You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Geography Solutions Term 2 Chapter 1 Resources
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Resources Textual Exercises
I. Choose the correct answer:
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Social Science Question 1.
Which one of the following is renewable resource?
(a) Gold
(b) Iron
(c) Petrol
(d) solar energy
Answer:
(d) solar energy
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Solutions Question 2.
Where is the largest solar power project situated in India?
(a) Kamuthi
(b) Aralvaimozhi
(c) Muppandal
(d) Neyveli
Answer:
(a) Kamuthi
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Social Question 3.
Which is one of the first metals known and used by man?
(a) Iron
(b) Copper
(c) Gold
(d) Silver
Answer:
(b) Copper
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Guide Question 4.
_______ is one of the indispensable minerals used in electrical and electronics Industry.
(a) Limestone
(b) Mica
(c) Manganese
(d) Silver
Answer:
(b) Mica
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Social Science Guide Question 5.
Electricity produced from coal is called ________.
(a) Thermal Power
(b) Nuclear power
(c) Solar power
(d) Hydel power
Answer:
(a) Thermal Power
II. Fill In the blanks
- ______ is the largest producer of hydroelectricity.
- Iron ores found at ______ in Tamil Nadu.
- ______ is produced from bauxite ore.
- ______ is used in making electrical batteries.
- Petroleum and its derivatives are called ______.
Answers:
- China
- Kanjamalai
- Aluminium
- Manganese
- Black Gold
III. Match the following
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Guide Question 1.
- Renewable resource – Iron
- Metallic resource – Mica
- Non-metallic resource – Wind energy
- Fossil fuel – Sedimentary rock
- Limestone – Petroleum
Answers:
- Renewable resource – Wind energy
- Metallic resource – Iron
- Non-metallic resource – Mica
- Fossil fuel – Petroleum
- Limestone – Sedimentary rock
IV. Consider the following statement and tick (✓) the appropriate answer
Samacheer Kalvi.Guru 7th Social Question 1.
Assertion (A): Wind power is Clean Energy.
Reason (R): Wind turbines do not produce any emissions
(a) A and R are correct and R explains A
(b) A and R are correct but R does not explain A
(c) A is incorrect but R is correct
(d) Both A and R are incorrect
Answer:
(a) A and R are correct and R explains A
Samacheerkalvi.Guru 7th Social Question 2.
Assertion (A): Natural gas is found with petroleum deposits.
Reason (R): it can be used as a domestic and industrial fuel.
(a) A and R are correct and R explains A
(b) A and R are correct but R does not explain A
(c) A is incorrect but R is correct
(d) Both A and R are incorrect
Answer:
(a) A and R are correct and R explains A
V. Answer the following
Samacheer Kalvi Guru Social 7th Question 1.
Define – Resource.
Answer:
Anything which can be used for satisfying the human needs is called resource.
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Standard Social Question 2.
What are the uses of iron?
Answer:
(i) Iron is used to manufacture steel and also used in civil engineering like reinforced concrete, griders etc.
(ii) It is used to make alloy steels like carbon steels with additives such as nickel, chromium, vanadium, tungsten and manganese.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Book Solutions Question 3.
What are the major utilizers of solar energy in the world?
Answer:
India, China, Japan, Italy and States of America are major utilizers of solar energy in the world.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Book Question 4.
Name the types of coal based on carbon content.
Answer:
Coal is classified into four types based on carbon content. They are :
- Anthracite
- Bituminous
- Lignite
- Peat
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Book Solutions Question 5.
Give a short note on Duralumin.
Answer:
Duralumin is an alloy, a trade name given to the earliest types of the age hardenable aluminum alloys. It is an alloy made up of 90% aluminum, 4% copper, 1 % magnesium and 0.5% to 1 % manganese. Duralumin is.a hard, but a lightweight alloy of aluminum.
VI. Distinguish the following
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Books Answers Question 1.
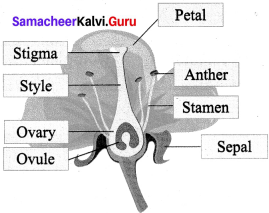
Biotic resources and abiotic resources.
Answer:
Biotic resources:
- Biotic resources are found in the biosphere which are obtained from living and organic materials.
- Biotic resources depend on abiotic resources for their survival.
- Example : Plants, trees, animals, microorganisam etc.
Abiotic resources :
- Abiotic resources are the non-living parts of an environment.
- Abiotic resources do not depend on biotic resources for their survival.
- Example : Sunlight, temperature, water, soil, air, etc.
Samacheer Kalvi Term 2 Question 2.
Renewable resources and non-renewable resources.
Answer:
Renewable resources:
- Renewable resources can be used again and again throughout its life.
- These resources are present in unlimited quantity.
- These resources are pollution free
- Example : Solar energy, wind energy and hydropower.
Non-renewable resources:
- Non-renewable resources cannot be used again and again as it is limited which can be depleted one day.
- These resources are present in a limited quantity only.
- These resources are not pollution free.
- Example : Fossil fuels, iron, copper, gold silver etc.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Question 3.
Metallic resources and non-metallic resources.
Answer:
Metallic resources:
- Metallic resources are the types of resources that are composed of metals.
- These are hard substances, which are the good conductors of heat and electricity.
- Example for metallic resources are iron, copper, gold, bauxite, silver, manganese, etc.
Non-metallic resources:
- Non-metallic resources can be described as the resources that do not comprise of metals.
- These are not hard substances and are not good conductors of heat and electricity.
- Example for non-metallic resources are mica, limestone, gypsum, dolomite, phosphate, etc.
VII. Give reason
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Standard Social Guide Question 1.
Aluminium has wide range of uses compared to other metals.
Answer:
- Aluminium is light in weight, tough and cheaper, which makes it popular metal for constructional purpose.
- It is mainly used in the construction of aircrafts, ship, automobiles, railway coaches and etc.
- So, Aluminium has wide range of use compared to other metals.
Question 2.
Water is considered as a great source of energy.
Answer:
At present, water is used for producing hydroelectric power. Hydroelectricity is generated from moving water with high velocity and great falls with the help of turbines and dynamos. So water is considered as a great source of energy.
VIII. Answer in a paragraph
Question 1.
Explain the different types of renewable resources.
Answer:
Solar energy :
- The sun produces energy in the form of heat and light. Solar energy is not harmful to the environment.
- Photovoltaic devices or solar cells, directly convert solar energy into electricity.
- India, China, Japan, Italy and States of America are major utilizers of solar energy in the world.
Hydropower:
- Hydroelectricity power is the cheapest and most versatile source of energy out of all the know energy. Hydroelectric power is a renewable resource.
- China, Canada, Brazil, United States of America, Russia, India, Norway and Japan are some countries producing hydroelectricity. China is the largest producer of hydro-electricity.
Wind energy :
- Wind power is clean energy since wind turbines does not produce any emission.
- In recent years, wind energy has become one of the most economical and renewable energy technologies.
- Major wind energy producing countries are United States, China, Germany, Spain, India, United Kingdom, Canada and Brazil.
Question 2.
Describe the non-metallic resources.
Answer:
Non-metallic resources:
- Non-metallic resources can be described as the resources that do not comprise of metals.
- These are not hard substances, and are not good conductors of heat and electricity.
- Example for non-metallic resources are mica, limestone, gypsum, dolomite, phosphate, etc.
Mica:
- Muscovite and Biotite are the common ores of Mica.
- It is one of the indispensable minerals used in electrical and electronics industry.
- In powder form, it is used for making lubricating oils and decorative wallpapers.
Limestone:
- Limestone is a sedimentary rock, composed mainly by skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral, foraminifera and molluscs.
- About 10% of sedimentary rocks are limestones. Mostly limestone is made into crushed stone and used as a construction material.
- It is used for facing stone, floor tiles, stair treads, windows sills and many other purposes.
- Crushed limestone is used in smelting and other metal refining process. Portland cement is made from limestone.
Question 3.
What are the different types of fossil fuel resources? Explain them.
Answer:
Fossil fuel resources:
- Fossil fuel resources are normally formed from the remains of dead plants and animals.
- They are often referred to as fossil fuels and are formed from hydrocarbon.
Coal:
- This is the most abundantly found fossil fuel that forms when dead plant matter is converted into peat.
- It is used as a domestic fuel, in industries such as iron and steel, steam engines to generate electricity.
Petroleum:
- Petroleum is found between the layers of rocks and is drilled from oil fields located in Offshore and coastal areas.
- Petroleum and its derivatives are called Black Gold as they are very valuable.
Natural gas:
- Natural gas is found with petroleum deposits and is released when crude oil is brought to the surface.
- It can be used as a domestic and industrial fuel.
IX. Activity
Question 1.
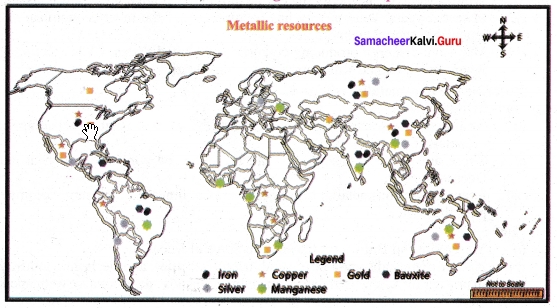
Mark the metallic resources on the given outline map of the world.
Question 2.
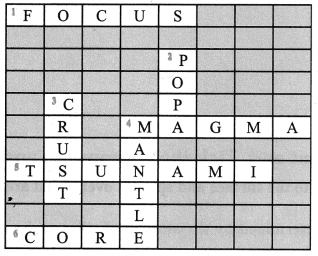
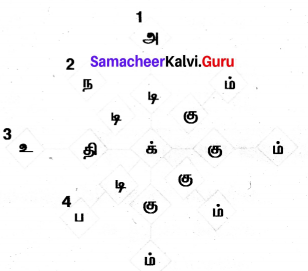
Crossword puzzle
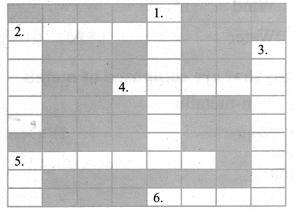
Across:
2. The leading coal producers of the world
4. Considered as a great source of energy
5. Precious metal like gold
6. Used as an insulating material in electrical industry
Down:
1. Used in making electrical batteries
2. Good conductor of heat and electricity
3. The largest producer of gold in India
5. Produces energy in the form of heat and light

Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Resources Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
______ are the non-living parts of an environment.
(a) Biotic resources
(b) Abiotic resources
(c) Both
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Abiotic resources
Question 2.
______ is not harmful to the environment.
(a) Sotar energy
(b) Wind energy
(c) Hydropower
(d) None of these
Question 3.
Kamuthi solar power project is situated in ______ district in Tamil Nadu.
(a) Madurai
(b) Tirunelveli
(c) Ramanathapuram
(d) Kancheepuram
Answer:
(c) Ramanathapurami
Question 4.
______ ¡s considered as a great source of energy.
(a) Air
(b) Wind
(c) Land
(d) Water
Answer:
(d) Water
Question 5.
_______ resources are the type of resources that are composed of metals.
(a) Metallic
(b) Non-metallic
(c) Both
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Metallic
Question 6.
Iron ores found at _______ in Tamil Nadu.
(a) Shervaroy hills
(b) Kanjamalai
(c) Palani hills
(d) None of these
Ans:
(b) Kanjamalai
II. Fill in the blanks:
- _________ are resources that exist without action of humankind.
- _________ resources harvested and used rationally will not produce pollution.
- The installed capacity of Kamuthi solar power project is _________ MW.
- Hydro electric power is a _________ resource.
- _________ is the largest producer of hydro-electricity.
- _________ is regarded as a symbol of prosperity and a form of wealth.
- _________ has a wider variety of uses that gold.
Answers:
- Natural resources
- Renewable
- 648
- Renewable
- China
- GoId
- Silver
III. Match the following:
- Gold – (a) electrical batteries
- Silver – (b) Black Gold
- Manganese – (c) Sedimentary rock
- Petroleum – (d) Mexico
- Limestone – (e) China
Answers:
- e
- d
- a
- b
- c
IV. Consider the following statements: Tick the appropriate answer
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Fossil fuel resources are normally formed from the remains of dead plants and animals.
Reason (R) : They are often referred to as fossil fuels and are formed from hydrocarbon.
(a) A and R are correct and R explains A
(b) A and R are correct but R does not explain A
(c) A is incorrect but R is correct
(d) Both A and Rare incorrect
Answer:
(a) A and R are correct and R explain A
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : Mica is used as an insulating material in electrical industry.
Reason (R) : Non-metallic resources are hard substances, and are good conductors of heat and electricity.
(a) A and R are correct and R explains A
(b) A and R are correct but R does not explain A
(e) A is incorrect but R is correct
(d) A is correct but R is incorrect
Answer:
(d) A is correct but R is incorrect
V. Answer in one or two sentences
Question 1.
What are the importance of resources?
- Natural resources satisfy daily needs of man such as food, clothing and shelter.
- Natural resources also contribute immensely to boost up a nation’s economy.
Question 2.
What is renewable resources?
Answer:
A renewable resource is a resource which can be used repeatedly and replaced naturally. Renewable resources harvested and used rationally will not produce pollution. The use of renewable resources and energy sources is increasing worldwide.
Example: solar energy, wind energy, and hydropower.
Question 3.
Write a note on Kamuthi Solar Project.
Answer:
Kamuthi solar power project is one of the largest solar power projects in the world. It is situated in Ramanathapuram District in Tamilnadu. The Kamuthi solar power project was completed on 21st September 2016. The installed capacity of this project is 648 MW.
Question 4.
Describe the major wind farms in India.
Answer:
Wind Forms:
- Muppandal
- Jaisalmer
- Brahmanvel
- Dhalgaon
- Damanjodi
Question 5.
What are Non-renewable resources?
Answer:
Natural resources that once consumed and cannot be replaced is called non-renewable resources. Continuous consumption of non-renewable resources ultimately leads to exhaustion. Examples of non-renewable resources include fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, natural gas and mineral resources such as iron, copper, bauxite, gold, silver and others.
Question 6.
What are the types of Non-renewable resources?
Non-renewable resources can be divided into three types. They are:
- Metallic resources
- Non – Metallic resources
- Fossil fuel resources
VI. Answer the following in detail
Question 1.
What are the types of resources on the basis of origin?
Answer:
On the basis of origin, resources may be divided into two types. They are:
- Biotic resources
- Abiotic resources
1. Biotic resources:
Biotic resources are found in the biosphere which are obtained from living and organic materials. It includes forests, crops, birds, animals, fishes, man and materials that can be obtained from them. Fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum are also included in this category because they are formed from decayed organic matter.
2. Abiotic resources:
Abiotic resources are the non-living parts of an environment. Examples of abiotic resources include land, water, air, sunlight and heavy metals including ores such as gold, iron, copper, silver etc.
Question 2.
Briefly explain any four of the metallic resources.
Answer:
Metallic resources Metallic resources are the type of resources that are composed of metals. These are hard substances, which are the good conductors of heat and electricity. Example for metallic resources are iron, copper, gold, bauxite, silver, manganese, etc.
Iron : Iron is the fourth most common element in the Earth’s crust and the most widely available metal. Magnetite and hematite are the common ore for iron, which occurs normally in the rocksof the crust.
Copper : Copper is one of the first metals known and used by man. Copper ranks as the third most consumed industrial metal in the world after Iron and Aluminium. Copper is good conductor of heat and electricity. Chile is the world’s number one country in the production of copper.
Gold : It is a rare and precious metal. Hence, ithas high demand in world markets. Formerly, it was used for minting coins, but now it is used for making ornaments and in dentistry. It is regarded as a symbol of prosperity and a form of wealth. China is the world’s largest producer of gold.
Silver : Silver is also a precious metal like gold. It has a wider variety of uses than gold. It is used in making jewellery, dentistry, photographic goods, electroplating industry and in the manufacture of luxury goods. Mexico is the world’s leading silver producer.
VII. Give reason.
Question 1.
Manganese is used in drafting electrical batteries.
Answer:
Manganese is used in making electrical batteries. It is also used as colouring material in bricks, pottery, floor tiles.
Question 2.
Silver is also a precious metal like Gold.
Answer:
Silver is also a precious metal like gold. It has a wider variety of uses than gold. It is used in making jewellery, dentistry, photographic goods, electroplating industry and in the manufacture of luxury goods.