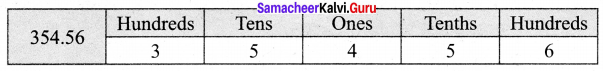
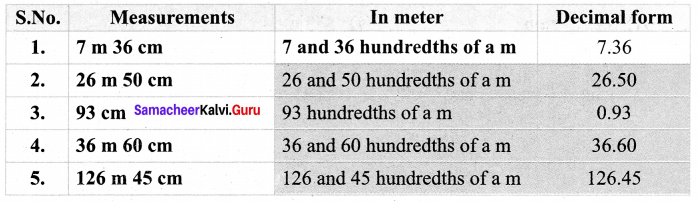
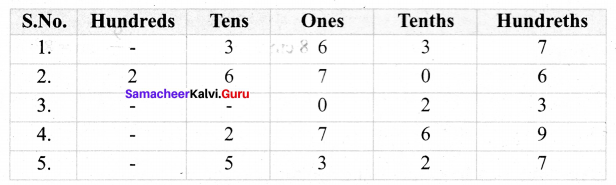
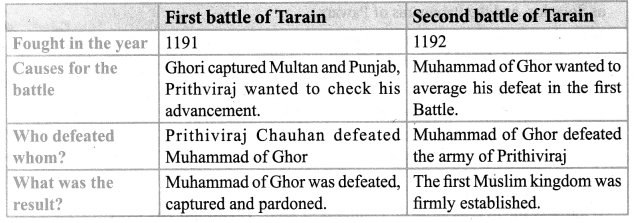
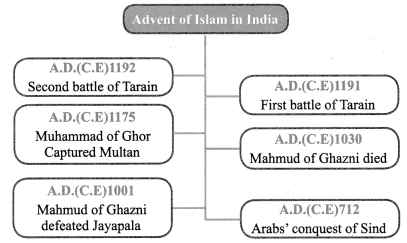
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Civics Solutions Term 2 Chapter 1 State Government
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science State Government Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer:
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Social Science Question 1.
What is the minimum age for becoming a member of the State Legislative Council?
(a) 18 years
(b) 21 years
(c) 25 years
(d) 30 years
Answer:
(d) 30 years
Samacheerkalvi.Guru 7th Social Question 2.
How many states does India have?
(a) 26
(b) 27
(c) 28
(d) 29
Answer:
(d) 29
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Social Question 3.
The word State government refers to
(a) Government departments in the states
(b) Legislative Assembly
(c) both a and b
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) both a and b
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Books Answers Question 4.
The overall head of the government in the state is the .
(a) President
(b) Prime Minister
(c) Governor
(d) Chief Minister
Answer:
(b)Prime Minister
Samacheer Kalvi.Guru 7th Social Question 5.
Who appoints the Chief Minister and other Ministers?
(a) President
(b) Prime Minister
(c) Governor
(d) Election Commissioner
Answer:
(c) Governor
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Book Answers Question 6.
Who becomes the Chief Minister?
(a) Leader of the Majority party
(b) Leader of the opposition party
(e) Both
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Leader of the Majority party
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Book Question 7.
What are the three branches of the state government?
(a) Mayor, governor, MLA
(b) Panchayat, municipality, corporation
(c) Village, City, State
(d) Legislative, executive and judiciary
Answer:
(d) Legislative, executive and judiciary
II. Fill in the blanks
- The Governor is appointed by the _______
- The leader of the majority party is appointed as _______ in the state assembly.
- _______ is the highest judicial organ of the state.
- MLA stands for _______.
- _______ is a particular area form where all the voters living there choose their representatives.
- The elected representatives who are not the member of ruling party are called _______.
Answers:
- President of India
- the Chief Minister
- The High Court
- Member of Legislative Assembly
- Electoral Constituencies
- Opposition Party
III. Match the following
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Question 1.
- MLAs – Secretariat
- Governor – 7
- Chief Minister – Head of the state
- Union territories – Legislative Assembly
- Fort St. George – leader of the Majority party
Answers:
- MLAs – Legislative Assembly
- Governor – Head of the state
- Chief Minister – leader of the Majority party
- Union territories – 7
- Fort St. George – Secretariat
IV. Consider the following statements: Tick the appropriate answer
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Question 1.
Which of the following statement is/are not correct?
To become a governor, one
a. should be the citizen of India
b. should have completed 25 years of age
c. should have sound mind
d. should not hold any office of profit.
i. a & b
ii. c & d
iii. a
iv. b
Answer:
iv. b
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Solutions Question 2.
Consider the following statements and state true or false.
a. MLAs are together responsible for the working of the government
b. All the MLAs of other political party who do not belong to the ruling party are called opposition.
e. MLAs are not the representatives of people.
Answers:
a. True
b. True
c. False
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Standard Social Question 3.
Find out the correct meaning of bicameral legislature.
a. It means that there are cameras in the legislature.
b. It means that the legislature has men and women members.
c. It means that there are two houses like upper house and lower house..
d. It means that the governor is the leader over the members of the legislature.
Answer:
c. It means that there are to houses like upper house and lower house.
Samacheer Kalvi Guru Social 7th Question 4.
Assertion: India has a federal system of government.
Reason: According to our constitution the power is divided between central and state governments.
a. A is correct and R explains A
b. A is correct and R does not explain A
c. A is correct and R is wrong
d. Both are wrong
Answer:
a. A is correct and R explains A
Social Samacheer Kalvi 7th Question 4.
Assertion: India has a federal system of government.
Reason: According to our constitution the power is divided between central and state governments.
a. A is correct and R explains A
b. A is correct and R does not explain A
c. A is correct and R is wrong
d. Both are wrong
Answer:
a. A is correct and R explains A
V. Answer in one or two sentences
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Standard Social Question 1.
What are the qualifications to become the Governor of a state?
Answer:
A person to be eligible to the post of Governor should be :
- A citizen of India.
- Should have completed 35 years of age.
- Should have sound mind and
- Should not hold any public office of Profit.
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Social Science Guide Question 2.
Who are called oppositions?
Answer:
All the MLAs of other political parties who do not belong to the ruling party are called opposition party.
Samacheer Kalvi 7 Social Question 3.
Write a note on Lok Adalat.
Answer:
Lok Adalat (people’s court) also have been established by the Government of India to settle dispute through conciliation and compromise. Lok adalats have been given statutory status under the Legal Service Authorities Act, 1987.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Books Question 4.
What is a constituency?
Answer:
Political parties nominate their candidates to each constituency. All the people residing in that constituency who has completed 18 years of age cast their vote.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Books Answers Question 5.
Who appoints the chief minister and other ministers?
Answer:
The Chief Minister is appointed by the Governor who also appoints other ministers on the advice of the Chief Minister. The council of Minister is collectively responsible to legislative assembly of the state.
VI. Answer the following in detail
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Book Solutions Question 1.
Describe the powers of the Governor.
Answer:
- The Governor is an integral part of the State Legislature.
- Governor is the head of the state executive and he has enormous powers.
- All the administration is carried on in his name. He is the chancellor of Government universities in the state.
- All bills become law only after his assent. He appoints important officials of the state government such as advocate General, Chairman and members of State Public Service Commission,
- State Election Commissioner, Vice chancellors of state universities etc.
Question 2.
Who is an MLA?
Answer:
- The term MLA stands for a Member of Legislative Assembly.
- The member of the Parliament is called MP whereas the member of the Legislative Assembly is called MLA. Both the Central and State Governments work according to our constitution.
- He / She is elected through a general election and represents a particular constituency.
- It is not necessary for one to be a member of a political party to become a MLA.
- He / She can contest the election as an independent candidate also.
Question 3.
What is the role of Chief Minister and other Council of Ministers at the state level?
Answer:
- The Chief Minister is the real executive head of the state administration.
- He allocates the portfolios among the ministers.
- The Council of Ministers are collectively responsible to the State Legislature.
- All the ministers work as a team under the Chief Minister.
- The Chief Minister formulates programmes and policies for the welfare of the people of the state.
- The council of Ministers is collectively responsible to the Legislative Assembly of the state
VII. HOTs
Question 1.
Name some departments of the government
Answer:
- Health
- Railway
- Finance
- Education
- Revenue
- Agriculture
Question 2.
Tabulate: qualification, appointment and any two powers of governor, Chief Minister and MLAs. ;
Answer:
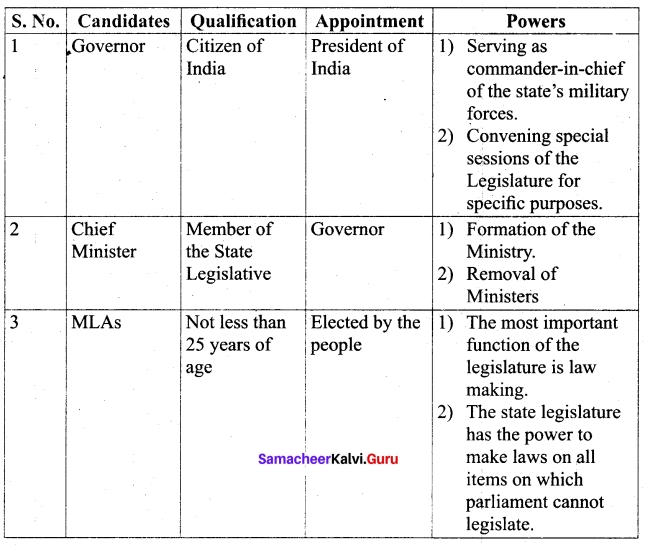
VIII. Activity
Question 1.
Make a list of the name of the Governor, Chief Minister and other Ministers with their departments.
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
Question 2.
Write an essay on ‘If you were the Chief Minister of the state’.
Answer:
First of all, I shall try my level best to make my country a strong and self respecting nation. India will be a great power and no other country will dare attack India.
The second thing I will do will be the fullest and genuine attention to the poorest and the lowliest. I shall endeavour to give full employment to at least one member of each house-hold. It will be my attempt to keep the prices under control. I shall try to stream-line the public distribution system further and supply the essential commodities to the poor at subsidized rates. I shall try to make the taxation system more useful and rational. Whereas the rich may be taxed heavily, the poor and the middle classes will be spared.
The third thing, to which I shall devote my energy, is the education system. I shall raise its standard and make it based on merit and for all. The examination system will be over-hauled, so that there is no copying and the real merit of a student is readily discernible. Much more attention will be given to admission to professional colleges on the basis of merit. There will be reservation only on economic grounds and not on caste basis.
The fourth thing deserving my fullest attention will be the population control. Without it, our country will be ruined. Then I shall also take care of important and productive fields like agriculture, industry, oil production, mining, increase in exports etc. Above all, I shall try to raise the moral standard of the people and make them more patriotic. I shall also try to root out evils of terrorism, communalism, provincialism, drug-taking, dowry system, drinking etc.
Question 3.
Make a student Legislative body in your class, (allocate the departments and do periodical review).
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science State Government Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
MLA’s are elected by _______.
(a) Children
(b) People
(e) Teachers
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) People
Question 2.
The Governor calls the leader of the majority party to form the ________.
(a) State Government
(b) Central Government
(c) Both
(d) None
Answer:
(a) State Government
Question 3.
The Governor is appointed by the President of India for the term of ________ years.
(a) 3
(b) 5
(c) 6
(d) 12
Answer:
(b) 51
Question 4.
MLA or MLC should have completed ________ years of age.
(a) 25
(b) 35
(c) 30
(d) 40
Answer:
(c) 30
Question 5.
________ is an integral part of the state legislature.
(a) MLA
(b) MLC
(c) Chief Minister
(d) Governor
Answer:
(d) Governor
Question 6.
All the Minisers work as a team under the ________.
(a) Chief Minister
(b) Prime Minister
(e) President
(d) MLA
Answer:
(a) Chief Minister
II. Fill in the blanks:
- Every state in India has a ________
- The ruling party members then form the government and some members are appoinied as ________
- ________ are representatives of the people.
- ________ conducts and monitors the elections.
- In India some of the states have two houšes in their.
- The ________ is the real executive head of the state administration.
Answers:
- Legislative Assembly
- Ministers
- MLAs
- The Election Commission of lndia
- state legislaturel
- Chief Minister
III. Match the following:
- States – (a) Chief Minister
- Integral part – b) People’s court
- Real executive power – (c) Highest judicial organ
- Lok Adalat – (d) President
- High Courts – (e) 29
Answers:
- – e
- – d
- – a
- – b
- – c
IV. True or False
- The powers and responsibilities between city governments and country governments are always the same in every state.
- Tamil Nadu is a unicamerate legislature.
- Governor is the chancellor of government universities in the state.
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
V. Consider the following statements: Tick the appropriate answer
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : The three main organs of government are the legislative, executive and judiciary.
Reason (R) : The High Courts are the highest judicial organ at the state level
(a) A is correct and R explains A
(b) A is correct and R does not explain A
(c) A is correct and R is wrong
(d) Both are wrong
Answer:
(b) A is correct and R does not explain A
VI. Answer in one or two sentences
Question 1.
What is Legislative Assembly?
Answer:
Legislative Assembly is the law making body of a state. The members of (his Assembly are directly elected by people, so they can be called as representatix e ol people or usually known as Member of Legislative Assembly (MLA).
Question 2.
How many states and union territories are there in India?
Answer:
29 States and 7 uni&n terriories are in India.
Question 3.
What is Central Government?
Answer:
India is a Parliamentary democratic republic where the President of India is the Head of Indian Union and the Prime Minister and all the Ministers are responsible for smooth running of the government. This is called central government.
Question 4.
Who are all included in the State Government?
Answer:
The Governor, the Chief Minister, Council of Ministers.
VI. Answer the following in detail
Question 1.
What is High Courts? and it briefly explain.
Answer:
- The High courts are the highest judicial organ at the State level.
- It is an independent body.
- As per the constitution there shall be a High Court in each state.
- The state high court consists of a Chief Justice and other judges.
- The number of Judges in the high court is not uniform and fixed.
- President appoints the Chief Justice and can hold the office until he completes the age of 62 years.
- Apart from High court there are district courts and tribunals.
- They ensure justice to the people without any bias. Apart from this, Family Courts are established to settle the disputes relating to marriages and family affairs.