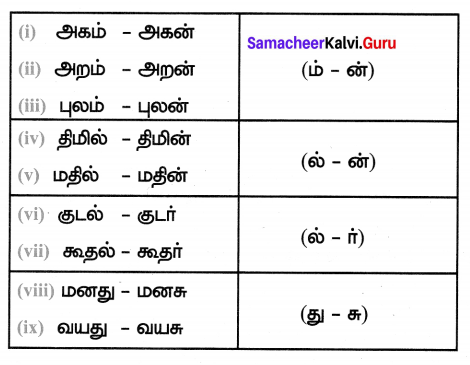
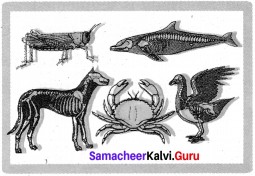
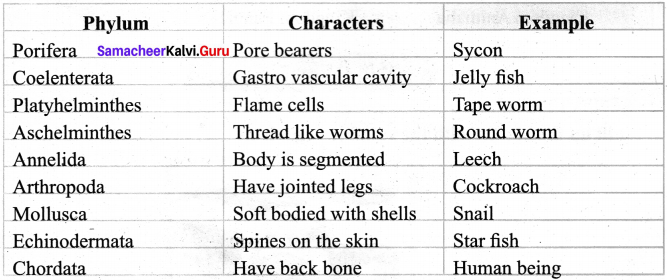
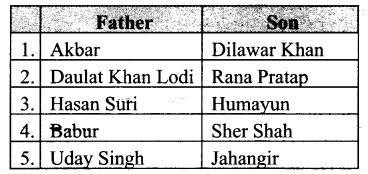
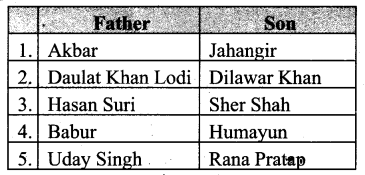
Students can Download Tamil Chapter 3.3 தேசியம் காத்த செம்மல் பசும்பொன் உ.முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவர் Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Tamil Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Tamil Solutions Term 1 Chapter 3.3 தேசியம் காத்த செம்மல் பசும்பொன் உ.முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவர்
மதிப்பீடு
சரியான விடையைத் தேர்ந்தெடுத்து எழுதுக.
Question 1.
முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவர் முதன்முதலில் உரையாற்றிய இடம் …….
அ) தூத்துக்குடி
ஆ) காரைக்குடி
இ) சாயல்குடி
ஈ) மன்னார்குடி
Answer:
இ) சாயல்குடி
Question 2.
முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவர் நடத்திய இதழின் பெயர்…
அ) இராஜாஜி
ஆ) நேதாஜி
இ) காந்திஜி
ஈ) நேருஜி
Answer:
ஆ) நேதாஜி
Question 3.
தேசியம் காத்த செம்மல் எனப் பசும்பொன் முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவரைப் பாராட்டியவர்…….
அ) இராஜாஜி
ஆ) பெரியார்
இ) திரு.வி.க.
ஈ) நேதாஜி
Answer:
இ) திரு.வி.க.
குறுவின
Question 1.
முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவரைப் பாராட்டிப் பெரியார் கூறியது யாது?
Answer:
(i) தேசியம் உடல், தெய்வீகம் உயிர் எனக் கருதி மக்கள் தொண்டு செய்தவர் பசும்பொன் முத்துராமலிங்கத் தேவர்.
(ii) இவர் வீரப்பேச்சால் எத்தனையோ தியாகிகளையும் விவேகப் பேச்சால் எத்தனையோ அறிவாளிகளையும் உண்டாக்கியவர்; உண்மையை மறைக்காமல் வெளியிடுவதில் தனித் துணிச்சல் பெற்றவர்; சுத்தத் தியாகி என்று தந்தைப் பெரியார் பாராட்டினார்.
Question 2.
முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவரின் பேச்சுக்கு வாய்ப்பூட்டுச் சட்டத்தின் மூலம் தடைவிதிக்கப்படக் காரணம் யாது?
Answer:
- முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவர் மேடைகளில் ஆற்றிய வீர உரையைக் கேட்ட மக்கள் ஆங்கில ஆட்சிக்கு எதிராக வீறுகொண்டு எழுந்தனர்.
- அதனால் அச்சமடைந்த ஆங்கில அரசு பலமுறை அவரைக் கைது செய்து சிறையில் அடைத்தது. மேலும் வாய்ப்பூட்டுச் சட்டம் மூலம் மேடைகளில் அரசியல் பேசக்கூடாது என்று அவருக்குத் தடை விதித்தது.
Question 3.
முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவர் பெற்றிருந்த பல்துறை ஆற்றலைப் பற்றி எழுதுக.
Answer:
முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவர் பெற்றிருந்த பல்துறை ஆற்றல் : சிலம்பம், குதிரை ஏற்றம், துப்பாக்கிச் சுடுதல், சோதிடம், மருத்துவம் போன்ற பலதுறைகளிலும் ஆற்றல் உடையவராக விளங்கினார்.
சிறுவினா
Question 1.
நேதாஜியுடன் முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவர் கொண்ட தொடர்புப் பற்றி எழுதுக.
Answer:
(i) வங்கச் சிங்கம் என்று போற்றப்பட்ட நேதாஜி சுபாஷ் சந்திரபோசுடன் நெருங்கிய தொடர்பு கொண்டிருந்தார். அவரைத் தமது அரசியல் குருவாக ஏற்றுக் கொண்டார்.
(ii) முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவரின் அழைப்பை ஏற்றுக் கி.பி. (பொ.ஆ.) 1939-ஆம் ஆண்டு செப்டம்பர்த் திங்கள் ஆறாம் நாள் நேதாஜி மதுரைக்கு வருகை தந்தார்.
(iii) நேதாஜி தொடங்கிய இந்திய தேசிய இராணுவத்தில் முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவரின் முயற்சியால் ஏராளமான தமிழர்கள் இணைந்தனர். விடுதலைக்குப் பின் நேதாஜி என்னும் பெயரில் வார இதழ் ஒன்றையும் நடத்தினார்.
Question 2.
தொழிலாளர் நலனுக்காக முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவர் செய்த தொண்டுகள் யாவை?
Answer:
(i) 1938 காலக்கட்டத்தில் மதுரையில் 23 தொழிலாளர் சங்கங்களின் தலைவராகத் தேவர் திகழ்ந்தார்.
(ii) மதுரையிலிருந்த நூற்பு ஆலை ஒன்றில் வேலை செய்த தொழிலாளர்களின் உரிமைக்காகத் தோழர் ப. ஜீவானந்தத்துடன் இணைந்து 1938 ஆம் ஆண்டு போராட்டம் நடத்தினார்.
(iii) அதற்காக ஏழு திங்கள் சிறைத் தண்டனைப் பெற்றார். உழவர்களின் நலன் காக்க இராஜபாளையத்தில் மிகப்பெரிய அளவிலான மாநாடு ஒன்றை நடத்தினார். பெண் தொழிலாளர்களுக்கு மகப்பேறு காலத்தில் ஊதியத்துடன் கூடிய விடுப்பு வேண்டும் என்று போராடினார்.
சிந்தனை வினா
Question 1.
சிறந்த தலைவருக்குரிய பண்புகள் எவை என நீங்கள் கருதுகிறீர்கள்?
Answer:
சிறந்த தலைவருக்குரிய பண்புகள் :
(i) நல்ல குண இயல்புகள் கொண்டு இருக்க வேண்டும். செயல்பாடுகள் நல்லதாக இருக்க வேண்டும். வெறும் அறிவு மட்டுமே இருந்தால் ஒருவருக்கு தலைமைப்பண்பு இருக்கின்றது என்ற கருத முடியாது. அறிவு, அனுபவம், மனிதர்களை மதித்து நடந்து கொள்ளும் பண்பு ஆகியவற்றைக் கொண்டவரே சிறந்த தலைவர்.
(ii) மக்களின் வறுமைகளையும், இன்னல்களையும் போக்குபவரே சிறந்தத் தலைவர். கீழ்மட்டத்திலுள்ள மக்களுக்கு உரிமைகளைப் பெற்றுத் தர வேண்டும்; மேல் மட்டத்திலுள்ள மக்களின் நலனையும் பேணி காக்க வேண்டும்.
(iii) இருவரையும் சமமாக நடத்த வேண்டும். உயர்ந்தவர் தாழ்ந்தவர் எனப் பிரிக்காமல், இருவரும் ஒருவரே என அரவணைத்து செல்பவரே சிறந்த தலைவருக்குரிய பண்புகளில் ஒன்றாகும்.
(iv) சிறந்த தலைவரானவர் பிறரது மனதில் தாக்கத்தை ஏற்படுத்தி திறமையாகச் செயல்பட வைக்கும் ஆற்றல் உள்ளவர்களாக இருப்பர். இதுவரை வெளிப்படுத்தாமலிருந்த திறமைகளையும் மக்களிடமிருந்து வெளிக்கொணரும் வகையில் இவர்களது செயல்பாடு அமையும், இவர்களது அணுகுமுறையும், செயல்பாடுகளும் பிறரையும் சிறப்பாக செயல்படத் தூண்டும் வகையில் இருக்கும்.
(v) மக்களிடத்தில் எந்தவித பாகுபாடும் இல்லாமல், பய உணர்ச்சியும் இல்லாமல், நடந்து கொள்ளுதல், செயல்களுக்கு பொறுப்பேற்றுக் கொண்டு செயல்படுதல், வெற்றி என்றாலும் சரி, தோல்வி என்றாலும் சரி அதற்கு பொறுப்பேற்றுக் கொள்ளும் மனப் பக்குவம் போன்ற தலைமைப் பண்புகள் கொண்டவர்களே! சிறந்த தலைவராக முடியும்.
கற்பவை கற்றபின்
Question 1.
நாட்டுக்கு உழைத்த சிறந்த பிற தலைவர்களைப் பற்றிய செய்திகளைத் திரட்டி எழுதுக.
Answer:
சுபாஷ் சந்திரபோஸ்(நேதாஜி) :
வங்காளத்தில் 1897-ஆம் ஆண்டு ஜனவரி 23-ஆம் நாள் கோதாலியா என்ற சிற்றூரில் ஜானகிநாத் – பிரபாவதி தம்பதிகளுக்கு மகனாகப் பிறந்தவர் சுபாஷ் சந்திரபோஸ். தாயார் பிரபாவதியிடம் வீரம் நிறைந்த காளிதேவியின் கதைகளைக் கேட்டு அறிவார். 1915 ஆம் ஆண்டு பள்ளியின் மாணவத் தலைவனாக தேர்வு செய்யப்பட்டார். ஐரோப்பாவில் வாழ்ந்த வெளிநாட்டுவாழ் இந்தியர்கள் சுபாஷை “நேதாஜி” என்று அழைத்தனர். அன்று முதல் சுபாஷ் சந்திரபோஸ் “நேதாஜி” என்று அழைக்கப்படுகிறார்.
இந்து, முஸ்லீம் என்று பிரிந்து கிடந்த இந்தியர்களை ஒன்றிணைக்க நேதாஜியால் அப்போது “ஜெய்ஹிந்த்” என்ற தாரக மந்திரம் எழுப்பப்பட்டது.
1945-ஆம் ஆண்டு ஆகஸ்டு 16-ஆம் நாள் ஜப்பானுடன் பேச்சுவார்த்தை நடத்த சைகோனிலிருந்து விமானத்தில் நேதாஜி புறப்பட்டார். ஆனால் வழியில் (தைவான்) தைஹோக் என்ற இடத்தில் அவர் சென்ற விமானம் விபத்துக்குள்ளானது என்றும், இதில் பலத்த காயமடைந்த நேதாஜி ஆகஸ்டு 18-ஆம் நாள் தனது இன்னுயிர் நீத்தார் என்றும் கூறப்பட்டது.
அம்பேத்கர் :
மகாராஷ்டிரா மாநிலம் ரத்னகிரி மாவட்டத்தில் அம்பாலாதே கிராமத்தில் 1891-ஆம் ஆண்டு ஏப்ரல் 14-ஆம் நாள் அம்பேத்கர் பிறந்தார். பெற்றோர் சுபேதார் இராம்ஜி சக்பால் – பீமாபாய் ஆவர். பெற்றோர் இட்ட பெயர் பீமாராவ் இராம்ஜி ஆகும்.
1913-ஆம் ஆண்டு கொலம்பியா பல்கலைக்கழத்தில் அரசியல் மற்றும் பொருளாதாரம் ஆகிய பிரிவுகளில் மேல் படிப்புக்காகச் சேர்ந்தார். 1915-ஆம் ஆண்டு எம்.ஏ. பட்டமும், 1916ஆம் ஆண்டு தத்துவப் பேரறிஞர் பட்டமும் பெற்றார்.
இந்திய நாட்டுக்குத் திரும்பியதும் பம்பாய் சைடன்ஹாம் கல்லூரியில் 1918 ஆம் ஆண்டிலிருந்து 1920-ஆம் ஆண்டு வரை பொருளாதாரப் பேராசிரியராகப் பணியாற்றினார்.
மீண்டும் லண்டன் சென்று 1923-இல் எம்.எஸ்.சி மற்றும் பாரிஸ்டர் பட்டங்களைப் பெற்றார். பம்பாயில் வழக்கறிஞர் தொழில் தொடங்கினார். 1956ஆம் ஆண்டு அம்பேத்கர் புத்த மதத்தில் இணைந்தார். அதே ஆண்டில் டிசம்பர் 6-ஆம் நாள் இந்திய அரசு 1990 ஆம் ஆண்டு பாரத ரத்னா” விருது வழங்கி கௌரவித்தது.
கூடுதல் வினாக்கள்
நிரப்புக :
Question 1.
சன்மார்க்க சண்டமாருதம் என்று அழைக்கப்படுபவர் ……
Answer:
முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவர்
Question 2.
பசும்பொன் முத்துராமலிங்கத் தேவரை ‘தென்னாட்டுச் சிங்கம்’ எனக் கூறியவர்
Answer:
அறிஞர் அண்ணா
Question 3.
முத்துராமலிங்கத் தேவர் மதுரையிலிருந்த நூற்பு ஆலை ஒன்றில் வேலைசெய்த தொழிலாளர்களின் உரிமைக்காக …………… உடன் இணைந்து 1938 ஆம் ஆண்டு போராட்டம் நடத்தினார்.
Answer:
ப.ஜீவானந்தம்
விடையளி :
Question 1.
பசும்பொன் முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவர் சிறை வாசம் பற்றி எழுது.
Answer:
பசும்பொன் முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவர் சுதந்திரப் போராட்டத்தில் மிகத் தீவிரமாக ஈடுபட்டதால் கைது செய்யப்பட்டு அலிப்பூர், அமராவதி, தாமோ, கல்கத்தா, சென்னை, வேலூர் போன்ற சிறைகளில் சிறை வைக்கப்பட்டிருந்தார். இரண்டாம் உலகப்போர் சமயத்தில் மத்திய பிரதேசத்தின் தாமோ என்னும் நகரில் உள்ள இராணுவச் சிறையில் அடைக்கப்பட்டுப் போர் முடிந்த பிறகுதான் விடுதலை செய்யப்பட்டார்.
Question 2.
முத்துராமலிங்கத்தேவரின் சிறப்புப் பெயர்கள் யாவை?
Answer:
தேசியம் காத்த செம்மல், வித்யா பாஸ்கர், பிரவசன கேசரி, சன்மார்க்க சண்டமாருதம், இந்து புத்த சமயமேதை.