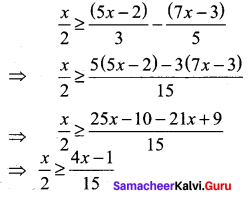
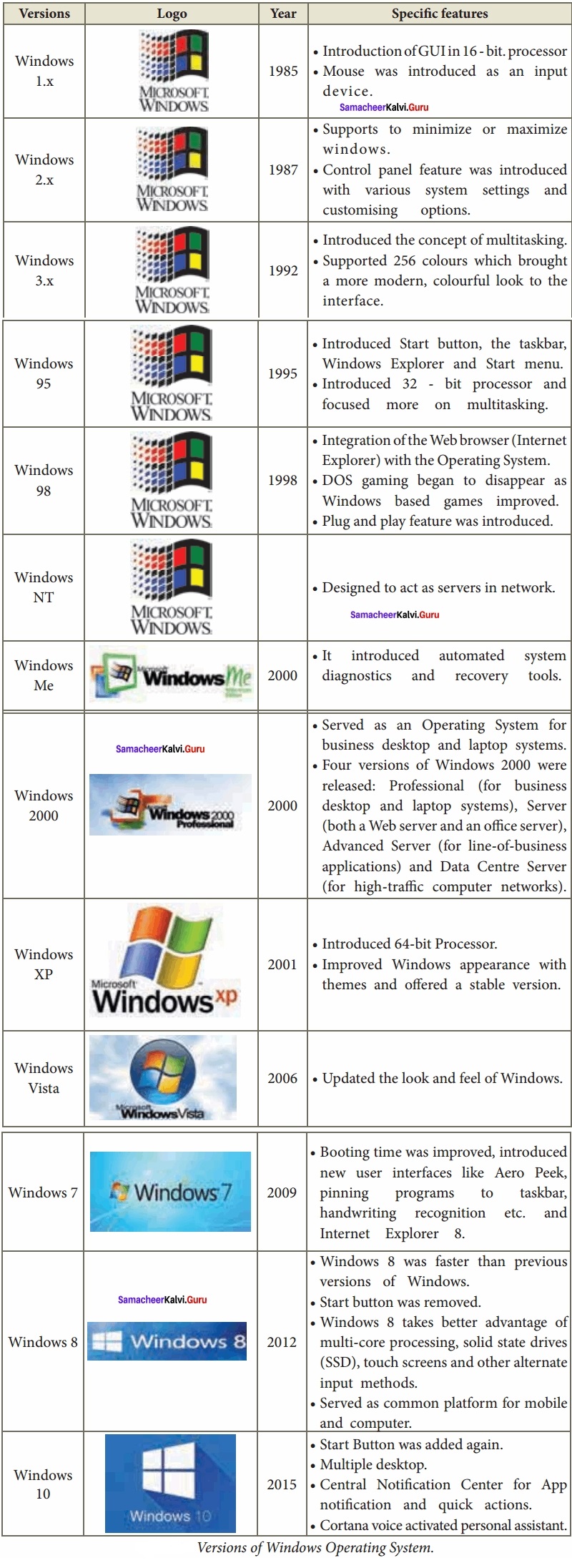
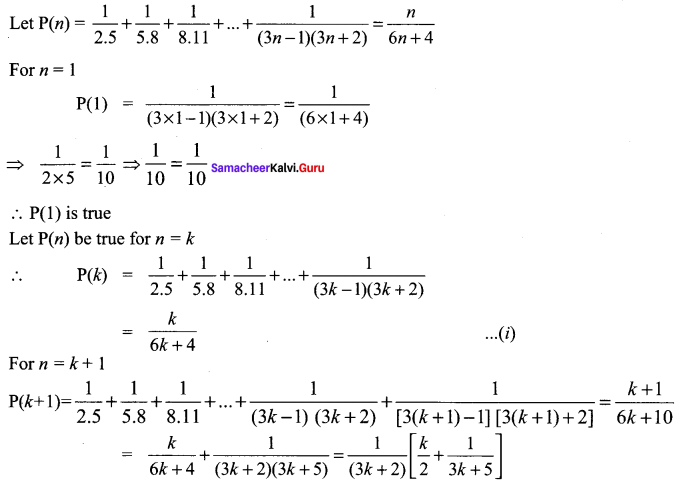
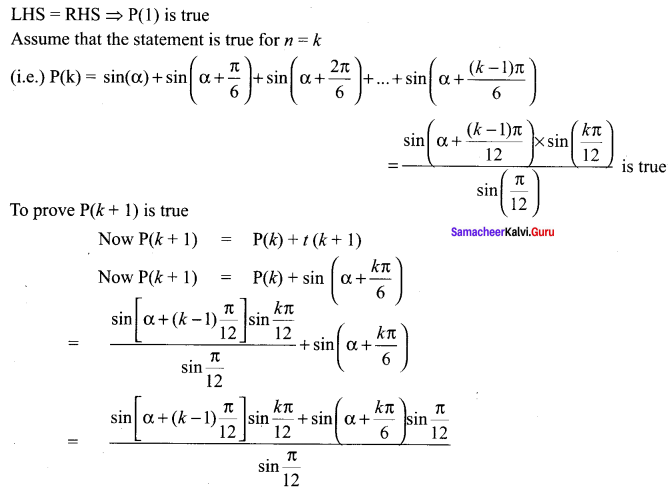
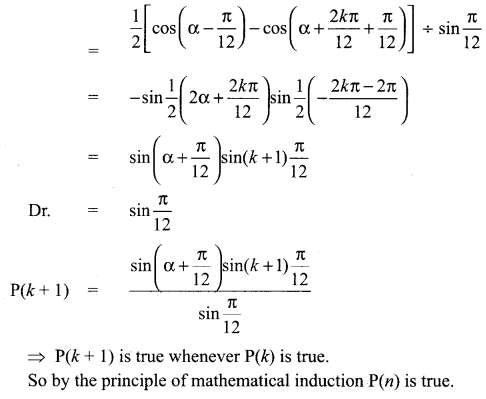
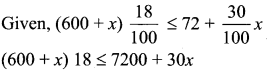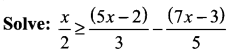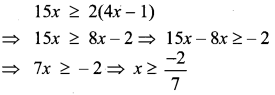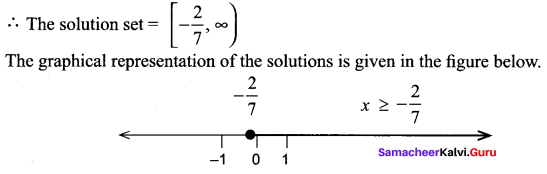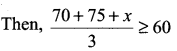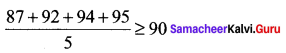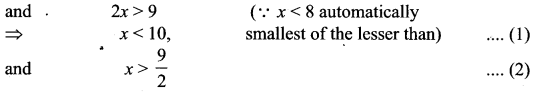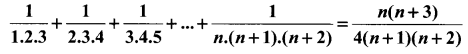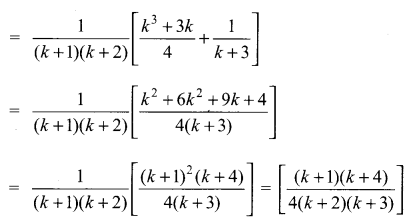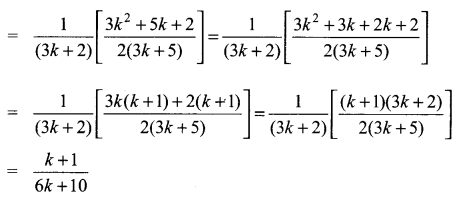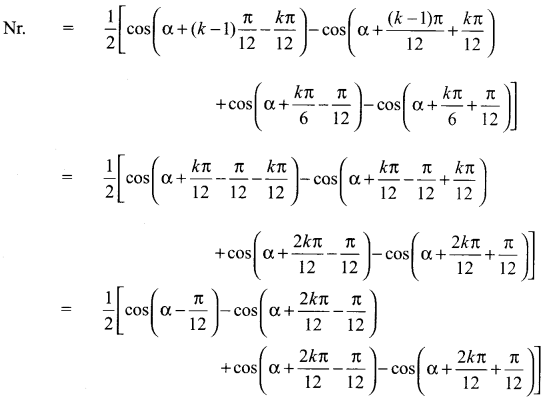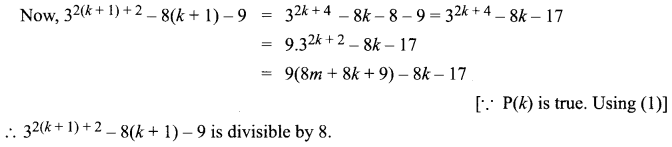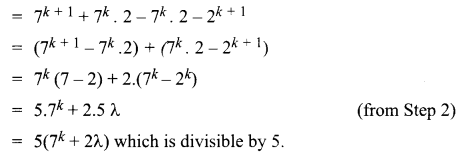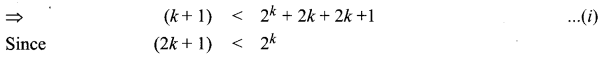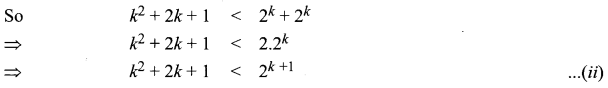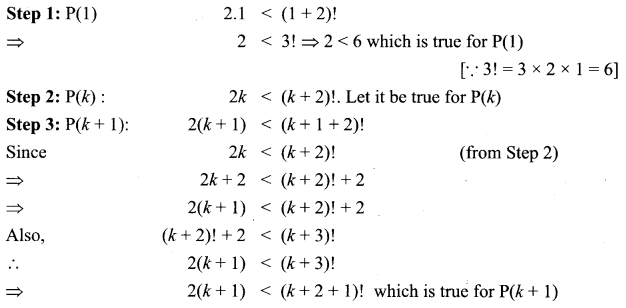Students can Download Computer Applications Chapter 6 Word Processor Basics (OpenOffice Writer) Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Applications Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Applications Solutions Chapter 6 Word Processor Basics (OpenOffice Writer)
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Applications Word Processor Basics (OpenOffice Writer) Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose The Correct Answer
11th Computer Application Chapter 6 Book Back Answers Question 1.
Which is the opening screen of OpenOffice?
(a) Star desktop
(b) Star Center
(c) Star Screen
(d) Star window
Answer:
(b) Star Center
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 11th Computer Application Question 2.
Which option allows you to assign text, tables, graphics and other items to a key or key combination?
(a) Automatic
(b) Autoformat
(c) Auto Text
(d) Autographies
Answer:
(c) Auto Text
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Application Question 3.
Which menu contains the Numbering option?
(a) File
(b) Edit
(c) Tools
(d) Format
Answer:
(c) Tools
Samacheer Kalvi Computer Application Question 4.
There are types of hyperlinks displayed on the left pane of the dialog box?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(d) 4
11th Computer Application Samacheer Kalvi Question 5.
………………….. menu contains the Numbering option.
(a) File
(b) Edit
(c) Tools
(d) Format
Answer:
11th Computer Applications Samacheer Kalvi Question 6.
The option inserts an image that overlaps the text which as a result will be hidden.
(a) Font style
(b) Wrap Through
(c) Font group
(d) Shadow
Answer:
(b) Wrap Through
Computer Application Samacheer Kalvi Question 7.
……………………….. is the default setting, with which the table occupies the entire width of the text area.
(a) Default
(b) Right
(c) Left
(d) Automatic
Answer:
(a) Default
Question 8.
……………………… icon on the drawing toolbar gets you a text box.
(a) Text icon
(b) Text box icon
(c) Draw icon
(d) Draw box icon
Answer:
(a) Text icon
Question 9.
……………………. allows you to assign text, tables, graphics and other items to a key or key combination.
(a) Auto
(b) Automatic
(c) AutoText
(d) Default
Answer:
(c) AutoText
Question 10.
……………………… is the shortcut key for finding and replacing text in a document.
(a) Ctrl + F
(b) Ctrl + F4
(c) Ctrl + F5
(d) Ctrl + F7
Answer:
(a) Ctrl + F
II. Short Answers
Question 1.
How do you insert pictures in to your document?
Answer:
Open office Writer has the ability to insert and edit images in a more simple way.
- Place the insertion pointer where you want the image to appear.
- Select Insert → Picture From file.
- The insert picture dialog box appears where the picture gallery opens from which the desired picture can be selected.
- Click on the Open button.
- The selected picture is inserted into the document.
Question 2.
What are Hyperlinks?
Answer:
There are four types of hyperlinks displayed on the left pane of the dialog box:
- Internet: A web address, normally starting with http://
- Mail and News: For example an email address.
- Document: A hyperlink that points to another document or to another place in the presentation.
- New document: The hyperlink creates a new document.
Question 3.
What is auto text in writer?
Answer:
AutoText allows you to assign text, tables, graphics and other items to a key or key combination. For example, rather than typing “Tamil Nadu” every time you use that phrase, you might just type “tn” and press F3. You can also save a formatted Tip as AutoText and then insert a copy by typing “tip” and pressing F3.
Question 4.
How do you merge cells in a table?
Answer:
To merge a group of cells:
- Select the cells to merge.
- Right click and choose Cell → Merge or choose Table → Merge Cells from the menu bar.
Question 4.
What is the use of Word Art in writer?
Answer:
Word Art is a text modifying feature in the open office writer. It includes effects such as shadows, outlines, colors, gradients, and 3D effects that can be added to a word or phrase. Word Art helps to apply Special effects and change the appearance of the text to make it more presentable and attractive.
III. Explain in Brief
Question 1.
Write about the drawing toolbar?
Answer:
Open office writer uses the drawing tools, to create various shapes by using the Drawing toolbar.
To use th e drawing tools repeatedly, you can move this toolbar to a convenient place on the window. The drawing toolbar can be obtained by clicking View → Toolbars → Drawing.
Question 2.
What are comments, footnotes and endnotes in writer?
Answer:
Footnotes appear at the bottom of the page on which they are referenced. Endnotes are collected at the end of a document. To work effectively with footnotes and endnotes.
→ Insert footnotes.
→ Define formate of footnotes.
→ Define the location of footnotes on the page.
To insert a footnote on an endnote, then select Insert → Footnote / Endnote from the Menu bar or click directly by icon Insert footnote or Insert endnote.
Question 3.
How do you insert cells, rows and columns?
Answer:
To insert rows or columns inside a table:
- Place the insertion pointer in the row or in the column where you would like to add new rows or columns and right-click.
- Choose Row → Insert – to insert a row or Column → Insert – to insert a column. A dialog box will appear, from which you can select the number of rows or columns to insert. You can also set the position of the new rows or columns to Before or After.
- Click OK to close the dialog box.
Question 4.
Write the steps to insert line numbers in writer?
Answer:
Line numbering puts automatic line numbers in the margin. The use of line numbers make it easier to identify specific locations in the document. The most common method of assigning numbers to lines is to assign every line a unique number, starting at 1 for the first line, and incrementing by 1 for each successive line. To apply line numbering:
Click Tools → Line Numbering and select the Show numbering option in the top left comer. Then click OK.
Question 5.
What is a Watermark?
Answer:
Watermarks are images or text displayed in transparency across the text. To create a watermark, it is best to use a Font works object wrapped in the background. The Wrap Through option inserts an image that overlaps the text which as a result will be hidden. To make the text appear, change the transparency of the picture, although the words under the image become visible, they may be difficult to read and will appear lighter than the rest of the text.
IV. Explain in detail
Question 1.
What are the different methods to change margin in writer?
Answer:
Page margins are the white space around the top, bottom, left, and right of your document. Margins let Writer know where to start placing the text at the top of a document, when to move on to the next page at the bottom, where to start typing text on the left side, and where to stop • and move to the next line on the right.
Changing or setting page margins in open office writer can be done in two ways:
- Using the Page rulers-quick and easy, but does not have precise values.
- Using the Page Style dialog box- can specify precise values for the margins.
Changing page margins – using Ruler:
- The shaded sections of the rulers are the margins.
- Hold the mouse pointer over the line between the gray and white sections.
- The mouse pointer turns into a double-headed arrow.
- Hold down the left mouse button and drag the mouse to move the margin and release it at the required point.
- The new margin is set.
Using the Page Style dialog box:
To change margins using the Page Style dialog box.
- Right-click anywhere on the page and select Page from the popup menu or select page tab of page style dialog box.
- In the Margins boxes, specify the values for left, right, top and bottom margins.
- Click on ok button.
Question 2.
What are Header and Footer? How do you insert page numbers?
Answer:
Header:
It is a section of the document that appears in the top margin, Which displays the title or chapter name, author name of a document.
Footer:
It is a section of the document that appears in the bottom margin of the page which displays the page number, date, time etc., which gets displayed on all the pages automatically.
Inserting Header and Footer:
- Select from the main menu Insert → Header → Default
- The header text area is separated from the normal text area.
- Enter the text that is to be repeated in all pages or Select Insert → Fields → Title.
Similarly to insert a Footer, the steps are as given below:
- Select from the main menu Insert → Footer → Default
- Place the insertion pointer in the footer part of the page.
- Select Insert → Fields → Date to insert date in all the pages.
- Once the headers and footers are given in the first page, the same text appears in all the pages.
Inserting and Formatting page numbers:
Once the Header / footer area is enabled, the page numbers can be inserted by performing the following steps:
- position the cursor where you want to insert the number
- choose Insert → Fields → Page Number
- The page number appears with a gray background
Question 3.
Write about the drawing toolbar?
Answer:
Open office writer uses the drawing tools, to create various shapes by using the Drawing toolbar. To use the drawing tools repeatedly, you can move this toolbar to a convenient place on the window. The drawing toolbar can be obtained by clicking View → Toolbars → Drawing.

To use a drawing tool, the steps are as given below:
- Click in the document where you want the drawing to be anchored.
- Select the tool from the Drawing toolbar. The mouse pointer changes to a drawing- functions pointer.
- Move the cross-hair pointer to the place in the document where you want the graphic to appear and then click-and-drag to create the drawing object.
- Release the mouse button. The selected drawing function remains active, so you can draw another object of the same type.
- To cancel the selected drawing function, press the Esc key or click on the Select icon on the Drawing toolbar.
- You can now change the properties (fill color, line type and weight, anchoring, and others) of the drawing object using either the Drawing Object Properties toolbar or the choices in the dialog box.
Question 4.
Explain Page formatting in writer?
Answer:
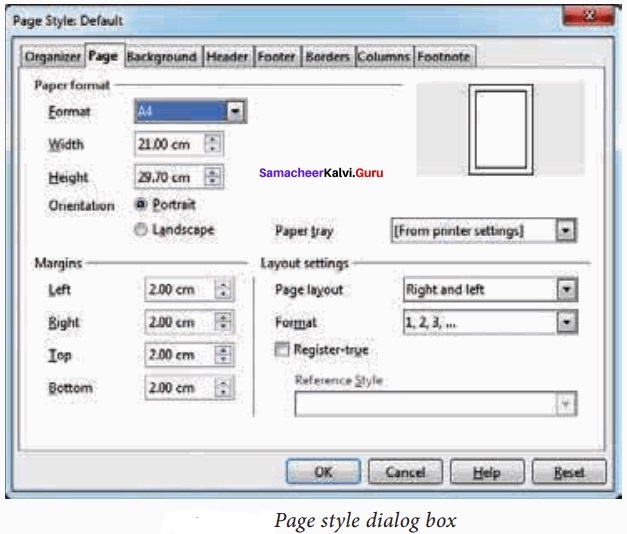
The most important thing in a word processor is how to format the page with elements such as margins, numbering, page layout, headers and footers. Formatting your pages makes them look more attractive and makes them easier to read.
Changing Page Size:
The default page size in writer is 8.5 × 11”, the same as that of a standard A4 printing paper. However, for different types of documents, you may need to change the page size. To change the paper size:
- Select the page whose page size is to be changed
- Select Format → Page, the page style dialog box.
- Select Page Tab.
- In the paper format group, select the format like A4, legal ….
- Or the width and height option can be used to set the page size.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Applications Solutions Word Processor Basics (OpenOffice Writer) Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
Which is the leading open-source office software to works on all common computers and available in many languages.
(a) OpenOffice
(b) StarOffice
(c) MSOffice
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) OpenOffice
Question 2.
Which company has developed by OpenOffice writer?
(a) Microsoft
(b) Kingsoft
(c) Apache
(d) Sun micro systems
Answer:
(c) Apache
Question 3.
The open screen of the OpenOffice is known as:
(a) starcenter
(b) desktop
(c) window
(d) screen
Answer:
(a) starcenter
Question 4.
The keyboard shortcut key can be used to open a new text document in OpenOffice:
(a) Ctrl + O
(b) Ctrl + A
(c) Ctrl + N
(d) Ctrl + S
Answer:
(c) Ctrl + N
Question 5.
The bar, that displayed at the top most part of the window:
(a) Toolbar
(b) Title bar
(c) Menu bar
(d) Scroll bar
Answer:
(b) Title bar
Question 6.
Which is called a flashing vertical bar appears at the beginning of the screen?
(a) Insertion pointer
(b) Cursor
(c) Horizontal ruler
(d) Vertical ruler
Answer:
(a) Insertion pointer
Question 7.
The keyboard shortcut key can be used to close a document in OpenOffice:
(a) Ctrl + N
(b) Ctrl + A
(c) Ctrl + W
(d) Ctrl + Q
Answer:
(c) Ctrl + W
Question 8.
The keyboard shortcut key can be used to open an existing document in OpenOffice:
(a) Ctrl + 0
(b) Ctrl + A
(c) Ctrl + N
(d) Ctrl + S
Answer:
(a) Ctrl + 0
Question 9.
Which key is used to delete the character left of the insertion pointer?
(a) Backspace key
(b) Delete key
(c) Shift key
(d) Home key
Answer:
(a) Backspace key
Question 10.
Which key is used to delete the character right of the insertion pointer?
(a) Backspace key
(b) Delete key
(c) Shift key
(d) Home key
Answer:
(b) Delete key
Question 11.
The key is used toggle between Insertion mode and overwritten mode:
(a) Insert key
(b) Home key
(c) Shift key
(d) Ctrl key
Answer:
(a) Insert key
Question 12.
The OpenOffice writer provides help window, which function key is used to getting the help window?
(a) F1
(b) F2
(c) F3
(d) F4
Answer:
(a) F1
Question 13.
Which option is used to removed by selecting highlighted text?
(a) Cancel
(b) No fill
(c) Change
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) No fill
Question 14.
For selecting whole document which shortcut key is used?
(a) Ctrl + A
(b) Ctrl + W
(c) Ctrl + M
(d) Ctrl + S
Answer:
(a) Ctrl + A
Question 15.
Which shortcut key is used to clear the formatting document?
(a) Ctrl + A
(b) Ctrl + W
(c) Ctrl + M
(d) Ctrl + A
Answer:
(c) Ctrl + M
Question 16.
A first-line indentation indents value is:
(a) positive
(b) negative
(c) zero
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) positive
Question 17.
The hanging indent value can be entered as:
(a) positive
(b) negative
(c) zero
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) negative
Question 18.
In page orientation, the height of the document is more than the width is called:
(a) portrait
(b) landscape
(c) legal
(d) A4 size
Answer:
(a) portrait
Question 19.
In page orientation-the width of the document is more than height is called:
(a) portrait
(b) landscape
(c) legal
(d) A4 size
Answer:
(b) landscape
Question 20.
Which shortcut key is used to find the replace the text?
(a) Ctrl + F
(b) Ctrl + B
(c) Ctrl + P
(d) Ctrl + S
Answer:
(a) Ctrl + F
Question 21.
Which menu option is choosed to open AutoCorrect dialog box?
(a) Tools → Change
(b) Tools → AutoCorrect
(c) Tools → Add
(d) Tools → Ignore
Answer:
(b) Tools → AutoCorrect
Question 22.
Which command is used to deselect the size of the picture?
(a) Crop
(b) Format
(c) Cut
(d) Delete
Answer:
(a) Crop
Question 23.
Which option is used to inserts an image that overlaps the text which result will be hidden?
(a) Drawing toolbar
(b) Wrap through
(c) Format
(d) Transparency
Answer:
(b) Wrap through
Question 24.
Which key is assign the AutoText shortcut?
(a) Ctrl + FI
(b) Ctrl + F2
(c) Ctrl + F3
(d) Ctrl + F4
Answer:
(c) Ctrl + F3
Question 25.
A specified number of rows and columns are called:
(a) Table
(b) Cell
(c) Column
(d) Row
Answer:
(a) Table
Question 26.
Which combination key is used to insert table dialog box?
(a) Ctrl + F10
(b) Ctrl + F11
(c) Ctrl + F11
(d) Ctrl + F12
Answer:
(d) Ctrl + F12
Question 27.
Multiple copies of a document to send to a list of different recipients is called:
(a) Mail merge
(b) Copy
(c) address book
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(a) Mail merge
Question 28.
Which opition can choose to print all colour text and graphics as gray scale in OpenOffice?
(a) Tools > options > OpenOffice.org > print
(b) Tools > options > OpenOffice.org > ok
(c) Tools > options > OpenOffice.org > Next
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Tools > options > OpenOffice.org > print
Question 29.
When using Tab key in OpenOffice writer by default moving insertion point is:
(a) 1 inch
(b) 1/4 inch
(c) 1/2 inch
(d) 2 inch
Answer:
(c) 1/2 inch
Question 30.
Which rules you can add to decorate any or all the four sides of a paragraph?
(a) Highlighted
(b) Borders
(c) Shading
(d) Bold
Answer:
(b) Borders
Question 31.
Which can you use as background for enhancing the appearance of a text or paragraph?
(a) Highlighted
(b) Borders
(c) Shading
(d) Bold
Answer:
(c) Shading
Question 32.
The section’of the document that appears in the top margin:
(a) header
(b) footer
(c) margin
(d) window
Answer:
(a) header
Question 33.
The section of the document that appears in the bottom margin:
(a) header
(b) footer
(c) margin
(d) window
Answer:
(b) footer
Question 34.
Which is the shortcut key to insert a comment within the text?
(a) Ctrl + Alt + C
(b) Ctrl + Alt + I
(c) Ctrl + Alt + V
(d) Ctrl + Alt + C
Answer:
(a) Ctrl + Alt + C
Question 35.
Which shortcut key is used to undo last action?
(a) Ctrl + C
(b) Ctrl + F
(c) Ctrl + Z
(d) Ctrl + E
Answer:
(c) Ctrl + Z
Question 36.
Which shortcut key is used to center aligned text?
(a) Ctrl + C
(b) Gtrl + F
(c) Ctrl + Z
(d) Ctrl + E
Answer:
(d) Ctrl + E
Question 37.
Which combination of shortcut is used subscript a number?
(a) Ctrl + Shift + B
(b) Ctrl + Shift + V
(c) Ctrl + Shift + P
(d) Ctrl + Shift + S
Answer:
(a) Ctrl + Shift + B
Question 38.
Which combination of shortcut key is used superscript a number?
(a) Ctrl + Shift + B
(b) Ctrl + Shift + V
(c) Ctrl + Shift + P
(d) Ctrl + Shift + S
Answer:
(c) Ctrl + Shift + P
Question 39.
Which shortcut key is used to inserting a new paragraph without numbering?
(a) Alt + Shift
(b) Alt + Enter
(c) Alt + Tab
(d) Ctrl + Enter
Answer:
(b) Alt + Enter
Question 40.
Which shortcut key is used to apply default paragraph style?
(a) Ctrl + 0
(b) Ctrl + 1
(c) Ctrl + 2
(d) Ctrl + 3
Answer:
(a) Ctrl + 0
Question 41.
……………………. is the pictorial representation of data.
(a) Object
(b) Charts
(c) Shapes
(d) Colour
Answer:
(b) Charts
II. Short Answers
Question 1.
What is meant by word processing?
Answer:
Word processor is a computer software to create, edit, manipulate, transmit, store and retrieve a text document. The above said activities are called as “Word Processing”. In other words, Word processing is an activity carried out by a computer with suitable software to create, edit, manipulate, transmit, store and retrieve text documents.
Question 2.
What are the familiar open source word processing software?
Answer:
OpenOffice Writer, LibreOffice Writer, Abiword etc.
Question 3.
What are the familiar Tamil word processor?
Answer:
Tamil OpenOffice writer, Tamil Libre, Kamban 3.0, Mentamizh 2017 there are familiar word processors exclusively for Tamil Language.
Question 4.
How to open the OpenOffice Writer?
Answer:
A new OpenOffice Writer document can be created by various methods. From windows, select
Start → All Programs → OpenOffice → OpenOffice Writer.
(or)
From Star Center (Welcome Screen): Double-click on “OpenOffice” icon the desktop.
Question 5.
What is meant by star center?
Answer:
In OpenOffice, open screen is called as “Star Center”. Writer is one of the components of OpenOffice. So, it may be invoked from the “Star Center” by simply clicking on the “Text Document” icon.
Question 6.
How can you close the OpenOffice application?
Answer:
This button is called as “Close” button,when you click this button, the application is closed and OpenOffice returns back to the desktop. So, the red colored close button may be called as “Exit” or “Quit”.
There is another (‘x’) mark on the right most comer of the menu bar. This is actually used to close your document. When you click this (‘x’) mark, your document will be closed, OpenOffice will be still opened.
Question 7.
What are the types of toolbar available in the menu bar?
Answer:
Under the menu bar, there are two toolbars available by default.
They are:
- Standard Tool bar
- Formatting Toolbar.
Question 8.
What are the types of ruler scale?
Answer:
The ruler is a scale below the formatting toolbar which shows the margins. There are two set of rulers
- Horizontal ruler and
- Vertical ruler. Horizontal rules is used to set left and right margins of a page and vertical ruler for top and button setting.
Question 9.
What is called insertion pointer?
Answer:
The work space is the blank area which is used to type the content of the file. A flashing vertical bar appears at the beginning of the screen which is called as “Insertion pointer”.
Question 10.
Which is known as word wrap?
Answer:
When the text reaches the end of the line, the word is automatically wrapped to the next line. This feature in any word processor is known as “Word Wrap”.
Question 11.
How to save the document?
Answer:
One can select the drive and folder where the file will be stored. To save a document for a first time,the following steps are used:
Click File → Save → (or) File → Save As (or) Ctrl + S.
Question 12.
How to set a password to protect your document while saving a file?
Answer:
In OpenOffice writer, a document can be protected with a password. You can set a password to protect your document while saving a file. To save a file with password, click on “Save with Password”check box and then click “Save” button. Immediately it shows “Set Password” dialog box. Enter a password in “Enter Password to open” text box and retype the same password in “Confirm Password” box for confirmation. Finally click ‘OK’ button.
Question 13.
What is the use of Insert key?
Answer:
To insert a text in between if something is left out, the insertion can be made by taking the insertion pointer to the current location and Press the Insert Key the newly typed text is inserted, so that the existing text moves to the right. Press the Insert Key again, the text is over written on the existing text. This is called ‘Type over mode’. You can toggle between the insert mode and type over mode by pressing the‘Insert key’.
Question 14.
What is the purpose of using paste special option?
Answer:
When you move or copy information, the paste option is used to send the information as a whole. But, to move or copy only some aspects of the data, like only its formatting or only value, the Paste Special option is used. To use the paste special, select the text and apply move or copy, then at the destination location,
Click Edit → Paste Special (or) press Ctrl + Shift + V, (or) Alt + E + S the Paste Special dialog box opens.
Question 15.
What is difference between paste and paste special?
Answer:
Paste:
Paste is a feature that lets a user cut or copy items from Cells and transfer them to another completely.
Paste Special:
Paste Special allows the items being transferred to be formatted in several different ways. Paste Special is a feature found in software like Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel and Open Office.
Question 16.
What is meant by Text formatting?
Answer:
A font is a set of characters in a particular style. Changing the default appearance of the text like changing the font type, size, color, style etc., are called as Text formatting.
Question 17.
What are the short cut commands using to make the text Formatting?
Answer:

Question 18.
What is the use of change case option of format menu?
Answer:
Normally any text can be typed in upper or lower case. The text can be changed to different cases like:
- Uppercase (Capital letters)
- Toggle case (reverse case),
- Sentence case (first letter of each sentence Capital),
- Capitalize every word (first letter of each word capital),
- Lower case. (Small letters)
- This can be done by:
- Select the text to change case
- Select Format → Change case.
Question 19.
What is meant by highlighting?
Answer:
Highlighting is used to draw attention to important information in a text. Highlighting is beneficial because it first asks the reader to pick out the important parts, and then gives an effective way to review that information later.
Highlighting can be applied by selecting the text and click Highlighting icon.
Question 20.
What is meant by hanging indent?
Answer:
This is a special kind of indent where the first line of the paragraph alone hangs outside leaving the rest of the text. To apply Hanging indent, a negative value is given in the “first line” option of the paragraph dialog box.
Question 21.
What are the types different page orientation?
Answer:
Page orientation refers to hgw the document will be displayed on screen and printed. There are two different orientations:
Landscape:
The width of the document is more than the height. This is best suited for displaying professional photos, invitations, albums, tables etc.,
Portrait:
This is the most common orientation. Here, the height of the document is more than the width. Normally books, newspapers will be displayed in this format.
Question 22.
What is the function of AutoCorrect?
Answer:
Auto Correct function has the facility to correct the common misspellings and typing errors, automatically. For example, “hte” will be changed to “the” which can be done through the menu option, Tools → AutoCorrect.
Question 23.
What is meant by spell check program?
Answer:
Spell check is a software program that corrects spl74568f.dfml d,589f fjidflfefelling errors in ewfword processing, email and documents, Spell check identifies and corrects misspelled words and the grammatical error is displayed with a green wavy line under the wrong word.
Question 24.
What is meant by table?
Answer:
A table is a grid with a specified number of rows and columns. Tables can often be used as an alternative to spreadsheet to organize materials. A well-designed table can help readers understand better what you are trying to convey.
Question 25.
What is meant by formatting table?
Answer:
Formatting a table involves formatting of the table layout, formatting of the table text, adjusting the size of the table, its position on the page, adding or removing rows or columns, merging and splitting cells, changing borders and the background.
III. Explain in Brief
Question 1.
What are the common software packages in OpenOffice?
Answer:
OpenOffice is a productive office suite with a collection of different software packages such as
OpenOffice Writer – Word Processor to create text documents
OpenOffice Calc – Spreadsheet to create worksheets
OpenOffice Base – Database
OpenOffice Impress – Presentation software
OpenOffice Draw – Drawing Software
OpenOffice Formula – Create formula and equations
Question 2.
What are the important features which provides OpenOffice writer?
Answer:
- Templates and styles.
- Page layout methods, including frames, columns, and tables.
- Embedding or linking of graphics, spreadsheets, and other objects.
- Built-in drawing tools.
- Master documents to group a collection of documents into a single document.
- Change tracking during revisions.
- Database integration, including a bibliography database.
- Export to PDF, including bookmarks.
Question 3.
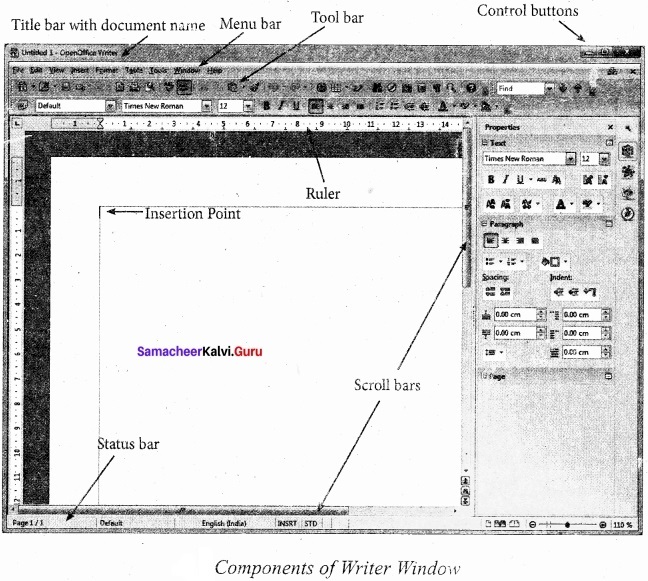
Draw a OpenOffice writer window? With mark the important components?
Answer:
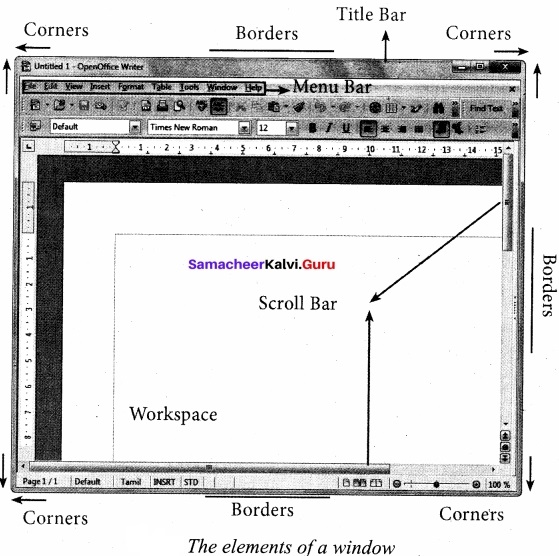
OpenOffice Writer window such as Title bar, Menu bar, Standard Toolbar, Formatting Toolbar, Ruler, Work space and Status bar. The components of a OpenOffice writer window are explained.
Question 4.
How to select a text continuous and discontinuous?
Answer:
In any word processor, the text has to be selected for performing any operation like copying, moving, formatting etc. This text selection can be done by two methods;
- Selecting the continuous text.
- Selecting the non continuous text.
Continuous text:
To select the text continuously take the insertion pointer to the starting of the text.
Selecting the continuous text:
To select the text continously take the insertion pointer to the starting of the text.
- Hold the SHIFT key and drag the mouse across until the required text is selected and then release the SHIFT key.
- The select text can be used for any operation.
Selecting the non continuous text:
To select the text not continuously, take the insertion pointer to the starting of the text,
- Hold the CTRL key and drag across it till the required text is selected and release the CTRL key.
- The required text is selected for any operation.
Question 5.
How to use the help system in open writer?
Answer:
Open Office Writer provides several forms of help. By pressing FI or select Help from the menu bar the help window appears.
- To activate tool tips, extended tips, and the help Agent, click Tools → Options → OpenOffice.
- For a more detailed explanation, select Help → What’s This? and hold the mouse pointer over the icon where you want more help with.
Question 6.
How can you change the line spacing adjustment?
Answer:
Line spacing determines the amount of vertical space between lines of text in a paragraph. By default, the lines are single-spaced, that is the spacing accommodates the largest font in that line, plus a small amount of extra space. In Open Office, setting line spacing is quite easy through the context menu, select the line or word or phrase, right-click → line spacing, select the type single, 1.5 or double. There are seven different types of line spacing.
- Select the entire document by Edit → Select All.
- Format → paragraph.
- The paragraph dialog box appears, click Indents and spacing tab.
- In the line spacing option, select the type and click ok button.
Question 7.
What is a indent? What are the types of Indent?
Answer:
Indent is the distance from the left and right margin of a paragraph. It is used to improve the efficiency and readability of the paragraph and makes the paragraph look more attractive.
There are four types of indents:
- Left Indent
- Right Indent
- First Line Indent and
- Hanging Indent.
Question 8.
How to change the page colour and borders?
Answer:
Changing the page color is not quite common. To do so, in the page style dialog box, in the Background option, click on color and select the “color” from the color palette or select “graphic” to apply an image as a page background.
Borders can be applied to an entire document, an entire page, paragraph, or just to certain sections of the document. From the page style dialog box, select the Border tab, the user defined area helps to define the area of borders, the line style of borders, color of borders can be selected.
Question 9.
Howto insert special characters and equations?
Answer:
Many symbols which are used in a mathematical equation like alpha (α), beta (β), pi (π) etc.,, are not available on the standard keyboard. However, representing these characters are very much essentia in mathematical equations. To insert such characters, the procedure given below
is folio-wed:
- Place the cursor in your document where you want the character to appear.
- Click on the Insert → Special character.
- The Special character dialog box appears from which the desired symbol can be selected by clicking on the character.
- As you select each character, it is shown on the lower right, along with the numerical code for that character.
- If you do not find a particular special character you want, try changing the font selection.
- Click the Ok button and the character is inserted at the current location.
Question 10.
How to inserted the chart in the worksheet?
Answer:
Charts are pictorial representations of data. The data can be either typed in cells in writer or it can be inserted.
Click inside the Writer table.
- Choose Insert → Object → Chart, You see a chart preview and the Chart Wizard.
- The chart toolbar at the top of the page which contains the formatting tools.
- The insert menu shows the various attributes of the chart like Title, Legends, Axis, grid, label etc.,
Question 11.
What are the steps needed to create watermark?
Answer:
- Insert the image or text of your choice
- Anchor the image to the page and
- Select the wrap through option form the Format Wrap menu or right-clicking on the image and selecting Wrap
- Wrap Through from the pop-up menu
- Move the image into the desired position
- The Picture toolbar should be displayed when the image is selected
- Change the transperency to a suitable value so that the text can be read.
Question 12.
What are the steps follows to assign Auto Text?
Answer:
To assign AutoText shortcut to some text, the steps arc as follows:
- Type the text into your document.
- Select the text so that it is highlighted.
- Select Edit → AutText (or press Ctrl+F3).
- Enter a name for your shortcut. Writer will suggest a one-letter shortcut, which you can change.
- Click the AùtoText button on the right and select New (text only) from the menu.
- Click Close to return to your document.
Question 13.
How can you merging and splitting cells?
Answer:
To merge a group of cells:
- Select the cells to merge.
- Right click and choose Cell → Merge or choose Table → Merge Cells from the menu bar.
- To split a cell:
- Place the insertion pointer inside the cell.
- Right click and choose Cell → Split, or choose Table → Split Cells from the menu bar.
- Select the direction of the split, horizontally (for rows), or vertically (for columns), as well as the total number of cells to create.
Question 14.
What are the basic types of graphics in OpenOffice writer?
Answer:
- Image files, including photos, drawings, scanned images, and others.
- Diagrams created using OOo’s drawing tools.
- Charts created using OOo’s Chart facility.
IV. Explain in detail
Question 1.
Explain the menu bar in OpenOffice writer?
Answer:
Menu Bar:
The menu bar is just below the title bar which comprises of various menus consisting of various options.

File:
The File menu contains the commands of all file management tasks like, Create a new file, Open an existing file, Close the current file, Save a file, Save As another file, print file, Export file etc.,
Edit:
The Edit menu contains the editing commands like, cut, copy, paste, Undo, Redo etc.,
View:
The View menu contains the commands which are used to modify the environment of write like display of toolbars, web layout, print layout, navigator etc.,
Insert:
The Insert menu contains commands for inserting various elements such as pictures, tables, charts, comments, headers, footers, special characters, cross reference etc.,
Format:
The Format menu contains the commands of various text and page formatting features like page size, layout, font characteristics, bullets and numbering etc.,
Tables:
The Table menu contains various tools to manage and manipulate tables such as create tajfie, insert rows, insert columns, s’plit cells, merge cells etc.,
Tools:
The Tools menu contains various tools and functions such as spell check, macros, mail merge, end notes/footnotes etc.,
Window:
The window menu shows display options such as New Window, Close Windows, Split and Freeze. .
Help:
The Help menu lists out the inbuilt help features available with OpenOffice.
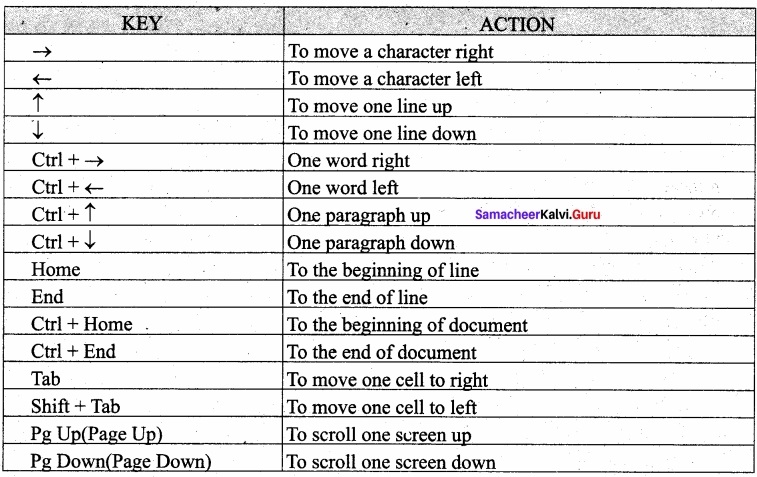
Question 2.
What are the different shortcut keys of moving within a document?
Answer:
There are different ways of moving within a document. There are many shortcut keys given in Table which are used to move easily within a document.
Question 3.
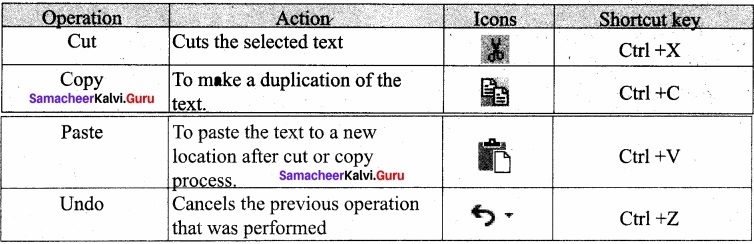
Explain the various editing operations using a document?
Answer:
The various editing operations like cut, copy and paste.
Moving: To move a text from one location to another.
- Select the text to he moved.
- Click Ctrl + X or Cut Icon or Edit → Cut.
- The text is removed from the source location and placed in the clipboard.
- Take the insertion pointer to the new location to be moved and
- Click Ctrl + V or Paste Icon or Edit → Paste.
The required text is moved to the required location.
Copying: To copy a text from one location to another.
- Select the text to be copied .
- Click Ctrl + C or Copy Icon or Edit → Copy
- A duplicate copy of the text is made and send to the clipboard
- Take the insertion pointer to the new location to be copied and
- Click Ctrl + V or Paste Icon or Edit → Paste
The required text is copied to the required location.
The Editing shortcut keys are:
Question 4.
What are the various alignment in formatting paragraph?
Answer:
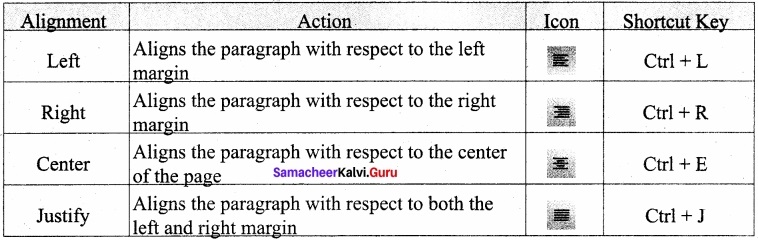
A paragraph is any text that ends with a hard return. A hard return is accomplished anytime you press the Enter key. Paragraph Alignment or justification refers to the way in which the lines of a paragraph are aligned. Paragraph alignment lets you control the appearance of individual paragraphs.
There are four types of alignment available in Open office Writer – left-alignment, Right-alignment, Center-alignment, and Justify-alignment. The paragraph formatting can also be done by icons using the formatting toolbar.
Question 5.
How can you use Bullets and Numbering in a document?
Answer:
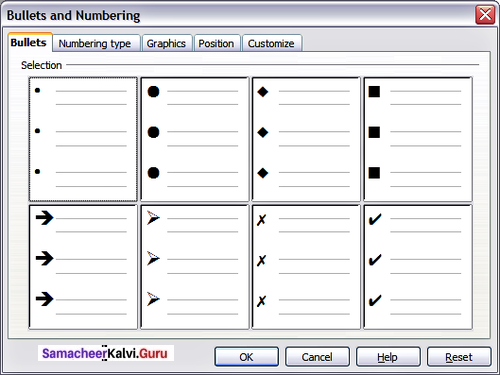
Bullets:
This is a paragraph level attribute that applies a bullet character to the start of the paragraph. In bulleted lists, each paragraph begins with a bullet character. This is suitable when the text has to be presented as a list of items preceded by a bullet symbol and no sequence has to be followed. Bullets are quickly created by clicking on the bullet icon.
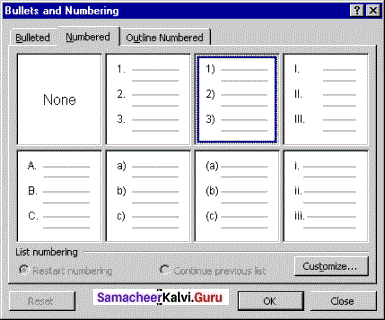
Numbering:
This attribute applies a numeral to the start of the paragraph. Numbering is more suitable when the text has to be presented as a sequence. In numbered list, each paragraph begins with an expression that includes a number or letter and a separator such as a period or parenthesis. The numbers in a numbered list are updated automatically when you add or remove paragraphs in the list. Numbering is quickly created by clicking on the numbering icon.
Style of Bullets and Numbering:
The default type of bullet is (•) and the default type of numbering is (1,2, 3 ……………….). The style of bullets and numbering can be changed by applying the following steps:
- Select the text to be bulleted.
- Format → Bullets and Numbering.
- Select Bullets Tab.
- The bullets and Numbering dialog box where different styles of bullets are displayed.
- Click on the required style.
- Click OK button.
- The selected text is bulleted
To apply Numbering:
- Select the text to be numbered.
- Format → Bullets and Numbering.
- Select Numbering Type Tab.
- The Bullets and Numbering dialog box where different styles of numbering are displayed.
- Click on the particular style.
- Click Ok button.
- The selected text is numbered.
Question 6.
How can you find a word in Find and Replace text?
Answer:
OpenOffice Writer has a Find and Replace feature that helps to locate for a text inside a document and replace it with another word. In addition to finding and replacing words and phrases, you can also use wildcards and regular expressions to perform advanced search. To search a word
- Click Edit → Find & Replace (or) Ctrl + F
- The Find & Replace dialog box appears.
Steps to find & replace a text
- Type the text you want to find in the Search for box.
Eg: To search a word “Bombay” in a document and replace with “Mumbai”, enter the word “Bombay” in the Search for box. - To replace the text with different text, type the new text in the Replace with box.
Enter the word “ Mumbai” in the Replace with box and Click Find button, to start the search, the found word is highlighted and the first occurance of “Bombay” is highlighted.
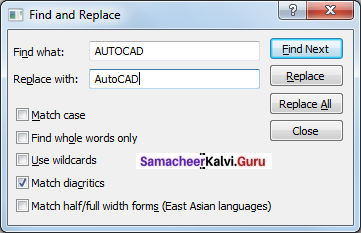
- To replace text, click Replace button. The highlighted word is replaced with the word given in the Replace with box.
- Click Find All, Writer selects all instances of the search text in the document. All occurrences of Bombay are highlighted.
- Click Replace All button, Writer replaces all matches. This will replace all occurances of “Bombay” with “Mumbai”.
- Enable Match case to perform the search case sensitively so that uppercase and lower cases are distinguished separately.
- Enable Whole Words only to make the search more specific to words used separately alone.
Question 7.
Discuss the Auto spell check?
Answer:
Auto spell check option checks each word as it is typed and displays a wavy red line under any misspelled words. Once the word is corrected, the red wavy line disappears. This can be done through clicking the icon.
To perform a separate spelling check on the document (or a text selection) click the Spelling and Grammar button. This checks the document or selection and opens the Spelling dialog box if any misspelled words are found, This can be achieved by clicking the icon
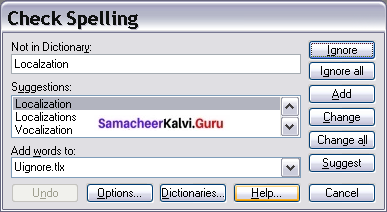
Here are some more features of the spelling tool:
- Right-click on a word with a wavy underline, to open a powerful context menu. Correct words can be selected from the suggested words on the menu. The selection will replace the misspelled word with correct word. Other menu options are discussed below.
- The dictionary language can be changed (For example, Spanish, French, or German) from the Spelling dialog box.
- The new words can be added to a dictionary. Click Add in the Spelling dialog box and pick the dictionary to add it to.
Question 8.
How can you using different techniques to insert tables?
Answer:
Different techniques to insert tables:
To insert a new table, position the insertion pointer where you want the table to appear, then use any of the following methods to open the Insert Table dialog box.
There are two methods to create a table:
1. Table Icon:
To insert a table quickly from the standard tool bar:
- Place the insertion pointer where you want the table to appear.
- Click the arrow to the right side of the Table icon

- In the drop down grid, select the number of rows and columns for the table. (iv) The table will appear at the location of your insertion pointer.
2. Insert table dialog box:
To insert a table with more control over the settings and properties, use the Insert Table dialog box.
To open the dialog box: Select Table → Insert → Table (or) Ctrl +F12 or left-click the Table icon. From this dialog box, you can:
- Select the number of rows and columns of the table.
- Give a Name to the table to later distinguish it in the Navigator.
- Select the Heading option to define the first row in the table as the heading.
- Select the Repeat heading option to repeat the heading row if the table more than one page.
- Select the Don’t split table option to prevent the table from spanning more than one page.
- Select the Border option to surround each cell of the table with a border.