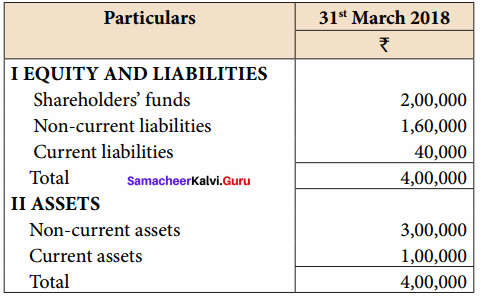
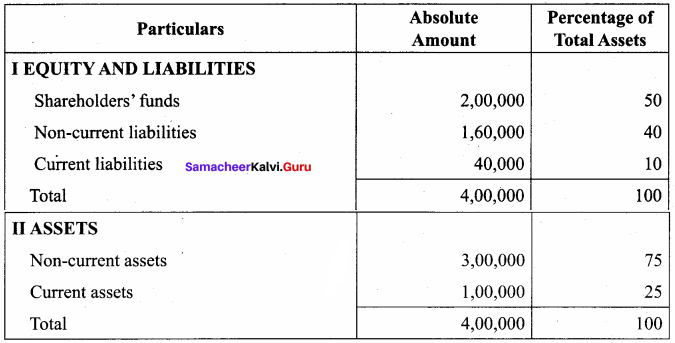
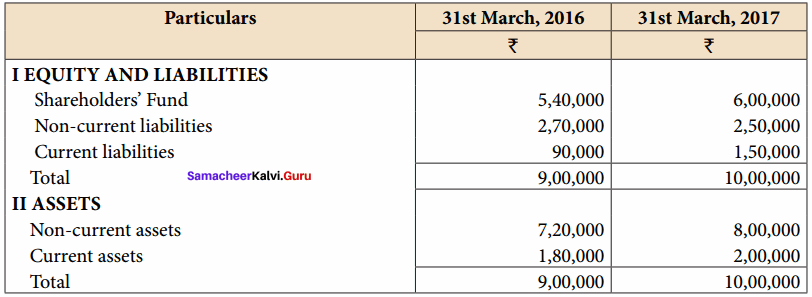
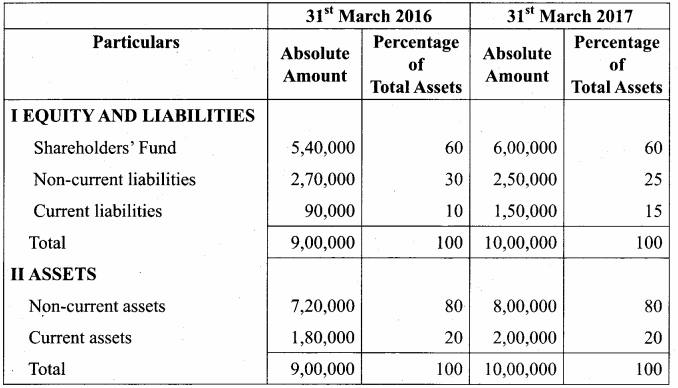
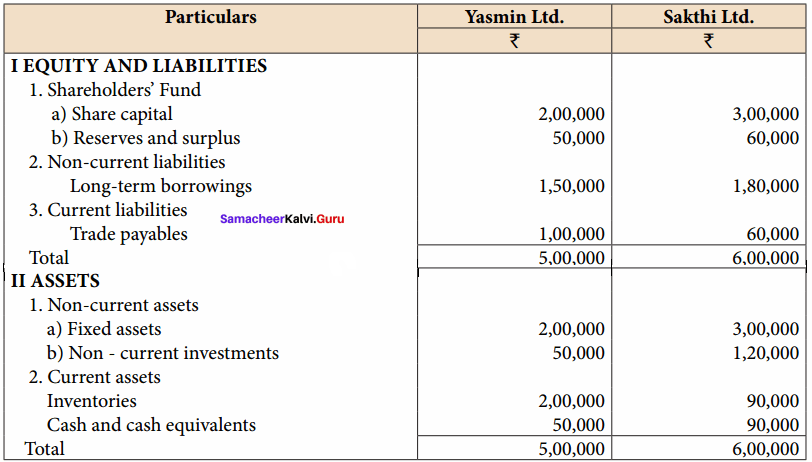
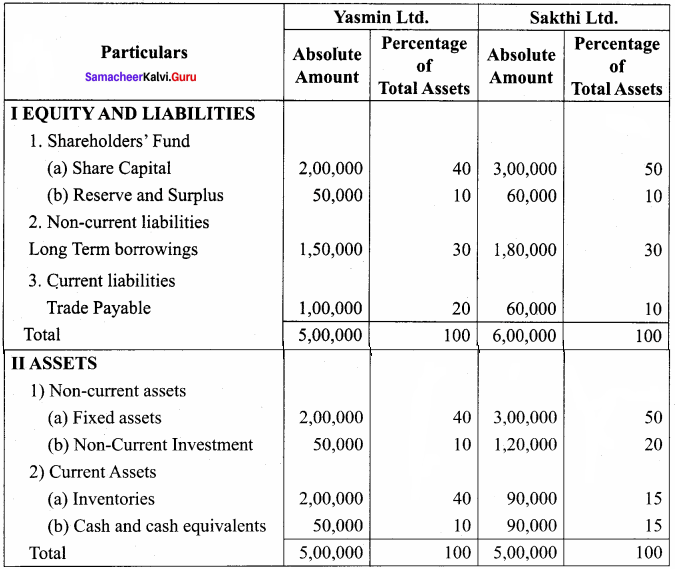
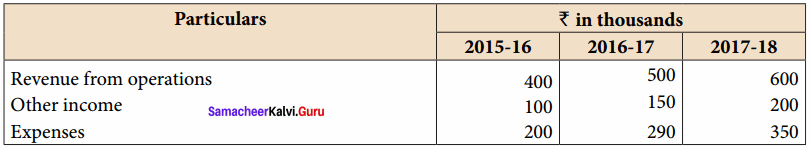
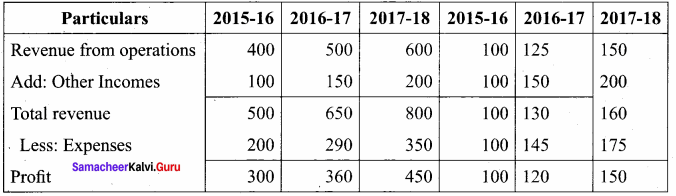
Students can Download Accountancy Chapter 6 Retirement and Death of a Partner Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Solutions Chapter 6 Retirement and Death of a Partner
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Retirement and Death of a Partner Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
12th Accountancy 6th Chapter Solutions Question 1.
A partner retires from the partnership firm on 30th June. He is liable for all the acts of the firm up to the …………………..
(a) End of the current accounting period
(b) End of the previous accounting period
(c) Date of his retirement
(d) Date of his final settlement
Answer:
(c) Date of his retirement
12th Accountancy Chapter 6 Question 2.
On the retirement of a partner from a partnership firm, accumulated profits and losses are distributed to the partners on the basis of …………………
(a) New profit sharing ratio
(b) Old profit sharing ratio
(c) Gaining ratio
(d) Sacrificing ratio
Answer:
(b) Old profit sharing ratio
12th Accountancy Chapter 6 Solutions Question 3.
On the retirement of a partner, general reserve will be transferred to the …………………..
(a) Capital account of all the partners
(b) Revaluation account
(c) Capital account of the continuing partners
(d) Memorandum revaluation account
Answer:
(a) Capital account of all the partners
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Guide Question 4.
On revaluation, the increase in liabilities leads to
(a) Gain
(b) Loss
(c) Profit
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Loss
Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 6 Solutions Question 5.
At the time of retirement of a partner, determination of gaining ratio is required …………………..
(a) To transfer revaluation profit or loss
(b) To distribute accumulated profits and losses
(c) To adjust goodwill
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) To adjust goodwill
Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 6 Retirement Solutions Question 6.
The final amount due to a retiring partner is not paid immediately, it is transferred to …………………..
(a) Bank A/c
(b) Retiring partner’s capital A/c
(c) Retiring partner’s loan A/c
(d) Other partners’ capital A/c
Answer:
(c) Retiring partner’s loan A/c
12 Accountancy Book Samacheer Kalvi Question 7.
‘A’ was a partner in a partnership firm. He died on 31st March 2019. The final amount due to him is ₹ 25,000 which is not paid immediately. It will be transferred to …………………..
(a) A’s capital account
(b) A’s loan account
(c) A’s Executor’s account
(d) A’s Executor’s loan account
Answer:
(d) A’s Executor’s loan account
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Solutions Question 8.
A, B and C are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 2:2:1. On retirement of B, goodwill of the firm was valued as ₹ 30,000. Find the contribution of A and C to compensate B:
(a) ₹ 20,000 and ₹ 10,000
(b) ₹ 8,000 and ₹ 4,000
(c) ₹ 10,000 and ₹ 20,000
(d) ₹ 15,000 and ₹ 15,000
Answer:
(b) ₹ 8,000 and ₹ 4,000
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Book Question 9.
A, B and C are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 4:2:3. C retires. The new profit sharing ratio between A and B will be ………………….
(a) 4:3
(b) 3:4
(c) 2:1
(d) 1:2
Answer:
(c) 2:1
12th Accountancy Samacheer Kalvi Question 10.
X, Y and Z were partners sharing profits and losses equally. X died on 1st April 2019. Find out the share of X in the profit of 2019 based on the profit of 2018 which showed ₹ 36,000.
(a) ₹ 1,000
(b) ₹ 3,000
(c) ₹ 12,000
(d) ₹ 36,000
Answer:
(b) ₹ 3,000
II. Very Short Answer Questions
12th Accountancy Solutions Samacheer Kalvi Question 1.
What is meant by retirement of a partner?
Answer:
When a partner leaves from partnership firm it is known as retirement. The reasons for the retirement of a partner may be illness, old age and disagreement with other partners, etc.
Samacheer Kalvi 12 Accountancy Guide Question 2.
What is gaining ratio?
Answer:
Gaining ratio is the proportion of the profit which is gained by the continuing partner. Gaining ratio = Ratio of share gained by the continuing partners.
Share gained = New share – Old share
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 12th Accountancy Question 3.
What is the purpose of calculating gaining ratio?
Answer:
The purpose of finding the gaining ratio is to bear the goodwill to be paid to the retiring partner.
Samacheer Kalvi Accountancy 12th Question 4.
What is the journal entry to be passed to transfer the amount due to the deceased partner to the executor of the deceased partner?
Answer:

III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
List out the adjustments made at the time of retirement.
Answer:
(a) Distribution of accumulated profits, reserves and losses
(b) Revaluation of assets and liabilities
(c) Determination of new profit sharing ratio and gaining ratio
(d) Adjustment for goodwill
(e) Adjustment for current year’s profit or loss up to the date of retirement
(f) Settlement of the amount due to the retiring partner
Question 2.
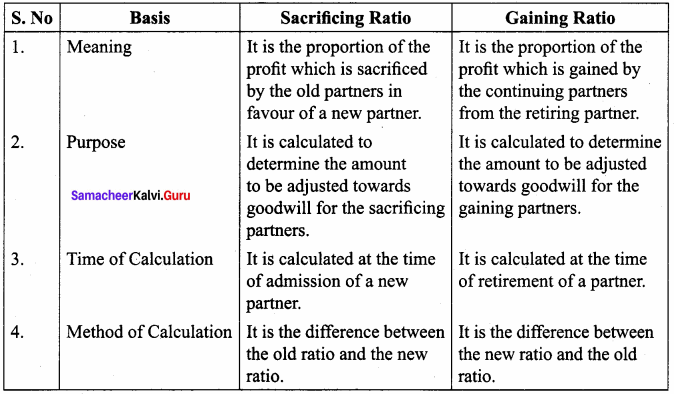
Distinguish between sacrificing ratio and gaining ratio.
Answer:
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accounts Guide Question 3.
What are the ways in which the final amount due to an outgoing partner can be settled?
Answer:
The amount due to the retiring partner may be settled in one of the following ways:
- Paying the entire amount due immediately in cash
- Transfer the entire amount due to the loan account of the partner
- Paying part of the amount immediately in cash and transferring the balance to the loan account of the partner.
IV. Exercises
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Question 1.
Dheena, Surya and Janaki are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 5:3:2. On 31.3.2018, Dheena retired. On the date of retirement, the books of the firm showed a reserve fund of ₹ 50,000. Pass journal entry to transfer the reserve fund.
Answer:
Journal Entries

12th Samacheer Kalvi Accountancy Solution Book Question 2.
Rosi, Rathi and Rani are partners of a firm sharing profits and losses equally. Rathi retired from the partnership on 1.1.2018. On that date, their balance sheet showed accumulated loss of ? 45,000 on the asset side of the balance sheet. Give the journal entry to distribute the accumulated loss.
Answer:

Samacheer Kalvi 12 Accountancy Question 3.
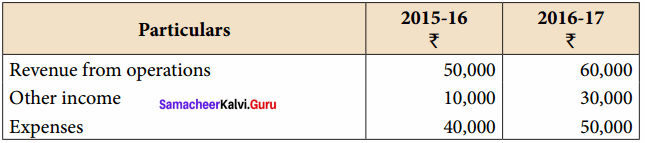
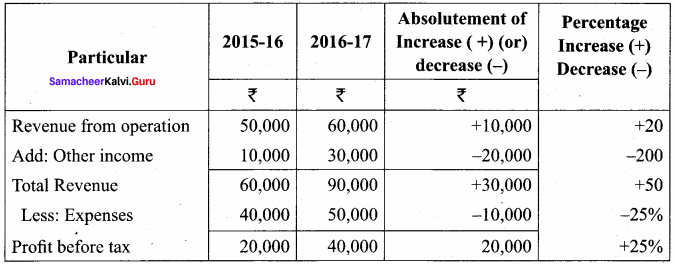
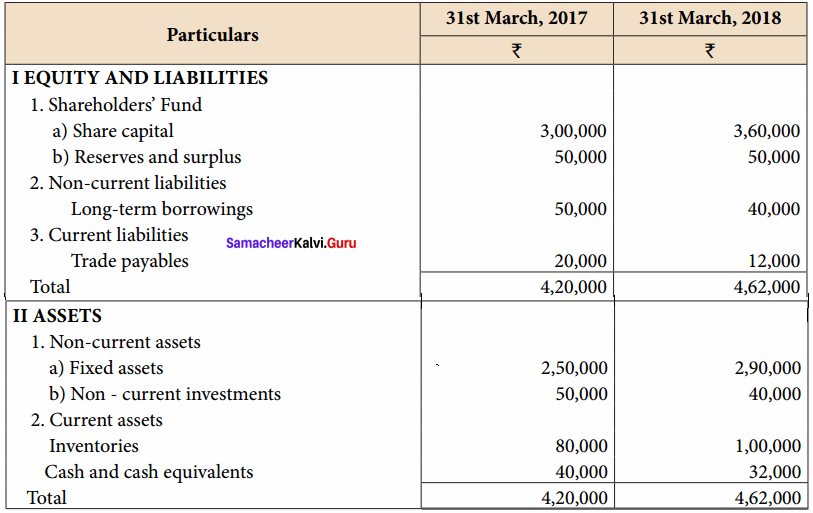
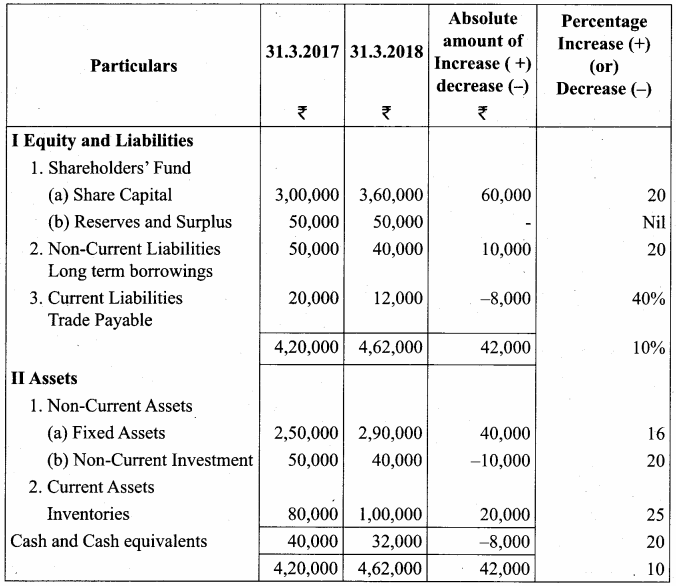
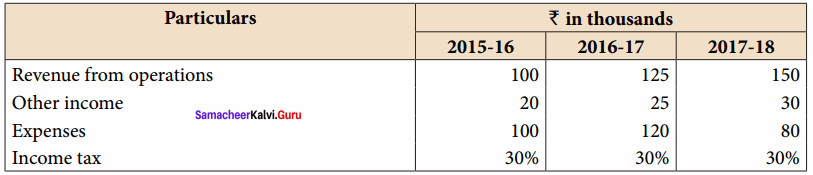
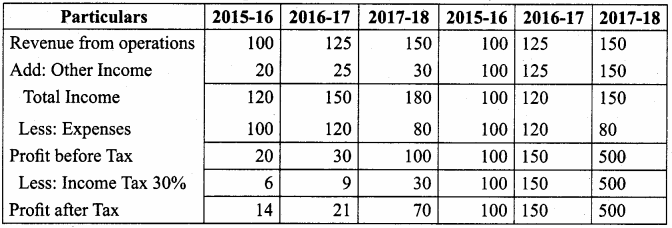
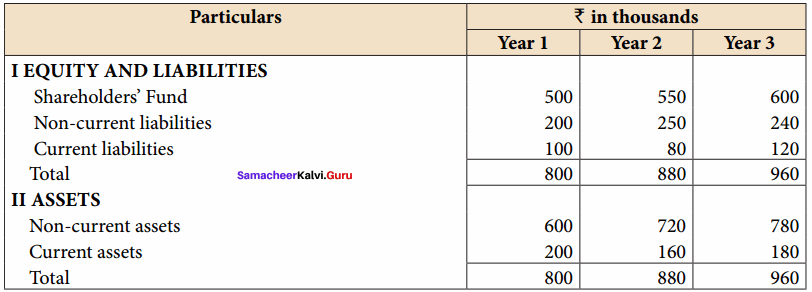
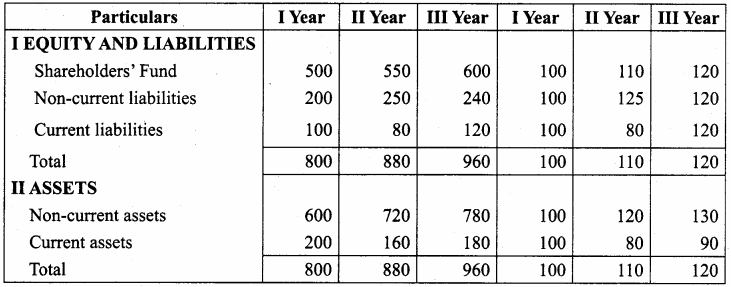
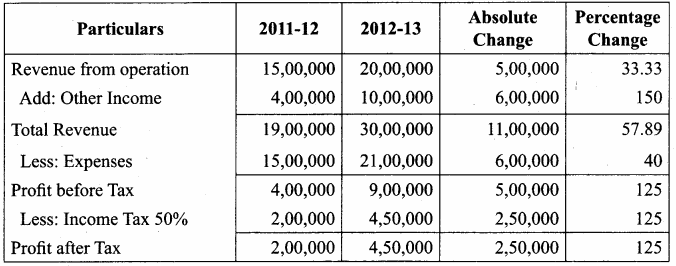
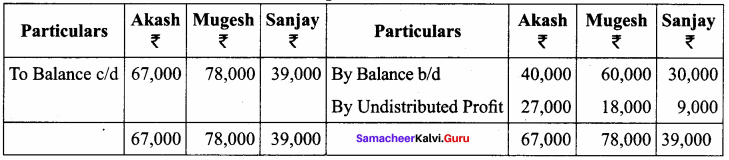
Akash, Mugesh and Sanjay are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2:1. Their balance sheet as on 31st March, 2017 is as follows:
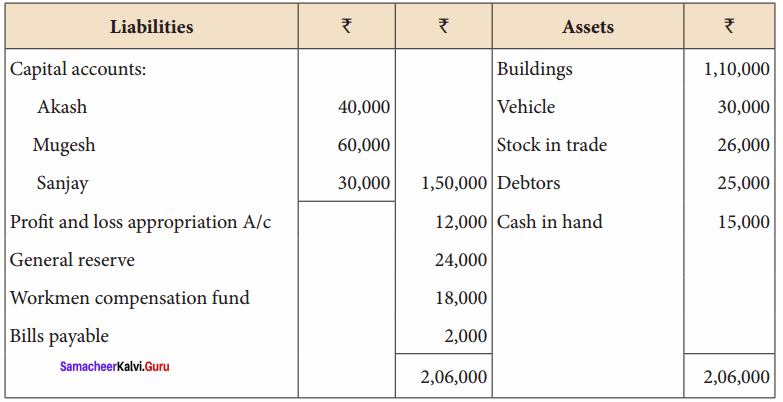 Answer:
Answer:
Pass journal entry to transfer accumulated Profit and prepare the capital account of the partners.
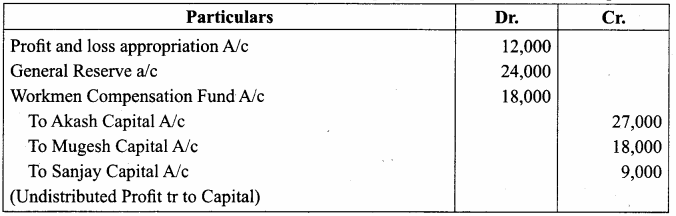
Capital Account
12th Accountancy Answer Pdf Question 4.
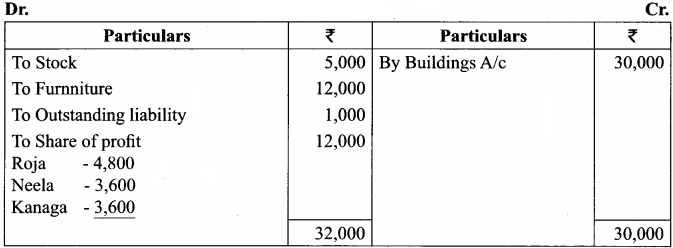
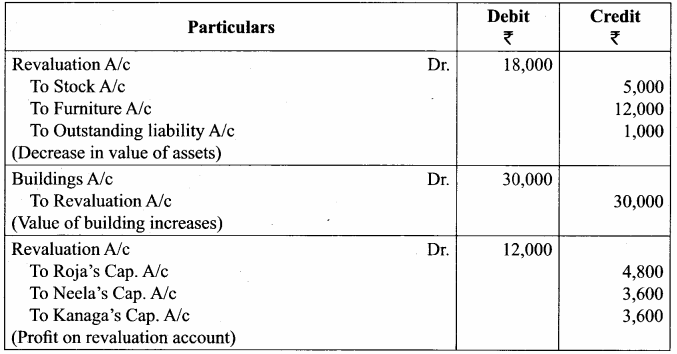
Roja, Neela and Kanaga are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 4:3:3. On 1st April 2017, Roja retires and on retirement, the following adjustments are agreed upon:
(i) Increase the value of building by ₹ 30,000.
(ii) Depreciate stock by ₹ 5,000 and furniture by ₹ 12,000.
(iii) Provide an outstanding liability of ₹ 1,000 Pass journal entries and prepare revaluation account.
Answer:
Revaluation Account
 Journal Entries
Journal Entries
Chapter 6 Retirement Of A Partner Solutions Question 5.
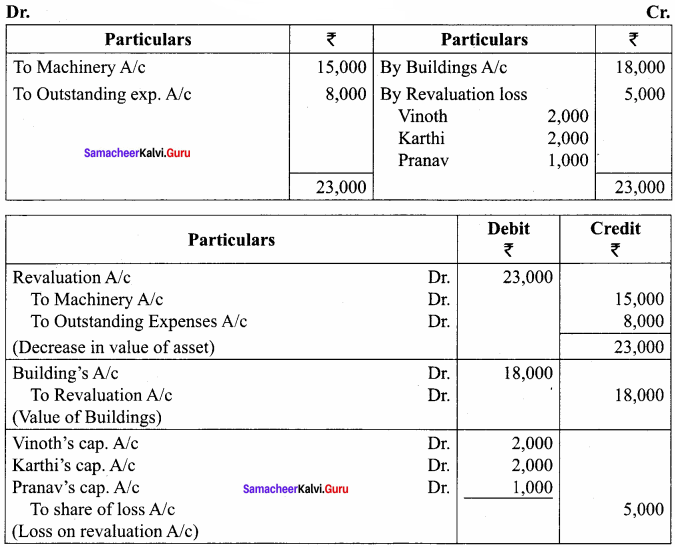
Vinoth, Karthi and Pranav are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2:2:1. Pranav retires from partnership on 1st April 2018. The following adjustments are to be made:
(i) Increase the value of land and building by ₹ 18,000
(ii) Reduce the value of machinery by ₹ 15,000
(iii) A provision would also be made for outstanding expenses for ₹ 8,000.
Give journal entries and prepare revaluation account.
Answer:
Revaluation Account
Question 6.
Chandru, Vishal and Ramanan are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses equally. Their balance sheet as on 31st March, 2018 is as follows:
Ramanan retired on 31 st March 2019 subject to the following conditions:
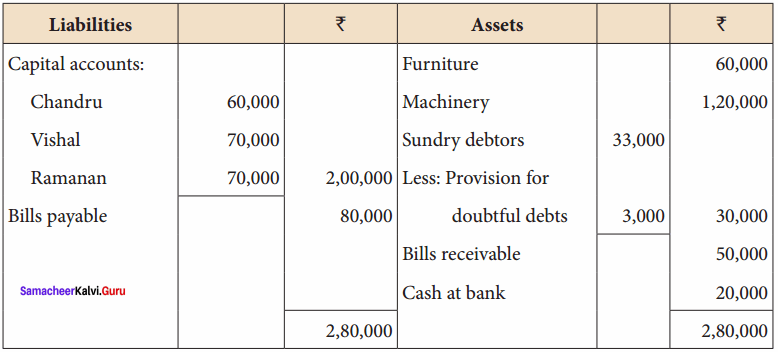
(i) Machinery is valued at ₹ 1,50,000
(ii) Value of furniture brought down by ₹ 10,000
(iii) Provision for doubtful debts should be increased to ₹ 5,000
(iv) Investment of ₹ 30,000 not recorded in the books is to be recorded now.
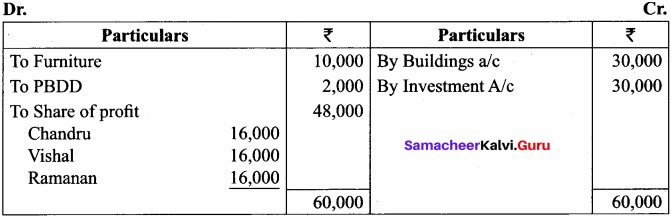
Pass necessary journal entries and prepare revaluation account and capital account of partners
Answer:
Revaluation Account
Capital Account
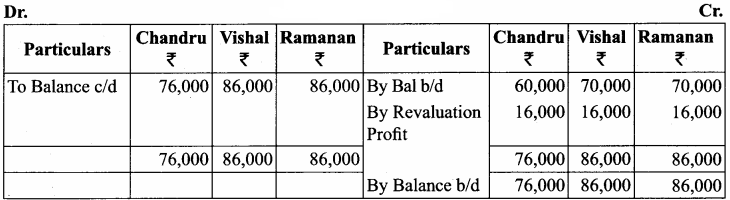
Question 7.
Kayal, Mala and Neela are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 2:2:1. Kayal retires and the new profit sharing ratio between Nila and Neela is 3:2. Calculate the gaining ratio.
Answer:
New Profit Sharing Ratio and Gaining Ratio
Gain Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio
Kayal –
Mala = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\) – \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\)
Neela = \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 5}\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\)
Gaining Ratio = 1:1
Question 8.
Sunil, Sumathi and Sundari are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3:3:4. Sundari retires and her share is taken up entirely by Sunil. Calculate the new profit sharing ratio and gaining ratio.
Answer:
New Ratio – Old Ratio
Sunil = \(\frac { 3 }{ 10 }\) + \(\frac { 4 }{ 10 }\) = \(\frac { 7 }{ 10 }\)
(Sundari share is added with old ratio)
Sumathi = \(\frac { 3 }{ 10 }\)
New Ratio = 7 : 3
Sacrificing Ratio = 1:1
Question 9.
Ramu, Somu and Gopu are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3:5:7. Gopu retires and the share is purchased by Ramu and Somu in the ratio of 3:1. Find the new profit sharing ratio and gaining ratio.
Answer:
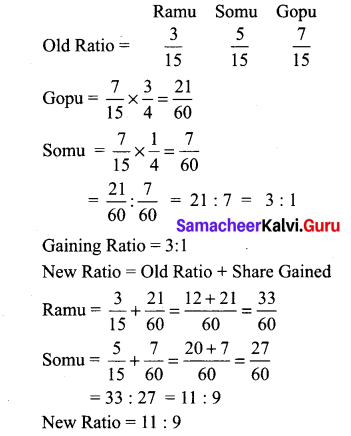
Question 10.
Navin, Ravi and Kumar are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 1/2,1/4 and 1/4 respectively, Kumar retires and his share is taken up by Navin and Ravi equally. Calculate the new profit sharing ratio and gaining ratio.
Answer:
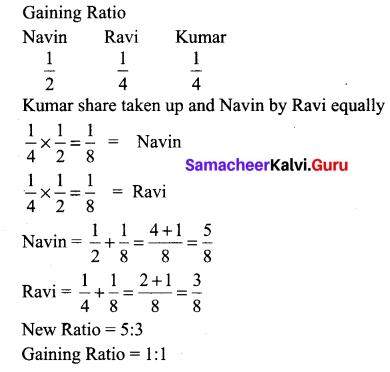
Question 11.
Mani, Gani and Soni are partners sharing the profits and losses in the ratio of 4:5:6. Mani retires from the firm. Calculate the new profit sharing ratio and gaining ratio.
Answer:
Since new profit sharing ratio, share gained and the proportion of share gained is not given, the new share is calculated by assuming that the share gained is in the proportion of old ratio.
Question 12.
Rajan, Suman and Jegan were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 4:3:2. Suman retired from partnership. The goodwill of the firm on the date of retirement was valued at ₹ 45,000. Pass necessary journal entries for goodwill on the assumption that the fluctuating capital method is followed.
Answer:
Value of Goodwill = 45,000 x \(\frac { 3 }{ 9 }\) = 15,000
Journal Entries
Adjustment for goodwill

Question 13.
Balu, Chandru and Nirmal are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 5:3:2. On 31st March 2018, Nirmal retires from the firm. On the date of Nirmal’s retirement, goodwill appeared in the books of the firm at ? 60,000. By assuming fluctuating capital account, pass the necessary journal entry if the partners decide to
(a) write off the entire amount of existing goodwill
(b) write off half of the existing goodwill.
Answer:
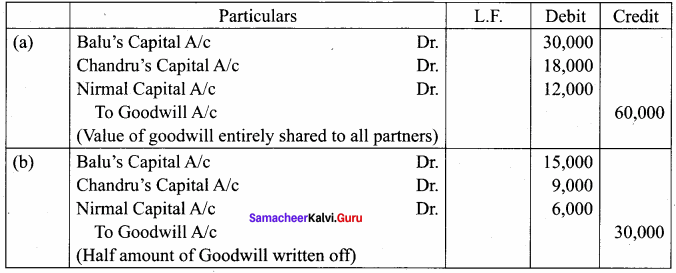
Question 14.
Rani, Jaya and Rathi are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2:2:1. On 31.3.2018, Rathi retired from the partnership. Profit of the preceding years is as follows: 2014: 10,000; 2015: ₹ 20,000; 2016: ₹ 18,000 and 2017: ₹ 32,000
Find out the share of profit of Rathi for the year 2018 till the date of retirement if
(a) Profit is to be distributed on the basis of the previous year’s profit
(b) Profit is to be distributed on the basis of the average profit of the past 4 years Also pass necessary journal entries by assuming partners capitals are fluctuating.
Answer:
(a) If the profit is to be distributed on the basis of previous year profit (2017) Rathi’s share distributed 3 months = ₹ 32,000 x \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) x \(\frac { 3 }{ 12 }\) = ₹ 1600

(b) Average Profit
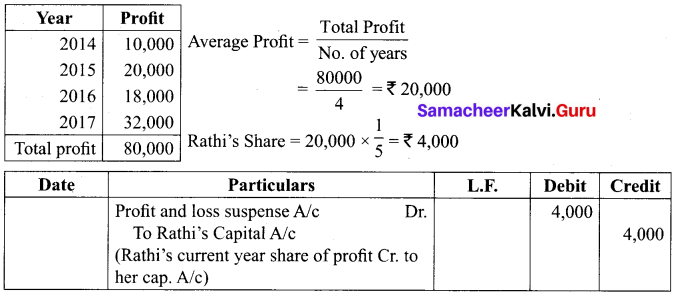
Question 15.
Kavin, Madhan and Ranjith are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 4:3:3, respectively. Kavin retires from the firm on 31st December, 2018. On the date of retirement, his capital account shows a credit balance of ₹ 1,50,000. Pass journal entries if:
(a) The amount due is paid off immediately.
(b) The amount due is not paid immediately.
(c) ₹ 1,00,000 is paid and the balance in future.
Answer:
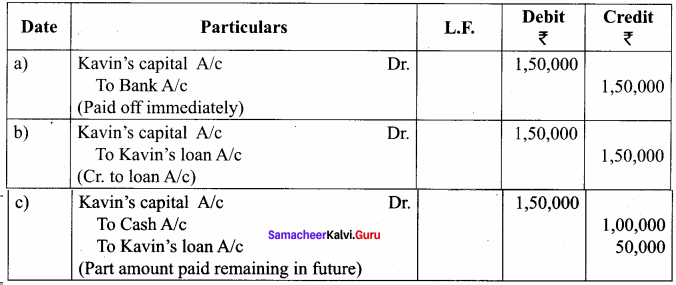
Question 16.
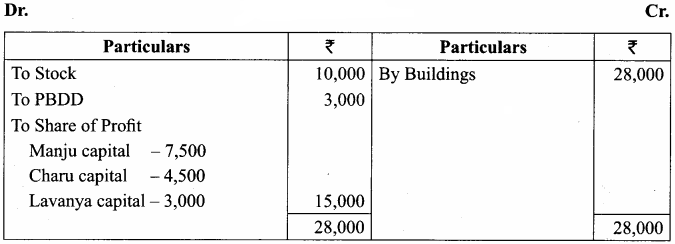
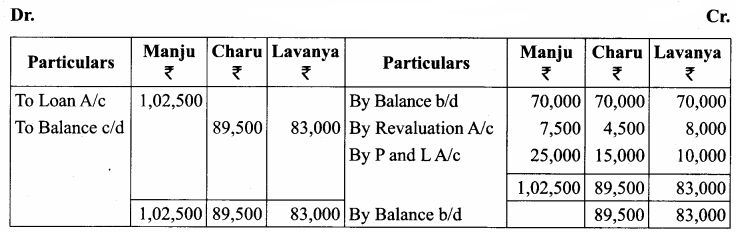
Manju, Charu and Lavanya are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 5:3:2. Their balance sheet as on 31st March, 2018 is as follows:
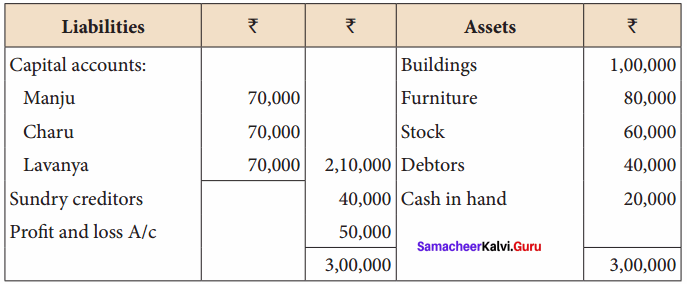
Manju retired from the partnership firm on 31.03.2018 subject to the following adjustments:
(i) Stock to be depreciated by ₹ 10,000
(ii) Provision for doubtful debts to be created for ₹ 3,000.
(iii) Buildings to be appreciated by ₹ 28,000
Prepare revaluation account and capital accounts of partners after retirement.
Answer:
Revaluation
Capital Account
Question 17.
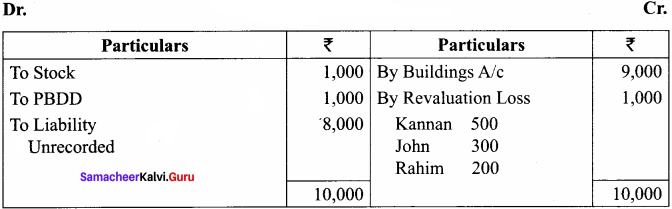
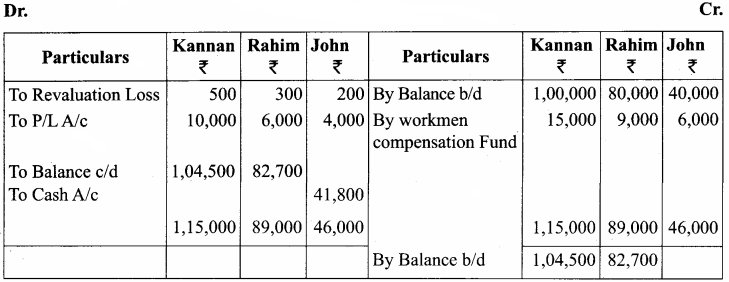
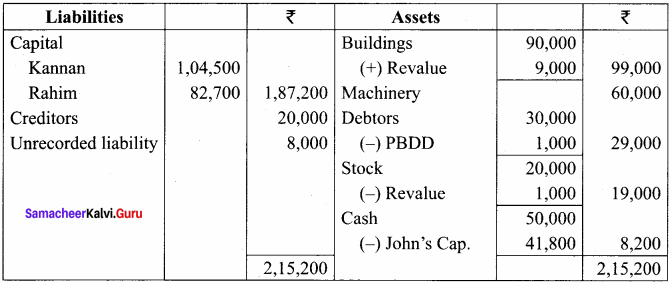
Kannan, Rahim and John are partners in a firm sharing profit and losses in the ratio of 5:3:2. The balance sheet as on 31st December, 2017 was as follows:
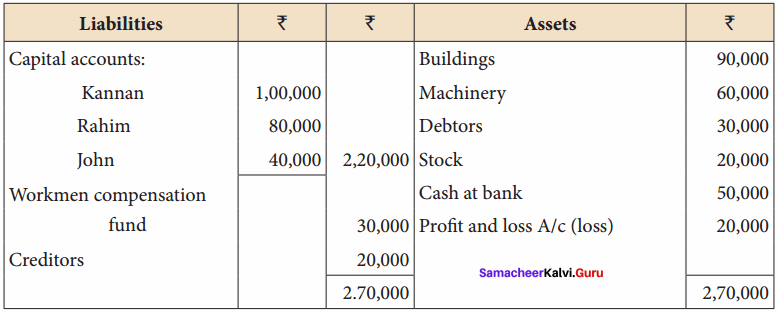
John retires on 1st January 2018, subject to the following conditions:
(i) To appreciate building by 10%
(ii) Stock to be depreciated by 5%
(iii) To provide ₹ 1,000 for bad debts
(iv) An unrecorded liability of ₹ 8,000 have been noticed
(v) The retiring partner shall be paid immediately
Prepare revaluation account, partners’ capital account and the balance sheet of the firm after retirement.
Answer:
Revaluation A/c
Capital
Balance Sheet
Question 18.
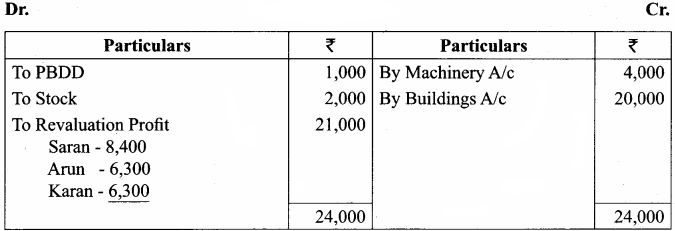
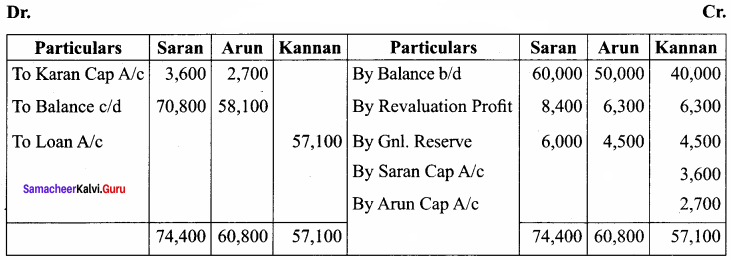
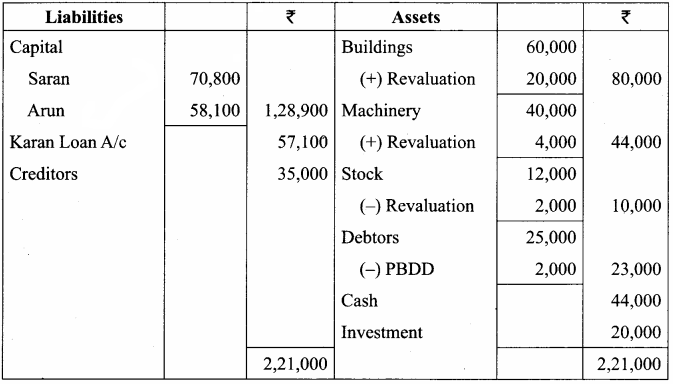
Saran, Arun and Karan are partners in firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 4:3:3. Their balance sheet as of 31.12.2016 was as follows:
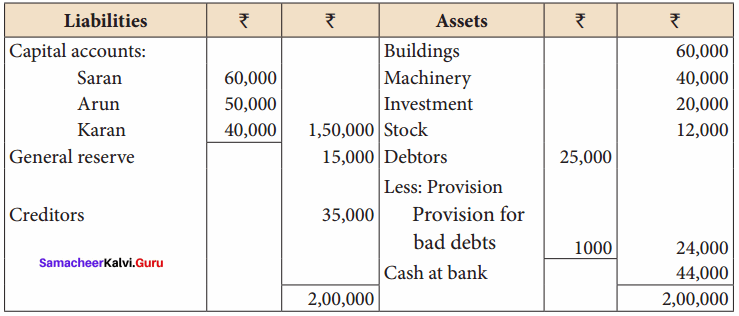
Karan retires on 1.1.2017 subject to the following conditions:
(i) Goodwill of the firm is valued at ₹ 21,000
(ii) Machinery to be appreciated by 10%
(iii) Building to be valued at ₹ 80,000
(iv) Provision for bad debts to be raised to ₹ 2,000
(v) Stock to be depreciated by ₹ 2,000
(vi) Final amount due to Karan is not paid immediately
Prepare the necessary ledger accounts and show the balance sheet of the firm after retirement.
Answer:
Revaluation Account
Capital Account
Balance Sheet
Question 19.
Rajesh, Sathish and Mathan are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2:1 respectively. Their balance sheet as on 31.3.2017 is given below.
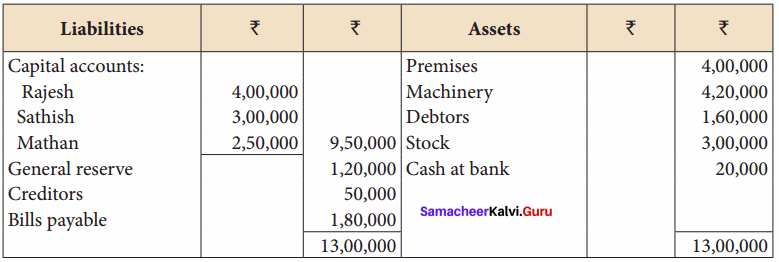
Mathan retires on 31st March, 2017 subject to the following conditions:
(i) Rajesh and Sathish will share profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2
(ii) Assets are to be revalued as follows: Machinery ₹ 4,50,000, Stock ₹ 2,90,000, Debtors ₹ 1,52,000.
(iii) Goodwill of the firm is valued at ₹ 1,20,000
Prepare necessary ledger accounts and the balance sheet immediately after the retirement of Mathan.
Answer:
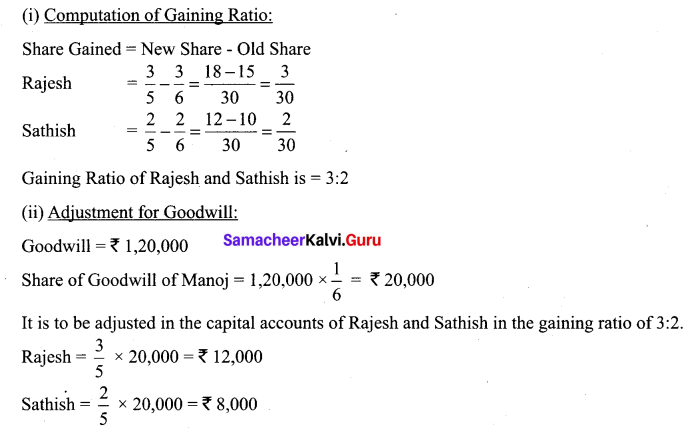
Revaluation Account
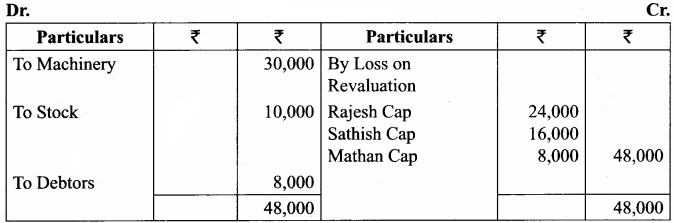
Capital Account
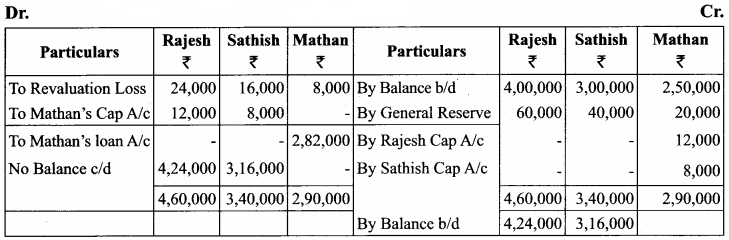
Balance Sheet as on 31.12.2017
Question 20.
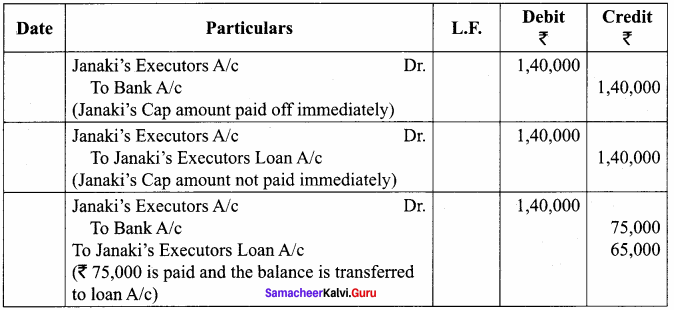
Janani, Janaki and Jamuna are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:3:1 respectively. Janaki died on 31st December, 2017. Final amount due to her showed a credit balance of ₹ 1,40,000. Pass journal entries if,
(a) The amount due is paid off immediately.
(b) The amount due is not paid immediately.
(c) ₹ 75,000 is paid and the balance in future.
Answer:
Journal Entries
Question 21.
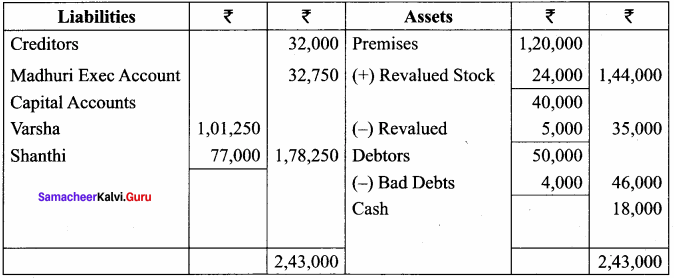
Varsha, Shanthi and Madhuri are partners, sharing profits in the ratio of 5:4:3. Their balance sheet as on 31st December 2017 is as under:
Balance Sheet as on 31st December 2017
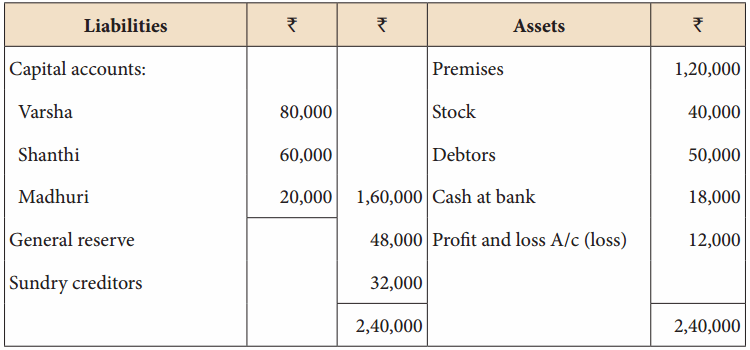
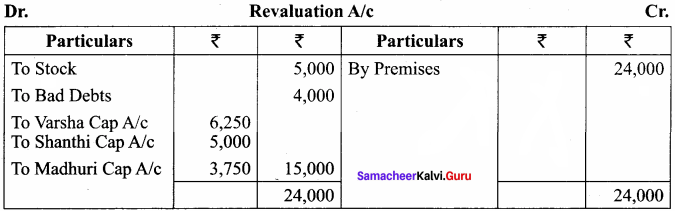
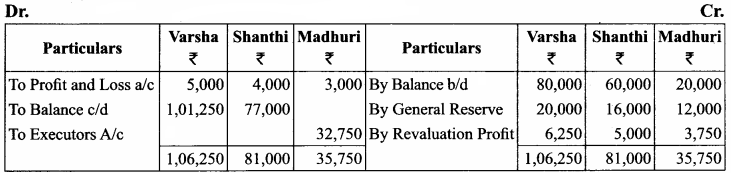
On 1.1.2018, Madhuri died and on her death the following arrangements are made:
(i) Stock to be depreciated by ₹ 5,000
(ii) Premises is to be appreciated by 20%
(iii) To provide ₹ 4,000 for bad debts
(iv) The final amount due to Madhuri was not paid
Prepare revaluation account, partners’ capital account and the balance sheet of the firm after death.
Answer:
Revaluation Account
Capital Account
Balance Sheet as on 1.1.2018
Question 22.
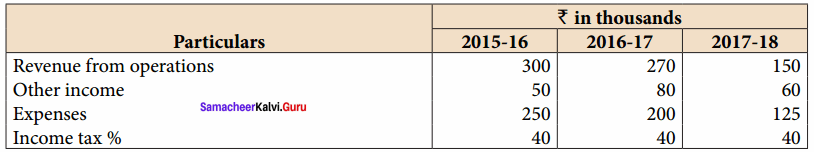
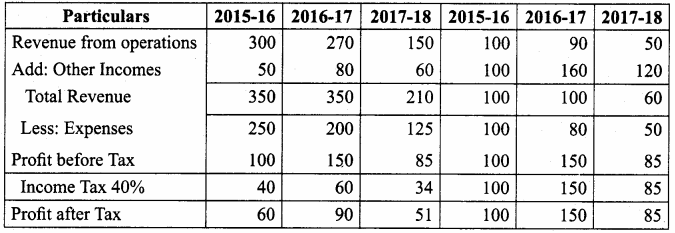
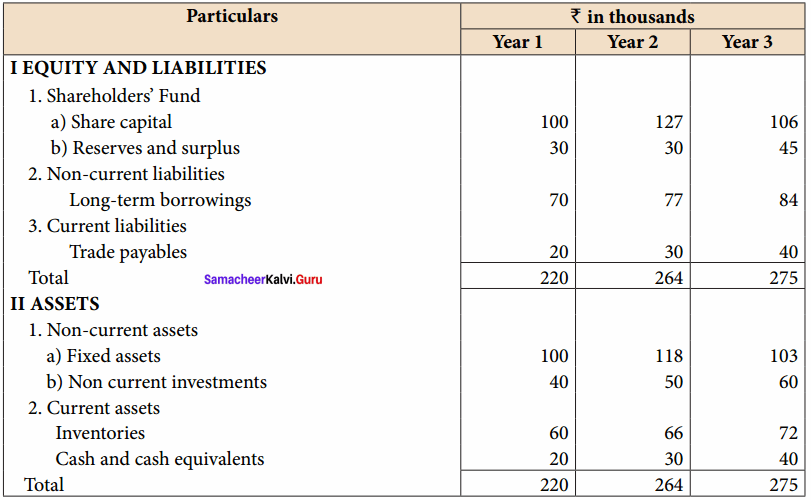
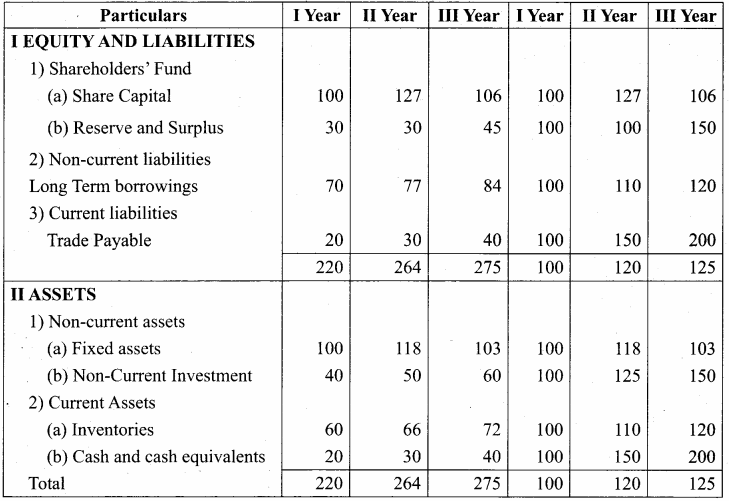
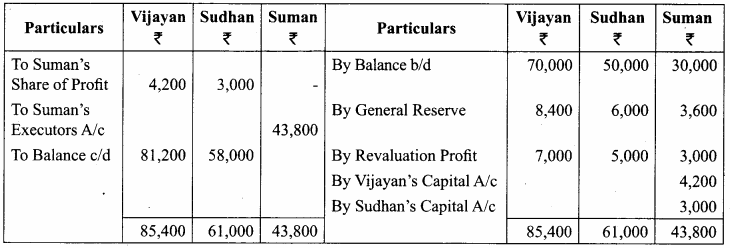
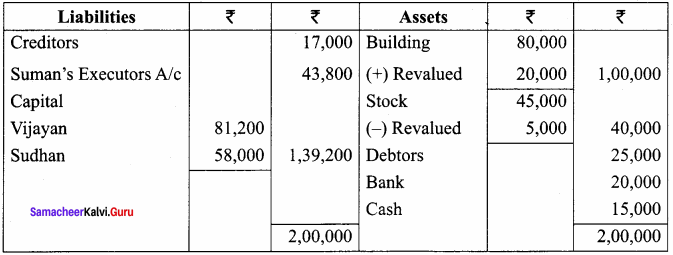
Vijayan, Sudhan and Suman are partners who share profits and losses in their capital ratio. Their balance sheet as on 31.12.2018 is as follows:
Balance Sheet as on 31.12.2018
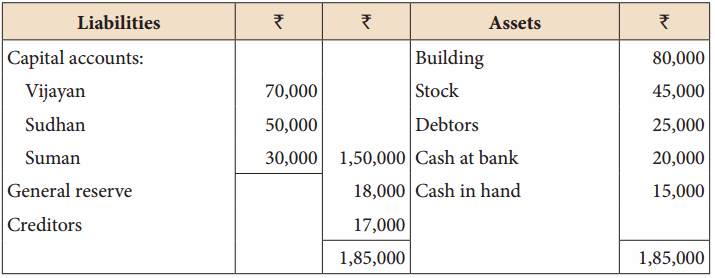
Suman died on 31.3.2019. On the death of Suman, the following adjustments are made:
(i) Building is to be valued at ₹ 1,00,000
(ii) Stock to be depreciated by ₹ 5,000
(iii) Goodwill of the firm is valued at ₹ 36,000
(iv) Share of profit from the closing of the last financial year to the date of death on the basis of the average of the three completed years’ profit before death.
Profit for 2016, 2017 and 2018 were ₹ 40,000, ₹ 50,000 and ₹ 30,000, respectively.
Prepare the necessary ledger accounts and the balance sheet immediately after the death of Suman.
Answer:
Profit-Sharing Ratio:
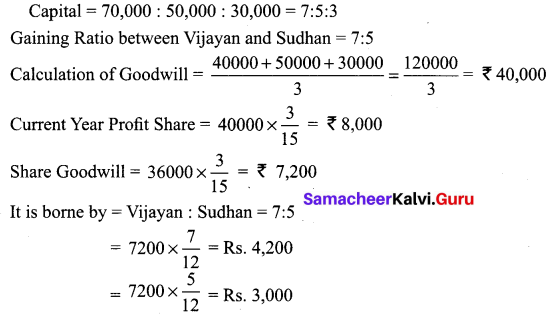
Revaluation Account
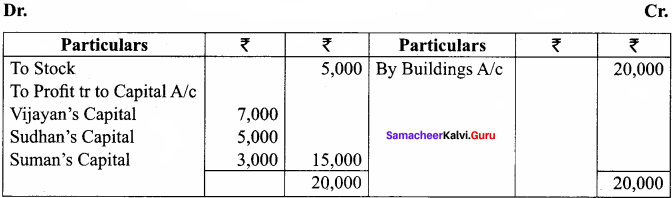
Capital Account
Balance Sheet as on 31.3.19
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Retirement and Death of a Partner Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
On the retirement of a partner, profit on revaluation of assets and liabilities should be credited to the capital accounts of …………………
(a) Retiring partner in their old ratio
(b) All partners in their old ratio
(c) Remaining partners in new ratio
(d) Remaining partners in old ratio
Answer:
(b) All partners in their old ratio
Question 2.
On the retirement of a partner, reserves should be transferred to the capital accounts of …………………
(a) Retiring partner
(b) Remaining partner
(c) All partners
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) All partners
Question 3.
Credit balance of Profit and Loss Account – appearing in the Balance sheet on the dealth of a partner is credited to …………………
(a) Deceased Partner’s Capital Account
(b) All partner’s capital account (including deceased partner’s capital account
(c) Remaining partner’s capital account
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) All partner’s capital account (including deceased partner’s capital account)
Question 4.
P, Q and R are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 4:3:1. P retires and his share is taken by Q and R equally. Calculate new profit sharing ratio of Q and R …………………
(a) 1:1
(b) 4:3
(c) 3:4
(d) 5:3
Answer:
(d) 5:3
Question 5.
In case of death of a partner, the whole amount standing to the credit of his capital account is transferred to ………………….
(a) Capital Accounts of all partners
(b) Capital Accounts of remaining partners
(c) His executor’s account
(d) Revenue Account of the Government
Answer:
(c) His executor’s account
Question 6.
A, B and C share profits in the ratio of \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\): \(\frac { 3 }{ 10 }\): \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) C dies. The gaining ratio of A and B will be …………………..
(a) 1:1
(b) 1:3
(c) 5:3
(d) 3:1
Answer:
(c) 5:3
Question 7.
On retirement of a partner, the continuing partner’s capital accounts are debited with retiring partner’s share of goodwill in
(a) Old profit sharing ratio
(b) Gaining ratio
(c) New profit sharing ratio
(d) Equal ratio
Answer:
(b) Gaining ratio
Question 8.
N, S, and K have been sharing profit in the ratio of 3:5:7. K retires and his share is taken by N and S in the ratio of 3:2, the new ratio will be
(a) 12:13
(b) 3:5
(c) 2:1
(d) 3:2
Answer:
(a) 12:13
Question 9.
If at the time of retirement, there is some unrecorded liability, it will be …………………..
(a) Debited to Revaluation A/c
(b) Credited to Revaluation A/c
(c) Transferred to Old partners Capital A/Cs
(d) Transferred to All Partners Capital A/Cs
Answer:
(a) Debited to Revaluation A/c
Question 10.
The gain of remaining partners is equal to ………………….
(a) Their new share
(b) Their old share
(c) New Share – Old share
(d) Old share – New share
Answer:
(c) New Share – Old share
Question 11.
Which of the following is debited to partner’s capital at the time of retirement of a partner?
(a) General Reserve
(b) Profit on revaluation
(c) Accumulated losses
(d) Accumulated profits
Answer:
(c) Accumulated losses
Question 12.
At the time of retirement, of a partner, workmen compensation reserve after meeting the legal requirement is transferred to
(a) Revaluation Account
(b) All Partner’s Capital Account .
(c) Sacrificing Partner’s Capital A/cs
(d) Old Partner’s Capital Account
Answer:
(b) All Partner’s Capital Account
Question 13.
On the retirement of a partner, increase in the value of assets is recorded in ………………..
(a) Revaluation A/c
(b) Cash a/c
(c) Old Partner’s Capital A/c
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Revaluation A/c
Question 14.
Undistributed profit and losses – transferred to all the partners at the time of retirement of a partner ………………….
(a) should be
(A) should not be
(c) maybe
Answer:
(a) should be