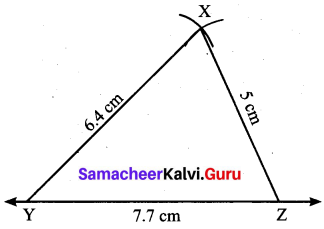
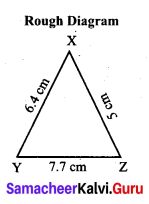
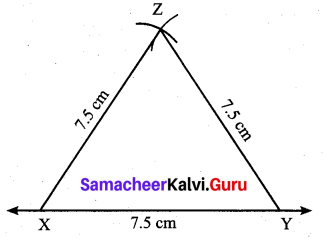
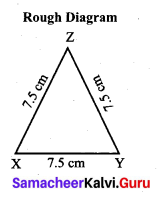
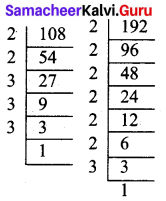
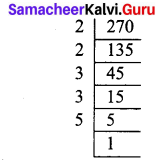
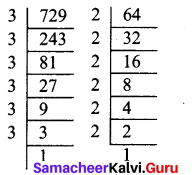
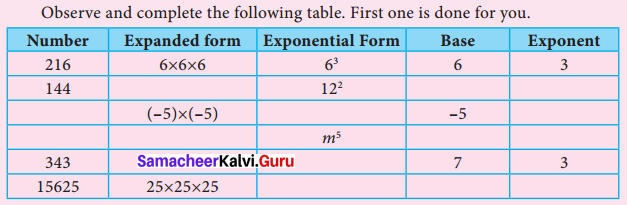
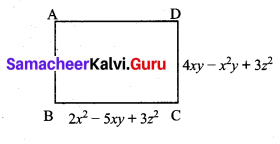
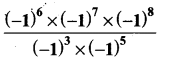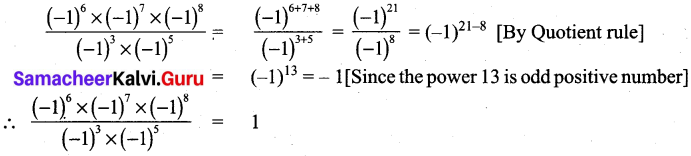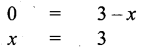Students can Download Maths Chapter 4 Geometry Additional Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Maths Solutions Term 2 Chapter 4 Geometry Additional Questions
Additional Questions and Answers
Exercise 4.1
Question 1.
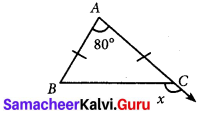
“The sum of any two angles of a triangle is always greater than the third angle”. Is this statement true. Justify your answer.
Solution:
No, the sum of any two angles of a triangle is not always greater than the third angle. In an isosceles right angled triangles, the angle will be 90°, 45°, 45°.
Here sum of two angles 45° + 45° = 90°.
![]()
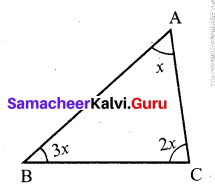
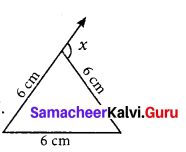
Question 2.
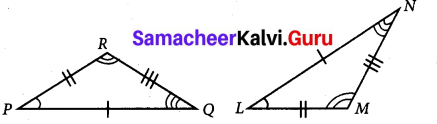
The three angles of a triangle are in the ratio 1:2:1. Find all the angles of the triangle. Classify the triangle in two different ways.
Solution:
Let the angles of the triangle be x, 2x, x.
Using the angle sum property, we have
x + 2x + x = 180°
4x = 180°
x = \(\frac{180^{\circ}}{4}\)
x = 45°
2x = 2 × 45° = 90°
Thus the three angles of the triangle are 45°, 90°, 45°.
Its two angles are equal. It is an isoscales triangle. Its one angle is 90°.
∴ It is a right angled triangle.
![]()
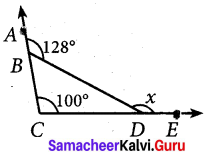
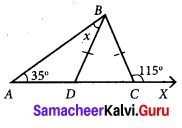
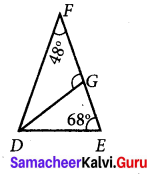
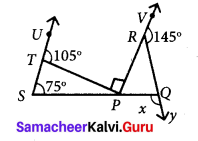
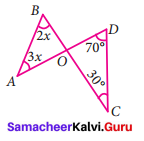
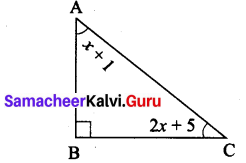
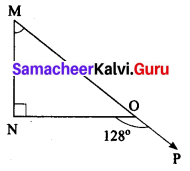
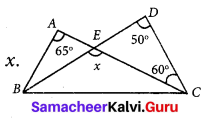
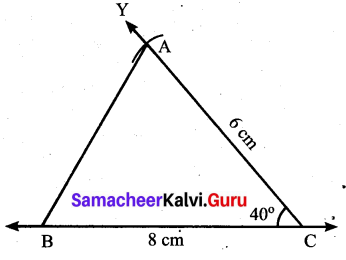
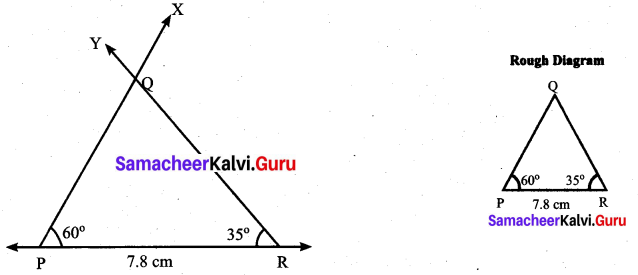
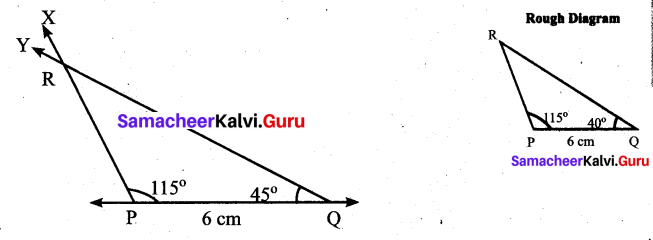
Question 3.
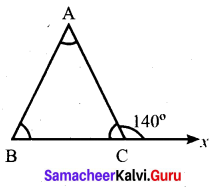
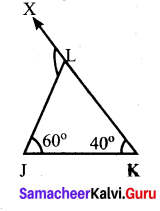
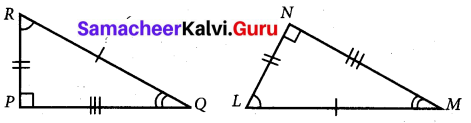
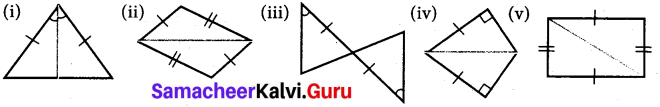
Find the values of the unknown x and y in the following figures
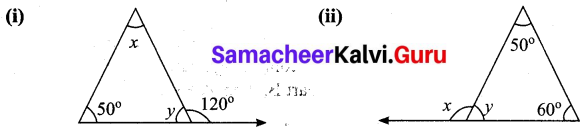
Solution:
(i) Since angles y and 120° form a linear pair.
y + 120° = 180°
y = 180° – 120°
y = 60°
Now using the angle sum property of a triangle, we have
x + y + 50° = 180°
x + 60° + 50° = 180°
x + 110° = 180°
x = 180° – 110°= 70°
x = 70°
y = 60
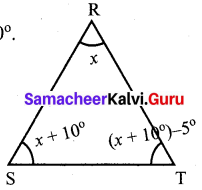
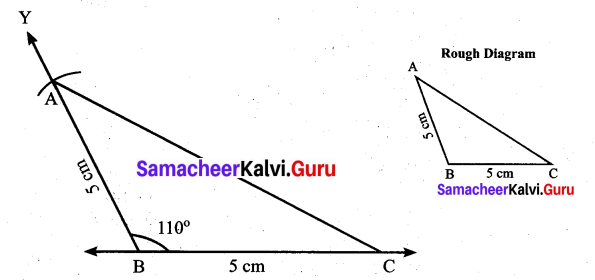
(ii) Using the angle sum property of triangle, we have
50° + 60° + y = 180°
110° + y = 180°
y = 180° – 110°
y = 70°
Again x and y form a linear pair
∴ x + y = 180°
x + 70° = 180°
x = 180° – 70°= 110°
∴ x = 110°; y = 70°
![]()
Question 4.
Two angles of a triangle are 30° and 80°. Find the third angle.
Solution:
Let the third angle be x.
Using the angle sum property of a triangle we have,
30° + 80° + x = 180°
x + 110° = 180°
x = 180° – 110° = 70°
Third angle = 70°.
Exercise 4.2
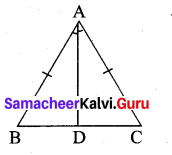
Question 1.
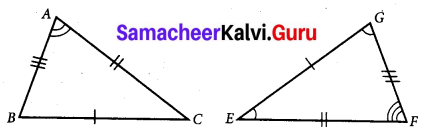
In an isoscleles ∆ABC, AB = AC. Show that angles opposite to the equal sides are equal.
Solution:
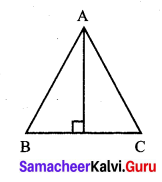
Given: ∆ABC in which \(\overline{A B}\) = \(\overline{A C}\).
To Prove: ∠B = ∠K.
Construction: Draw AD ⊥ BC.
Proof: In right ∆ADB and right ∆ADC.
we have side AD = side AD (common)
AB = AC (Hypoteneous) (given)
∆ADB = ADC (RHS criterion]
∴ Their corresponding parts are equal. ∠B = ∠C.
![]()
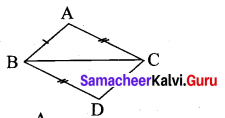
Question 2.
ABC is an isosceles triangle having side \(\overline{A B}\) = side \(\overline{A C}\). If AD is perpendicular to BC, prove that D is the mid-point of \(\overline{B C}\).
Solution:
In ∆ABD and ∆ACD, we have
∠ADB = ∠ADC [∵ AD ⊥ BC]
Side \(\overline{A D}\) = Side \(\overline{A D}\) [Common]
Side \(\overline{A B}\) = Side \(\overline{A C}\) [Common]
Using RHS congruency, we get
∆ABD ≅ ∆ACDc
Their corresponding parts are equal
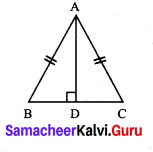
∴ BD = CD
∴ O is the mid point of BC.
![]()
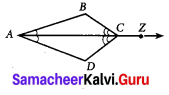
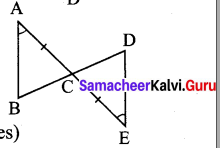
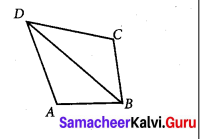
Question 3.
In the figure PL ⊥ OB and PM ⊥ OA such that PL = PM.
Prove that ∆PLO ≅ ∆PMO.
Solution:
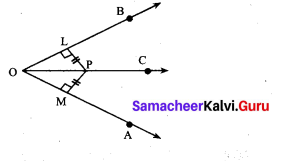
In ∆PLO and ∆PMO, we have
∠PLO = ∠PMO = 90° [Given]
\(\overline{O P}\) = \(\overline{O P}\) [Hypotenuse]
PL = PM
Using RHS congruency, we get
∆PLO ≅ ∆PMO