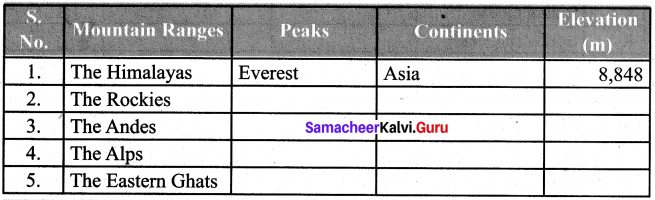
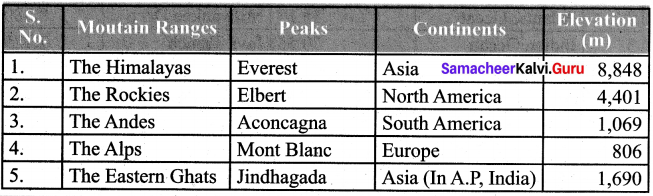
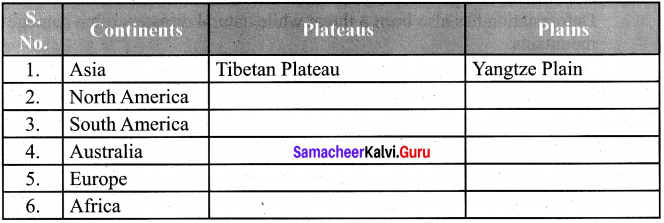
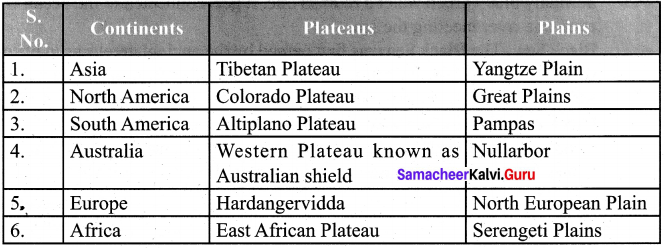
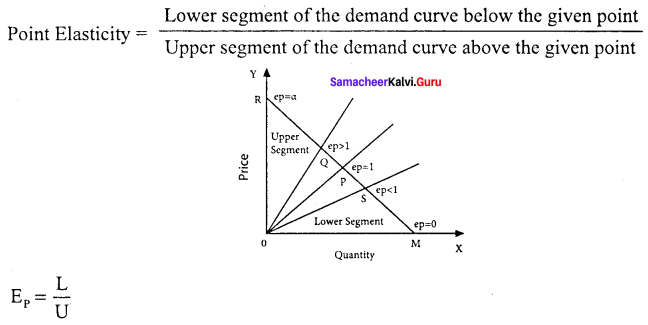
Students can Download English Poem 2 A Tragic Story A Memoir Questions and Answers, Summary, Activity, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th English Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th English Solutions Term 3 Poem Chapter 2 A Tragic Story
A Tragic Story Poem Summary Poem Overview
| Line No. | Poem Lines | Explanation |
| 1-2 | ‘There lived a sage in days of yore, And he a handsome pigtail wore; | Long ago, there lived a sage and he had a beautiful pigtail. |
| 3-4 | ‘But wondered much a sorrowed more, Because it hung behind him. | He wondered much about his pigtail’s position and was worried more, as it hung behind him. |
| 5-6 | ‘He mused upon this curious case, Ands wore he’d change the pigtail’s place,’ | He thought about this curious case and promised that he would change the position of the pigtail. |
| 7-8 | ‘And have it hanging at his face, Not dangling there behind him.’ | He would like to have it at his face and not swinging loosely behind him. |
| 9-10 | ‘Says he, “The mystery I’ve found- Says he, “The mystery I’ve found! ’ | The sage insists that he has found a solution to change the position of his pigtail. |
| 11-12 | ‘I ’ll turn me round, ’’ he turned him round; But still it hung behind him. ’ | He said that he would turn him round and so he turned him round. But still it hung steadily throughout the day. |
| 13-14 | ‘Then round and round, and out and in, All day the puzzled sage did spin;’ | The confused sage turned round and round, out and in continuously throughout the day. |
| 15-16 | ‘In vain-it mattered not a pin- The pigtail hung behind him.’ | Even though he turns continuously the whole day, it still hangs firmly behind him. |
| 17-18 | ‘And right and left and round about, And up and down and in and out ’ | He turned to his right and left and round about again. He turned up and down and in and out. |
| 19-20 | ‘He turned; but still the pistoil stout Hung stmdily bihind him’ | He turned and turned, but still the pigtail remained thick and hung steadily behind him. |
| 21-22 | ‘And though his efforts never slack, And though hi twist and twirtl and tack’ | Though his efforts were not slackened and though he twisted, twirled and tacked. |
| 23-24 | Alas! still faithful to his back The pigtail hangs behind him’ | The poet expresses his sorrow in a humorous way and says that though he tried his best to change the position of his pigtail, it remained faithfully behind him. |
A. Answer the following.
A Tragic Story Poem Questions And Answers Question 1.
What made the sage upset?
Answer:
The sage was upset, as his pigtail hung behind him.
The Tragic Story Questions And Answers Question 2.
Why did the sage spin all day?
Answer:
He spinned continually all day to change the position of his pigtail.
A Tragic Story Question 3.
What solution did he arrive at for the mystery that he found?
Answer:
He thought that if turned him round, he can change the position of his pigtail.
The Tragic Story Poem Summary In English Question 4.
Was he finally successful in changing his pigtail’s position? Support your answer with a line from the poem.
Answer:
No, he was not successful in changing his pigtail’s position. The line ‘Still faithful to his back, the pigtail hangs behind him’ supports this answer.
The Tragic Story Class 4 Question Answer Question 5.
Did something dreadful happen? How would you describe the events in the poem- comedy or tragedy?
Answer:
No, nothing dreadful happened. The events in the poem are humorous. The illogical behaviour of the sage creates humour throughout the poem.
B. Read the poem lines and answer the questions given below.
1. But wondered much and sorrowed more
Because it hung behind him.
Tragic Story Poem Summary Question a.
What was he wondering about?
Answer:
He was wondering about why his pigtail is behind him and how to change its position.
The Tragic Story Question b.
What does the word ‘it’ refer to here?
Answer:
It refers to the pigtail.
2. And though his efforts never slack
And though he twist, and twirl, and tack,
Alas! Still faithful to his back
The pigtail hangs behind him.
A Tragic Story Poem Lesson Plan Question a.
Pick out the rhyming words from the above lines and give the rhyme scheme for the same.
Answer:
The rhyming words are slack – tack – back. The rhyming scheme for this stanza is ‘a a a b’.
A Tragic Story Poem Pdf Question b.
Did he quit his trying? How can you say?
Answer:
No, he did not quit his trying. The lines ‘Though his efforts never slack and though he twist and twirl and tack’ indicate that he kept on trying.
3. ‘He mused upon this curious case ’
A Tragic Story Poem Question a.
What is the figure of speech used in this line?
Answer:
The figure of speech used here is hyperbole, as it exaggerates a simple foolish thing of changing the position of his pigtail to a curious case.
4. Irony is a figure of speech in which words are used in such a way that their intended meaning is different from the actual meaning. It may also be a situation that ends up in quite a different way than what is generally anticipated. In simple words, it is a difference between appearance and reality.
Can this poem be called an ironic poem? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Yes, this poem is an ironic poem because the word ‘sage’ is used in an ironic sense to refer to a person who is dull witted. It insists on how learned men lack practical common sense.
C. Fill in the table with the appropriate poem lines. A few lines may be used more than one time.

D. The summary of the poem is given. But there are some words missing. Fill in the blanks with the help of the box given below.
faithfully, change, pigtail, round, sage, down, slack, out, hung, place, behind, wain, face
Once upon a time there lived a sage. He had a handsome pigtail. He was worried and pondered over his pigtail’s place. He wanted to change its place. He wanted it hanging at his face. He didn’t like it hanging there behind him. So he turned right and left and round about, up and down, and in and out but it still hung behind him. However he tried, his efforts were in vain. But he didn’t slack in his efforts. Nevertheless his pigtail hung faithfully behind him.
E. Role Play.
Work with a partner. Let one student read the poem and the other to pantomime (communication by means of gesture and -facial expression) the poem as he or she reads.
(To be done by the students)
A Tragic Story Additional Questions
I. Poem Comprehension and Poetic Devices.
1. ‘There lived a sage in days of yore,
And he a handsome pigtail wore ’.
The Tragic Story Poem Summary In Hindi Question a.
Who lived long ago?
Answer:
A sage lived long ago.
Tragic Story Poem Question b.
What did he have?
Answer:
He had a beautiful pigtail.
The Tragic Story Poem Question c.
Pick out the rhyming words in these lines.
Answer:
The rhyming words are ‘yore – wore’.
2. ‘And swore he’d change the pigtail s place,
And have it hanging at his face
Not dangling there behind him.
Question a.
What did the sage swear?
Answer:
He swore that he would change his pigtail’s place.
Question b.
Where did he wants to have it?
Answer:
He wanted to have it hanging at his face.
Question c.
Pick out the alliterated words in these lines.
Answer:
The alliterated words are:
(1) pigtail’s – place
(2) have – hanging – his
3. ‘Then round and round, and out and in
All day the puzzled sage did spin;
In vain – it mattered not a pin
The pigtail hung behind him.
Question a.
What did the sage do?
Answer:
He turned round and round, out and in all day.
Question b.
Why was the sage puzzled?
Answer:
He was puzzled because he could not change the position of his pigtail, even though he turned round and round all day.
Question c.
What Is the rhyme scheme of the poem?
Answer:
The rhyme scheme is ‘a a a b’.
4. ‘Alas! Still faithful to his back’.
Question a.
Who Is faithful?
Answer:
The pigtail is faithful.
Question b.
Why did the poet use the word Alas’?
Answer:
He criticizes the sage’s ignorance and pities him in a serious tone, using the word ‘Alas’.
Question c.
Whose bag is referred to here?
Answer:
The back of the sage is referred to here.
II. Paragraph Questions.
Question 1.
What makes the poem humorous?
Answer:
The antics of the sage, usage of mock serious tone, absurdity of the sage’s ‘curious case’ and his solution, the way the poet organizes his materials and arranges the sentence structures makes the poem humorous. The repetition of the last line of each stanza add humour to the poem because it always brings to focus how the pigtail mocks at the sage’s efforts by stubbornly remaining behind him. The ending of the poem indicates the readers that the sage didn’t stop his rotation, although it is useless. This also gives a humorous touch to the poem.
Question 2.
What is the theme of the poem and what message does the poet convey?
Answer:
The theme of the poem is ‘when men are too learned or too wise, they lose the sight of reality. Sages are considered more wise. The irony of the poem is that the sage shows total foolishness. The poet uses the words in old English such as ‘sage’, ‘yore’, ‘mused’ to emphasize that right from the olden days, the highly learned people are too foolish and irrational. He attacks them as people, who do not have practical common sense. He also conveys a message to the readers to be alert and thoughtful and always act in a meaningful manner.
A Tragic Story Summary
The poem ‘A tragic story’ written by William Makepeace Thackeray is a humorous poem which revolves around a foolish act done by a sage. Throughout the poem, the poet laughs at this wise man, who does not have any practical knowledge, but uses his theatrical knowledge and does foolish things.
The poet narrates us about a sage, who lived in the past with a beautiful pigtail. He was worried about his pigtail, being hung behind him. He thought about this for a long time and swore that he would change the pigtail’s place, which is apparently impossible and funny.
He would like to have it at his face and not dangling there behind him. This small thing is a serious problem for this wise man. He said that he had found a solution to change the position of his pigtail. So he turned him round continuously without stopping, throughout the day. He turned in different directions – he turned right and left, out and in, up and down. But the pigtail didn’t change a bit. Though his efforts were not slackened, and though he twisted, twirled and tacked, his pigtail hung faithfully and steadily behind him. Thus, this poem is amusing and the poet brings out the theme
“How learned man lack practical common sense.”





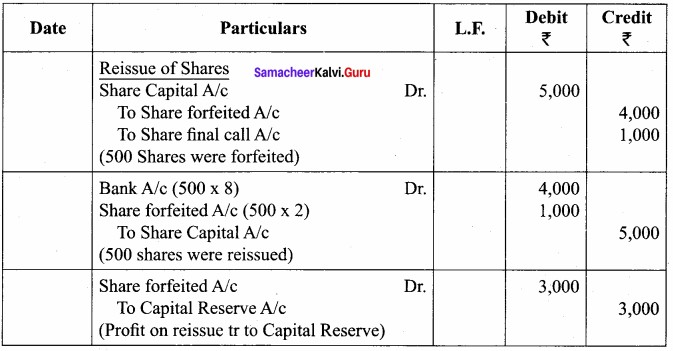
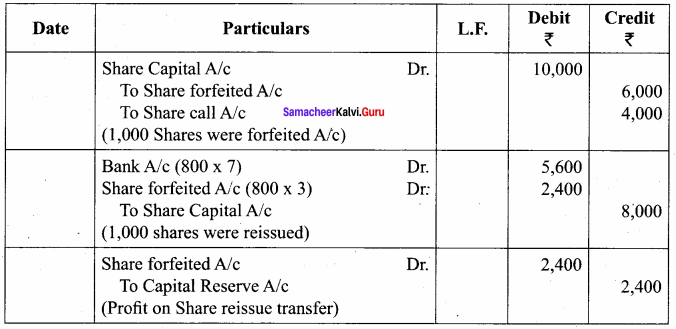
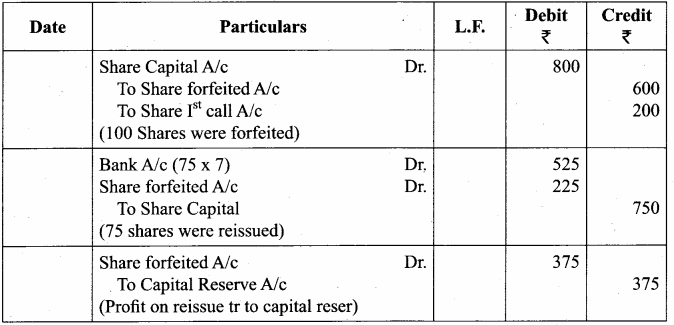
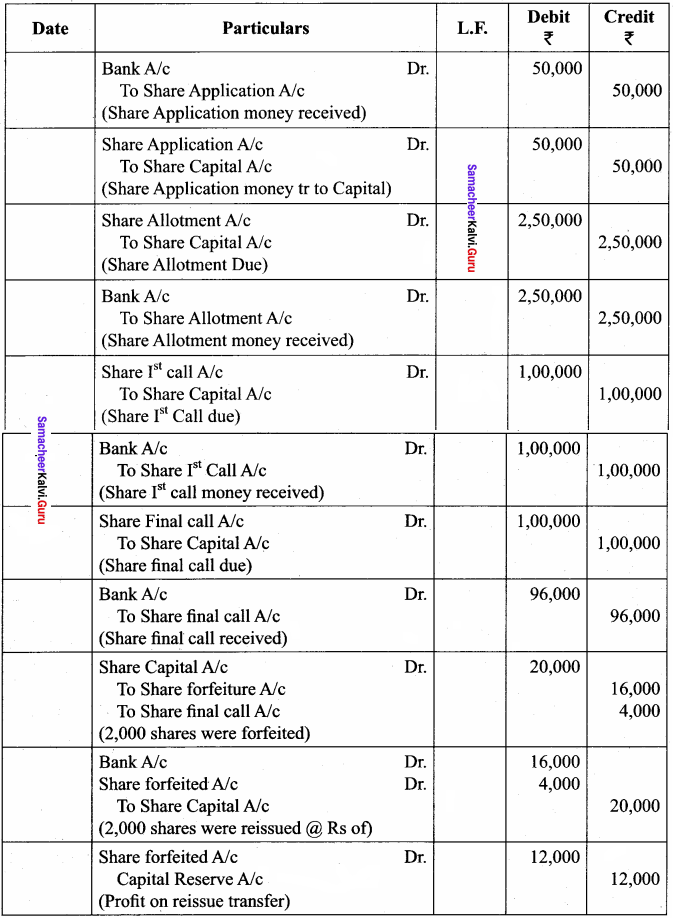

 “321” class=”alignnone size-full wp-image-36721″ />
“321” class=”alignnone size-full wp-image-36721″ />