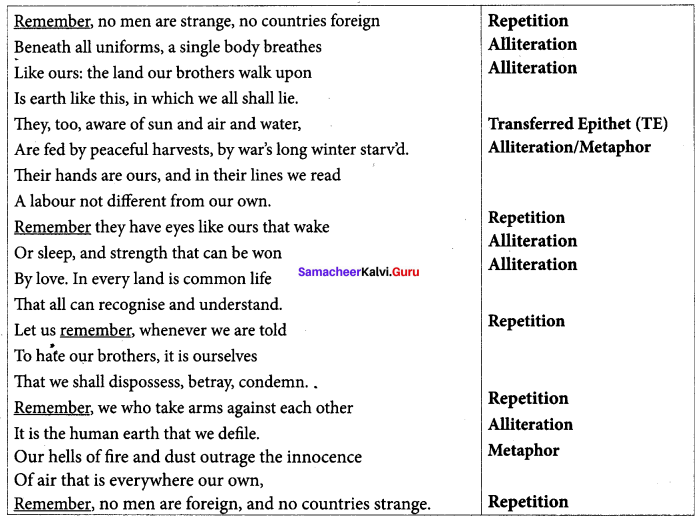
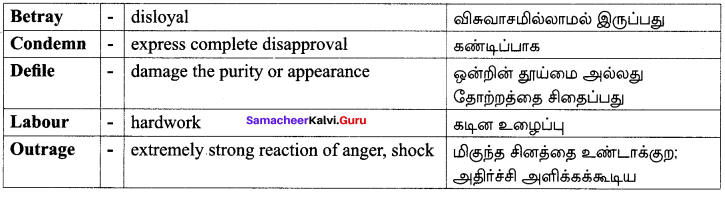
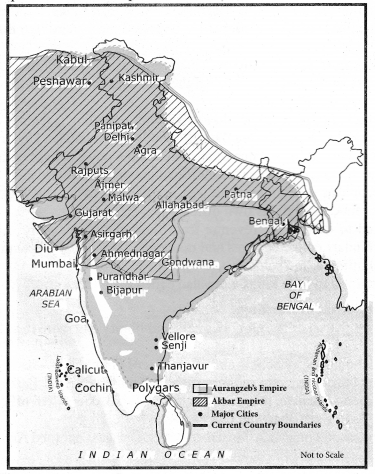
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Solutions Term 2 Chapter 3 Air
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Air Text Book Exercises
I. Choose the best answer
8th Science Air Lesson Question 1.
Which of the following is true about oxygen?
(a) Completely burning gas
(b) Partially burning gas
(c) Doesn’t support burning
(d) Supports burning
Answer:
(d) Supports burning
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 8th Science Question 2.
Aerated water contains –
(a) air
(b) oxygen
(c) carbon dioxide
(d) nitrogen
Answer:
(c) carbon dioxide
Question 3.
Solvay process is a method to manufacture –
(a) lime water
(b) aerated water
(c) distilled water
(d) sodium carbonate
Answer:
(d) sodium carbonate
Question 4.
Carbon dioxide with water changes –
(a) blue litmus to red
(b) red litmus to blue
(c) blue litmus to yellow
(d) doesn’t react with litmus
Answer:
(a) blue litmus to red
Question 5.
Which of the following is known as azote?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Sulphur
(d) Carbon dioxide
Answer:
(b) Nitrogen
II. Fill in the blanks
- ……………. is called as vital life.
- Nitrogen is ……………. than air.
- ……………. is used as a fertilizer.
- Dry ice is used as a …………….
- The process of conversion of iron into hydrated form of oxides is called …………….
Answer:
- Oxygen
- lighter
- Nitrogen
- refrigerant
- rusting
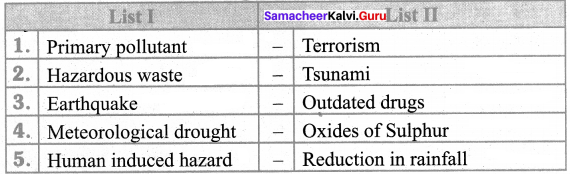
III. Match the following
Question 1.
- Nitrogen – Respiration in living animals
- Oxygen – Fertilizer
- Carbon dioxide – Refrigerator
- Dry ice – Fire extinguisher
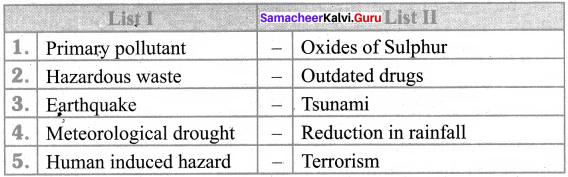
Answer:
- Nitrogen – Fertilizer
- Oxygen – Respiration in living animals
- Carbon dioxide – Fire extinguisher
- Dry ice – Refrigerator
IV. Answer briefly
Question 1.
What are the sources of oxygen?
Answer:
- Atmospheric air, water.
- Plants and animals.
- Minerals in the form of silicates, carbonates, oxides.
Question 2.
Mention the physical properties of oxygen.
Answer:
Physical properties of oxygen:
- Oxygen is a colorless, odorless and tasteless gas.
- It is a poor conductor of heat and electricity
- Oxygen dissolves readily in cold water.
- It is denser than air.
- It can be made into liquid (liquefied) at high pressure and low temperature.
- It supports combustion.
Question 3.
List out the uses of nitrogen.
Answer:
Uses of nitrogen:
- Liquid nitrogen is used as a refrigerant.
- It provides an inert atmosphere for conducting certain chemical reactions.
- It is used to prepare ammonia (by Haber’s process) which is then converted into fertilizers and nitric acid.
- It is used for inflating tyres of vehicles.
Question 4.
Write about the reaction of nitrogen with non metals.
Answer:
Nitrogen reacts with non-metals like hydrogen, oxygen etc., at high temperature to form their corresponding nitrogen compounds.
Non-metal + Nitrogen \(\underrightarrow { \Delta } \) Nitrogen compound
Example:
![]()
Question 5.
What is global warming?
Answer:
The increased green house effect is caused due to increase in the air pollutants and it results in the average increase of temperature of the atmosphere. This is called as Global warming.
Question 6.
What is dry ice? What are its uses?
Answer:
- Solid carbon dioxide, called as dry ice is used as a refrigerant.
- The gas is so cold that moisture in the air condenses on it, creating a dense fog which is used in stage shows and movie effects.
V. Answer in detail
Question 1.
What happens when carbon dioxide is passed through lime water? Write the equation for this reaction.
Answer:
When a limited amount of CO2 is passed through lime water, it turns milky due to the formation of insoluble calcium carbonate.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
When an excess amount of CO2 is passed through lime water, it first turns milky and the milkyness disappears due to the formation of soluble calcium hydrogen carbonate, Ca(HCO3)2.
Question 2.
Name the compounds produced when the following substances burn in oxygen:
- Carbon
- Sulphur
- Phosphorous
- Magnesium
- Iron
- Sodium
Answer:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Sulphur dioxide (SO2)
- Phosphorus trioxide (P2O3) (or) Phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5)
- Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
- Iron Oxide (Fe2O3)
- Sodium Oxide (Na2O)
Question 3.
How does carbon dioxide react with the following?
- Potassium
- Lime water
- Sodium hydroxide
Answer:
1. Potassium combine with CO2 to form potassium carbonate.
4K + 3CO2 → 2K2CO3 + C
2. When a limited amount of CO2 is passed through lime water, it turns milky due to the formation of insoluble calcium carbonate.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
(Calcium carbonate)
Sodium hydroxide (base) is neutralized by carbon dioxide (acidic) to form sodium carbonate (salt) and water.
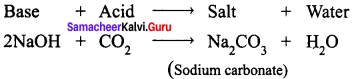
Question 4.
What are the effects of acid rain? How can we prevent them?
Answer:
Acid rain affects us in many ways. Some of the consequences are given below.
- It irritates eyes and skin of human beings.
- It inhibits germination and growth of seedlings.
- It changes the fertility of the soil, destroys plants and aquatic life.
- It causes corrosion of many buildings, bridges, etc.
Preventive measures:
Acid rain and its effects can be controlled by the following ways.
- Minimizing the usage of fossil fuel such as petrol, diesel etc.
- Using CNG (Compressed Natural Gas).
- Using non – conventional source of energy.
- Proper disposal of the industrial wastes.
VI. Higher Order Thinking Questions
Question 1.
Soda bottle bursts sometimes when it is opened during summer. Why?
Answer:
- In soda bottle carbon dioxide gas is dissolved in water under pressure.
- The gas in the bottle expands.
- Hence, the pressure inside the bottle increases.
- Thus the bottle may burst in hot summer.
Question 2.
It is said that sleeping beneath the tree during night is bad for health. What is the reason?
Answer:
During night trees absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide. Therefore, anyone who sleeps under tree, will not get oxygen, which can cause breathing problems, suffocation etc.
Question 3.
Why does the fish die when it is taken out of water?
Answer:
- Gills are richly supplied with blood capillaries and can readily absorb the oxygen dissolved in water.
- When fishes are taken out of water, the supply of oxygen to the fishes is cut as the fishes cannot absorb and breathe using the oxygen present in the atmosphere.
- Hence they die, when it is taken out of water.
Question 4.
How do astronauts breathe when they go beyond earth’s atmosphere?
Answer:
- Astronauts cannot breathe in space unless they carry their own oxygen with them.
- They can make their own oxygen by using energy from the solar arrays to split hydrogen and oxygen from water.
Do you know?
Question 1.
Nowadays nitrogen is used as a substitute for compressed air in tyres. Have you noticed it? Why do people prefer nitrogen instead of compressed air in tyres?
Answer:
It is because nitrogen tyres hold pressure longer as compared to compressed air. Nitrogen gas in the tyre escapes more slowly than compressed air does.
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Air Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Question 1.
…………… is necessary for all acids.
(a) Nitrogen
(b) CO2
(c) Oxygen
(d) Hydrogen
Answer:
(c) Oxygen
Question 2.
Tri oxygen molecule is known as ……………
(a) hydrogen
(b) oxygen
(c) nitrogen
(d) ozone
Answer:
(d) ozone
Question 3.
About 78% by volume of air is ……………
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Argon
(d) Oxygen
Answer:
(b) nitrogen
Question 4.
Carbon dioxide gas is ……………
(a) heavier than air
(b) lighter than air
(c) as heavy as air
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) heavier than air
Question 5.
A gas which neither burns nor supports burning is …………….
(a) Oxygen
(b) Helium
(c) Hydrogen
(d) Carbon dioxide
Answer:
(d) Carbon dioxide
Question 6.
A gas which is used to remove carbon impurities from steel.
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Oxygen
(c) Carbon dioxide
(d) Hydrogen
Answer:
(b) Oxygen
Question 7.
Venus atmosphere consists of roughly 96 – 97% of …………….
(a) Oxygen
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Carbon dioxide
(d) none
Answer:
(c) Carbon dioxide
Question 8.
Carbon dioxide gas is …………… in nature.
(a) basic
(b) acidic
(c) sweet
(d) none
Answer:
(b) acidic
Question 9.
…………… gas is essential for the proper growth of all plants.
(a) Nitrogen
(b) CO2
(c) Oxygen
(d) none
Answer:
(a) Nitrogen
Question 10.
Lighter metals like Na, K combine with CO2 to form corresponding …………….
(a) Nitrates
(b) Carbonates
(c) Oxide
(d) none
Answer:
(b) Carbonates
II. Fill in the Blanks
- …………… exists in nature as silicates, carbonates, oxides and water.
- Metals like magnesium, iron and sodium bum with oxygen and give basic …………….
- …………… has pH less than 5.6.
- CO2 is along with …………… in the manufacture of fertilizers like urea.
- CO2, N2O, CH4 and CFC are known as …………….
- ……………. is used to prepare soft drinks or aerated drinks.
- ……………. is used as a substitute for compressed air in tyres.
- Liquid nitrogen is used as a ……………..
- Oxygen is used to oxidize …………….
- Phosphorous bums with suffocating smell and gives ……………..
Answer:
- Oxygen
- Oxides
- Acid rain
- ammonia
- Greenhouse gases
- CO2
- Nitrogen
- refrigerant
- rocket fuel
- Phosphorous pentaoxide
III. Match the following
Question 1.
| 1. | Oxygen | (a) | Carbon dioxide |
| 2. | Azote | (b) | Nitrogen |
| 3. | Solvay process | (c) | Vital life |
| 4. | Gun powder | (d) | No life |
Answer:
- c
- d
- a
- b
Question 2.
| 1. | Nitrogen | (a) | Acid rain |
| 2. | CO2 | (b) | Global warming |
| 3. | Melting of glaciers | (c) | Volcanic gases |
| 4. | Corrosion of bridges | (d) | Aerated drinks |
Answer:
- c
- d
- b
- a
IV. True or False – if false give the correct statement
Question 1.
Oxygen is the poor conductor of heat and electricity.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Nitrogen is about two times more soluble in water then oxygen.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
Oxygen is about two times more soluble in water than Nitrogen.
Question 3.
Nitrogen is an essential element present in proteins and nucleic acids which are the building blocks of living things.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Non-metal + Nitrogen \(\underrightarrow { \Delta } \) Nitrogen compound.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Solid form of CO2 is called as dry ice which undergoes condensation.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
Solid form of CO2 is called as dry ice which undergoes sublimation.
Question 6.
Acid rain inhibits germination and growth of seedlings.
Answer:
True
Question 7.
An average increase in the temperature of the atmosphere is called as acid rain.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
An average increase in the temperature of the atmosphere is called as global warming.
Question 8.
Rain water is actually the purest form of water.
Answer:
True
Question 9.
The increase in the levels of greenhouse gases results in the gradual increase of temperature of the earth’s surface.
Answer:
True
Question 10.
Nitrogen gas is so cold that moisture in the air condenses on it, creating a dense fog.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
Solid CO2 gas is so cold that moisture in the air condenses on it, creating a dense fog.
V. Assertion and Reason
Question 1.
Mark the correct choice as:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If the assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) If the assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Question 1.
Assertion : Green house gases maintain the temperature.
Reason : Green house gases absorb the infra red rays.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
Question 2.
Assertion : Carbon dioxide occurs as carbonates in nature.
Reason : Carbon dioxide can exist as a liquid at atmospheric pressure.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
VI. Answer briefly
Question 1.
What is acid rain?
Answer:
Rain mixed with sulphuric acid is called acid rain.
Question 2.
Name some green house gases.
Answer:
CO2, N2O, CH4, CFC (Chlorofluorocarbon) etc.
Question 3.
Name the microbe which converts atmospheric nitrogen directly into soluble nitrogen compounds.
Answer:
Bacteria.
Question 4.
Write the reaction of oxygen with hydrocarbons.
Answer:
Hydrocarbon + O2 > CO2 + Water vapour + Heat energy + Light.
Question 5.
Write the reaction of carbon dioxide with lime water.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O.
Question 6.
Write any two preventive measures for acid rain.
Answer:
- Using CNG
- Proper disposal of the industrial wastes.
Question 7.
Write about the combustible property of Oxygen.
Answer:
Oxygen is a non – combustible gas as it does not bum on its own. It supports the combustion of other substances.
Question 8.
Write any two effects of global warming.
Answer:
- Increase in frequency of floods, soil erosion and unseasonal rains.
- Loss of biodiversity due to the extinction of coral reefs and other key species.
Question 9.
What do you mean by aerated water?
Answer:
Aerated water is nothing but carbon dioxide dissolved in water under pressure. This is also called soda water.
Question 10.
Write any two preventive measures of global warming.
Answer:
- Reduction in the use of fossil fuels.
- Restricting the use of CFC’s.
Question 11.
Write the reaction of oxygen with non – metals.
Answer:
Oxygen reacts with various non – metals like hydrogen, nitrogen, carbon, sulphur, phosphorus etc., to give corresponding non – metallic oxides which are generally acidic in nature.
Non – metal + Oxygen → Non – metallic oxide
Example:
C + O2 → CO2
Question 12.
Write a note on rusting process.
Answer:
The process of conversion of iron into its hydrated form of oxide in the presence of air and moisture (humid atmosphere) is called rusting. Rust is hydrated ferric oxide.
4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3
Fe2O3 + X H2O → 2Fe2O3 . X H2O
(X = Number of water molecules which is variable).
Question 13.
Write the reaction of nitrogen with metals.
Answer:
Nitrogen reacts with metals like lithium, calcium, magnesium etc., at high temperature to form their corresponding metal nitrides.
Metal + Nitrogen \(\underrightarrow { \Delta } \) Metal nitride
Example:
![]()
Question 14.
Write about occurrence of carbon dioxide.
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is present in air to the extent of about 0.03% in volume. It is evolved by the plants and animals during respiration and is produced during fermentation reactions. Much of the naturally occurring CO2 is emitted from the magma through volcanoes. CO2 may also originate from the bio – degradation of oil and gases. Human CO2 emissions upset the natural balance of the carbon cycle.
Question 15.
Write the reaction of carbon dioxide with metals.
Answer:
Lighter metals like sodium, potassium and calcium, combine with CO2 to form corresponding carbonates whereas magnesium gives its oxide and carbon.
Example :
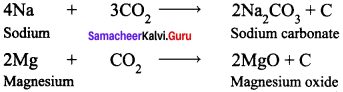
Question 16.
What are the effects of global warming?
Answer:
- Melting of ice cap and glaciers.
- Increase in frequency of floods, soil erosion and un – seasonal rains.
- Loss of biodiversity due to the extinction of coral reefs and other key species.
- Spreading of waterborne and insectborne diseases.
Question 17.
Complete the following:
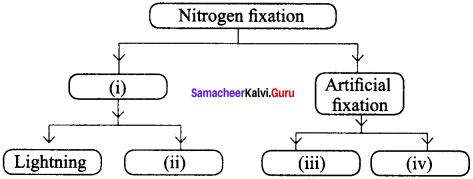
Answer:
- Natural fixation
- From leguminous plants
- From ammonia and ammonium salts
- From nitric acid and nitrate salts
Question 18.
What is green house effect?
Answer:
- Certain gaseous molecules present in the atmosphere absorb the infra red rays and reradiate the heat in all directions.
- Hence, these gases maintain the temperature of earth’s surface.
- The gases which absorb these radiations are called green house gases and this effect is called green house effect.
Question 19.
Complete the table:
| Metal | Condition | Product formed |
| K | Room temperature | (i) |
| Ca | (ii) | CaO |
| (iii) | Even at high temperature | No action |
| Fe | High temperature | (iv) |
Answer:
- Potassium oxide (K2O)
- Heating slightly
- Au or Pt
- Iron Oxide (Fe3O4)
VII. Answer in detail
Question 1.
Explain the uses of oxygen.
Answer:
Uses of oxygen:
- It is used as oxy – acetylene light for cutting and welding metals.
- It is used to remove carbon impurities from steel.
- Plants and animals use oxygen from the air for respiration.
- It is used to oxidize rocket fuel.
- It is used for artificial respiration by scuba divers, mountaineers, astronauts, patients etc.
- Mixed with powdered charcoal it is used as explosives.
- It is used in the synthesis of methanol and ammonia.
Question 2.
Write the physical properties of nitrogen.
Answer:
- Physical properties of nitrogen
- It is a colorless, tasteless and odorless gas.
- It is slightly lighter than air.
- It is slightly soluble in water.
- Nitrogen becomes a liquid at low temperature and looks like water. When it freezes, it becomes a white solid.
- It is neutral to litmus like oxygen.
Question 3.
Write the uses of nitrogen.
Answer:
Uses of Nitrogen:
- Liquid nitrogen is used as a refrigerant.
- It provides an inert atmosphere for conducting certain chemical reactions.
- It is used to prepare ammonia (by Haber’s process) which is then converted into fertilizers and nitric acid.
- It is used for inflating tyres of vehicles.
- It is used for filling the space above mercury in high temperature thermometer to reduce the evaporation of mercury.
- Many explosives such as TNT (Trinitrotoluene), nitroglycerin and gun powder contain nitrogen.
- It is used for the preservation of fresh foods, manufacturing of stainless steel, reducing fire hazards and as part of the gas in incandescent light bulbs.
Question 4.
- Explain the physical properties of carbon dioxide.
- Write the preventive measures to control the effect of global warming.
Answer:
1. Physical properties of carbon dioxide:
- Carbon dioxide is a colorless and odorless gas.
- It is heavier than air.
- It does not support combustion.
- It is fairly soluble in water and turns blue litmus slightly red. So it is acidic in nature.
- It can easily be liquefied under high pressure and can also be solidified. This
- solid form of CO2 is called dry ice which undergoes sublimation.
2. Preventive measures:
- Reduction in the use of fossil fuels.
- Controlling deforestation.
- Restricting the use of CFCs.
- Planting more trees.
- Reducing, reusing and recycling resources.
VIII. Higher Order Thinking Questions
Question 1.
What will happen if oxygen has the capacity to burn itself?
Answer:
If oxygen has the capacity to bum itself, striking a match stick will be enough to bum all the oxygen in our planet’s atmosphere.
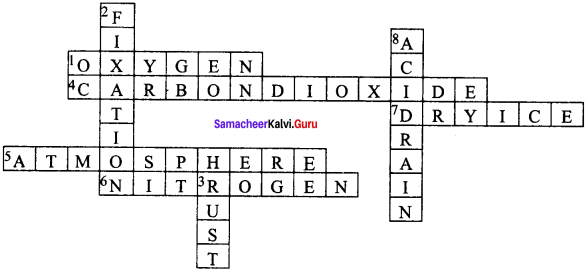
IX. Solve the crossword Puzzle by using the clues given below.
Question 1.
Across:
1. A gas that supports combustion.
4. The compound that turns lime water milky.
5. The Gaseous jacket that surrounds the Earth.
6. It is used as a refrigerant.
7. Solid form of carbon dioxide.
Down:
2. The process by which atmospheri&oitrogen is converted into nitrates.
3. The common name of the compound formed when nails are exposed to moist air.
8. It changes the fertility of the soil, destroys plants and aquatic life.
Answer: