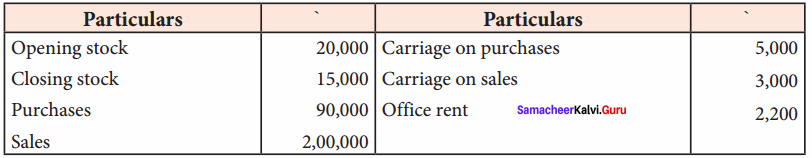
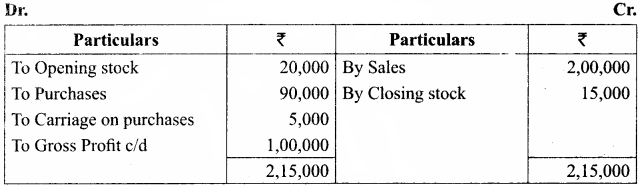
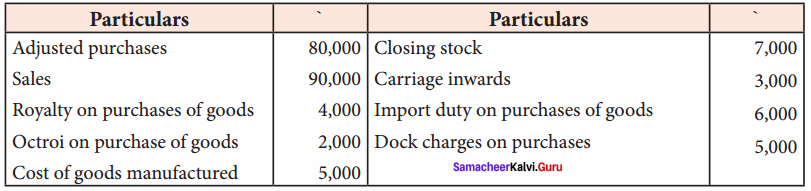
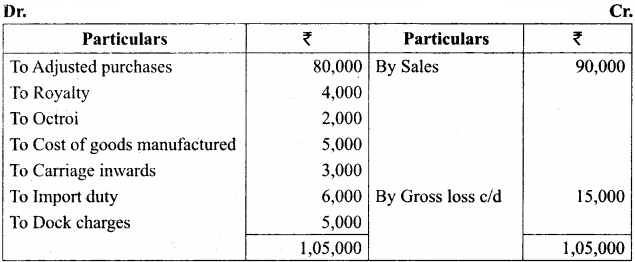
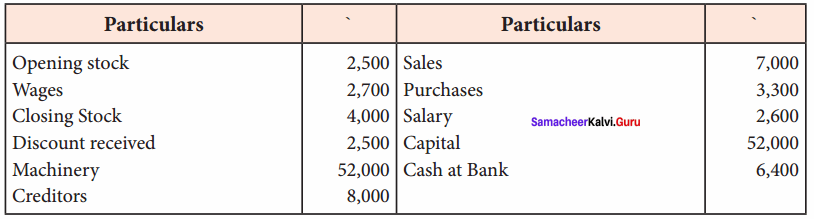
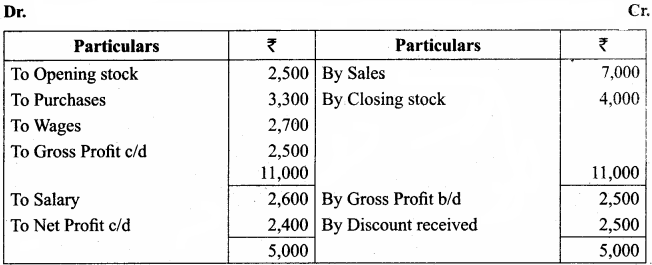
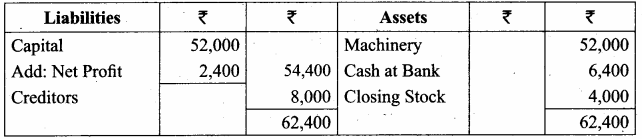
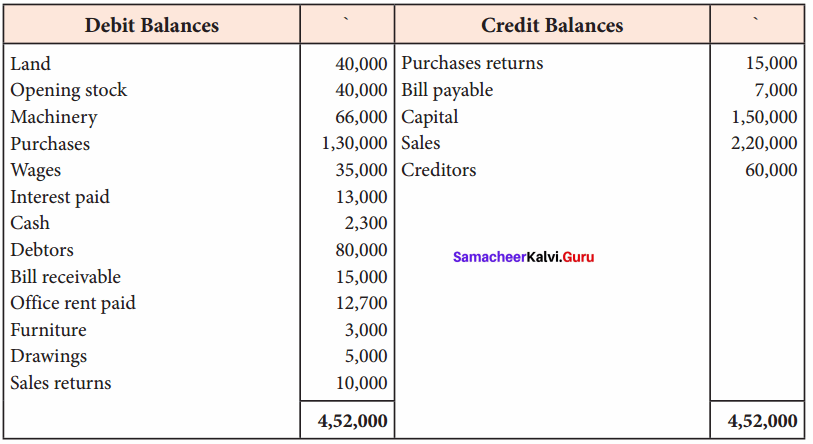
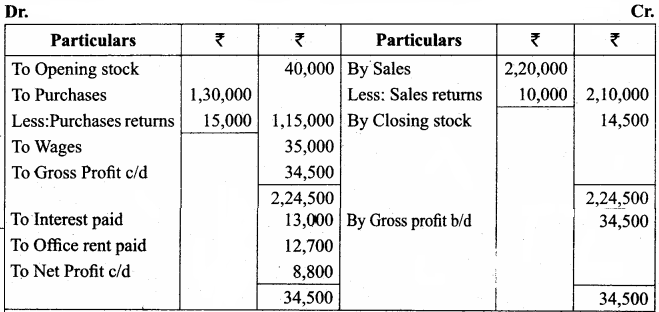
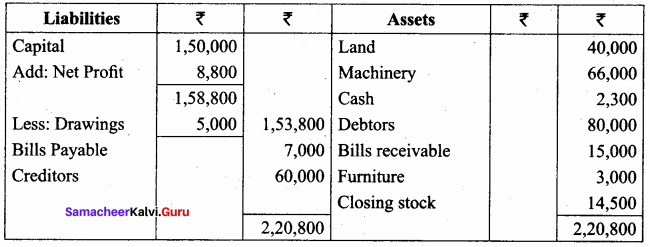
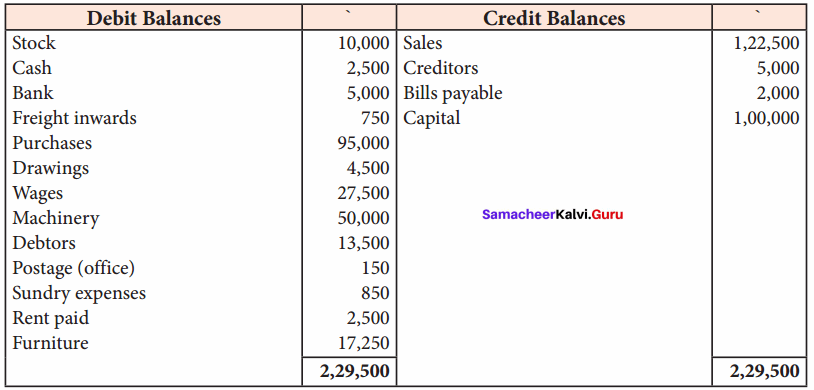
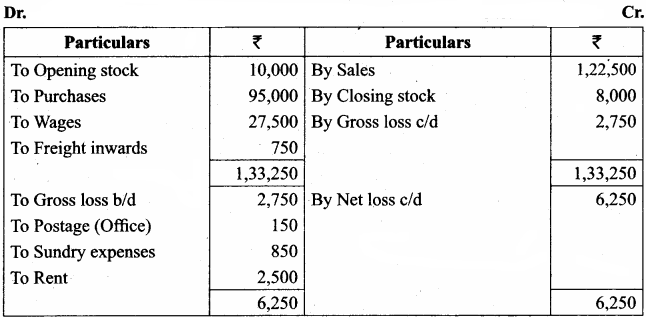
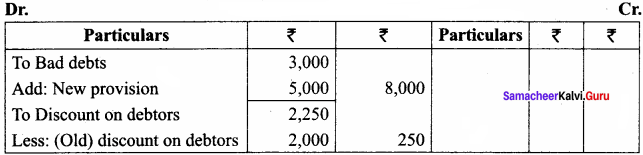
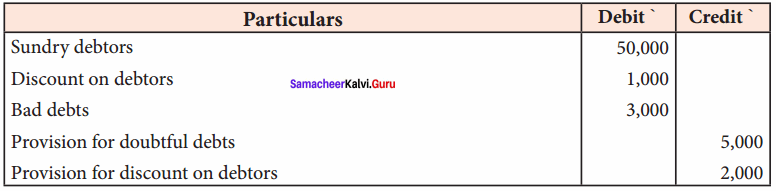
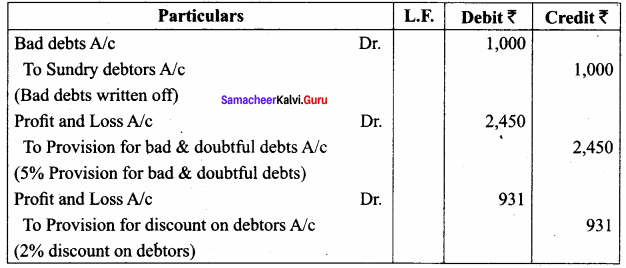
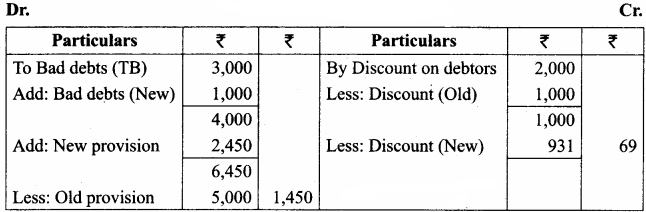
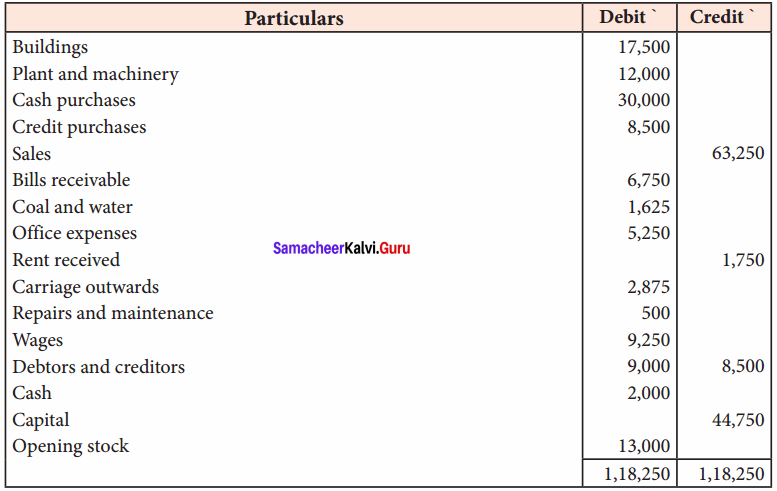
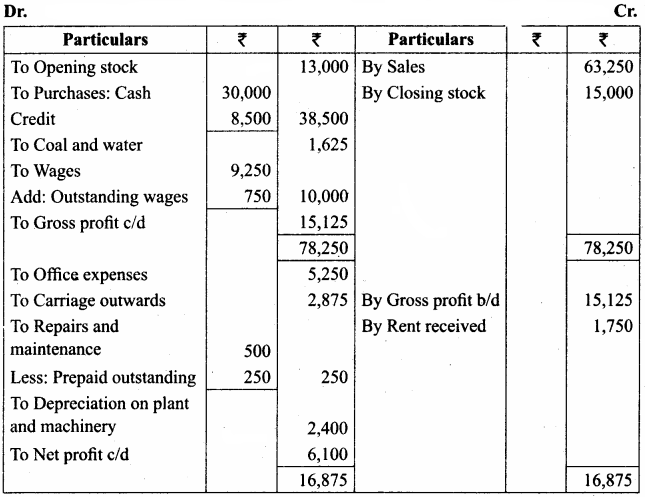
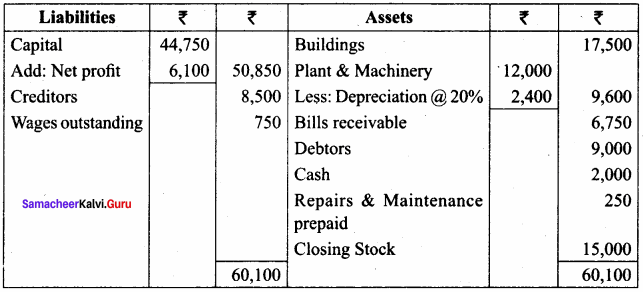
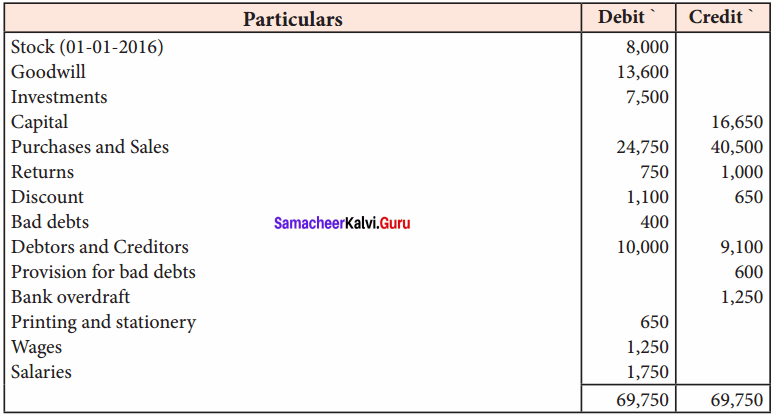
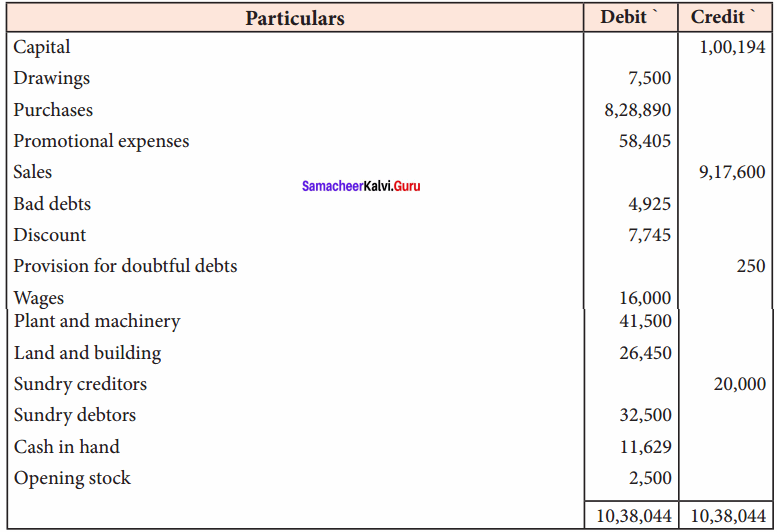
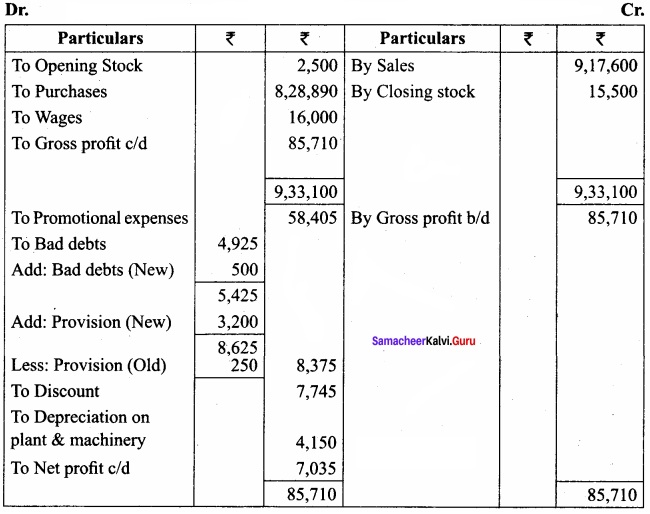
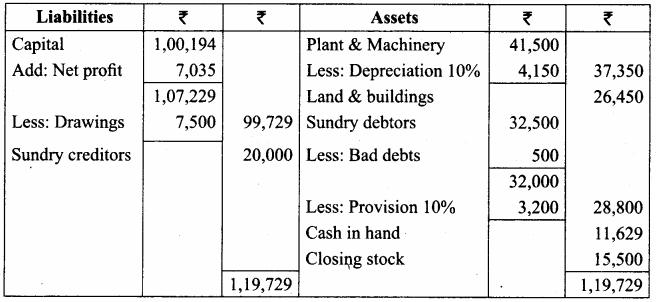
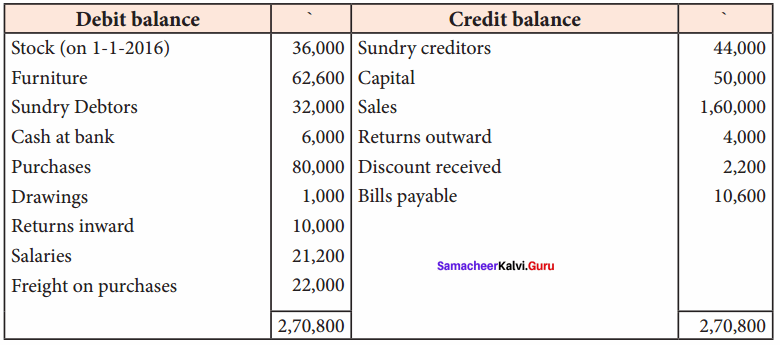
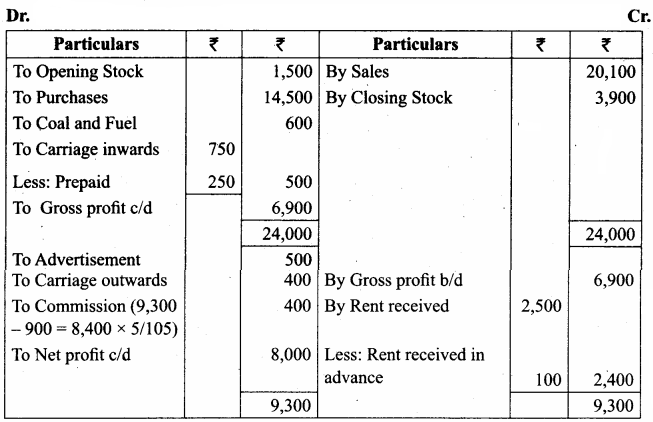
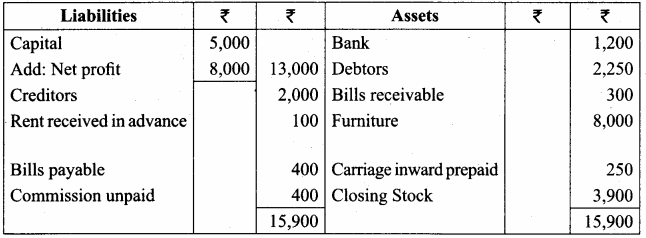
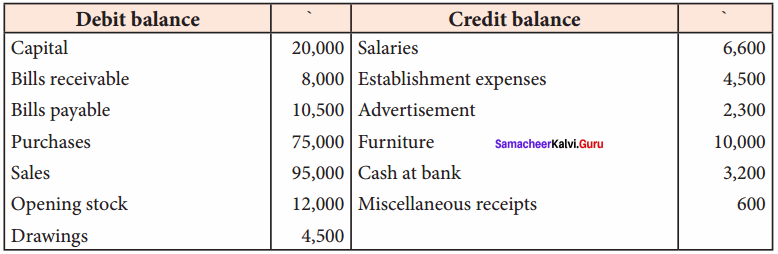
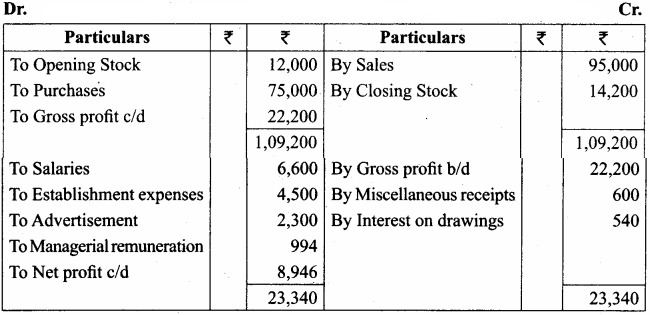
Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Economics Model Question Paper 1 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Economics Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 11th Economics Model Question Paper 1 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- questions of Part I, II. III and IV are to be attempted separately
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are objective type questions of one -mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer
- Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Parr III are three-marks questions, These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-marks questions. These are to be answered) in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
Part – I
Choose the correct answer. Answer all the questions: [20 × 1 = 20]
Question 1.
The shape of the indifference curve is …………..
(a) Price line
(b) Budget line
(c) ISO – cost line
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
![]()
Question 2.
The basic problem studied in Economics is ……………
(a) Unlimited wants
(b) Unlimited means
(c) Scarcity
(d) Strategy to meet all our wants
Answer:
(c) Scarcity
Question 3.
The man – made physical goods used to produce other goods and services are referred to as …………….
(a) Land
(b) Labour
(c) Capital
(d) Organisation
Answer:
(c) Capital
Question 4.
Identify the advantages of rural roads
(a) rural marketing
(b) rural employment
(c) rural development
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 5.
In monopoly, MR curve lies below ……………
(a) TR
(b) MC
(c) AR
(d) AC
Answer:
(c) AR
Question 6.
The concept of elasticity of demand was introduced by……………..
(a) Ferguson
(b) Keynes
(c) Adam Smith
(d) Marshall
Answer:
(d) Marshall
![]()
Question 7.
The Secondary factors are……………..
(a) Capital
(b) Organisation
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Labour
Answer:
(a) Capital
Question 8.
When marginal utility reaches zero, the total utility will be ………….
(a) minimum
(b) maximum
(c) zero
(d) negative
Answer:
(b) maximum
Question 9.
Author of “An inquiry into the Nature and causes of wealth of Nations”.
(a) Alfred Marshall
(b) Adam Smith
(c) Lionel Robbins
(d) Paul A Samuelson
Answer:
(b) Adam Smith
Question 10.
In investment proposals filed by MSMEs, TN ranks ………………
(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
Answer:
(a) I
Question 11.
Identify the formula of estimating average cost.
(a) AVC/Q
(b) TC/Q
(c) TVC/Q
(d) AFC/Q
Answer:
(b) TC/Q
Question 12.
The Goods and Services Tax came into effect on
(a) 1st July 2017
(b) 1st July 2016
(c) 1st January 2017
(d) 1st January 2016
Answer:
(a) 1st July 2017
![]()
Question 13.
Pick the odd one out:
(a) Luxuries
(b) Comforts
(c) Necessaries
(d) Agriculture goods
Answer:
(d) Agriculture goods
Question 14.
The concept of consumer’s surplus is associated with ………..
(a) Adam Smith
(b) Marshall
(c) Robbins
(d) Ricardo
Answer:
(b) Marshall
Question 15.
Who has given scarcity definition of economics?
(a) Adam Smith
(b) Alfred Marshall
(c) Robbins
(d) Robertson
Answer:
(c) Robbins
Question 16.
Saved amount is called …………..
(a) Capital
(b) Income
(c) Production
(d) Output
Answer:
(a) Capital
Question 17.
Which theory is generally included under micro economics?
(a) Price theory
(b) Income theory
(c) Employment theory
(d) Trade theory
Answer:
(a) Price theory
Question 18.
Expansion of FDI
(a) Foreign Private Investment
(b) Foreign Port folio Investment
(c) Foreign Direct Investment
(d) Forex Private Investment
Answer:
(c) Foreign Direct Investment
Question 19.
Marginal Utility is measured by using the formula of
(a) TUn – TUn-1
(b) TUn – TUn+1
(c) TUn + TUn+1
(d) TUn – TUn+1
Answer:
(a) TUn – TUn-1
Question 20.
The indifference curve are
(a) vertical
(b) horizontal
(c) positive sloped
(d) Negatively sloped
Answer:
(d) Negatively sloped
![]()
Part-II
Answer any seven question in which Question No. 30 is compulsory. [7 × 2 = 14]
Question 21.
Mention any two types of price discrimination?
Answer:
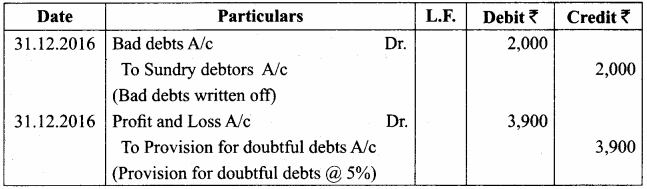
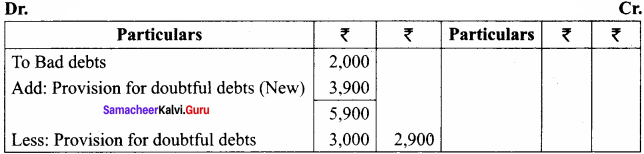
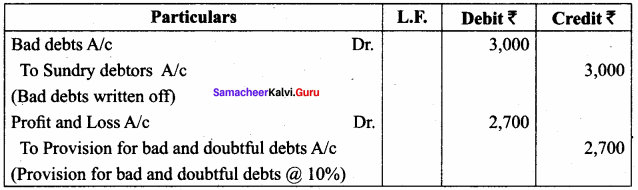
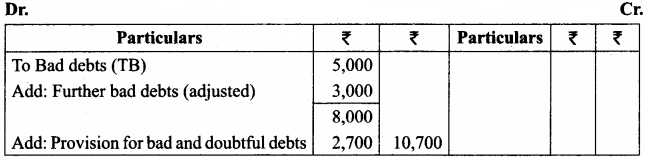
- Personal: Different prices are charged for different individuals. For example, the railways give tickets at concessional rate to the ‘Senior citizens’ for the same journey.
- Geographical: Different prices are charged at different places for the same product. For example, a book sold within India at a price is sold in a foreign country at lower price.
Question 22.
Distinguish between real and money wages.
Answer:
Money Wages :
- Money wages are referred to the wages paid in terms of money.
- Depend upon the standard of living workers in a country.
Real Wages :
- Real wages are the wages paid in terms of goods and services.
- Depend upon the purchasing power of money.
Question 23.
Mention the classification of wants.
Answer:
Wants are broadly classified into three categories.
- Necessaries: Goods which are indispensable for the human beings to exist in the world are called “Necessaries”. For example, food, clothing and shelter.
- Comforts: Goods which are not indispensable for life but to make our life easy, convenient and comfortable are called “Comforts”. Ex: TV, Fan, Refrigerator and Air conditioner.
- Luxuries: Goods which are not very essential but are very costly are known as “Luxuries”. ( Ex: Jewellery, Diamonds and Cars. However, for people with higher income they may look necessaries or comforts.
Question 24.
What are the degrees of price elasticity of demand?
Answer:
The price elasticity of demand, commonly known as the elasticity of demand refers to the responsiveness and sensitiveness of demand for a product to the changes in its price. In other words, the price elasticity of demand is equal to
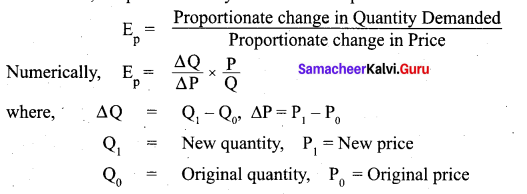
Question 25.
State any two features of developed economy.
Answer:
- High National Income
- High Per Capita Income
Question 26.
Define Utility.
Answer:
- Utility is the capacity of a commodity to satisfy human wants.
- Utility cannot be cardinally measured, but can be ranked or compared or ordered by ordinal number such as I, II, III and so on.
![]()
Question 27.
Name the basic approaches to consumer behaviour.
Answer:
There are two basic approaches, namely:
1. Utility approach
- The utility approach involves the use of measurable (cardinal) utility to study consumer behaviour.
- Marshall is the chief exponent of the utility approach to the theory of demand. It is known cardinal utility analysis or Marginal utility analysis or marshallian utility analysis.
2. Indifference curve approach
The indifference curve approach was the idea of comparable utility [ordinal utility] J.R. Hicks and R.G.D. Allen introduced the indifference curve approach.
Question 28.
What are the conditions for produces’s equilibrium?
Answer:
- Producer equilibrium implies the situation where producer maximizes his output.
- It is also known as optimum combination of the factors of production.
- In short, the producer manufactures a given amount of output with ‘ least cost combination of factors’, with his given budget.
Question 29.
State the meaning of liquidity preference.
Answer:
- Liquidity preference means the preference of the people to hold wealth in the form of liquid cash rather than in other non – liquid assets like bonds, securities, bills of exchange, land, building, gold etc.
- “Liquidity Preference is the preference to have an equal amount of cash rather than of claims against other”.
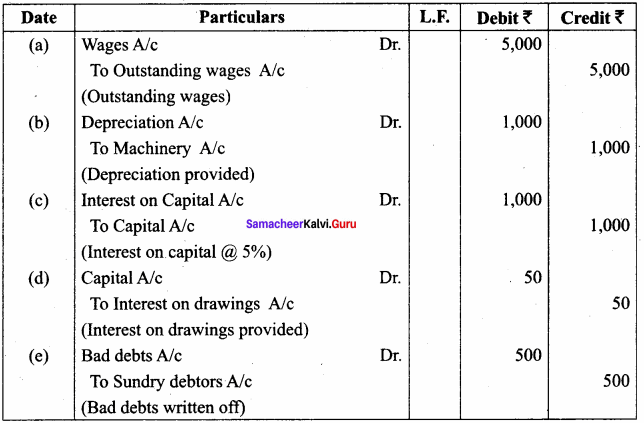
Question 30.
Explicit Cost- Define.
Answer:
Payment made to other for the purchase of factors of production is known as Explicit Costs. It refers to the actual expenditures of the firm to purchase or hire the inputs the firm needs.
![]()
Part – III
Answer any seven question in which Question No. 40 is compulsory. [7 × 3 = 21]
Question 31.
Explain the concept of consumer’s equilibrium with a diagram.
Answer:
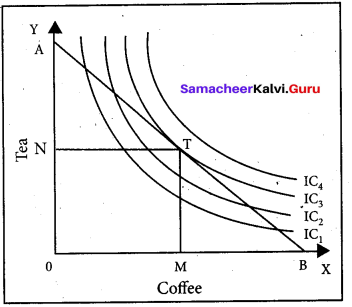
Consumer Equilibrium: The consumer reaches equilibrium at the point where the budget line is tangent on the indifference curve.
‘T’ is the point of equilibrium as budget line AB is tangent on indifference curve IC3 the upper most IC which implies maximum possible level of satisfaction.
At equilibrium point, the slope of IC refers to MRSxy and the slope of BL (Budget Line) refers to ratio of price of x to price of y.
i.e., \(\frac{P_{x}}{P_{y}}\) Therefore \(\mathrm{MRS}_{\mathrm{xy}}=\frac{\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{x}}}{\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{y}}} \)
Question 32.
Explain social infrastructure.
Answer:
- Social infrastructure refers to those structures which are improving the quality of manpower and contribute indirectly towards the growth of an economy.
- These structures are outside the system of production and distribution.
- The development of these social structures help in increasing the efficiency and productivity of manpower.
- For example, schools, colleges, hospitals and other civic amenities.
- It is a fact that one of the reasons for the low productivity of Indian workers is the lack of development of social infrastructure.
The status and developments in the social infrastructure in India are discussed below:
Education in India:
The India education system has flourished and developed with the growing needs of the economy.
Health in India:
- Health in India is a state government responsibility.
- The Central Council of Health and Welfare formulates the various health care projects and health department reform policies.
Question 33.
Write a short note on welfare economics given by Amartya Sen.
Answer:
- Amartya Kumar Sen has included the concept of entitlement items like nutrition, food, medical and health care, employment, security of food supply in times of famine etc.
- He considered famine as arising out of the failure of establishing a system of entitlements.
Question 34.
What are the characteristics of land?
Answer:
- Land is a primary factor of production
- Land is a passive factor of production
- Land is the free gift of nature
- Land has no cost of production
- Land is fixed in supply. It is inelastic in supply
- Land is permanent
- Land is immovable
- Land is heterogeneous as it differs in fertility
- Land has alternative uses
- Land is subject to Law of Diminishing Returns.
Question 35.
Briefly explain the concept of consumer’s equilibrium.
Answer:
The consumer reaches equilibrium at the point where the budget line is tangent on the indifference curve.
T is the point of equilibrium as budget line AB is tangent on indifference curve IC3 the upper IC which implies maximum possible level of satisfaction’.
At equilibrium point, the slope of IC refers to MRSXY and the slope of BL (Budget Line) refers to ratio of price of X to price of Y z.e. P x/ Py . Therefore MRSxy = Px / Py
Question 36.
The Handicrafts were declined in India in British period. Why?
Answer:
- The Indian handicrafts products had a worldwide market.
- Indian exports consisted chiefly of hand weaved cotton and silk fabrics, calicoes, artistic
wares, wood carving etc. , - Through discriminatory tariff policy, the British Government purposefully destroyed the
handicrafts. - With the disappearance of Nawabs and Kings. There was no one to protect Indian handicrafts.
- Indian handicraft products could not complete with machine – made products.
- The introduction of railways in India increased the domestic market for the British goods.
Question 37.
Elucidate the different types of land tenure system in colonial India.
Answer:
Land Tenure refers to the system of land ownership and management. The features that distinguish a land tenure system from the others relate to the following:
- Who owns the land.
- Who cultivates the land.
- Who is responsible for paying the land revenue to the government.
Based on these questions, three different types of land tenure existed in India before Independence. They were:
- Zamindari System or the Landlord – Tenant System.
- Mahalwari System or Communal System of Farming.
- Ryotwari System or the Owner Cultivator System.
Zamindari System or the Land lord Tenant System:
- Under this system the land lord or the Zamindars were declared as the owners of the land and they were responsible to pay the land revenue to the government.
- The share of the government in total rent collected was fixed as 10/11th the balance going to the
Zamindars as remuneration.
Mahalwari System or Communal System of Farming:
- After introduction of this system, it was later extended to Madhya Pradesh and Punjab.
- The ownership of the land was maintained by the collective body usually the villagers which served as a unit of management.
Ryotwari System (or) the Owner Cultivator System:
- This system was initially introduced in Tamil Nadu and later extended to Maharashtra,
- Gujarat, Assam, Coorg, East Punjab and Madhya Pradesh.
- Under this system the ownership rights of use and control of land were held by the tiller himself.\
![]()
Question 38.
State and explain the elasticity of supply.
Answer:
- Elasticity of supply may be defined as the degree of responsiveness of change in supply to change in price on the part of sellers.
- It is Mathematically expressed as,
Elasticity of supply = Proportionate change in supply / Proportionate change in price
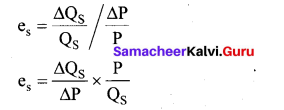
Where Qs represents the supply, P represents price , A denotes a change.
Question 39.
Write the strategy of Jawaharlal Nehru in India’s planning.
Answer:
- Jawaharlal Nehru was responsible for the introduction of planning in our country.
- To Jawaharlal Nehru, the Plan was essentially an integrated approach for development.
- Initiating the debate on the Second Plan in the Lok Sabha in May 1956, Nehru spoke on the theme of planning.
- Nehru Said “the essence of planning is to find the best way to utilize all resources of manpower, of money and so on”.
- Planning for Nehru was essentially linked up with industrialization and eventual self-reliance for the country’s economic growth on a self-accelerating growth.
- Nehru carried through this basic strategy of planned development.
Question 40.
What are the reasons for upward sloping supply curve?
Answer:
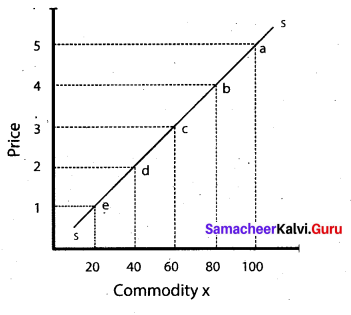
A supply curve represents the data given in the supply schedule. As the price of the commodity increases, the quantum supplied of the commodity also increases. Thus the supply curve has a positive slope from left to right.
The quantum supplied of commodity x is represented on X axis. And the price of the commodity is represented on the Y axis. The points such as e, d, c, b and a on the supply curve SS’, represent various quantities at different prices.
![]()
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [7 × 5 = 35]
Question 41.
(a) Discuss the short run cost curves with suitable diagram.
Short run Cost Curves:
Total Fixed Cost (TFC):
Answer:
All payments for the fixed factors of production are known as Total Fixed Cost. A hypothetical TFC is shown in below table and diagram .
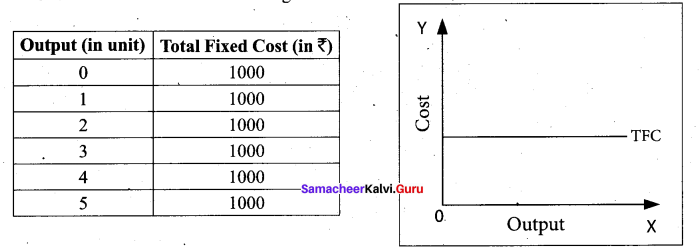
For instance if TC = Q3 – 18Q2 + 91Q + 12, the fixed cost here is 12. That means, if Q is zero, the Total cost will be 12, hence fixed cost.
It could be observed that TFC does not change with output. Even when the output is zero, the fixed cost is ₹ 1000. TFC is a horizontal straight line, parallel to X axis.
Total Variable Cost (TVC):
All payments to the variable factors of production is called as Total Variable Cost. Hypothetical TVC is shown in the below table and diagram.
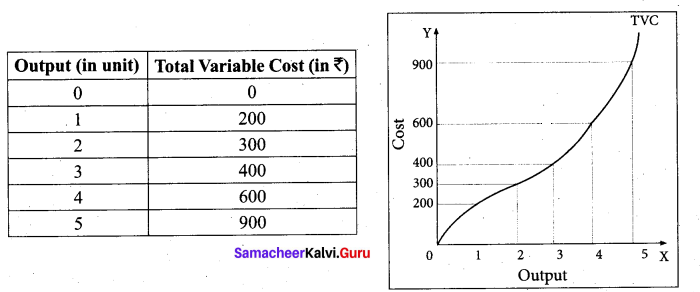
In the diagram the TVC is zero when nothing is produced. As output increases TVC also increases. TVC curve slopes upward from left to right.
For instance in TC = Q3 – 18 Q2 + 91 Q + 12, variable cost, TVC = Q3 – 18Q2 + 91Q
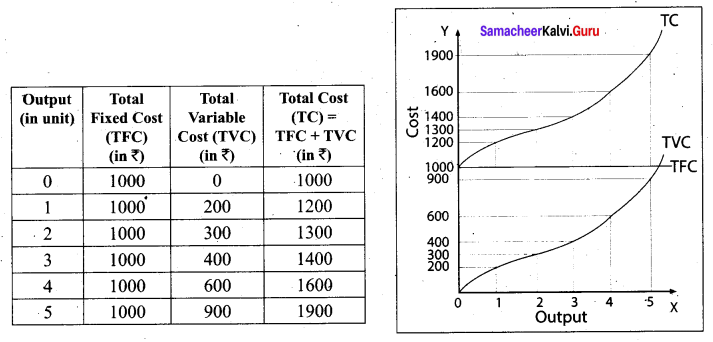
Total Cost Curves:
Total Cost means the sum total of all payments made in the production. It is also called as Total Cost of Production.
Total cost is the summation of Total Fixed Cost (TFC) and Total Variable Cost (TVC). It is written symbolically as
TC = TFC + TVC. For example, when the total fixed cost is ₹ 1000 and the total variable cost is ₹ 200 then the Total cost is = ₹ 1200 (₹1000 + ₹ 200).
If TFC = 12 and
TVC = Q3– 18 Q2 + 91 Q
TC = 12 + Q3 – 18 Q2 + 91 Q
Average Fixed Cost (AFC):
Average Fixed Cost refers to the fixed cost per unit of output. It is obtained by dividing the total fixed cost by the quantity of output. AFC = TFC / Q where, AFC denotes average fixed cost, TFC denotes total fixed cost and Q denotes quantity of output. For example, if TFC is 1000 and the quantity of output is 10, the AFC is ₹ 100, obtained by dividing ₹ 1000 by 10. TVC is shown in below table and diagram.
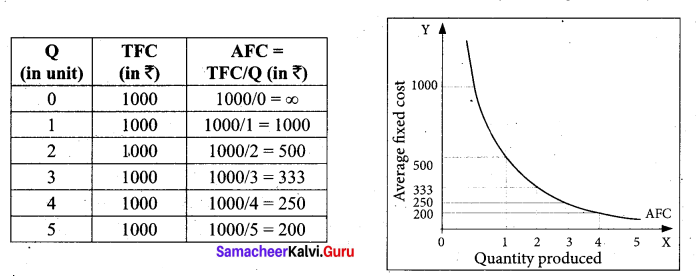
It is to be noted that
- AFC declines as output increases, as fixed cost remains constant.
- AFC cuiwe is a downward sloping throughout its length, never touching X and Y axis. It is asymptotic to both the axes.
- The shape of the AFC curve is a rectangular hyperbola.
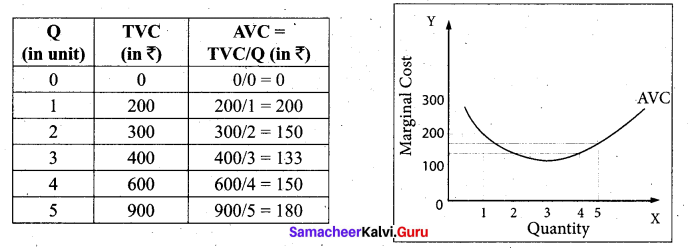
Average Variable Cost (AVC):
Average Variable Cost refers to the total variable cost per unit of output. It is obtained by dividing total variable cost (TVC) by the quantity of output (Q). AVC = TVC / Q where, AVC denotes Average Variable cost, TVC denotes total variable cost and Q denotes quantity of output. For example, When the TVC is ₹ 300 and the quantity produced is 2, the AVC is ₹ 150,
(AVC = 300/2 = 150) AVC is shown in the below table and diagram.
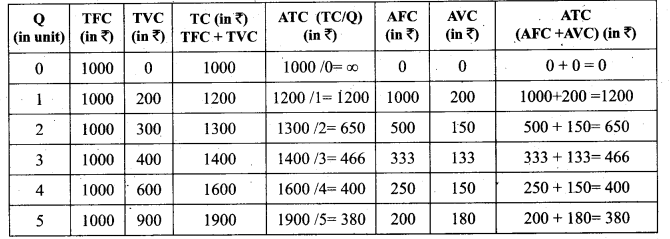
Average Total Cost (ATC) or Average Cost (AC):
Average Total Cost refers to the total cost per unit of output.
It can be obtained in two ways.
1. By dividing the firm’s total cost (TC).by the quantity of output (Q). ATC = TC / Q.
For example, if TC is ₹ 1600 and quantity of output is Q = 4, the Average Total Cost is ₹ 400. (ATC = 1600/4 = 400)
If ATC is Q3 – 18 Q3 + 91 Q + 12, then AC = Q2 – 18 Q +91 + 12/Q
2. By ATC is derived by adding together Average Fixed Cost (AFC) and Average Variable Cost (AVC) at each level of output. ATC = AFC + AVC:
For example, when Q = 2, TFC = 1000, TVC = 300; AFC = 500; AVC =150; ATC=650. ATC or AC is shown in the below table and diagram
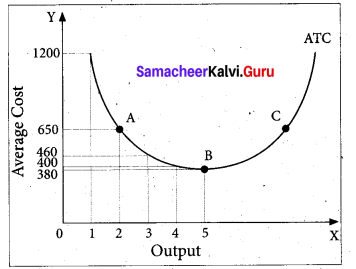
Marginal Cost (MC):
Marginal Cost is the cost of the last single unit produced. It is defined as the change in total costs resulting from producing one extra unit of output. In other words, it is the addition made to the total cost by producing one extra unit of output. Marginal cost is important for deciding whether any additional output can be produced or not. MC = ATC / AQ where MC denotes Marginal Cost, ATC denotes change in total cost and AQ denotes change in total quantity. For example, a firm produces 4 units of output and the Total cost is ₹ 1600. When the firm produces one more unit (4+1 = 5 units) of output at the total cost of ₹ 1900, the marginal cost is ₹ 300.
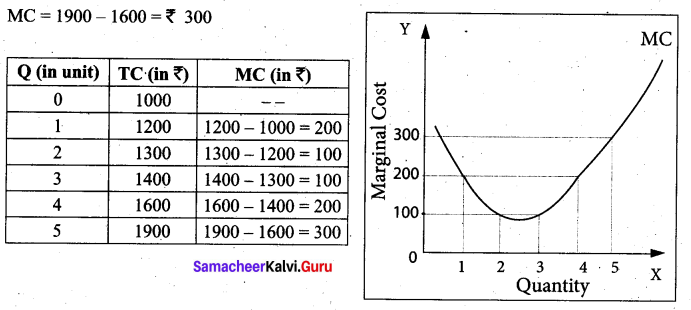
[OR]
(b) Bring out the features of perfect competition.
Answer:
(i) Large Number of Buyers and sellers
- “A large number of buyers” implies that each individual buyer buys a very very small quantum of a product as compared to that found in the market.
- This means that he has no power to fix the price of the product.
- He is only a price-taker and not a price-maker
- Large number of sellers” implies that share of each individual seller is a very very small quantum of a product.
- No power to fix the price of the product.
(ii) Homogeneous Product and Uniform Price
- The product sold and bought is homogeneous in nature, in the sense that the units of the product are perfectly substitutable.
- All the units of the product are identical i.e., of the same size, shape, colour, quality etc.
- Therefore, a uniform price prevails in the market.
(iii) Free Entry and Exit
- In the short run, it is possible for the very efficient producer, producing the product at a very low cost, to earn super normal profits.
- An inefficient producer, who is unable to bring down the cost incurs loss.
(iv) Absence of Transport Cost :
The prevalence of the uniform price is also due to the absence of the transport cost.
(v) Perfect Mobility of Factors of Production
- The prevalence of the uniform price is also due to the perfect mobility of the factors of production.
- As they enjoy perfect freedom to move from one place to another and from one occupation to another, the price gets adjusted.
(vi) Perfect Knowledge of the Market
All buyers and sellers have a thorough knowledge of the quality of the product, prevailing price etc.
(vii) No Government Intervention
There is no government regulation on supply of raw materials, and in the determination of price etc.
Question 42.
(a) Describe the features of oligopoly.
Answer:
Features of oligopoly:
- Few large firms: Veiy few big firms own the major control of the whole market by producing major portion of the market demand.
- Interdependence among firms: The price and quality decisions of a particular firm are dependent on the price and quality decisions of the rival firms.
- Group behaviour: The firms under oligopoly realise the importance of mutual . co-operation.
- Advertisement cost: The oligopolist could raise sales either by advertising or improving the quality of the product.
- Nature of product: Perfect oligopoly means homogeneous products and imperfect oligopoly deals with heterogeneous products.
- Price rigidity: It implies that prices are difficult to be changed. The oligopolistic firms do not change their prices due to the fear of rival’s reaction.
[OR]
(b) Discuss about the Indian Economy during British period.
Answer:
Indian Economy during the British period:
- India’s sea route trade to Europe started only after the arrival of Vasco da Gama in Calicut, India on May 20, 1498.
- The Portuguese had traded in Goa as early as 1510.
- In 1601 the East India Company was chartered, and the English began their first inroads into the Indian ocean.
- In 1614 Sir Thomas Roe was successful in getting permission from Jahangir for setting up factories and slowly moved all parts of India.
- Hundred years after Battle of Plassey, the rule of the East India Company finally did come
to an end. - In 1858, British Parliament passed a law through which the power for governance of India was transferred from the East India Company [EIC] to the British Crown.
- Even the transfer of power from the East India Company to the British Crown did not materially alter the situation.
- Britain had exploited India over a period of two centuries of its colonial rule.
On the basis of the form of colonial exploitation, economic historians have divided the whole period into three phases:
- The period of merchant Capital
- The period of Industrial Capital
- The period of Finance Capital
![]()
Question 43.
(a) What is GST? Write its advantages.
Answer:
- GST – Goods and Services Tax. GST is defined as the tax levied when a consumer buys a good or service.
- Removing cascading tax effect
- Single point tax
- Higher threshold for registration
- Composition scheme for small business
- Online simpler procedure under GST
- Defined treatment for e-commerce
- Increased efficiency in logistics
- Regulating the unorganized sector
[OR]
(b) What are the remedial measures for Rural unemployment?
Answer:
Remedial measures for Rural unemployment:
In order to reduce rural unemployment in the country there is a need to take integrated and coordinated efforts from various levels. A few remedial measures are listed below:
Subsidiary Occupation: To reduce the seasonal unemployment rural people should be encouraged to adopt subsidiary occupations. Loans should be granted and proper arrangements should be made for marketing their products.
Rural Works Programme: Rural Works Programme such as construction and maintenance of roads, digging of drains, canals etc., should be planned during off season to provide gainful employment to the unemployed.
Irrigation Facilities: Since rainfall is uncertain irrigation facilities should be expanded to enable the farmers to adopt multiple cropping.
Rural Industrialization: To provide employment new industries should be set up in rural areas. Technical Education: Employment oriented courses should be introduced in schools and colleges to enable the literate youth to start their own units.
Question 44.
(a) The demand function is given by x = 20 – 2p – p2 where p and x are the price and the quantity respectively. Find the elasticity of demand for p = 2.5.
Answer:
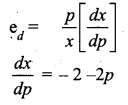
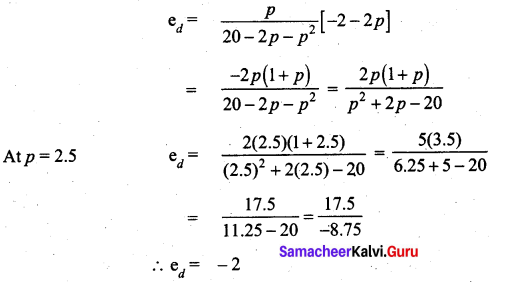
[OR]
(b) Solve for x quantity demanded if 16x – 4 = 68 + 7x.
Answer:
16x – 4 = 68 + 7x
16x – 7x = 68 + 4
9x = 72
x = 72/9
∴ x = 8
Question 45.
(a) Bring out Jawaharlal Nehru’s contribution to the idea of economic development.
Answer:
- Jawaharlal Nehru, one of the chief builders of Modem India, was the first Prime Minister of Independent India.
- He was a great patriot, thinker and statesman.
(i) Democracy and Secularism:
- Jawaharlal Nehru was a firm believer in democracy.
- He believed in free speech civil liberty, adult franchise and the Rule of Law and Parliamentary democracy.
- Secularism, is another signal contribution of Nehru to India.
(ii) Planning:
- Jawaharlal Nehru was responsible for the introduction of planning in our country.
- Jawaharlal Nehru, the Plan was essentially an integrated approach for development.
- Nehru Spoke on the theme of planning.
- He said “the essence of planning is to find the best way to utilize all resources of manpower, of money and so on”.
- “Planning for Nehru was essentially linked up with Industrialization and eventual self-reliance for the country’s economic growth on a self-accelerating growth.
- Nehru carried through this basis strategy of planned development.
- Nehru’s contribution to the advancement of science, research, technology and industrial development cannot be forgotten.
- It was during is period, many IITs and Research Institutions were established.
- Nehru always in insisted on “ scientific temper”.
[OR]
(b) – Describe the performance of 12 five year plans in India.
Answer:
Performance of Five Year Plans:
First Five Year Plan – [1951 -1956]
- It was based on the Harrod – Domar Model.
- Its main focus was on the agricultural development of the country. ,
- This plan was successful and achieved the GDP growth rate of 3.6%. [more than its target]
Second Five Year Plan – [1956 – 1961]
- It was based on the P.C. Mahalanobis Model.
- Its main focus was on the industrial development of the country.
- This plan was successful and achieved growth rate of 4.1%
Third Five Year Plan- [1961-1966].
- This plan was called ‘Gadgil Yojana’.
- The main target of this plan was to make the economy independent and to reach self propelled position or take off.
- Due to Indo – China war, this plan could not achieve its growth target of 5.6%.
Fourth Five Year Plan – [1969 -1974]
- There are two main objectives of this plan (i.e) growth with stability and progressive achievement of self reliance.
- This plan failed and could achieve growth rate of 3.3% only against the target of 5.7%.
Fifth Five Year Plan – [1974 1979]
- In this plan top priority was given to agriculture, next came industry and mines.
- This plan achieved the growth of 4.8% against the target of 4.4%.
Sixth Five Year Plan-[1980-1985]
- The basic objective of this plan was poverty eradication and technological self reliance.
- Its growth target was 5.2% but it achieved 5.7%
Seventh Five Year Plan – [1985 – 1990]
- This plan establishment of the self sufficient economy, opportunities for productive employment.
- Its growth target was 5.0% but it achieved 6.0%
Eighth Five Year Plan – [1992-1997]
- In this plan the top priority was given to development of the human resources (i.e) employment, education and public health.
- This plan was successful and got annual growth rate of 6.8%.
Ninth Five Year Plan-[1997-2002]
- The main focus of this plan was “growth with justice and equity”.
- This plan failed to achieve the growth target of 7% and Indian economy grew only at the rate of 5.6%.
Tenth Five Year Plan – [2002 – 2007]
- This plan aimed to double the per capita income of India in the next 10 years.
- It aimed to reduce the poverty ratio of 15%
- Its growth target was 8.0% but it achieved only 7.2%
Eleventh Five Year Plan – [2007 – 2012]
- Its main theme was “faster and more inclusive growth”.
- Its growth rate target was 8.1% but it achieved only 7.9%
Twelfth Five Year Plan – [2012 – 2017]
- Its main theme is “faster, more inclusive and sustainable growth”.
- Its growth rate target is 8%
- Since the Indian Independence the five year plans of India played a very prominent role in the economic development of the country.
![]()
Question 46.
(a) If TC = 2.5q3 – 13q2 + 50q + 12 derive the MC function and AC function.
Answer:
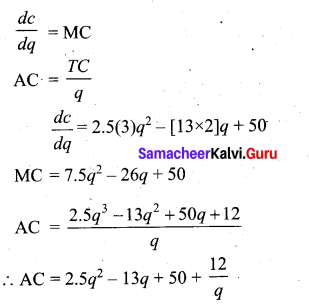
[OR]
(b) What are the ideas of information and communication technology used in Economics?
Answer:
Information and communication Technology [ICT] is the infrastructure that enables computiftg faster and accurate.
The following table given an idea of range of technologies that fall under the category of ICT
| S.No | Information | Technologies |
| 1. | Creation | Personal computers, Digital Camera, Scanner, Smart Phone |
| 2. | Processing | Calculator, PC – Personal Computer, Smart Phone |
| 3. | Storage | CD, DVD, Pen Drive, Microchip, Cloud |
| 4. | Display | PC – Personal computer, TV – Television, Projector, Smart Phone |
| 5. | Transmission | Internet, Teleconference, Video, Conferencing, Mobile, Technology, Radio |
| 6. | Exchange | E – mail, Cell Phone |
The evaluation of ICT has five phases:
They are evaluation in: (a) Computer (b) PC – Personal Computer (c) Micro Processor ‘ (d) Internet (e) Wireless links
In Economics, the uses of mathematical and statistical tools need the support of ICT for: (a) Data Compiling (b) Editing (c) Manipulating (d) Presenting the results
![]()
Question 47.
(a) Bring out the relationship between AR and MR curves under various price conditions.
Answer:
Relationship between AR and MR Curves: If a firm is able to sell additional units at the same price then AR and MR will be constant and equal. If the firm is able to sell additional units only by reducing the price, then both AR and MR will fall and be different.
Constant AR and MR (at Fixed Price): When price remains constant or fixed, the MR will be also constant and will coincide with AR. Under perfect competition as the price is uniform and fixed, AR is equal to MR and their shape will be a straight line horizontal to X axis. The AR and MR Schedule under constant price is given in the below table and in the diagram.
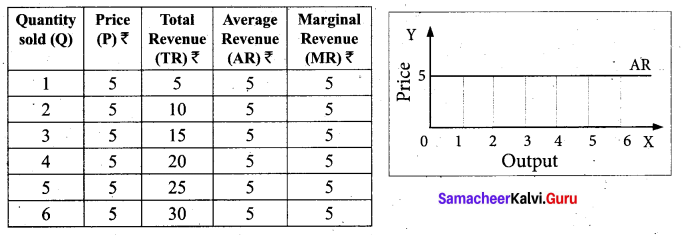
Declining AR and MR (at Declining Price)
When a firm sells large quantities at lower prices both AR and MR will fall but the fall in MR
will be more steeper than the fall in the AR.
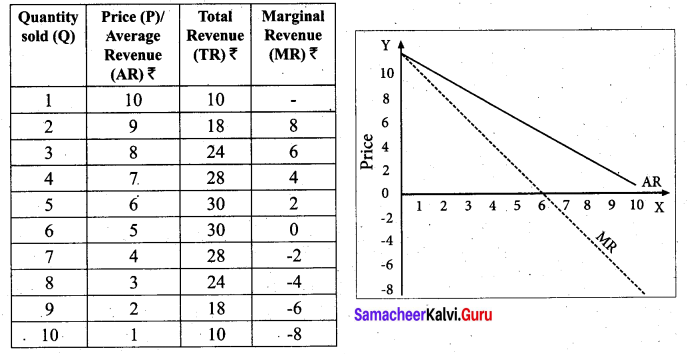
It is to be noted that MR will be lower than AR. Both AR and MR will be sloping downwards straight from left to right. The MR curve divides the distance between AR Curve and Y axis into two equal parts. The decline in AR need not be a straight line or linear. If the prices are declining with the increase in quantity sold, the AR can be non-linear, taking a shape of concave or convex to the origin.
[OR]
(b) Define Market.
Answer:
- Market refers to a physical place, where commodities and services are bought and sold. In Economics, The term “market” refers to a system of exchange between the buyers and the sellers of a commodity.
- Besides direct exchanges, there are exchanges that are carried out through correspondence, telephones, online, e-mail etc.
A market has the following characteristic features:
- Buyers and sellers of a commodity or a service
- A commodity to be bought and sold
- Price agreeable to buyer and seller
- Direct or indirect exchange.