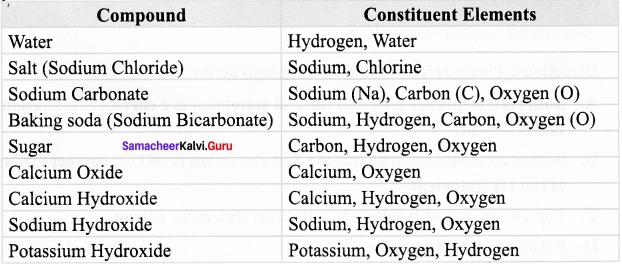
Students can Download English Lesson 1 Alice in Wonderland Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes Pdf, Activity, Samacheer Kalvi 7th English Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th English Solutions Term 2 Supplementary Chapter 1 Alice in Wonderland
Read And Understand
A. Identify the character / speaker.
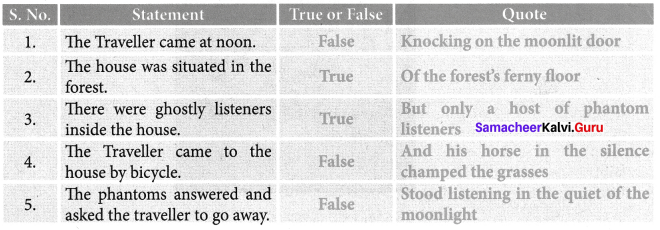
1. I must find out why he’s in such a hurry!
2. Go to my cottage and fetch my gloves and fan.
3. Oh no, I’ll never get back to the right size.
4. One side makes you big, the other side makes you small.
5. I’ll see you later at the Queen’s croquet game.
6. You may stay if you answer my riddle.
7. Wake up. You’ve been sleeping for too long.
Answer:
Alice
White Rabbit
Alice
Green Caterpillar
Cheshire Cat
Mad Hatter
Alice’s sister
B. Discuss and Answer.
Alice In Wonderland Book Back Answers Question 1.
Why did Alice follow the rabbit?
Answer
Alice saw a rabbit hurrying down a rabbit’s hole. She wanted to find out why the rabbit was in such a hurry. So she followed him.
Alice In Wonderland Questions And Answers Pdf Question 2.
Do you think this was a good idea?
Answer:
No, it was not a good idea.
Alice In Wonderland 7th Standard Book Question 3.
Why can’t Alice get through the little door into the garden?
Answer:
She couldn’t get into the garden through the little door because she was too big.
Alice In Wonderland 7th Standard Question 4.
Why does Alice drink from the bottle that says ‘DRINK ME’ and why does she eat from the cake that says ‘EAT ME’?
Answer:
Out of curiosity, Alice drank from the bottle that said ‘DRINK Me’. As she was hungry, she ate the cake that said ‘EAT ME’.
Alice In Wonderland Questions And Answers Question 5.
How does Alice feel after all these changes?
Answer:
She felt strange and realized that she would never get back to the right size.
7th Standard Alice In Wonderland Question 6.
What do you think is going to happen next?
Answer:
She may shrink again, after eating or touching anything.
C. Think and Answer.
Alice In Wonderland Supplementary 7th Standard Question 1.
What challenges does Alice face and how does she overcome them?
Answer:
Alice goes through a variety of strange physical changes. The discomfort she feels at never being the right size acts as a symbol for the changes that occur during her adolescence. She continually finds herself in a situation in which she risks death. She gets in trouble because of her curiosity. As Alice progresses through her dream, she loses her sense of identity. At. the beginning of her journey, she was confused, anxious and timid. Finally, she becomes a strong and confident girl, who is able to stand up for her.
Alice In Wonderland Question Answer Question 2.
Have you ever had a strange dream? Share your dream in the class.
Answer:
Yes, I had a strange dream last night. I went to bed late and was fast asleep. Suddenly, I felt that I was in a fairyland. There was a big garden. The flowers were blooming. The fairies were singing beautiful songs. One fairy came to me and offered me a small chair to sit on and enjoy the song. There I saw a little child playing on the flute. He arrived in the midst of the fairies. Some dwarfs and elves were sitting nearby. The child brought fruits for me. Everyone was dancing and singing happily. It was a pleasant and strange sight for me. Suddenly, I could hear my mother shouting at me to get up and to get ready to go to school. I woke up and was surprised to realize that it was only a pleasant and a strange dream.
D. Role play
Put students in pairs to role play a conversation between:
- Alice and her sister.
- Alice and White Rabbit
Alice and her sister.
Answer:
Alice : it Alice and White Rabbit.
Sister : Alice and her sister
Alice : What are you doing?
Sister : I am reading a book.
Alice : Let me see the book.
Sister : Here it is.
Alice : Are you reading a book without pictures or conversations in it?
Sister : Yes, I love to read these books.
Alice : What is the use of reading such a book? It is boring to read.
Sister : If it is boring for you, Please stay away from me.
Alice : This hot day makes me feel sleepy. Let me have a nap.
Alice and White Rabbit
Rabbit : Let me check the time. Oh my God. It’s late. I have to hurry.
Alice : Why are you in such a hurry?
Rabbit : I need to hurry for an important work.
Alice : Stop! Don’t run. I will chase you wherever you go.
Rabbit : I will go into my hole. You cannot enter it.
Alice : Why can’t I enter into the hole?
Rabbit : You are too big to enter into this hole.
Alice : Then what should I do?
Rabbit : You have to drink the little bottle on top of the table.
Alice : Oh Yes. I have shrunk in size after drinking from the bottle.
Rabbit : (Mistaking Alice for his maid). Go to my cottage and fetch my gloves and fan.
Alice : (confused) May be I’ll find something at the cottage to help me find my way out. I am hopeful.
E. Activity
It’s fun to help out in the kitchen. You can even practise reading aloud when reading the recipe. And you can learn a little math by figuring out how to measure. Here are a few fun items to make that are “Alice” themed.
Activity to be done by the Students.
F. Learning About Nature
Learn about caterpillars and.butterflies. Read a book about a caterpillar turning into a butterfly. You can get one from the library or go online and find information with pictures.
Students individual work.
Read a book about Caterpillars and Butterfly
Connecting to self
G. Tackling the issues
Ask the class to discuss solutions to an issue that plagues contemporary society at large or just your community for example, homelessness, violence, environmental degradation, hunger.
Half the class should mention idealistic solutions to the chosen issue; the Other half should mention only realistic approaches to solving the problem.
See if, in listening to both sides, someone can come up with a proposal that is both realistic and unconventional an idea that hasn’t been tried yet.
Answer:
Homelessness – Idealistic Solutions
Student No. 1 :
A permanent and sustainable end to homelessness requires four essential components.
1. Housing is the essential foundation to ending homelessness.
2. Housing is essential, but it is not sufficient. Housing alone, without attention to health, behavioural health, employment and education will continue to result in instability and recurrent homelessness for many people.
Student No. 2 :
1. A key to an apartment is great. But we have to stay connected with the society. Staying lonely in an apartment is not advisable.
2.People should be aware of new home loan plans and housing
Student No. 3 :
Proposal that is both realistic and unconventional:
We can end the homelessness crisis by stabilizing people through shelter, moving them into permanent housing and implementing assistance programs to keep them in their housing. Only then we can reduce and eliminate homelessness in India.
PROJECT
H. Imagine you are a marketing executive for a company in a specific industry (toothpaste, soup, hair care products, automobiles, etc) and are developing a product with a brand name that refers to a character from the story.
For example: You want to sell bandages that have little pictures of Don Quixote on them. Your company’s name is Kure-All and you decide to call them “Kure-All Quixote Bandages”.
The slogan might be: “Had a tough day with windmills? When you take a fall, use Kure-All.”
You can use exciting words, a catchy new slogan, and a jingle, among other things, to promote sales of your item.
Answer:
Marketing Products
1. “Are you tired chasing the rabbit for a long time?” Feel energetic, after a chase. Have “Alice Soup” for refreshment”.
2. “Cool your body with Cheshire hair oil and feel fresh”.
3. Want to reach your destination quickly? Go for “Lae March Hare Cars”.
Step To Success
J. Look at the number pattern. Fill the blank in the middle of the series or end of the series.
7th English Alice In Wonderland Question 1.
SCD,TEF,UGH,______,WKL
A) CMN
B) UJI
C) VIJ
D) IJT
Answer:
(C) VIJ
7th Standard English Alice In Wonderland Question 2.
FAG. GAF. HAL IAH,______,
A) JAK
B) HAL
C) HAK
D) JAI
Answer:
(A) JAK
Alice In Wonderland In Tamil 7th Standard Question 3.
F.T.FA. GT.HA. TLTA,______,MLNA
A) OLPA
B) KLMA
C) LLMA
D) KLLA
Answer:
(D) KLLA
Alice In Wonderland Answer Key Question 4.
CMM. F.OO. GOO,______,KUU
A) GRR
B) GSS
C) ISS
D) ITT
Answer:
(C) ISS
7th English Book Alice In Wonderland Question 5.
OPO. NML. KTI,______,EDC
A) HGF
B) CAB
C) JKL
D) GHI
Answer:
(A) HGF
Alice in Wonderland Additional Questions
I. Choose the Correct Answers (MCQ).
Question 1.
Alice was beginning to get_____
(a) upset
(b) tired
(c) irritated
(d) bored
Answer:
(b) tired
Question 2.
The hot day made her feel very ______ and stupid.
(a) sleepy
(b) frustrated
(c) calm
(d) active
Answer:
(a) sleepy
Question 3.
The Rabbit pulled a ______ out of his pocket.
(a) Twig
(b) brush
(c) watch
(d) paper
Answer:
(c) watch
Question 4.
There was nothing on it except a tiny ______ Key
(a) golden
(b) silver
(c) round
(d) iron
Answer:
(a) golden
Question 5.
She opened the door and saw a beautiful ______
(a) sight
(b) room
(c) garden
(d) paper
Answer:
(c) garden
II. dentify the Character / Speaker.
- “Why, I’m no bigger than the insects that crawl on these flowers.
- “Get out of my way! You’re blocking the door!”.
- “I want to be big again”.
- “There isn’t any”.
- “Why is a raven like a writing desk?”
Answer:
- Alice
- The White Rabbit
- Alice
- March Hare
- Mad Hatter
III. Write True or False against each statement.
- Out of curiosity, Alice followed the rabbit.
- Alice was unhappy with her tiny size at first
- The magical toy made her small again.
- Alice grew to her normal size after eating the mushroom.
- The Dormouse smiled at Alice while the Cheshire cat was sleeping.
Answer:
- True
- False
- False
- True
- False
IV. Very Short Questions with Answers.
Question 1.
Why was Alice tired of sitting by her sister?
Answer:
Alice was doing nothing, as her sister was reading a book.
Question 2.
Why did the rabbit pull out a watch out of his pocket?
Answer:
The rabbit did so to check the time.
Question 3.
What did Alice do at the rabbit’s hole?
Answer:
Alice ran to the rabbit’s hole and peeped through the entrance.
Question 4.
What was there on a three-legged table?
Answer:
There was a tiny golden key on it.
Question 5.
What was the green Caterpillar wearing?
Answer:
The green Caterpillar was wearing a pink jacket.
Question 6.
What did the Cheshire cat tell Alice before disappearing?
Answer:
The Cheshire cat told him that it would see Alice later at the Queen’s croquet game.
Question 7.
What were March Hare and Mad Hatter having?
Answer:
The March Hare and Mad Hatter were having tea.
Question 8.
Where was the Dormouse sitting?
Answer:
The Dormouse was sitting between March Hare and Mad Hatter.
Question 9.
Did Alice solve the riddle?
Answer:
Alice did not solve the riddle.
Question 10.
Why did the trumpet sound?
Answer:
The trumpet sounded in a distance calling the court to session
V. Short Questions with Answers.
Question 1.
What did Alice think of doing when she got bored?
Answer:
She thought that it was a pleasure to make a daisy-chain by getting up and picking the daisies fallen on the ground.
Question 2.
Describe the green Caterpillar.
Answer:
The green Caterpillar was dressed in a pink jacket. He was sitting on the top of a large mushroom, smoking a bubble pipe.
Question 3.
What did a gardener do?
Answer:
One gardener had planted white roses by mistake. He then painted them red, as the Queen hated white roses.
VI. Paragraph Questions with Answers.
Question 1.
What happened to Alice, when she drank from the bottle?
Answer:
Alice finds a tiny key and fits it into the tiny lock of a 15 inch high door. She peers inside and sees a beautiful garden. She wishes she could get through it. But even her head was too big. She then notices a bottle with a printed label that reads ‘Drink me’. She drinks the liquid from the bottle. She realizes that she is shrinking
down. She shrinks down to 10 inches high. She feels happy because she will be able to reach the garden. She is soon reassured that she will not shrink anymore, as she was a bit worried that she could keep shrinking down.
Question 2.
What is the most important literary element and message in ‘Alice in Wonderland’?
Answer:
The most important literary element in ‘Alice in Wonderland’ is fantasy. The message conveyed in this story for children is about the value of questioning our identity. One can question one’s identity at any age, but Alice in particular, questions her identity throughout the story, which marks her transition from childhood to adulthood. It is symbolized by her physical changes in size and shape. As we read the story, we can even see Alice reflecting on how different she was before her adventure began.
VII. Rearrange the following sentences in coherent order.
1. The Dormouse slept and the Cheshire cat smiled at her.
2. “And now you must be punished. Off with her head” yelled the Queen
3. “What’s going on?” asked Alice.
4. “Court is now in session” announced the white rabbit.
5. “How silly”, replied Alice. ‘I did not have the slightest idea what you were talking about. I was only playing croquet.
6. “You are guilty of stealing the delicious heart-shaped tarts” accused the Queen.
7. Everyone rushed into the courtroom.
8. “Will Alice please come to the stand?”
9. Alice felt someone touch her shoulder, ‘wake up’.
10. Alice took the stand and looked at the jury box, where March Hare and the Mad Hatter were making noise.
Answer:
7, 4, 8,10,1, 3, 6, 2, 5, 9.
7. Everyone rushed into the courtroom.
4. “Court is now in session” announced the white rabbit.
8. “Will Alice please come to the stand?”
10. Alice took the stand and looked at the jury box, where March Hare and the Mad Hatter were making noise.
1. The Dormouse slept and the Cheshire cat smiled at her.
3. “What’s going on?” asked Alice.
6. “Your are guilty of stealing the delicious heart-shaped tarts” accused the Queen.
2. “And now you must be punished. Off with her head” yelled the Queen.
5. “How silly”, replied Alice. ‘I did not have the slightest idea what you were talking about. I was only playing croquet.
9. Alice felt someone touch her shoulder, ‘wake up’.
VIII. Read the passage and answer the questions.
A.
When she turned around towards the three-legged table, Alice found a green bottle that said ’ “DRINK ME” magically appeared on it. Out of curiosity, Alice took the bottle and drunk the
entire potion. Then, she began to shrink until she was no bigger than a doll.
Question 1.
What did Alice find on the three legged table?
Answer:
She found a green bottle that said, “DRINK ME”.
Question 2.
Why did Alice take the bottle?
Answer:
Alice took the bottle because she was curious to know about it.
Question 3.
What happened to her, when she drank the entire potion in it?
Answer:
She began to shrink, until she was no bigger than a doll.
B.
There was a table set out under a tree in front of the house, and the March Hare and the Hatter were having tea at it: A Dormouse was sitting between them, fast asleep, and the other two were using it as a cushion, resting their elbows on it, and talking over its head.
Question 1.
What was there in front of the house?
Answer:
There was a table set under a tree in front of the house.
Question 2.
Where was the Dormouse sitting? What was it doing?
Answer:
Dormouse was sitting between Mad Hatter and March Hare. It was fast asleep.
Question 3.
What were Mad Hatter and March Hare doing?
Answer:
They were resting their elbows on the Dormouse, talking over its head and having tea.
C.
Alice felt someone touch her shoulder, “Wake up. You’ve been sleeping for too long,” said her sister softly. “I had a strange dream,” said Alice. She told her sister about the White Rabbit, the mad tea party, the Queen of Hearts and the trial. But her sister wasn’t paying attention.”
Question 1.
Who touched Alice’s shoulder?
Answer:
Alice’s sister touched her shoulder and woke her up.
Question 2.
What did Alice tell her?
Answer:
Alice told her that she had a strange dream. She told her about the white rabbit, the mad tea party, the Queen of Hearts and the trial.
Question 3.
Was her sister paying attention to her?
Answer:
No, her sister was not paying any attention to her.
Alice in Wonderland Summary
Lewis Carroll’s “Alice in Wonderland” opens with a scene of Alice reading over her sister’s shoulder. Alice sees a White Rabbit down a rabbit hole and decides to follow him. In Wonderland, she meets an assortment of strange characters including the Cheshire cat, who advises her to attend to tea party thrown by the March Hare. After the Mad Hatter tries to cut her hair, Alice runs away from the tea party. She soon finds herself in a garden, where servants are painting white roses red to satisfy the Queen of Hearts. Alice is called upon to testify against a bad thief. When Alice says that she knows nothing about the crime, the Queen orders her execution. Alice wakes up at the last minute to realize that was all a dream.