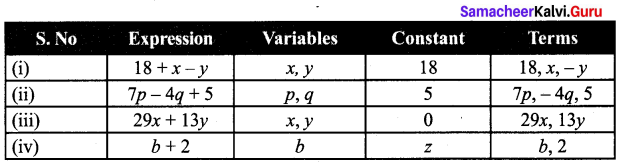
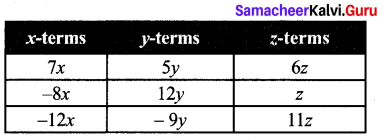
Students can Download Maths Chapter 2 Measurements Additional Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Maths Solutions Term 2 Chapter 2 Measurements Additional Questions
Additional Questions and Answers
Exercise 2.1
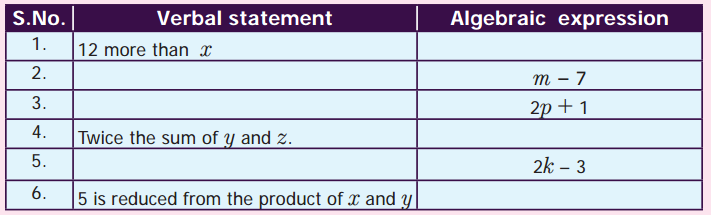
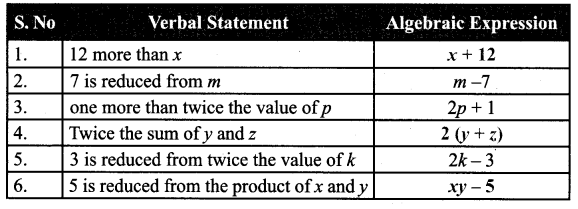
Question 1.
A circular disc of radius 28 cm is divided into two equal parts. What is the perimeter of each semicircular shape disc? Also find the perimeter of the circular disc.
Answer:
Radius of the circular disc = 28 cm
∴ circumference of the circle = 2 π r units
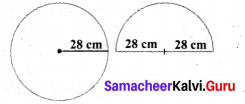
= 2 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) × 28 cm
= 2 × 22 × 4 = 44 × 4 = 176 cm
Perimeter of the circular disc = 176 cm
Now circumference of the semicircular disc = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) × (2 π r) = π r units
Perimeter of the semicircular disk = π r + r + r = \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) × 28 + 28 + 28
= 22 × 4 + 28 + 28 = 88 + 28 + 28 = 144
Perimeter of each semicircular disc = 144 cm
![]()
Question 2.
A gardener wants to fence a circular garden of diameter 14m. Find the length of the rope he needs to purchase if he makes 3 rounds of fence. Also find the cost of the rope, if it costs ₹ 4 per metre.
Solution:
Diameter of the circular garden (d) = 14 m
Circumference = π d = \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) × 14 = 44 m
Since the rope makes 3 rounds of fence,
length of the rope needed = 3 × circumference of the garden
= 3 × 44 m = 132 m
Cost of rope per meter = ₹ 4 × 132 = ₹ 528
Question 3.
Latha wants to put a lace on the edge of a circular table cover of diameter 3 m. Find the length of the lace required and also find the cost if one metre of the lace costs ₹ 30 (Take π = 3.15 )
Solution:
Diameter of the circular table cover = 3m
Circumference C = π d units = 3.15 × 3 m = 9.45 m
Length of the lace required = 9.45 m
Cost of lace per meter = ₹ 30
∴ Cost of 9.45m lace = ₹ 30 × 9.45 = ₹ 283.50
![]()
Exercise 2.2
Question 1.
The circumference of two circles are on the ratio 5 : 6. Find the ratio of their areas.
Solution:
Let the radii of the given circles be r1 and r2
Let their circumference be C1 and C2 respectively
C1 = 2πr1 and C2 = 2πr2
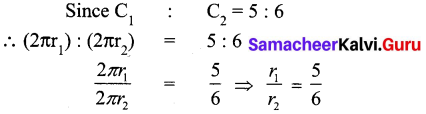
Now let the area of the given circles the A1 and A2
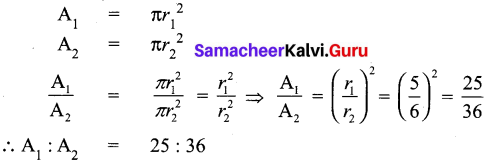
∴ The areas of two circles are in the ratio 25 : 36.
Question 2.
Find the area of the circle whose circumference is 88 cm.
Solution:
The circumference of the circle = 88 cm
2πr = 88 cm
2 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) × r = 88 cm
r = \(\frac{88 \times 7}{2 \times 22}\) = 14 cm
r = 14 cm
Area of the circle A = πr2
= \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) × 14 × 14 cm2
= 22 × 2 × 14 cm2
= 616 cm2
![]()
Question 3.
Find the cost of polishing a circular table top of diameter 16 dm if the rate of polishing is ₹ 15 per dm2.
Solution:
Diameter of the circular table top = 16 dm
Radius (r) = \(\frac { 16 }{ 2 } \) = 8cm
Area of the circular table top
= πr2 sq.units
= \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) × 8 × 8 dm2 = \(\frac { 1408 }{ 7 } \) dm2
= 201.14 dm2
Rate of the polishing per dm2 = ₹ 15
∴ Rate of the polishing 201.14 dm2
= ₹ 15 × 201.14
= ₹ 3,017
![]()
Exercise 2.3
Question 1.
From a circular sheet of radius 5 cm a circle of radius 3 cm is removed. Find the area of the remaining sheet.
Solution:
Radius of the outer circle R = 5 cm
Radius of the inner circle r = 3 cm
Area of the remaining sheet = Area of the outer circle
– Area of the inner circle
= πR2 – πr2 sq. units = π(R2 – r2) sq. units
= \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) (52 – 32) cm2 = \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) (52 – 32) cm2
= \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) × (5 + 3) (5 – 3) = \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) × (8) (2)
= \(\frac { 352 }{ 7 } \) = 50.28 cm2
![]()
Question 2.
A picture is painted on a cardborad 8 cm long and 5 cm wide such that there is a margin of 1.5 cm along each of its sides. Find the total area of the margin.
Solution:
Length of the outer rectangle L = 8 cm
Breadth of the outer rectangle B = 5 cm
Area of the outer rectangle = L × B sq. units = 8 × 5 cm2 = 40 cm2
Length of the inner rectangle l = L – 2W = 8 – 2(1.5)cm = 8 – 3cm
l = 5cm
Breadth of thqnner rectangle b = B – 2W = 5 – 2(1.5) cm
= 5 – 3cm = 2cm
∴ Area of the margin = Area of the outer rectangle
– Area of the inner rectangle
= (40 – 10) cm2 = 30cm2
![]()
Question 3.
A circular piece of radius 2 cm is cut from a rectangle sheet of length 5 cm and breadth 3 cm. Find the area left in the sheet.
Solution:
Radius of the portion removed r = 2 cm
Area of the circular sheet = πr2 sq.units
= \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) × 2 × 2 cm2 = \(\frac { 88 }{ 7 } \) cm2 = 12.57 cm2
Length of the rectangular sheet L = 5 cm
Breadth of the rectangular sheet B = 3 cm
Area of the rectangle = L × B sq. units = 5 × 3 cm2 = 15 cm2
Area of the sheet left over = Area of the rectangle – Area of the circle
= 15 cm2 – 12.57 cm2 = 2.43 cm2





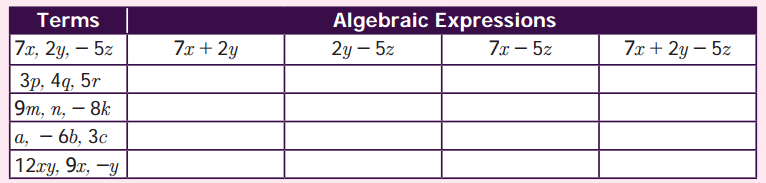
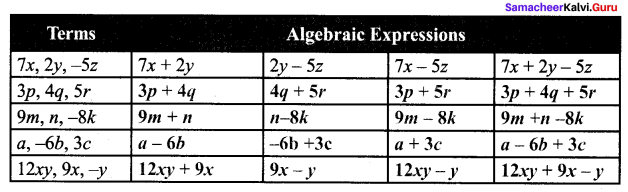
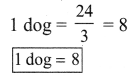

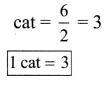 ditional Questions 63″ width=”107″ height=”87″ />
ditional Questions 63″ width=”107″ height=”87″ />