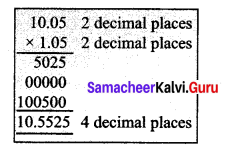
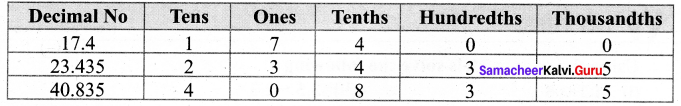
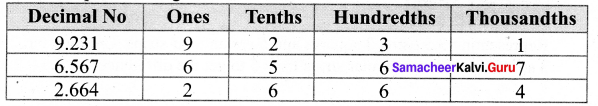
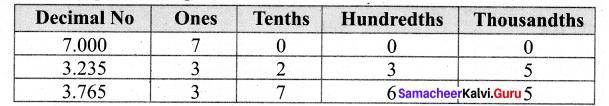
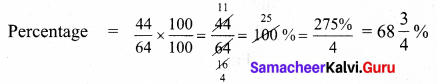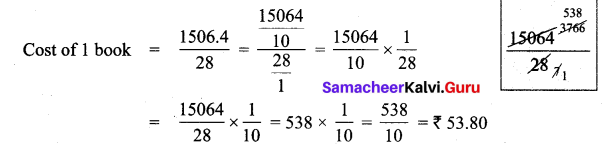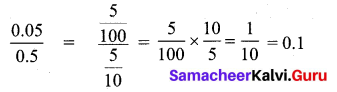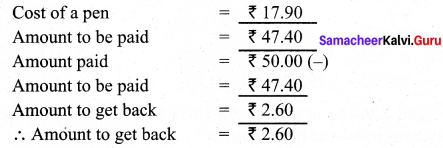Students can Download Maths Chapter 1 Number System Ex 1.5 Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Maths Solutions Term 3 Chapter 1 Number System Ex 1.5
Miscellaneous Practice problems
Question 1.
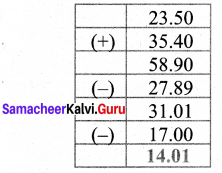
Malini bought three ribbon of lengths 13.92 m, 11.5 m and 10.64 m. Find the total length of the ribbons?
Solution:
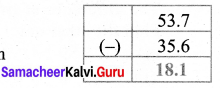
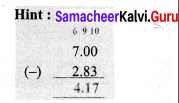
Length of ribbon 1 = 13.92 m
Length of ribbon 2 = 11.50 m
Length of ribbon 3 = 10.64 m

Total Length of the ribbons = 13.92 m + 11.5 m + 10.64 m = 36.06 m
Totla length of the ribbons = 36.06 m
![]()
Question 2.
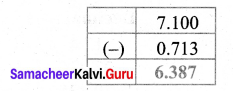
Chitra has bought 10 kg 35 g of ghee for preparing sweets. She used 8 kg 59 g of ghee. How much ghee will be left?
Solution:
Total weight of ghee bought = 10 kg 35 g
Weight of ghee used = 8 kg 59 g
Weight of ghee left = 10.35 kg – 8.59 kg = 1.76 kg

∴ Weight of ghee left= 1 kg 76 g = 1.76 kg
Question 3.
If the capacity of a milk can is 2.53 l, then how much milk is required to fill 8 such cans?
Solution:
Capacity of 1 milk can= 2.53 l
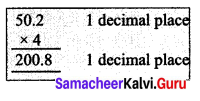
∴ Capacity of 8 milk cans= 2.53 l × 8 = 20.24 l

To fill 8 cans 20.24 l of milk is required.
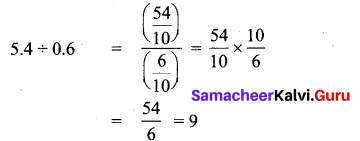
Question 4.
A basket of orange weighs 22.5 kg. If each family requires 2.5 kg of orange, families can share?
Solution:
Total weight of orange = 22.5 kg
Weight of orange required for 1 family = 2.5 kg
∴ Number of families sharing orange = 22.5 kg ÷ 2.5 kg
= \(\frac { 22.5 }{ 2.5 } \) = \(\frac { 22.5 }{ 2.5 } \) × \(\frac { 10 }{ 10 } \) = \(\frac { 225 }{ 25 } \) = 9
∴ 9 families can share the oranges.
![]()
Question 5.
A baker uses 3.924 kg of sugar to bake 10 cakes of equal size. How much sugar is used in each cake?
Solution:
For 10 cakes sugar required = 3.924 kg
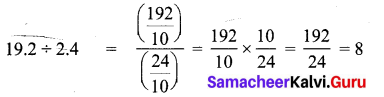
For 1 cake sugar required = 3.924 ÷ 10 = \(\frac { 3.924 }{ 10 } \) = 0.3924 kg
For 1 cake sugar required = 0.3924 kg.
Question 6.
Evaluate:
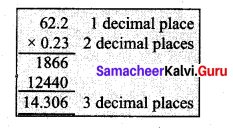
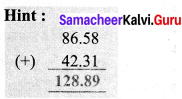
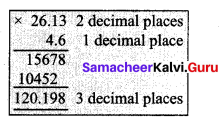
(i) 26.13 × 4.6
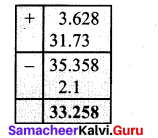
(ii) 3.628 + 31.73 – 2.1
Solution:
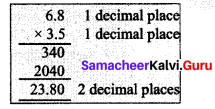
(i) 26.13 × 4.6
26.13 × 4.6 = 120.198
(ii) 3.628 + 31.73 – 2.1 = 33.258
Question 7.
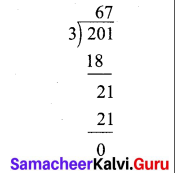
Murugan bought some bags of vegetables. Each bag weighs 20.55 kg. If the total weight of all the bags is 308.25 kg, how many bags did he buy?
Solution:
Total weight of all bags = 308.25 kg
Weight of 1 bag = 20.55 kg
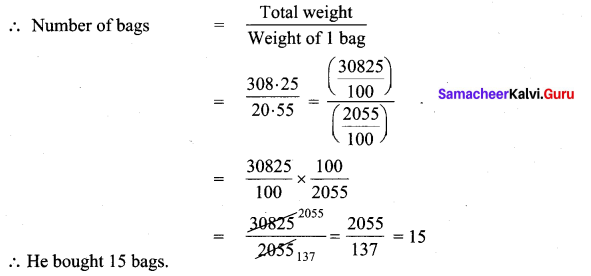
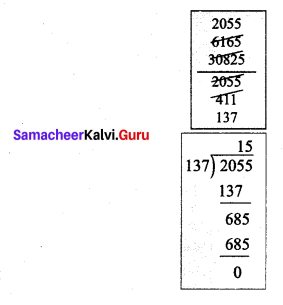
![]()
Question 8.
A man walks around a circular park of distance 23.761 m. How much distance will he cover in 100 rounds?
Solution:
In 1 round distance covered = 23.761 m
∴ In 100 rounds distance = 23.761 × 100
= 2376.1 m
∴ In 100 round he covers 2376.1 m.
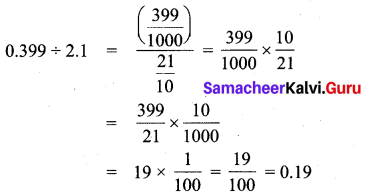
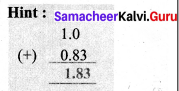
Question 9.
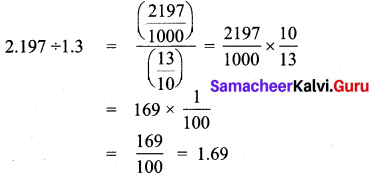
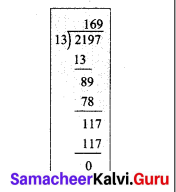
How much 0.0543 is greater than 0.002?
Solution:
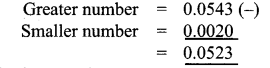
∴ Required answer is 0.0523
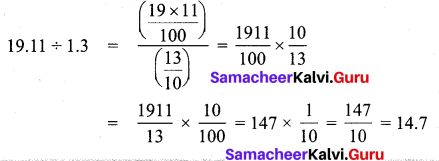
Question 10.
A printer can print 15 pages per minute. How many pages can it print in 4.6 minutes?
Solution.
In 1 minute the pages printed = 15
In 4.6 minutes the pages printed = 15 × 4.6
= 69
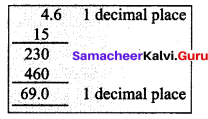
The printer prints 69 pages.
![]()
Challenge Problems
Question 1.
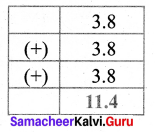
The distance travelled by Prabhu from home to Yoga centre is 102 m and from Yoga centre to school is 165 m. What is the total distance travelled by him in kilometres (in decimal form)?
Solution:

∴ 267 metres = \(\frac { 267 }{ 1000 } \) km = 0.267 km
∴ Total distance travelled = 0.267 km
Question 2.
Anbu and Mala travelled from A to C in two different routes. Anbu travelled from place A to place B and from there to place C. A is 8.3 km from B and B is 15.6 km from C. Mala travelled from place A to place D and from there to place C. D is 7.5 km from A and C is 16.9 km from D. Who travelled more and by how much distance?
Solution:
Distance travelled by Anbu:
From place A to place B = 8.3 km
Distance from place B to place C = 15.6 km
∴ Total distance travelled by Anbu = 8.3 + 15.6
= 23.9 km
Distance travlled by Mala:
Distance travelled place A to D = 7.5 km
Distance from place D to place C = 16.9 km
Total distance travelled by mala = (7.5 + 16.9) km = 24.4 km
24.4 > 23.9
∴ Mala travelled more distance. She travelled (24.4 – 23.9) km more i.e she travelled 0.5 km more
![]()
Question 3.
Ramesh paid ₹ 97.75 per hour for a taxi and he used 35 hours in a week. How much he has to pay totally as taxi fare for a week?
Solution:
Payment for the taxi for an hour = ₹ 97.75
Total hours the taxi was used = 35 hrs
∴ Total payment for the taxi for the week
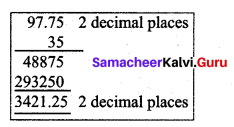
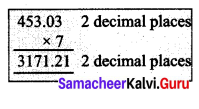
= 97.75 × 35
= 3421.25
Total payment for a week = ₹ 3421.25
Question 4.
An Aeroplane travelled 2781.20 kms in 6 hours. Find the average speed of the aeroplane in Km/hr.
Solution:
In 6 hours the distance travelled = 2781.20 km
In 1 hour the distance travelled = \(\frac { 2781.20 }{ 6 } \) km

Average speed of the aroplane = 463.53 km/hr.
![]()
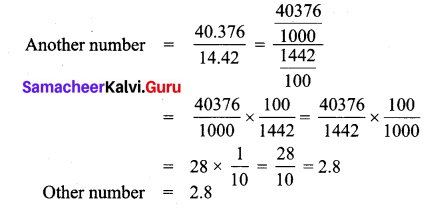
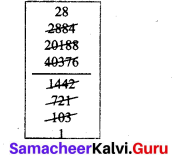
Question 5.
Kumar’s car gives 12.6 km mileage per litre. If his fuel tank holds 25.8 litres then how far can he travel?
Solution.
Distance travelled with 1 litre fuel = 12.6 km
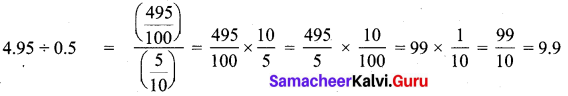
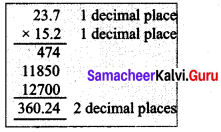
∴ with 25.8 litres distance travelled = 12.6 × 25.8
= 325.08 km
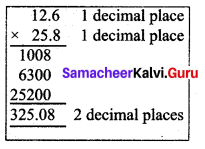
The car can travel 325.08 km