Students can Download Science Chapter 2 Universal and Space Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Solutions Term 3 Chapter 2 Universal and Space
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Universal and Space Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
The Moon takes ________ days to complete one revolution around the Earth.
(a) 25
(b) 26
(c) 27
(d) 28
Answer:
(c) 27
Question 2.
If the Moon is appeaing in the sky today near the star Karthikai, the position of the Moon after 27 days is near the Star
(a) Bharani
(b) Karthikai
(c) Rohini
(d) Asvini
Answer:
(d) Asvini
![]()
Question 3.
Telescope was invented by
(a) Han Lippershey
(b) Galilio
(c) Nicolus Coppernicus
(d) Ptolomy
Answer:
(a) Han Lippershey
Question 4.
The galaxy containing young and hot stars is
(a) elliptical galaxy
(b) irregular galaxy
(c) cluster
(d) spiral galaxy
Answer:
(d) spiral galaxy
Question 5.
With the launch of this satellite, ISRO became capable of launching 4 ton heavy satellites
(a) GSAT- 13
(b) GSAT- 14
(c) GSAT-17
(d) Way par GSAT-19
Answer:
(d) Way par GSAT-19
II. Fill in the blanks
- Waxing of Moon means _______
- Heliocentric model is proposed by _______
- _______ is the prevailing model of Evolution of the Universe.
- _______ is a large constellation which covers a large part of the sky.
- _______ is the first satellite launched by India
Answer:
- growing or expanding
- Nicolus copernicus
- The Big Bang Theory
- Ursa Major
- Aryabhatta
III. True or False – If False give the correct answer
Question 1.
On a full Moon day, when the Sun is setting in the west, Moon rises in the West.
Answer:
False Correct statement: On a full Moon day, when the Sun is setting in the west, Moon rises in the East
Question 2.
The word crescent refers to the phases where the Moon is less than half illuminated.
Answer:
True.
![]()
Question 3.
Galilio accepted the Geo-centric model.
Answer:
False
Correct statement: Galilio did nof accepted the Geo-centric model.
Question 4.
Our Milky Way galaxy is identified as an elliptical galaxy.
Answer:
False Correct statement: Our Milky Way galaxy is identified as an galaxy.
Question 5.
The planet Venus in our solar system doesn’t have a Moon.
Answer:
True
IV. Match the following:
| 1. | Rohini | GSLV-Mark III |
| 2. | GSAT-14 | GSLV Mark III D l |
| 3. | GSAT-19 | SLV-3 |
| 4. | Chandrayaan-2 | PSLV-XL C25 |
| 5. | Mangalyaan | GSLV-D5 |
Answer:
| 1. | Rohini | SLV-3 |
| 2. | GSAT-14 | GSLV-D5 |
| 3. | GSAT-19 | GSLV Mark III D1 |
| 4. | Chandrayaan-2 | GSLV-Mark III |
| 5. | Mangalyaan | PSLV-XL C25 |
V. Analogy:
Question 1.
Older stars : elliptical galaxies :: younger stars : ___________
Answer:
Irregular galaxies.
Question 2.
Nearest galaxy: Andromeda :: Nearest star : ___________
Answer:
Alpha Centauri.
![]()
VI. Very short answer:
Question 1.
The word _______ refers to the phases where the Moon is less than half illuminated (cresent / gibbous)
Answer:
cresent.
Question 2.
___________ and ___________ planets never appear in the mid-night sky.
Answer:
Mercury, Venus.
Question 3.
Number of days taken by the Mars to orbit around the Sun.
Answer:
687 days.
Question 4.
In which phase does the size of the planet Venus is small?
Answer:
When it was in Gibbous phase.
Question 5.
The only evidence of the big bang theory is
Answer:
The only evidence of the big bang theory is a faint glow in space, called cosmic microwave background.
![]()
Question 6.
The galaxy which contains abundant amount of gas and dust is ___________ ?
Answer:
Spiral galaxy.
Question 7.
Which country launched the world’s first artificial launch vehicle?
Answer:
Russia launched the world’s first artificial launch vehicle.
VII. Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
What is epicyclic model?
Answer:
- To explain the puzzling phenomena astronomers in early times proposed a change in the simple geocentric model. This is called as epicycle model.
- A small circle whose centre is on the circumference of a larger circle, in ptolemic astronomy.
- It was seen as the basis of revolution of the seven plants, given a fixed central Earth.
Question 2.
Name the four different types of Galaxies.
Answer:
- Spiral galaxy
- Elliptical galaxy
- Irregular galaxy
- Barred spiral galaxy
Question 3.
What is constellation?
Answer:
A constellation is a recognizable pattern of stars in the night sky when viewed from the Earth.
![]()
Question 4.
Give the expansions of PSLV and GSLV.
Answer:
PSLV : Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle.
GSLV : Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle.
VIII. Answer in Detail:
Question 1.
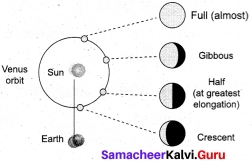
Explain the waxing and waning phases in Venus.
Answer:
- As the Venus went around the epicycle, as shown in the diagram Venus would exhibit phases.
- Also at times the planet would be nearer, making the apparent size grow bigger and at times far making the apparent size smaller.
- If the Venus was going around the Sun, and its orbit is inside that of Earth, Venus would appear always near the Sun in the sky.
- It can never be seen in the midnight sky. Two when it is near the Earth, it would be brighter and bigger compared to when it is on the other side of the Sun.
- Thirdly only if the Venus is revolving around the Sun, it can exhibit gibbous phase, and the size of the gibbous phase smaller than the crescent phase.
- If the Venus was revolving around the Earth, we can never see the gibbous phase of the Venus and it would be seen only if it is orbiting the Sun.
Question 2.
Write short notes on constellations.
Answer:
- A constellation is a recognizable pattern of stars in the night sky when viewed from the Earth.
- International Astronomical Union has classified 88 constellations to cover the entire celestial sphere.
- Many of the old constellations have Greek or Latin names and are often named after mythological characters.
- Ursa Major (Saptha Rishi Mandalam) is a large constellation and it covers a large part of the sky.
- The most striking feature of this constellation is a group of seven bright stars known as big dipper (seven Sages in Indian astronomy).
- Ursa Minor in Lattin means ‘the little bear’ it lies in the northern sky.
- The Pole star – Polaris (Dhrua) lies within this constellation.
- The main group, ‘little dipper’, consists of seven stars and is quite similar to that found in Ursa Major.
IX. HOT Question:
Question 1.
Neelan and Mala are having a conversation about our Universe. Neelan is telling our Earth will be the only planet in the entire Universe to have a life with. But, Mala is opposing his view by citing certain points. What would be the argument of Mala? Do you support Mala? Justify your stand.
Answer:
I would like to support Neelan, because Life is possible only on the Earth due to presence of water, oxygen, various gases and suitable temperature, which enables us to live.
Mala opposed Neelan’s view based on the following points :
- Like the Sun, there might be billions of other stars with their own planets revolving around them.
- Thus there are many chances of any planet getting the suitable conditions for supporting life.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Universal and Space Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
What type of galaxy is the milky way?
(a) Spherical
(b) Irregular
(c) Spiral
(d) Elliptical
Answer:
(c) Spiral
![]()
Question 2.
Stars mainly consists of ___________
(a) Oxygen and hydrogen
(b) hydrogen and helium
(c) Oxygen and nitrogen
(d) Carbon and helium
Answer:
(b) hydrogen and helium
Question 3.
The Great Bear or Saptha Rishi Mandalam are the names of
(a) The Ursa Major
(b) Orion
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) The Ursa Major
Question 4.
GSLV means ___________
(a) Global Satellite Locus Verification
(b) Geostationary Satellite Launch Vehicle
(c) German Satellite Launching Vehicle
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Geostationary Satellite Launch Vehicle
![]()
Question 5.
Parsec is equal to ___________
(a) 2 light years
(b) 5 light years
(c) 4.56 light years
(d) 3.26 light years
Answer:
(d) 3.26 light years
Question 6.
The hottest planet in the solar system is ___________
(a) Mercury
(b) Venus
(c) Sun
(d) Mars
Answer:
(b) Venus
Question 7.
The first artificial satellite is ___________
(a) Sputnik -1
(b) Sputnik – II
(c) Apollo – II
(d) Vostok
Answer:
(a) Sputnik -1
![]()
Question 8.
The nearest galaxy to our Milky way is ___________
(a) Andromeda
(b) Proxima centauri
(c) Large megallanic cloud
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Andromeda
Question 9.
Earth orbit around Sun in ___________days.
(a) 465
(b) 365
(c) 687
(d) 24
Answer:
(b) 365
Question 10.
According to Big Bang theory, space and time emerged together about ___________billions of years ago.
(a) 20
(b) 24
(c) 14
(d) 50
Answer:
(c) 14
II. Fill in the blanks.
- _______ is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists or is known to exist.
- At all times one half of _______ is illuminated by Sun and the opposite side is shroud in darkness.
- The reversal of direction of planets is called as _______
- Telescope was invented by _______ but Galilio used it for studying the sky for the first time.
- To naked eye, _______ is just a gleaming bright spot.
- The event when the matter confined in a single point and began to expand is called _______
- The distance travelled by light in one year is called a _______
- The average distance between the Earth and the Sun is called an _______
- The diameter of Milky Way is over _______ light years.
- The solar system travels at an average speed of _______
- ISRO built India’s first satellite _______ which was launched by the Soviet Union on 19 April 1975.
Answer:
- Universe
- Moon
- retrograde motion
- Hans Lippershey
- Venus
- ‘big bang
- light year
- astronomical unit
- 100,000
- 828,000 km/h
- Aryabhatta
III. True or False – If false, give the correct statement.
Question 1.
On the full Moon day, when the Sun is setting in west, at the same time, Moon rises at the west.
Answer:
False
Correct statement: On the full Moon day, when the Sun is setting in west, at the same time, Moon rises at the same time
![]()
Question 2.
Moon going around Earth with 27 days period.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
The word gibbous refers to phases where the Moon is more than half illuminated.
Answer:
False
Correct statement: The word refers to phases where the Moon is more than half illuminated.
Question 4.
Kepler found that his observation of Venus gave the observational evidence to support the heliocentric theory.
Answer:
False
Correct statement: found that his observation of venus gave the observational evidence to support the heliocentric theory.
Question 5.
All the galaxies are appearing to move away from us.
Answer:
True
Question 6.
Solar system is located, is classified as a barred spiral galaxy.
Answer:
True
Question 7.
Unlike galaxy, constellations are more optical appearance and not real objects.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 8.
All planets except mercury in our solar system have Moons.
Answer:
False
Correct statement: All planets except mercury and in our solar system have Moons.
Question 9.
The vision of ISRO is to harness space technology for national development while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration.
Answer:
True
Question 10.
NASA sent a lunar orbiter, Chandrayan -1 on 22 October- 2008.
Answer:
Correct statement: sent a lunar orbiter, Chandrayan -1 on 22 October-2008
IV. Match the following :
Question 1.
| 1. | Galileo Galilei | (a) | Earth is at the centre |
| 2. | Heliocentric theory | (b) | Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam |
| 3. | Geo-centric theory | (c) | Jupiter – bound space probe |
| 4. | ‘ Missile man of India | (d) | Sun is at the centre |
Answer:
- c
- d
- a
- b
Question 2.
| 1. | Ursa Minor | (a) | Hunter |
| 2. | Ursa Major | (b) | Dhruva |
| 3. | Orion | (c) | Big dipper |
| 4. | Pole star | (d) | Little bear |
Answer:
- d
- c
- a
- b
Question 3.
| 1. | Spiral galaxy | (a) | Globular clusters |
| 2. | Elliptical galaxy | (b) | Bar-shaped structure |
| 3. | Irregular galaxy | (c) | Young, hot stars |
| 4. | Barred spiral galaxy | (d) | Abundant amount of gas, dust |
Answer:
- c
- a
- d
- b
V. Very short Answers:
Question 1.
Name the planets which have no Moon.
Answer:
Mercury and Venus.
Question 2.
Name the galaxy in which we live.
Answer:
Milky way.
![]()
Question 3.
Name the star that appears to be stationary in the night sky.
Answer:
Pole star.
Question 4.
What is the Indian name of Ursa Minor?
Answer:
Laghu Saptarishi.
Question 5.
Name the planets which have more than 60 Moons.
Answer:
Jupiter and Saturn.
Question 6.
What is the distance of our solar system from the centre of the galaxy?
Answer:
27,000 light years.
![]()
Question 7.
What is the distance that light travels in one year called?
Answer:
Light year.
Question 8.
The constellation Big dipper is known by another name also. What is it?
Answer:
Ursa Major.
Question 9.
What are constellations?
Answer:
Constellations are stars that appear to form a pattern when viewed from the Earth.
VI. Short Answer.
Question 1.
Why does the Moon changes its shape daily?
Answer:
Moon changes its shape daily because, it revolves around the Earth and the light from the Sun continuously changes due to the presence of Earth between Moon and the Sun.
Question 2.
What is first quarter?
Answer:
- When the Sun, Earth and Moon are in 90 degree angle.
- Half if it illuminated and half is dark side.
- The Moon will appear as half Moon.
- The half Moon during the waxing period is called as first quarter
Question 3.
Write a note on planet.
Answer:
- Planets are heavenly bodies that revolve around the Sun.
- They do not give out light of their own.
- Their surface reflects the light of the Sun to us.
Question 4.
Write a note on ISRO.
Answer:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is the space agency of the Government of India headquartered in the city of Bangalore.
- Its vision is to “harness space technology for national development while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration.”
![]()
Question 5.
Why Earth is called a unique planet?
Answer:
- Earth is unique because it is the only planet on which life is known to exist.
- The presence of atmosphere, water and suitable temperature make life possible here.
Question 6.
Write a note on artificial satellites.
Answer:
- Artificial satellites are man-made objects placed in an obit to rotate around a planet – usually the Earth.
- The world’s first artificial satellite launched was Sputnik-lby Russia, Aryabhatta was the first satellite launched by India.
- These satellites are used in television and radio transmission, studying agriculture yield, locating mineral resources, weather forecasting, locate different places on Earth.
Question 7.
Stars appear to twinkle. Give reason.
Answer:
- The stars are remotely located and appear as tiny dots of light.
- Their light travels long distances to reach us.
- The atmosphere disturbances do not allow light to reach us in a straight line path.
- Because of this the stars appear to twinkle.
VII. Long Answer:
Question 1.
Explain about the origin of the universe.
Answer:
- All the galaxies were appearing to move away from us. Further, farther they are faster they appear to move.
- Cosmologists, scientists who study the structure and evolution of universe that is cosmos, reason that this imply at one point of time in the past all matter was confined in a single point and since then it has started to expand.
- The event when the matter confined in a single point and began to expand is called ‘big bang’.
- This is considered as the origin of our universe as we know it.
- The Big Bang Theory is the prevailing model of the evolution of the Universe.
- Under this theory, space and time emerged together about 14 billions of years ago.
- At that time, the entire Universe was inside a bubble that was thousands of times smaller than a pinhead.
- It was hotter and denser than anything we can imagine.
- Then it suddenly expanded. The present Universe emerged.
- Time, space and matter all began with the Big Bang.
VIII. Creative questions: HOTS
Question 1.
It Do stars emit light only during night?
Answer:
No. Stars emit light all the time. But we are not able to see their light due to excess brightness of the Sun.
![]()
Question 2.
In the given picture out of the positions P, Q, R and S which will indicate the position of the Sun. Draw the Sun at the appropriate position.
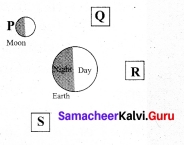
Answer:
Sun will be at position R.
Question 3.
We never see the backside of the Moon from the Earth. Is it true?
Answer:
Yes, as the Moon revolves around the Earth facing one part of the Moon towards the Earth, then we never see back side of the Moon from the Earth.