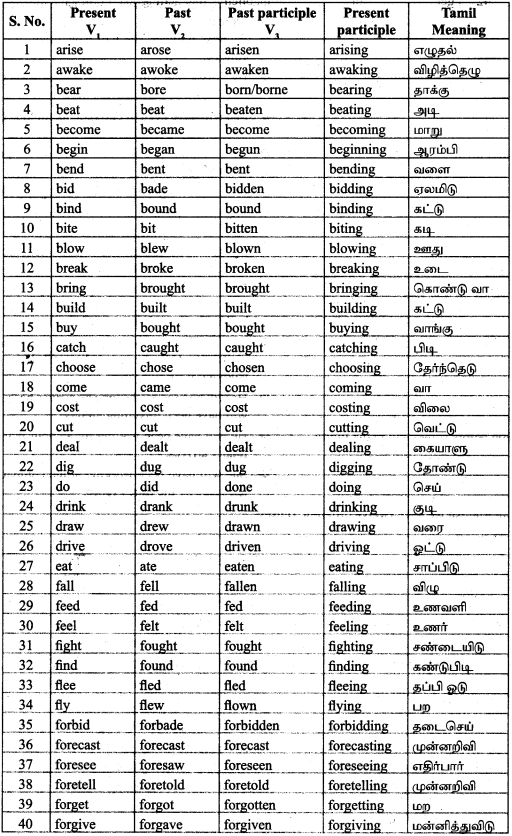
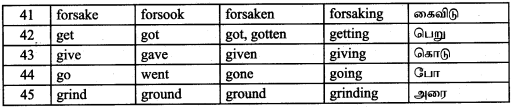
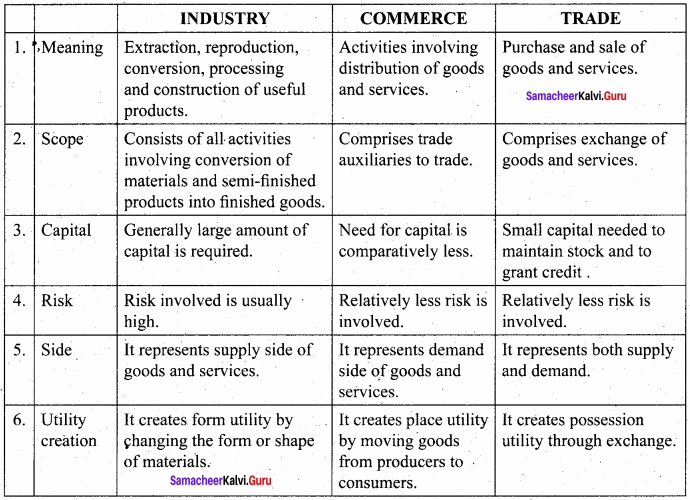
Students can Download Accountancy Chapter 9 Rectification of Errors Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Solutions Chapter 9 Rectification of Errors
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Rectification of Errors Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the Correct Answer
Rectification Of Errors Questions With Answers Pdf Question 1.
Error of principle arises when ………………
(a) There is complete omission of a transaction
(b) There is partial omission of a transaction
(c) Distinction is not made between capital and revenue items
(d) There are wrong postings and wrong castings
Answer:
(c) Distinction is not made between capital and revenue items
Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 9 Solutions Question 2.
Errors not affecting the agreement of trial balance are ………………
(a) Errors of principle
(b) Errors of overcasting
(c) Errors of undercasting
(d) Errors of partial omission
Answer:
(a) Errors of principle
11th Accountancy Chapter 9 Book Back Answers Question 3.
The difference in trial balance is taken to ………………
(a) The capital account
(b) The trading account
(c) The suspense account
(d) The profit and loss account
Answer:
(c) The suspense account
Rectification Of Errors Questions With Solutions Class 11 Pdf Question 4.
A transaction not recorded at all is known as an error of ………………
(a) Principle
(b) Complete omission
(c) Partial omission
(d) Duplication
Answer:
(b) Complete omission
Rectification Of Errors Questions With Answers Question 5.
Wages paid for installation of machinery wrongly debited to wages account is an errs of ………………
(a) Partial omission
(b) Principle
(c) Complete omission
(d) Duplication
Answer:
(b) Principle
Accountancy Class 11 Chapter 9 Solutions Question 6.
Which of the following errors will not affect the trial balance?
(a) Wrong balancing of an account
(b) Posting an amount in the wrong account but on the correct side
(c) Wrong totalling of an account
(d) Carried forward wrong amount in a ledger account
Answer:
(b) Posting an amount in the wrong account but on the correct side
Rectification Of Errors Problems With Solutions Pdf Question 7.
Goods returned by Senguttuvan were taken into stock, but no entry was passed in the books. While rectifying this error, which of the following accounts should be debited?
(a) Senguttuvan account
(b) Sales returns account
(c) Returns outward account
(d) Purchases returns account
Answer:
(b) Sales returns account
Rectification Of Errors Questions With Solutions Class 11 Question 8.
A credit purchase of furniture from Athiyaman was debited to purchases account. Which of the following accounts should be debited while rectifying this error?
(a) Purchases account
(b) Athiyaman account
(c) Furniture account
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Furniture account
Rectification Of Errors In Tamil Question 9.
The total of purchases book was overcast. Which of the following accounts should be debited in the rectifying journal entry?
(a) Purchases account
(b) Suspense account
(c) Creditor account
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Suspense account
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Solutions Question 10.
Which of the following errors will be rectified using suspense account?
(a) Purchases returns book was undercast by ₹ 100
(b) Goods returned by Narendran was not recorded in the books
(c) Goods returned by Akila ₹ 900 was recorded in the sales returns book as ₹ 90
(d) A credit sale of goods to Ravivarman was not entered in the sales book
Answer:
(a) Purchases returns book was undercast by ₹ 100
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 11th Accountancy Question 1.
What is meant by rectification of errors?
Answer:
Correction of errors in the books of accounts is not done by erasing, rewriting or striking the figures which are incorrect. Correcting the errors that has occured is called Rectification.
Chapter 9 Accountancy Class 11 Solutions Question 2.
What is meant by error of principle?
Answer:
It means the mistake committed in the application of fundamental accounting principles in recording a transaction in the books of accounts.
Rectification Of Errors Meaning In Tamil Question 3.
What is meant by error of partial omission?
Answer:
When the accountant has failed to record a part of the transaction, it is known as error of partial omission. This error usually occurs in posting. This error affects only one account.
Class 11th Accounts Chapter 9 Solutions Question 4.
What is meant by error of complete omission?
Answer:
It means the failure to record a transaction in the journal or subsidiary book or failure to post both the aspects in ledger. This error affects two or more accounts.
Accountancy Chapter 9 Class 11 Question 5.
What are compensating errors?
Answer:
The errors that make up for each other or neutralize each other are known as compensating errors. These errors may occur in related or unrelated accounts. Thus, excess debit or credit in one account may be compensated by excess credit or debit in some other account. These are also known as offsetting errors.
III. Short Answer Questions
Rectification Of Errors Class 11 Solutions Question 1.
Write a note on error of principle by giving an example.
Answer:
It means the mistake committed in the application of fundamental accounting principles in recording a transaction in the books of accounts.
Example:
Entering the purchase of an asset in the purchases book. Machinery purchased on credit for ₹ 10,000 by M/s. Anbarasi garments manufacturing company entered in the purchases book.
Question 2.
Write a note on suspense account.
Answer:
When the trial balance does not tally, the amount of difference is placed to the debit (when the total of the credit column is higher than the debit column) or credit (when the total of the debit column is higher than the credit column) to a temporary account is known as ‘suspense account’.
Question 3.
What are the errors not disclosed by a trial balance?
Answer:
Certain errors will not affect the agreement of trial balance. Though such errors occur in the books of accounts, the total of debit and credit balance will be the same. The trial balance will tally. Errors of complete omission, error of principle, compensating error, wrong entry in the subsidiary books are not disclosed by the trial balance.
Question 4.
What are the errors disclosed by a trial balance?
Answer:
Certain errors affect the agreement of trial balance. If such errors have occurred in the books of accounts, the total of debit and credit balances will not be the same. The trial balance will not tally. Error of partial omission and error of commission affect the agreement of trial balance.
Question 5.
Write a note on one – sided errors and two – sided errors.
Answer:
- One – sided errors: When preparing the trial’balance, if the total of debit balances and credit balances are not the same, there is disagreement of trial balance.
- Two – sided errors: Rectification of two – sided errors at the time of preparing the trial balance is just similar to that of their rectification before preparation of trial balance.
IV. Exercises
Question 1.
State the account/s affected in each of the following errors: (2 marks)
(a) Goods purchased on credit from Saranya for ₹ 150 was posted to the debit side of her account.
(b) The total of purchases book ₹ 4,500 was posted twice.
Answer:
(a) Purchases from Saranya should have been posted to the credit of Saranya’s A/c, but it has been debited. Hence, credit Saranya’s A/c with double the amount i.e., Rs. 300.
(b) Credit the Purchases A/c.
Question 2.
State the account/s affected in each of the following errors: (2 marks)
(a) Goods sold to Vasu on credit for ₹ 1,000 was not recorded in the sales book.
(b) The total of sales book ₹ 2,500 was posted twice.
Answer:
(a)
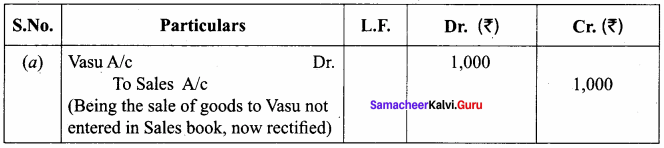
(b) Debit the Sales A/c
Question 3.
Rectify the following errors discovered before the preparation of the trial balance: (2 marks)
(a) Sales book was undercast by ₹ 100
(b) Purchases returns book was overcast by ₹ 200
Answer:
(a) Sales account should be credited with ₹ 100
(b) Purchases returns account should be debited with ₹ 200
Question 4.
Rectify the following errors before the preparation of trial balance: (3 marks)
(a) Returns outward book was undercast by ₹ 2,000
(b) Returns inward book total was taken as ₹ 15,000 instead of ₹ 14,000
(c) The total of the purchases account was carried forward ₹ 100 less.
Answer:
(a) Returns outward Account should be credited with ₹ 2,000
(b) Sales returns account should be credited with ₹ 1,000
(c) Purchases account should be debited with ₹ 100
Question 5.
Rectify the following errors assuming that the trial balance is yet to be prepared: (5 marks)
(a) Sales book was undercast by ₹ 400
(b) Sales returns book was overcast by ₹ 500
(c) Purchases book was undercast by ₹ 600
(d) Purchases returns book was overcast by ₹ 700
(e) Bills receivable book was undercast by ₹ 800
Answer:
(a) Sales account should be credited with ₹ 400
(b) Sales returns account should be credited with ₹ 500
(c) Purchases account should be debited with ₹ 600
(d) Purchases returns account should be debited with ₹ 700
(e) Bills receivable account should be debited with ₹ 800
Question 6.
Rectify the following errors before preparing trial balance: (5 marks)
(a) The total of purchases book was carried forward ₹ 90 less.
(b) The total of purchases book was carried forward ₹ 180 more
(c) The total of sales book was carried forward ₹ 270 less.
(d) The total of sales returns book was carried forward ₹ 360 more.
(e) The total of purchases returns book was carried forward ₹ 450 less.
Answer:
(a) Purchases account should be debited ₹ 90
(b) Purchases account should be credited ₹ 180
(c) Sales account should be credited ₹ 270
(d) Sales returns account should be credited with ₹ 360
(e) Purchases returns account should be credited with ₹ 450
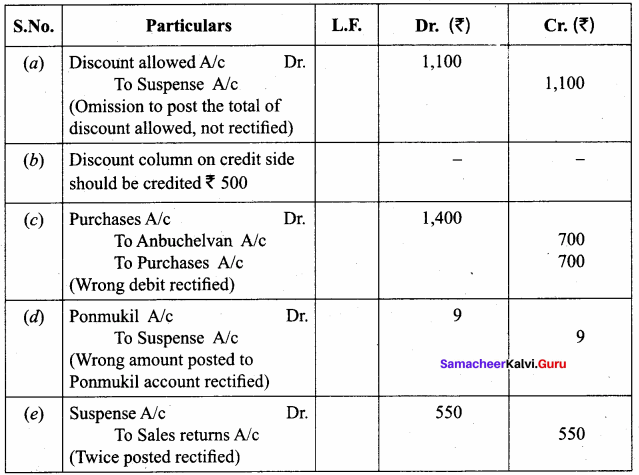
Question 7.
The following errors were located by the accountant before preparation of trial balance. Rectify them. (5 marks)
(a) The total of the discount column of ₹ 1,100 on the debit side of the cash book was not yet posted.
(b) The total of the discount column on the credit side of the cash book was undercast by ₹ 500.
(c) Purchased goods from Anbuchelvan on credit for ₹ 700 was posted to the debit side of his account.
(d) Sale of goods to Ponmukil on credit for ₹ 78 was posted to her account as ₹ 87.
(e) The total of sales returns book of ₹ 550 was posted twice.
Answer:
Question 8.
The accountant of a firm located the following errors before preparing the trial balance. Rectify them. (5 marks)
(a) Machinery purchased for ₹ 3,000 was debited to purchases account.
(b) Interest received ₹ 200 was credited to commission account.
(c) An amount of ₹ 1,000 paid to Tamilselvan as salary was debited to his personal account.
(d) Old furniture sold for ₹ 300 was credited to sales account.
(e) Goods worth ₹ 800 purchased from Soundarapandian on credit was not recorded in the books of accounts.
Answer:
Rectifying Journal
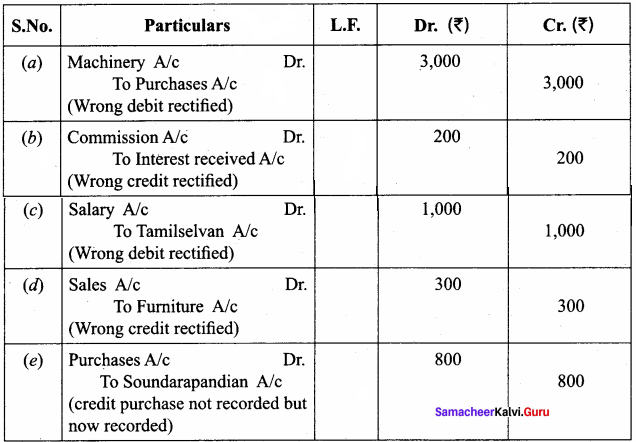
Question 9.
Rectify the following errors which were located before preparing the trial balance. (5 marks)
(a) Wages paid ₹ 2,000 for the erection of machinery was debited to wages account.
(b) Sales returns book was short totalled by ₹ 1,000.
(c) Goods purchased for ₹ 200 was posted as ₹ 2,000 to purchases account.
(d) The sales book was overcast by ₹ 1,500.
(e) Cash paid to Mukil ₹ 2,800 which was debited to Akhil’s account as ? 2,000.
Answer:
Rectifying Journal
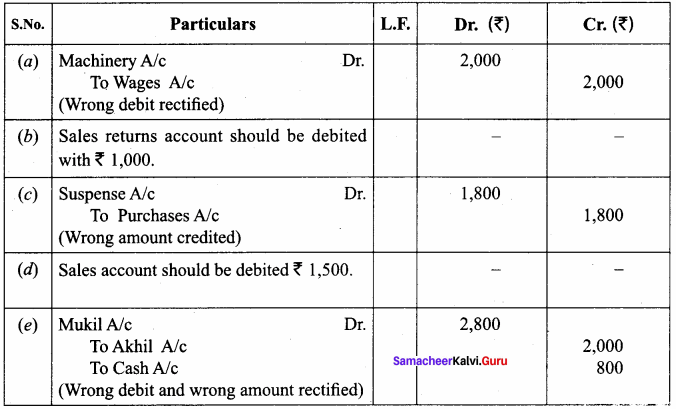
Question 10.
Rectify the following errors which were located at the time of preparing the trial balance: (5 marks)
(a) The total of the discount column on the debit side of the cash book of ₹ 225 was posted twice.
(b) Goods of the value of ₹ 75 returned by Ponnarasan was not posted to his account.
(c) Cash received from Yazhini ₹ 1,000 was not posted.
(d) Interest received ₹ 300 has not been posted.
(e) Rent paid ₹ 100 was posted to rent account as ₹ 10.
Answer:
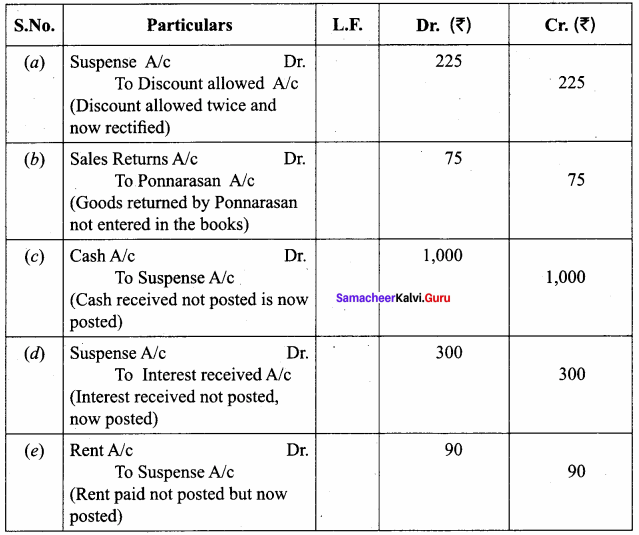
Question 11.
The following errors were located at the time of preparing trial balance. Rectify them. (5 marks)
(a) A personal expense of the proprietor ₹ 200 was debited to travelling expenses account.
(b) Goods of ₹ 400 purchased from Ramesh on credit was wrongly credited to Ganesh’s account.
(c) An amount of ₹ 500 paid as salaries to Mathi was debited to his personal account.
(d) An amount of ₹ 2,700 paid for extension of the building was debited to repairs account.
(e) A credit sale of goods of ₹ 700 on credit to Mekala was posted to Krishnan’s account.
Answer:
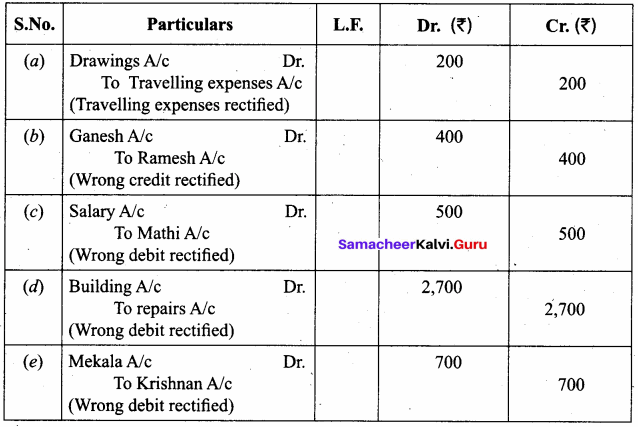
Question 12.
Rectify the following journal entries. (5 marks)
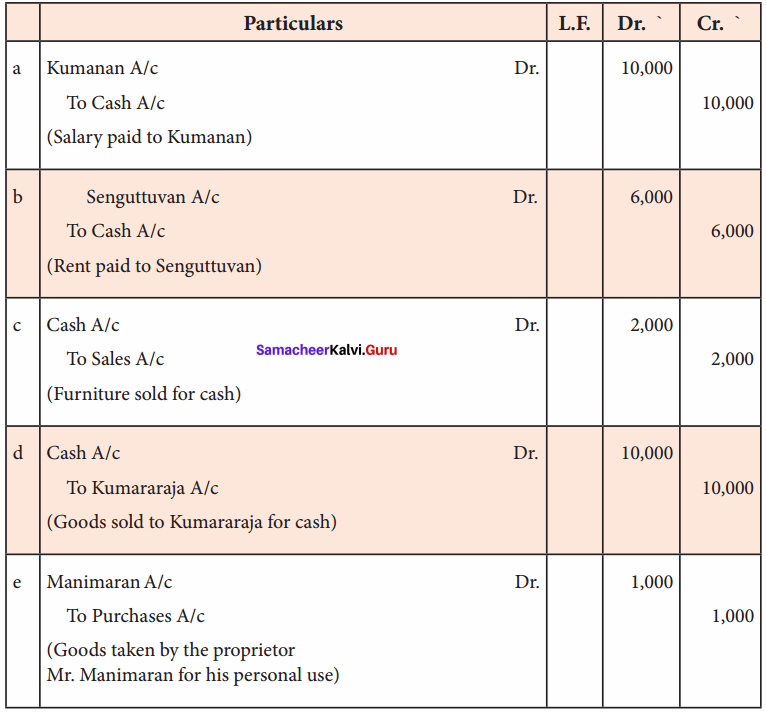
Answer:
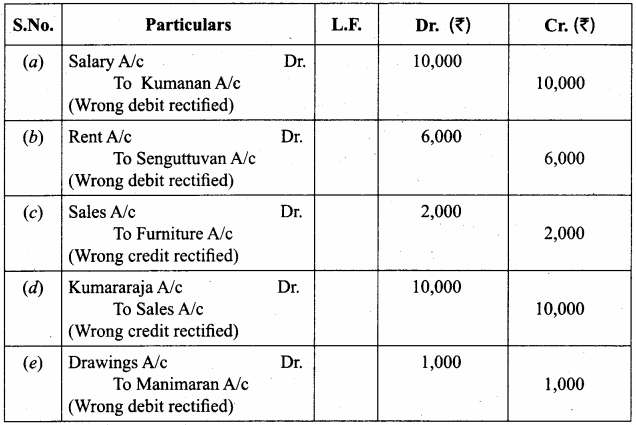
Question 13.
Rectify the following errors discovered after the preparation of the trial balance: (5 marks)
(a) Rent paid was carried forward to the next page ₹ 500 short.
(b) Wages paid was carried forward ₹ 250 excess.
Answer:
(a) Rent account is to be debited with ₹ 500.
(b) Wages account is to be credited with ₹ 250.
Question 14.
Rectify the following errors after preparation of trial balance: (5 marks)
(a) Salary paid to Ram ₹ 1,000 was wrongly debited to his personal account.
(b) A credit sale of goods to Balu for ₹ 450 was debited to Balan.
Answer:
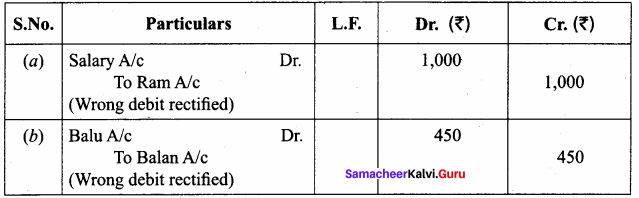
Question 15.
Pass necessary journal entries to rectify the following errors located after the preparation of trial balance: (5 marks)
(a) Sales book was undercast by ₹ 1,000.
(b) An amount of ₹ 500 paid for wages was wrongly posted to machinery Account.
Answer:
(a) Sales account should be credited ₹ 1,000.
(b)
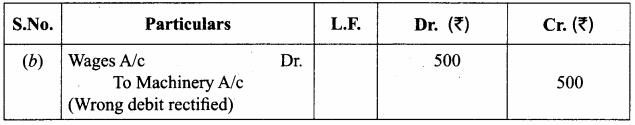
Question 16.
Give journal entries to rectify the following errors discovered after the preparation of trial balance: (5 marks)
(a) Purchases book was overcast by ₹ 10,000.
(b) Repairs to furniture of ₹ 500 was debited to furniture account.
(c) A credit sale of goods to Akilnilavan for ₹ 456 was credited to his account as ₹ 654.
Answer:
(a) Purchases account should be credited ₹ 10,000.
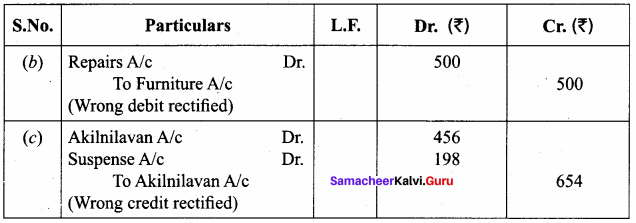
Question 17.
Rectify the following errors located after the preparation of trial balance: (5 marks)
(a) Purchases book was undercast by ₹ 900.
(b) Sale of old furniture for ₹ 1,000 was credited to sales account.
(c) Purchase of goods from Arul for ₹ 1,500 on credit was not recorded in the books.
Answer:
(a) Purchases account should be debited with ₹ 900.
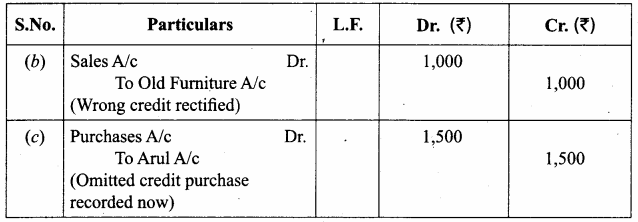
Question 18.
The following errors were located after the preparation of trial balance. Pass journal entries to rectify them. Assume that there exists a suspense account. (5 marks)
(a) The total of sales book was undercast by ₹ 350.
(b) The total of the discount column on the debit side of cash book ₹ 420 was not posted.
(c) The total of one page of the purchases book of ₹ 5,353 was carried forward to the next page as ₹ 5,533.
(d) Salaries ₹ 2,400 was posted as ₹ 24,000.
(e) Purchase of goods from Sembiyanmadevi on credit for ₹ 180 was posted to her account as ₹ 1,800.
Answer:
Rectifying Journals
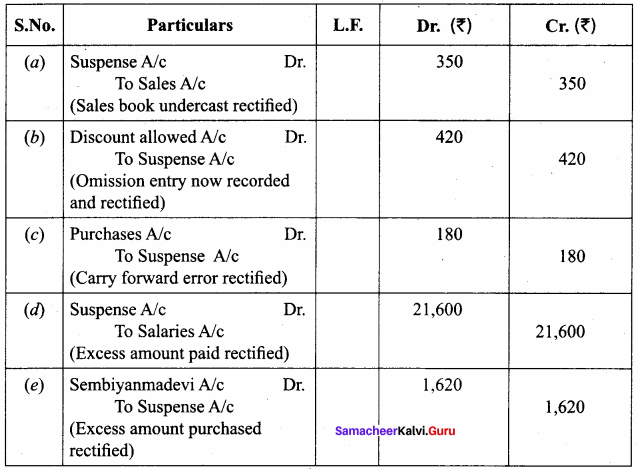
Question 19.
Rectify the following errors assuming that, the trial balance is already prepared and the difference was placed to suspense account: (5 marks)
(a) Sales book was undercast by ₹ 250.
(b) Purchases book was undercast by ₹ 120.
(c) Sales book was overcast by ₹ 130.
(d) Bills receivable book was undercast by ₹ 75.
(e) Purchases book was overcast by ₹ 35.
Answer:
(a) Sales account should be credited ₹ 250.
(b) Purchases account should be debited ₹ 120.
(c) Sales account should be debited ₹ 130.
(d) Bills receivable account should be debited ₹ 75.
(e) Purchases account should be credited ₹ 35.
Question 20.
The following errors were located after the preparation of trial balance. The difference in trial balance has been taken to suspense account. Rectify them. (5 marks)
(a) The total of purchases book was carried forward ₹ 70 less.
(b) The total of sales book was carried forward ₹ 340 more.
(c) The total of purchases book was carried forward ₹ 150 more.
(d) The total of sales book was carried forward ₹ 200 less.
(e) The total of purchases returns book was carried forward ₹ 350 less.
Answer:
Rectifying Journals
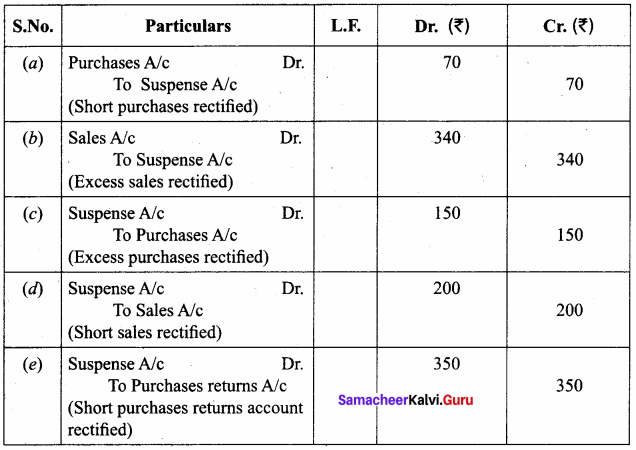
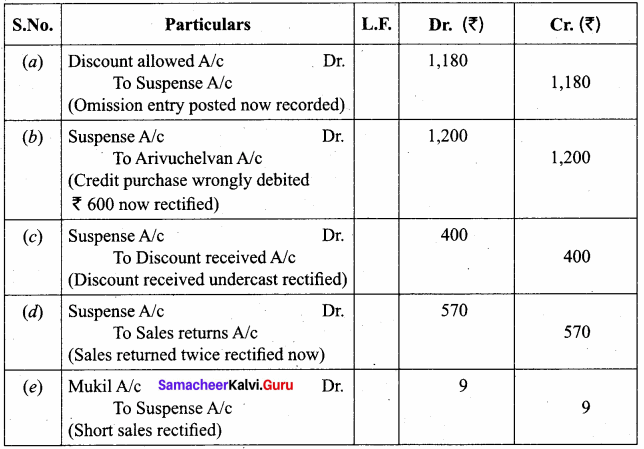
Question 21.
The following errors were located by the accountant after the preparation of trial balance. There exists a suspense account. Rectify them. (5 marks)
(a) The total of the discount column of ₹ 1,180 on the debit side of the cash book was not posted.
(b) Purchase of goods from Arivuchelvan on credit for ₹ 600 was posted to the debit side of his account.
(c) The total of the discount column on the credit side of the cash book was undercast by ₹ 400.
(d) The total of sales returns book of ₹ 570 was posted twice.
(e) Sold goods to Mukil on credit for ₹ 87 was posted to her account as ₹ 78.
Answer:
Question 22.
The accountant of a firm located the following errors after preparing the trial balance. Rectify them assuming that there is a suspense account. (5 marks)
(a) Machinery purchased for ₹ 3,500 was debited to purchases account.
(b) ₹ 1,800 paid to Raina as salary was debited to his personal account.
(c) Interest received ₹ 200 was credited to commission account.
(d) Goods worth ₹ 1,800 purchased from Amudhanila on credit was not recorded in the books of accounts.
(e) Used furniture sold for ₹ 350 was credited to sales account.
Answer:
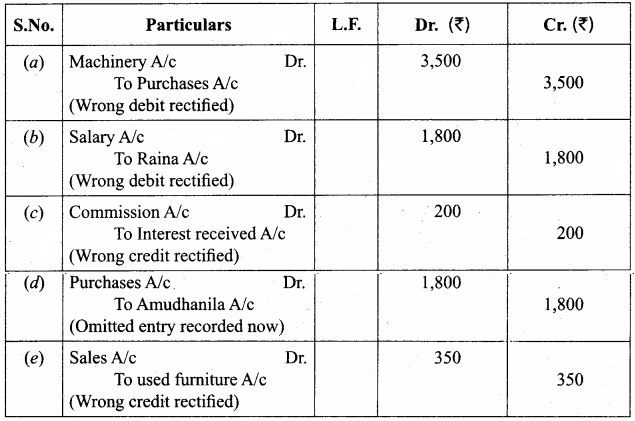
Question 23.
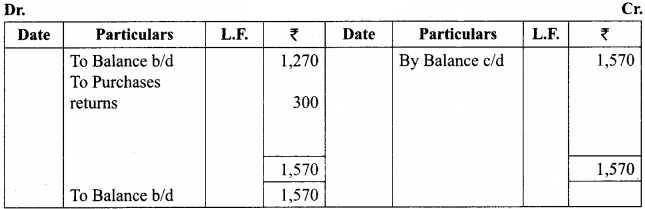
The book – keeper of a firm found that the trial balance was out by ₹ 922 (excess credit). He placed the amount in the suspense account and subsequently found the following errors: (5 marks)
(a) The total of discount column on the credit side of the cash book ₹ 78 was not posted in the ledger.
(b) The total of purchases book was short by ₹ 1,000.
(c) A credit sale of goods to Natarajan for ₹ 375 was entered in the sales book as ₹ 735.
(d) A credit sale of goods to Mekala for ₹ 700 was entered in the purchases book. You are required to give rectification entries and prepare suspense account.
Answer:
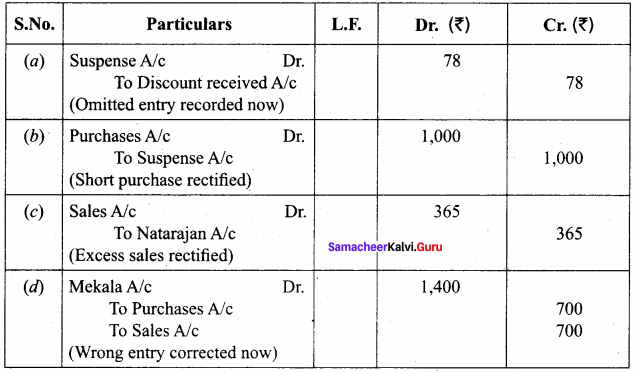
Suspense Account
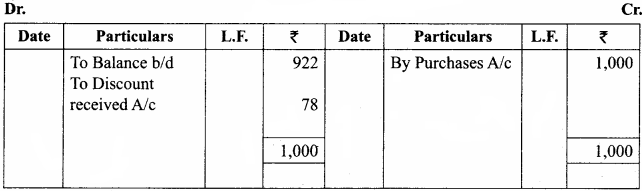
Question 24.
The books of Raman did not agree. The accountant placed the difference of ₹ 1,270 to the debit of suspense account. Rectify the following errors and prepare the suspense account:
(a) Goods taken by the proprietor for his personal use ₹ 75 was not entered in the books.
(b) A credit sale of goods to Shanmugam for ₹ 430 was credited to his account as ₹ 340.
(c) A purchase of goods on credit for ₹ 400 from Vivek was entered in the sales book. However, Vivek’s account was correctly credited.
(d) The total of the purchases returns book ₹ 300 was not posted.
Answer:
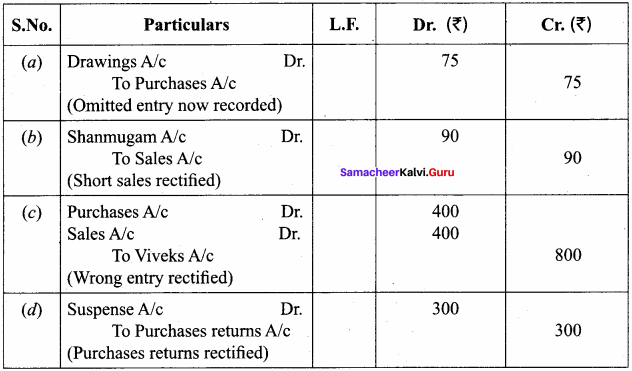
Suspense Account
Textbook Case Study Solved
Question 1.
Rameela, a class 11 student, visited one of her relative’s furniture shop. She met the accountant of the shop. He was busy with preparing final accounts. At that time, one of the staff approached the accountant with a list of errors found in ledger postings. Rameela asked the accountant, in a surprised tone, “Is it possible to rectify the errors before preparing the final accounts?” The accountant replied, “Yes, it is!” final accounts?” The accountant replied,
“Yes, it is!”
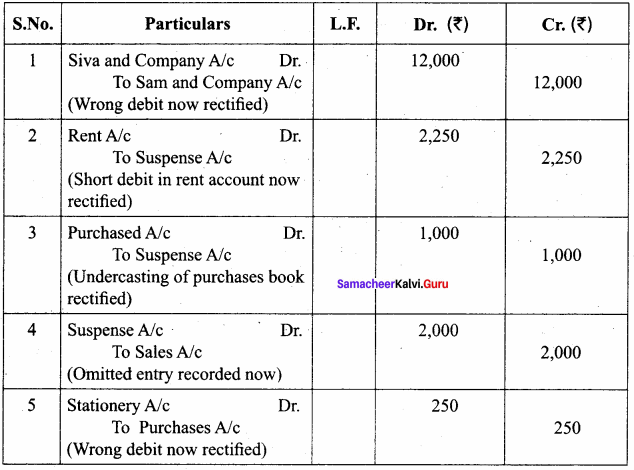
Rameela was curious to analyse the errors. She found the following:
- Furniture sold on credit to Siva and company for ₹ 12,000 was debited to Sam and company;
- Rent paid ₹ 2,500, was debited to rent account as ₹ 250.
- The total of purchase journal was undercast by ₹ 1,000.
- A sales invoice for ₹ 2,000, completely omitted from the books.
- Stationery bought for ₹ 250, was posted to purchases account.
Can you help Rameela to identify and rectify the errors?
Answer:
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Rectification of Errors Additional Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The errors can be classified into ……………… types.
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
Answer:
(d) Four
Question 2.
When the accountant has failed to record a part of the transaction is known as ………………
(a) Error of partial omission
(b) Error of commission
(c) Compensating errors
(d) Error of principle
Answer:
(a) Error of partial omission
Question 3.
The errors that make up for each other or neutralise each other are known as ………………
(a) Errors of commission
(b) Errors of principle
(c) Errors of omission
(d) Compensating errors
Answer:
(d) Compensating errors
Question 4.
The total of salary account is carried forward ₹ 1200 excess ……………….
(a) Errors in carry forward
(b) Errors in posting
(c) Errors in casting
(d) Errors of commission
Answer:
(a) Errors in carry forward
Question 5.
Sales book is undercast by ₹ 100, classify the error
(a) Errors of principle
(b) Errors of commission
(c) Errors in casting
(d) Errors of omission
Answer:
(c) Errors in casting
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is error of omission?
Answer:
The failure of the accountant to record a transaction or an item in the books of accounts is known as an error of omission. It can be complete omission or partial omission.
Question 2.
What is error of commission?
Answer:
When a transaction is incorrectly recorded, it is known as error of commission. It usually occurs due to lack of concentration or carelessness of the accountant.
Question 3.
What do you mean by errors?
Answer:
Errors means recording or classifying or summarising the accounting transactions wrongly or omissions to record them by a clerk or an accountant unintentionally.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the types of errors at the stage of journalising?
Answer:
- Error of omission
- Error of commission
- Error of principle
Question 2.
What are the types of errors at the stage of posting?
Answer:
(i) Errors of Omission:
(a) Error of complete omission
(b) Error of partial omission
(ii) Errors of Commission:
(a) Posting to wrong account
(b) Posting of wrong account
(c) Posting to the wrong side
Question 3.
What are the types of errors at the stage of preparing trial balance?
Answer:
(i) Error of Omission
(ii) Error of Commission:
(a) Entering to wrong account
(b) Entering wrong amount
(c) Entering to the wrong side of trial balance, etc.