Looking to improve English skills and gain more subject knowledge then the best resources that you can use here is Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Solutions for Supplementary Chapter 3 The Story of Mulan Questions and Answers.
In the Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Guide for Chapter 3 The Story of Mulan textbook solutions, subject experts covered all types of questions and answers related to the topics, quick notes, summary, solved & unsolved exercises, etc. If you are planning to prepare Chapter 3 The Story of Mulan via textbook, then you’re suggested to go with this Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Book Solutions Questions and Answers PDF for better understanding and preparation.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Solutions Supplementary Chapter 3 The Story of Mulan
English Subject experts who are having max years of experience prepared this Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for 10th English Supplementary Chapter 3 The Story of Mulan Questions and Answers. They have explained all the topics covered in the board prescribed latest syllabus in a simple way to understand easily. So, students can prepare Chapter 3 English from this Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Book Questions and Answers PDF. Download the Tamilnadu State Board 10th English Chapter 3 The Story of Mulan Workbook Solutions PDF by accessing the below links and learn properly for the final exams to score well.
The Story of Mulan Textual Questions
A. Choose the best answers.
1. Mulan goes to the battle instead of her father because ……………….. .
(a) she wants to be a soldier
(b) she was asked to join the army
(c) her father is old
(d) her brother is sick
Answer:
(c) her father is old
2. What did Mulan do before leaving the house?
(a) took leave from her mother
(b) cut off her hair
(c) prayed
(d), made a dress for war
Answer:
(b) cut off her hair
3. What is the story about?
(a) winning
(b) friendship
(c) women empowerment
(d) patriotism
Answer:
(c) women empowerment
4. The emperor asked Mulan to stay with him in the palace as his ……………….. .
(a) wife
(b) royal adviser
(c) army general
(d) friend
Answer:
(b) royal adviser
5. The emperor gave Mulan ……………….. .
(a) six horses and six swords
(b) a death sentence
(c) gold
(d) six camels
Answer:
(a) six horses and six swords
6. How did people of the village react to Mulan after her return from the battle?
(a) cheered her
(b) mocked her
(c) punished her
(d) scolded her
Answer:
(a) cheered her
The Story Of Mulan 10th Standard Additional Questions
1. The classic story of Mulan is based on the legend of ………………….. .
(a) Hua Mulan
(b) Hans Mulan
(c) Fa Mulan
(d) Hua Mulan
Answer:
(a) Hua Mulan
2. Many years ago, China was in the …………………. of a great war.
(a) beginning
(b) end
(c) middle
(d) process
Answer:
(c) middle
3. Mulan, a …………… girl who lived in a faraway village of China, heard the news.
(a) young
(b) married
(c) widowed
(d) teenage
Answer:
(d) teenage
4. Mulan heard the Emperor’s command while ……………….. .
(a) grazing the cows
(b) feeding the horses
(c) washing clothes
(d)making porridge
Answer:
(c) washing clothes
5. Mulan’s father was sitting in a chair, ……………………. a piece of wood.
(a) carving
(b) chiseling
(c) scraping
(d) fixing
Answer:
(a) carving
6. Mulan’s father said that Mulan’s brother was a ……………. .
(a) sickly child
(b) child
(c)deserter
(d) traitor
Answer:
(b) child
7. Mulan poured her father a cup of …………… and handed it to him.
(a) coffee
(b) green tea
(c)cold coffee
(d) tea
Answer:
(d) tea
8. Mulan cut off her long, ……………….. hair.
(a) blonde
(b) grey
(c) black
(d) lustrous
Answer:
(c) black
9. For years, Mulan was trained in ………….. by her father.
(a) Judo
(b) Kung Fu
(c) Taekwondo
(d) Aikido
Answer:
(b) Kung Fu
10. Mulan climbed on a family ………….. and set off to join the Emperor’s army.
(a) pony
(b) elephant
(c) tiger
(d) horse
Answer:
(d) horse
B. Identify the character or speaker of the following lines.
1. I heard about it in town.
Answer:
Mulan’s father
2. I am your son now.
Answer:
Mulan
3. The General is a woman?
Answer:
The soldiers
4. Mulan, stay with me in the palace.
Answer:
The Emperor of China
5. You are too kind sir.
Answer:
Mulan
The Story Of Mulan Summary Additional:
1. One man from each Chinese family must join the army.
Answer:
The Emperor
2. Did you hear what the Emperor says each family must do?
Answer:
Mulan
3. Well, I may as well go pack up.
Answer:
Mulan’s father
4. Why at your age must you keep up with all those young men?
Answer:
Mulan
5. What else can be done?
Answer:
Mulan’s father
6. Of course that’s true.
Answer:
Mulan
7. Please sit for a minute. I will be right
Answer:
back.
Mulan
8. Look at me. I am your son now.
Answer:
Mulan
9. I will go to your place. I will do my part for China.
Answer:
Mulan
10. “Na, you c.unot do this!
Answer:
Mulan’s father :
11. You showed me boss to use a sword.
Answer:
Mulan
12. Only so that you could stay safe
Answer:
Mulan’s father
13. I never meant for you logo to war.
Answer:
Mulan’s father
14. You know as well as I do that you will die!
Answer:
Mulan’s father
15. Take care of yourself.
Answer:
Mulan
16. What I wish most of all is to return home to my family.
Answer:
Mulan
17. “How can this be?”
Answer:
Some soldiers
18. “She tricked us!”
Answer:
Some soldiers
19. “We will not fight for a woman!”
Answer:
Some soldiers
20. “Punish her! Make her pay!
Answer:
Some soldiers
21. The cost is for her to die!
Answer:
Some soldiers
22. With Mulan, we win every battle!”
Answer:
Other soldiers
23. “Stay away from our General!”
Answer:
Other soldiers
24. “Everyone! A surprise attack is coming!”
Answer:
A soldier
25. Someone as smart as you would be a fine royal adviser.
Answer:
The Emperor
26. Then at least take these fine gifts.
Answer:
The Emperor
27. So everyone at your home and village will know I think of you.
Answer:
The Emperor
28. Tell my brother I said goodbye.
Answer:
Mulan
29. I love you.
Answer:
Mulan to her father
30. Listen please.
Answer:
Mulan
C. Answer the following questions in a sentence or two.
The Story Of Mulan Question Answer Question 1.
What was the emperor’s order?
Answer:
The Emperor’s order was that one man from each Chinese family must leave his family. to join the army.
The Story Of Mulan Summary 10th Standard Question 2.
Where did Mulan’s father hear about the emperor’s order?
Answer:
Mulan’s father heard about the Emperor’s order in town.
Mulan Questions And Answers Question 3.
Why couldn’t Mulan’s brother go to war?
Answer:
Mulan’s brother couldn’t go to the war because he was a child.
The Story Of Mulan Paragraph Question 4.
Why did Mulan disguise herself as a man?
Answer:
Mulan disguised herself as a man because women were not allowed to join the army.
10th English Supplementary Story In English Question 5.
How did the soldiers become sick?
Answer:
A bad fever swept through the army. So, many soldiers became sick.
Story Of Mulan Summary Question 6.
How would she be punished if found guilty?
Answer:
if found guilty, she would be killed.
10th English Unit 3 Supplementary Question 7.
Why did the emperor give her fine gifts?
Answer:
The Emperor gave her fine gifts because she won the battle and saved China.
The Story Of Mulan Summary In Tamil Question 8.
How did the soldiers come to know about Mulan’s real identity?
Answer:
When a bad fever swept the army, all the soldiers became sick. Even Mulan was affected by this fever. When the doctor examined Mulan in her tent, the doctor came to know that she was a woman and informed the soldiers.
The Story Of Mulan 10th English Additional:
The Story Of Mulan Supplementary Question 1.
W,here did the story of Mutan come from?
Answer:
Hua Mulan was a Chinese warrior woman who lived during the Northern and Southern dynasties, which was between 420 and 589 CE and her story was told through the “Ballad of Mulan.”
10th English Supplementary Story In Tamil Question 2.
How do you know that the story of Mulan ¡s a true story?
Answer:
Any legend is a story from ancient times and it is believed to be based mostly on true stories. Now, it’s possible that she was a real person, but it is largely believed that her story is fictional.
Question 3.
Why did Mutan take a decision risking her life?
Answer:
In response to the Emperor’s order, Mulan decided to risk her life since her father was aged and her only brother was a child. To add to these, she was also trained in Kung Fu by her father to stay safe.
Question 4.
Why should Mutan be considered a hero?
Answer:
Hua Mulan should be considered as a hero because she joined the all-male army to interchange her father’s place. It was really hard for a woman to make this choice in ancient China. She is my hero because she showed filial respect for her father, made an impact among her countrymen and was brave.
D. Answer the following questions in a paragraph.
Question 1.
Sketch the character of Mulan.
Answer:
Mulan was a brave warrior who saved China from the enemies. She was determined, courageous and intelligent. She was unselfish too. The incident which best attests to this trait was after returning from the war, the Emperor offered her the post of royal advisor. She refused the post and simply told that she wanted to return home. Mulan’s determination helped her through her adventures defeating the enemies’ army. She never gave up in bad situations. At war, she was very intelligent and was a quick planner. This attitude won her the war for the Chinese. She fought in the battle for twelve years and gained high merit. She refused any rewards except for six fine horses and six fine swords.
Question 2.
Do you agree with Mulan’s decision to go to war? Justify.
Answer:
Yes, Mulan’s decision to go to the war was correct. She is a patriotic girl who wanted to fight for her country. When the Emperor of China insisted that one man from each family should join the army, she was ready to join the army disguised as a man. At first, her father decided to join the army. But Mulan protested that he could not go as he was old and sick. Her brother was a child. So she decided to join the army. Her father was afraid that the Emperor would kill her, if he knew that she was a woman. But Mulan was confident that no one would find her. She cut her hair like a man and picked up the sword. She bade him goodbye, climbed on a horse and went to join the Emperor’s army.
Additional:
A. Rearrange the following sentences in coherent order.
1. a. With her sword, she cut off her long, black hair.
b. No, my daughter, you cannot do this!
c. Many years ago, China was in the middle of a great war.
d. Look at me, I am your son now.
e. I will do my part for China.
Answers:
c, a, d, e, b
c. Many years ago, China was in the middle of a great war.
a. With her sword, she cut off her long, black hair.
d. Look at me, I am your son now.
e. I will do my part for China.
b. No, my daughter, you cannot do this!
2. a. But, I never meant for you to go to war.
b. Father, for years, you trained me in Kung Fu.
c. No one will find out, Father, said Mulan and kissed him goodbye.
d. Take care of yourself, father and tell my brother I said goodbye.
e. If they find out you are a woman, you know as well as I do that you will die!
Answers:
b, a, e, c, d
b. Father, for years, you trained me in Kung Fu.
a. But, I never meant for you to go to war.
e. If they find out you are a woman, you know as well as I do that you will die!
c. No one will find out, Father, said Mulan and kissed him goodbye.
d. Take care of yourself, father and tell my brother I said goodbye.
B. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate phrases given below to form a complete meaningful paragraph.
1. (put on/cannot do this / into her room /cut off her long / Going back to her father)
Mulan went (i) ………………. With her sword, she (ii) ……………., black hair. She (iii) …………… her father’s robe, (iv) …………….., Mulan said, “Look at me. I am your son now. I will go in your place. I will do my part for China.” “No, my daughter!” said the old man. “You (v) ……………. !”
Answers:
(i) into her room
(ii) cut off her long
(iii) put on
(iv) Going back to her father
(v) cannot do this
2. (she was safe / returned to her village / stay with me in the palace / smart as you / so glad that)
The Emperor was (i) ……………. Mulan had ended the long war. He set aside the rule about being a woman. “Mulan, (ii) ………………..,” he said. “Someone as (iii) …………….. would be a fine royal adviser.” Politely refusing the offer, Mulan (iv) ………….. with six fine horses and six fine swords. Everyone cheered that (v) ……………. The person who had saved China was their very own Mulan!
Answers:
(i) so glad that
(ii) stay with me in the palace
(iii) smart as you
(iv) returned to her village
(v) she was safe
C. Match the following appropriately:
1.


Answer:
(i)(c), (ii)(e), (iii)(d), (iv)(b), (v)(a).
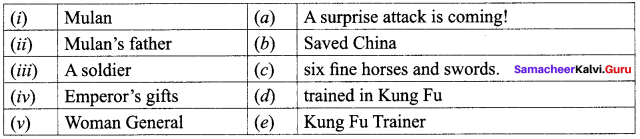
2. 
Answer:
(i)(d), (ii)(e), (iii)(a), (iv)(c), (v)(b).
D. Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
1. Many years ago, China was in the middle of a great war. The Emperor said that one man from each Chinese family must leave his family to join the army. Mulan, a teenage girl who lived in a faraway village of China, heard the news when she was outside, washing clothes.
Mulan ran into the house. Her father was sitting in a chair, carving a piece of wood. “Father!” she said. “Did you hear what the Emperor says each family must do?” “Yes,” said her old father, “I heard about it in town. Well, I may as well go pack up.” He put down his carving, stood up and walked very slowly to his room.“Wait!” said Mulan, “Father, you have not been well.
If I may say so, why at your age must you keep up with all those young men?” “What else can be done?” said her father. “Your brother is a child. He cannot go.” “Of course that’s true,” said Tvfrulan. “He is too little. But I have an idea.” She poured her father a cup of tea and handed it to him. “Father, have some tea. Please sit for a minute. I will be right back.” “Very well, dear,” said the father.
Mulan went into her room. With her sword, she cut off her long, black hair. She put on her father’s robe. Going back to her father, Mulan said, “Look at me. I am your son now. I will go in your place. I will do my part for China.” “No, my daughter!” said the old man. “You cannot do this!”
(а) What was order to the people of China in the middle of war from the Emperor?
Answer:
The Emperor ordered that one man from every Chinese family must leave his family to join the army.
(b) How did Mulan react to this order from the Emperor?
Answer:
Mulan, a teenage girl heard the news when she was washing clothes outside and decided to replace her dad who wasn’t feeling well.
(c) What was Mulan’s father doing at home when she ran into the house?
Answer:
When Mulan ran into the house, her father who was unwell was sitting on a chair and carving a piece of wood.
(d) Why didn’t Mulan want her father to respond to the Emperor’s order?
Answer:
Mulan did not want her father to go to war because he was aged and was unwell. She was sure that he would not be able to keep up with all the young men in the opponent’s army.
(e) How did Mulan prove to be a different kind of a girl child?
Answer:
Mulan was quick in thinking. She quickly went in, cut off her long black hair with her sword, put on her father’s robe and told her father that she would go as a son of a family to fight in the war.
2. “Father, listen please,” said Mulan. “For years, you trained me in Kung Fu. You showed me how to use a sword.” Mulan swung the sword back and forth with might.
“Only so that you could stay safe!” said her father. “I never meant for you to go to war. If they find out you are a woman, you know as well as I do that you will die!”
“No one will find out, Father,” said Mulan. She picked up her sword.
“Mulan!” said the Father. He tried to get up but had to hold on to his chair.
The daughter kissed him goodbye. “I love you, Father,” she said. “Take care of yourself. Tell my brother I said goodbye.” She climbed on a family horse. And off she went to join the Emperor’s army.
In the army, Mulan proved to be a brave soldier. In time, she was put in charge of other soldiers. Her battles went so well that she was put in charge of more soldiers. Her battles kept on going well. After a few years Mulan was given the top job – she would be General of the entire army. Not long after that, a very bad fever swept through the army. Many soldiers were sick. And Mulan, the General of the Army, became sick, too. When the doctor came out of Mulan’s tent, he knew the truth.
(a) What martial art did Mulan’s father teach her? Why?
Answer:
Mulan’s father taught her the art of Kung Fu. He showed her how to use the sword so that she could stay safe and protect herself.
(b) What did the father fear about Mulan’s decision?
Answer:
Mulan’s father feared that she would be put to death if the army men found out that she was a woman and not a man.
(c) What did Mulan do before leaving to war?
Answer:
Mulan kissed her father goodbye and said that she loved him. She also asked him to take care of himself and convey her ‘goodbye’ to her little brother who was a child.
(d) What were Mulan’s accomplishments in the army?
Answer:
In the army, Mulan proved to be a brave soldier. Within a short time, she was put in charge of other soldiers. Her battles went so well that she was put in charge of more soldiers and after a few years she was given the top job – General of the entire army.
(e) What caused the other’s to identify Mulan’s identify?
Answer:
A bad fever swept through the army and Mulan was also a prey to it. This fever revealed her identity to others through the doctor who came to treat her.
E. Study the given mind map and fill in the incomplete details:
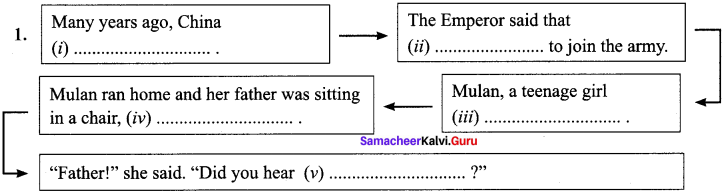
Answers:
(i) was in the middle of a great war.
(ii) one man from each Chinese family must leave his family.
(iii) heard the news when she was outside, washing clothes.
(iv) carving a piece of wood.
(v) what the Emperor says each family must do.
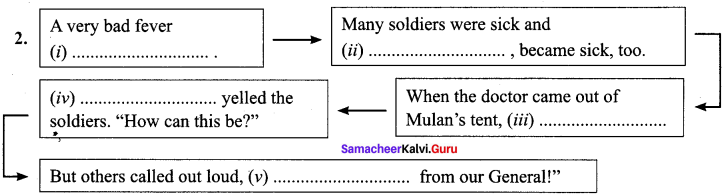
Answers:
(i) swept through the army.
(ii) Mulan, the General of the army,
(iii) he knew the truth
(iv) “The General is a woman?
(v) With Mulan, we win every battle! Stay away
The Story of Mulan Summary:

Introduction:
The Story of Mulan portrays the legendary Chinese warrior Hua Mulan and is mostly based on the information of her from the poem, ‘The Ballad of Mulan’. This restating of the old Chinese folktale is about the story of the young Chinese maiden who learns that her wizened, old and frail father is to be called up into the army in order to fight the invading Huns by the Chinese Emperor.

Announcement from the Chinese:
When the Huns invade China, one man from every family is called to arms. She hears of the order that every family must send one man to the army while washing clothes. She discusses the same with her father who had also heard of it when he had gone to the town. Mulan’s father, who is frail and aged decides to fight for his country and the honour of his family though it is clear that he will not survive an enemy encounter. He decides to go to war but is prevented by her daughter with her outrageous decision. Knowing that her father will never endure the rigours of war in his frail state, she decides to disguise herself and join in his place without second thoughts yet convincing him. Mulan’s only brother who is a small child cannot pitch in.

Mulan joins the battle:
She takes blessings from her father, kisses him goodbye, wore his army clothes and rode on his horse after cutting her long hair short. In the army, Mulan proves to be a brave soldier who is later put in charge of other soldiers. Her battles go so well that more soldiers are added. After a few years, Mulan becomes the General of the entire army.

Truth about Mulan:
Suddenly, bad fever swept through the army. Many soldiers including Mulan become prey. The arrival of the doctor brings to light the hidden truth. Many soldiers disprove such a thought and want her to be punished to death because of gender disparity. However, some soldiers are broad minded and see the winning chances.

Mulan’s bravery and the acceptance of soldiers:
Just then a soldier announces the surprise attack by the enemies. With no time to debate, the soldiers spring to action at the command of the General who hears this from inside her tent. She gets dressed and goes outside. Though not strong, she stands tall. She instructs the soldiers to attack knowing very well her strategic planning that all her soldiers acknowledge. It worked! The battle was won. It was such a big victory that the enemy gave up, at last. The war was over, and China was saved! You can be sure that after that last battle, no one cared anymore that Mulan was a woman.

Mulan’s final decision and the emperor’s gift:
The Emperor was glad that Mulan had ended the long war that he set aside the rule about being a woman. He wanted Mulan to stay with him in the palace and be an advisor but she chose to go to her family, thanking the emperor. The emperor gave her six horses and six fine swords so that her people will know that he thinks of her. Everyone cheered that she was safe and well honoured.

Conclusion:
The story depicts the daughter’ love for her fajher. Father wanted the girl to be able to defend herself and thus taught her sword fight and Kung Fu. How this girl hails to become a commander of an army from learning the art of war from her father is narrated in a fine manner to readers delight.

The Story of Mulan Glossary:
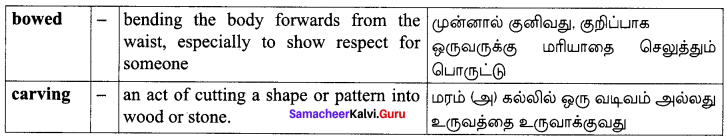
Textual:

Additional:

We hope the data given here will benefit you to the fullest extent at the time of preparation. For better understanding of English subject this Samacheer Kalvi 10th English Solutions for Class 10th English Supplementary Chapter 3 The Story of Mulan PDF is the best resource. Download & ace up your preparation. Keep in touch with us and get the latest information on Tamilnadu State board Textbook Solutions PDF.