerakkal)
Question 3.
Name five thinais mentioned in the Sangam literature.
The five thinais mentioned in the Sangam literature are
Answer:
- Kurinji.
- Mullai.
- Marutham.
- Neithal.
- Palai.
Question 4.
Name any two archaeological sites related to the Sangam period.
Answer:
- Adichanallur
- Arikamedu
Question 5.
Name the seven patrons (KadaiyeluVallalgal).
The seven patrons were
- Pari
- Kari
- Ori
- Pegan
- Ay
- Adiyaman
- Nalli
Question 6.
Name any three Tamil poetic works of Kalabhra period.
Answer:
- Tamil Navalar Charithai
- Yaperunkalam
- Periapuranam
VII. Answer the following :
Question 1.
Discuss the status of women in the Sangam Society.
Answer:
- There was no restriction for women in social life.
- There were learned and wise women.
- Forty women poets had lived and left behind their valuable works.
- Marriage was a matter of self-choice.
- However, Chastity (Karpu) was considered the highest virtue of women.
- Sons and daughters had equal shares in their parent’s property.
- Women poets of Sangam Age were Arraiyar, Velliveethiyar, Kakkaipadiniyar, AathiManthiyar, Ponmudiyar.
VIII. Hots
Question 1.
KarikalValavan Is regarded as the greatest Chela king. Justify.
Answer:
- KarikalValavan or Karikalan was the most famous of the Chola kings.
- He defeated the combined army of the Cheras, Pandyas and the eleven Velir Chieftains who supported them at Venni, a small village in the Thanjavur region.
- He converted forests into cultivable lands.
- He built Kallanai across the river Kaveri to develop agriculture.
- Their port Puhar attracted merchants from various regions of the Indian Ocean.
- The Pattinapaalai a poetic work in the pathinenkeezhkanakku gives elaborate information of the trading activity during the rule of Karikalan.
Question 2.
The period of Kalabhra is not a dark age. Give reasons.
Answer:
- The literary sources include Tamil Navalar Charithai, Yapernkalam and Periapuranam for the period of Kalabhra.
- Seevaka Chinthamani and Kundalakesi were aslo written during this period. Many works under pathinenkeezh kanakku were composed.
- During this period Jainism and Buddhism became prominent.
- The – introduction of Sanskrit and Prakrit developed Vattezhuththu script.
- Trade and commerce flourished.
So the Kalabhra Period is not a dark age.
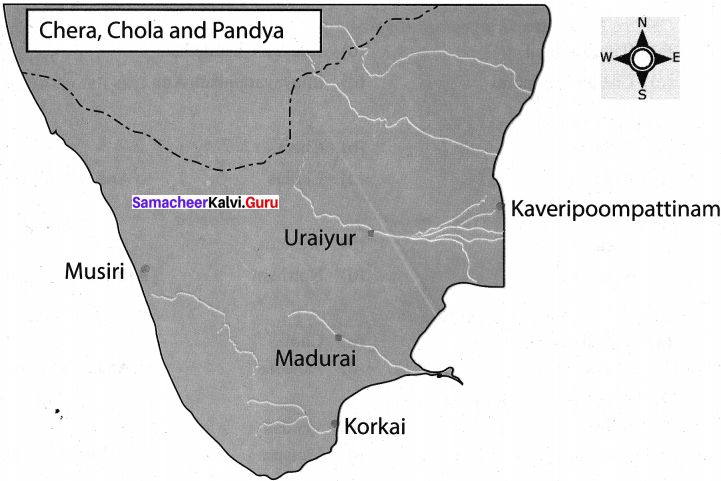
IX. Map Work :
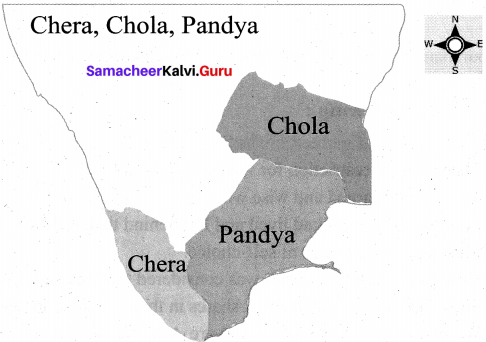
Question 1.
Mark and colour the extent of Chera, Chola and Pandya empires on the river map of South India.
Question 2.
Mark the following places,
a. Kerkil
b. Kaveripoompattinam
c. Mwsiri
d. Uratyur
e. Madurai
XI. Answer Grid
Society And Culture In Ancient Tamizhagam :The Sangam Age Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Cheran Senguttuvan’s younger brother was .
(a) IlangoAdigal
(b) Udayan Cheralathan
(c) Cheran Irumporai
(d) Imayavaramban
Answer:
(a) Ilango Adigal
Question 2.
The epic character from Silappathikaram
(a) Kannagi
(b) Manimegalai
(c) Sita
(d) Panjali
Answer:
(a) Kannagi
Question 3.
The Pandyas ruled the present day Tamilnadu.
(a) Eastern
(b) Western
(c) Southern
(d) Northern
Answer:
(c) Southern
Question 4.
The first emporium of India is …………….
(a) Muziri
(b) Madurai
(c) Vanchi
(d) Puhar
Answer:
(a) Muziri
Question 5.
One of the Seven patrons were
(a) Nalli
(b) Vendan
(c) Valavan
(d) Vanaran
Answer:
(a) Nalli
Question 6.
The place served as the court of .Justice was .
(a) Padai
(b) Mandram
(c) Avai
(d) Ariyanai
Answer:
(b) Mandram
Question 7.
Mudur means
(a) big village
(b) small village
(c) old village
(d) developing village
Answer:
(c) old village
Question 8.
Paddy and Sugarcane were produced in .
(a) Marutham
(b) Neithal
(c) Palai
(d) Mullai
Answer:
(a) Marutham
Question 9.
Yapernkalam was one of the liter a sources of the
(a) Pandyas
(b) Pallavas
(c) Kalabhras
(d) Cholas
Answer:
(c) Kalabhras
II. Read the Statement and tick the appropriate answer :
Question 1.
Assertion (A) :Marutham w as called fertile land.
Reason (R) :Marutham produced Paddy and Sugarcane.
a. A is true but R is false.
b. Both A and R is not true.
c. Both A and R are true ; But R is not the correct explanation of A.
d. Both A and R are true ; R is the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(d) Both A and R are true. R is the correct explanation of A
Question 2.
Which of the following statement is / are not true.
a. Tholkappiam is a work on Tamil grammar.
b. Perunarkilli was a prominent Chera ruler.
c. Sembiyan was a title assumed by the Cholas.
d. Madurai was the capital of the Cholas.
- a and b only
- b and d only
- c only iv. c and d only
Answer:
- b and d only
Question 3.
Which of the following statement is / are true?.
a. Nanmaran was praised as the lord of Korkai.
b. Paddaikottil was a place where weapons were kept.
c. Women had many restrictions in social life during Sangam age.
d. Koothu means folk drama.
- a and b are true
- b is true
- c and d are true
- b and d are true
Answer:
- b and d are true
Question 4
Match the following dynasties with the garlands they signified.
a. Chera – i. Margosa.
b. Chola – ii. Fig
c. Pandya – iii. Palmyra
- iii, ii, i
- ii, iii, i
- i, ii, iii
Answer:
- iii, ii, ii
III. Fill in the blanks:
- Sangam age belonged to ______ age.
- Cheran Irumporai issued ______ in his name.
- The ______ region remained the central part of the Kingdom.
- Kallanai means a dam ______
- MudukudimiPeruvazhuthi issued coins to commemorate his performance of many ______
- The crown prince was known as ______
- Veera kazhal means ______
- Pattinam was the name for a ______
Answer:
- Iron
- Coins
- Kaveri delta
- Made of stone
- vedic rituals
- Komahan
- coin
- Kaveri deltas
- made of stone
- Vedic rituals
- Komahan
- Heroic anklet
- coastal town
IV. True or False :
- The King’s court was called Arasavai.
- The King’s army consisted of eight divisions.
- The entire kingdom was called Nadu.
- The eco-regions were five thinais.
- Varuna system existed in the Sangam age.
- Sangam age developed the concept of Muthamizh.
Answer:
- True
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True
V. Match:
- Kurinji – i. Herding
- Mullai – ii. Fishing
- Marutham – iii. Heroic Deeds
- Neithal – iv. Agriculture
- Palai – v. Hunting
Answer:
- v
- i
- iv
- ii
- iii
VI. Answer in one or two sentences
Question 1.
Mention the boundary of Tamizhagam.
Answer:
Tamizhagam started from Vengadam (Tirupathi hill) in the north to Kanyakumari (Cape comorin) in the south, bounded by sea on the east and the west.
Question 2.
What were the Festivals and Entertainments in the sangam period?
Answer:
Festivals:
- People celebrated sveral festivals.
- Some of them were the harvest festival (Pontal), the festival of spring and Karthigai.
- Indira vizha was celebrated in the capital.
Entertainments:
- There were many amusements and games.
- Dances, festivals, bull fights, cork fights, dice, hunting, wrestling and playing in swings were some of them.
- Children played with toy cart and with the sand houses made by them.
Question 3.
Where did the Cheras rule?
Answer:
The Cheras ruled over the central and north Travancore, Cochin, South Malabar and Kongu region of TamilNadu.
Question 4.
Mention about the Chera king Senguttuvan.
Answer:
- Cheran Senguttuvan went on a military expedition to North India.
- He brought stones from the Himalayas for making the idol of Kannagi, an epic character from Silappathikaram. He introduced Pattini cult.
Question 5.
Why was Kallanai built?
Answer:
- Kallanai was a dyke (thick wall), built with stones.
- It was constructed across the Kaveri to divert water throughout the delta region for irrigation.
- When it was built, Kallanai irrigated an area of about 69,000 acres.
Question 6.
Why is Nedunchezhian hailed on the most popular warrior?
Answer:
- Nedunchezhiyan is hailed as the most popular warrior.
- He defeated the combined army of the Chera, Chola and five Velir Chieftains at Talayalanganam.
- He is praised as the lord of Korkai.
Question 7.
What were the Symbols of royal used during the Sangam period?
Answer:
Kol, Murasu and Venkudai were used as the symbols of the royal authority.
Question 8.
What were the prominent weapons used during the Sangam period?
Answer:
- The prominent weapons used during this period were sword, kedayam (shield), tomaram (lance) spears, bows and arrows.
- Tomaram is mentioned as a missile to be thrown at the enemy from a distance.
- The place where the weapons were kept was known as Paddaikottil.
Question 9.
Mention the important towns of the Sangam period.
Answer:
Puhar, Uraiyur, Korkai, Madurai, Musiri, Vanji or Karur and Kanchi were the important towns of the Sangam period.
Question 10.
What were the festivals celebrated by the people of the Sangam Age?
Answer:
- People celebrate several festivals.
- The harvest festival, (Pongal) and the festival of spring, Kaarthigai, were some of them.
- Indira vizha was celebrated in the Capital.
Question 11.
What were the two kinds of markets or bazaars in Puhar and Madurai ?
Answer:
- There were two kinds of markets or bazaars in the leading cities like Puhar and Madurai.
- In Madurai, they were Nalangadi (the morning bazaar) and Allanga (the evening bazaar).
- In these markets, large varieties as well as large quantities of goods were sold and purchased.
Question 12.
Mention the major exports and imports of Musiri, Tondi, Korkai.
Answer:
- Main exports : Salt, pepper, Ivory, Silk, Spices, Diamonds, Saffron, Precious stones, Muslin, Sandal wood.
- Main imports : Topaz, tin, wine, glass, horses.
VII. Answer the following :
Question 1.
Write about the sources of the Sangam Age.
Answer:
(i) Inscriptions – Hathigumpha Inscription of King Karavela ofKalinga, Pugalur (near Karur) Inscription, Ashokan Edicts II and XIII, and
inscriptions found at Mangulam, Alagarmalai and Ki lavalavu (all near Madurai).
(ii) Copper plates – Velvikudi and Chinnamanur copper plates.
(iii) Coins – Issued by the Cheras, Cholas, Pandyas and the chieftains of Sangam Age as well as the Roman coins.
(iv) Megalithic
Monuments – Burials and Hero stones.
(v) Excavated
Materials from – Adichanallur, Arikamedu, Kodumanal, Puhar, Korkai, Alagankulan, Uraiyur.
(vi) Literary Sources – Tholkappiyam, Ettuthogai,Pathupattu, Pathinankeezhkanakku, Pattinapalai and Maduraikanji. Epics Silapathikaram and Manimegalai.
(vii) Foreign Notices – The Periplus of the Erythrean Sea, Pliny’s Natural History, Ptolemy’s Geography, Megasthenes’s Indica, Rajavali, Mahavamsa and Dipavamsa.
Question 2.
Write about the Kingship under the Sangam polity.
Answer:
- The kingship was hereditary.
- The eldest son of the reigning king generally succeeded to the throne.
- The coronation ceremony was known as Arasukattilerudhal or Mudisoottuvila.
- The crown prince was known as Komahan.
- King held a daily durbar (naalavai) at which he heard and resolved all the disputes.
- The income to the state was through taxation.
- The kings and soldiers wore the heroic anklet (Veera kazhal).
- Spies were used.
- A wound in the back was considered a disgrace.
Question 3.
Write a note on a) Arts and b) Occupation during Sangam age.
Answer:
Arts:
- There are many references to variety of musical instruments such as drum, flute and yazh.
- Karikalan was master of seven notes of music.
- Singing bards were called panar and vraliyar.
- Dancing was performed by kanigaiyar. Koothu was the most important cultural practice of the people of Sangam Age.
- They developed the concept of Muthamizh (Iyal, Isai, Naatakam).
Occupation :
- The major occupations of the people were : agriculture, cattle rearing, fishing and hunting.
- Other craftsmen like carpenter, blacksmith, goldsmith, and potters were also part of the population.
- Weaving was the most common part-time occupation of the farmers and a regular full time job for many others.
VIII. HOTS :
Question 1.
a. Write a note on Ornamental Gateway.
Answer:
Omainental gateway (Pailou) built during Han dynasty (202 BCE – 220 CE) across street lined with small shobs, Hanzhong, Shaanxi Province China in 1875.
b. Write a note on Pyramid Mayan civilisation
- Mayan pyramid : The Maya are a people of Southern Mexico and northern central America with some 3000 years of history.
- Archaeological evidence shows the Mayan started to build ceremonial architecture approximately 3000 yrs ago.
- Mesoamerican pyramids or pyramid shaped structures form a prominent part of ancient Mesoamerican architecture resemblance to Egyptian pyramids.