Students can Download English Lesson 3 A Prayer to the Teacher Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes Pdf, Activity, Samacheer Kalvi 7th English Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th English Solutions Term 1 Prose Chapter 3 A Prayer to the Teacher
Reading
I. Which of these statements do you find in the speech?
- Inclusion is essential for us to do well in life.
- We should neglect others.
- Communicate politely with the less privileged.
- Teachers teach us to communicate well.
- Effective Communication is inessential to excel in life.
Answer:
We find statement No. 1, 3 and 4 in the speech.
- [✓]
- [✗]
- [✓]
- [✓]
- [✗]
II. Read the statements. Tick [✓] the correct words. You can tick more than one.
A Prayer To The Teacher Question 1.
We should develop the ability to learn from _____
Answer:
[✓] self
[✓] others
[✓] books
A Prayer To The Teacher Question And Answer Question 2.
Teachers help me to learn _____ things.
Answer:
[✓] new
[ ] bad
[✓] difficult
A Prayer To The Teacher Summary Question 3.
Teach me to appreciate
Answer:
[✓] nature
[ ] destruction
[✓] small creatures
A Prayer To The Teacher Book Back Answers Question 4.
We should learn to questions.
Answer:
[✓] ask
[✓] answer
[ ] discard
III. Answer the following questions in a sentence or two.
A Prayer To The Teacher 7th Standard Question 1.
What is inclusion? Why is it important?
Answer:
Inclusion is to value everyone beyond the boundaries irrespective of their differences. Inclusion is important to be successful in life.
A Prayer To The Teacher 7th Std Question 2.
What is good or effective communication?
Answer:
Good and effective communication are to be able to speak and write to convey what . we actually feel.
Prayer To The Teacher Question 3.
What should we learn from our teachers?
Answer:
We should learn newer and more difficult things from our teachers.
A Prayer To The Teacher Lesson Plan Question 4.
What kind of learning brings joy to you?
Answer:
Learning new ways to learn brings joy to us.
A Prayer To The Teacher Theme Question 5.
In what ways are we doing injustice to nature?
Answer:
We do injustice to nature by felling trees, killing small creatures and causing urban decay.
A Prayer To The Teacher Prose 7th Standard Question 6.
What do you need to learn to live a good life in this world?
Answer:
To live a good life in this world we need to learn to appreciate the interconnected nature of things.
The Prayer To The Teacher Question 7.
How does the ability to question help us?
Answer:
The ability to question helps us to get answers, to establish better order of things, to be accountable and in the end it helps us to see the truth emerge.
A Prayer To The Teacher Lesson Question 8.
What do you think are the two most important lessons that the speaker mentions?
Answer:
The two most important lessons the speaker mentions are to stress our point without raising our voice and to raise our voice when our silence hurts another life.
IV. Answer the following questions in detail.
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th English Question 1.
What are the skills / values a teacher should teach their students to live in this competitive world?
Answer:
To live in this competitive world, our teachers should teach their students important skills and values like, the value of inclusion, ability to communicate both written and verbal, the ability to learn newer and more difficult things.
Samacheer Kalvi Guru English 7th Standard Question 2.
What kind of a life do you want to lead in this world?
Answer:
When I live in this world I want to live a patriotic life which means having tolerance towards others with a different opinion in matters like religion, race, etc. I would like to consider all people in the world suffering from poverty, disease and hunger as my own and help them. Violence should not be found in my environment. I should have the strength to love all my fellow human beings with all their short comings. I should see unity in diversity. I must not consider anyone from any part of the globe as foreigner or stranger but as brother and sister. I wish to live a peaceful life without any barbed wires or smoking guns.
Vocabulary
Prefix And Suffix
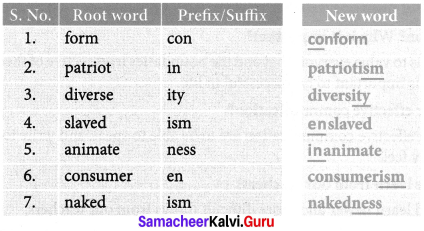
A. Match the suitable prefix and suffix to create new words of your own. One has been done for you.
Answer:
B. Refer to your dictionary. Add a prefix or suffix to the following words and find their antonyms.
Answer:
- privileged × underprivileged
- animate × inanimate
- discriminate × indiscriminate
- empty × unempty
- communicate × miscommunicate
- learn × unlearn
Listening
C. Listen to the story and fill in the blanks by selecting the right option.
- Raj was upset as he had done ______ (Well/poorly) in his english test
- His grandmother gave him a ______ (pen/pencil)
- Granny compared ______ (Raj / Ravi) with the pencil.
- Raj’s pain of not doing well in his test was compared with ______ of Pencil. (Sharping/ writing)
- Raj understood that failures are stepping stones to _____ (success/climbing)
Answer:
- Poorly
- Pencil
- Raj
- Sharping
- success
Speaking
D. Read the story. Divide yourselves into groups of four. Discuss what little Sarah wants to talk about. Take roles and enact the story.
Answer:
Anitha, Banu, Chitra and Daisy discuss what Little Sarah wants to talk about.
Anitha : Why is Sarah sad?
Banu : Sarah’s father got a transfer to another city. So Sarah was moved to a new house and a new school in the new city.
Chitra : Oh! Is she sad because she missed her old home and old school friends?
Daisy : Yes. She wanted to express her sad feelings to her close relatives.
Anitha : Do you mean to her parents and brother?
Banu : But poor thing, they did not listen to her in their busy work.
Chitra : Was she able to tell her feelings to any one?
Daisy : Her teacher Ms. Nancy saw her new student Sarah sad. She called her and asked the reason.
Anitha : Sure. Sarah would have told how badly she missed her dear friends and her home. Was the teacher able to make her happy?
Banu : Of course. The teacher listened to Sarah patiently and told her that the people near her present home and school are also good and assure she would earn good friends soon.
Chitra : The teacher had helped Sarah to develop a world view of things, to appreciate diversity and the power of loving her fellow human beings.
All : Yes!
Picto Grammar
E. Look at the pictures. Pick out the right preposition and fill in the speech bubbles given below.
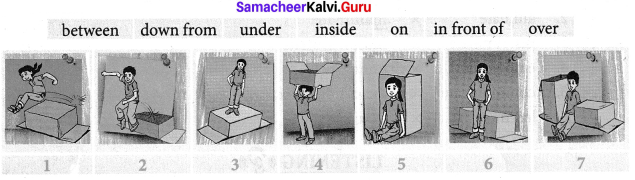
Answer:
- I’ am jumping over the box.
- I can jump down from the box.
- I’ am standing on the box.
- I’ am carrying the box on my head.
- I’ am sitting inside the box.
- I’ am standing in front of the box
- I’ am sitting in between the boxes.
Grammar
F. Read the following sentences carefully and underline the preposition
Answer:
- Julian placed her lunchbox inside her bag. – Place Preposition
- Vinothini left the house before sunrise. – Time Preposition
- Ben saw Daisy playing across the road. – Place Preposition
- Hema keeps all her teddy bears on top of her wardrobe. – Position Preposition
- Divya hid the sweets behind her back. – Place Preposition
- Sudha fell over during the basketball match. – Position Preposition
- Madhusudhan checked to see if his keys had fallen underneath his chair. – Position Preposition
- Mrs Meena asked the children to go into her classroom. – Place Preposition
- After lunch, the children were allowed to play. – Time Preposition
- Saravanan climbed onto the horse. – Position Preposition
G. Complete the following sentences using appropriate prepositions.
Question 1.
Is your mother _______ home?
(a) in
(b) at
(c) on
Answer:
(b) at
Question 2.
There is unity in diversity _______ the people.
(a) among
(b) between
(c) within
Answer:
(a) among
Question 3.
He discussed the problem _______ his parents.
(a) with
(b) to
(c) for
Answer:
(a) with
Question 4.
Lithisha was praised _______ her father.
(a) with
(b) for
(c) by
Answer:
(c) by
Question 5.
Can you finish the work _______ tomorrow?
(a) by
(b) in
(c) within
Answer:
(a) by
Question 6.
He has been absent _______ last week.
(a) since
(b) for
(c) by
Answer:
(a) since
H. Fill in the blanks using suitable positions from the box. Some options can be used more than once.
(across,with,on,to,by,since,from,about,into,at,during)
- What do you do ______ weekends?
- I am going to my village ______ Sunday.
- I haven’t met my friends ______ December.
- Run ______ the street and get me the ribbon.
- He told me in detail ______ the incident.
- ‘This picture was drawn ______ the girl ______ Charcoal
- The car was travelling ______ a great speed.
- The ball fell ______ the lake.
- There is a bridge ______ the river.
- The conference will be held ______ 10 a.m. ______ 5 p.m.
Answer:
- during
- on
- since
- on
- about
- by; with
- at
- into
- across
- from; tol
I. Fill up the blanks using suitable prepositions on your own.
- The soldier climbed ________ a horse and rode away.
- They have been here ________ a long time.
- Kumaravel has lived in this city ________ 2012.
- The paper was published ________ an International journal.
- When will you return ________ home?
- One ________ the four students wrote the answers correctly.
- This fruit is ________ the Mexican capital.
- The head offce is ________ Nungambakkam. It is College Road. As you go the station, the office is the right side.
- The sailors were taken ________ the forest and made to walk 10 miles.
- The girl standing ________ me was sneezing.
Answer:
- on
- for
- since
- in
- back
- of
- from
- at; on; through; at
- through for
- before
Writing
J. Fill in the value rees with the best qualities you like to follow ii ir life from the given list. Write a few lines about your favourite quality in the box.
Answer:
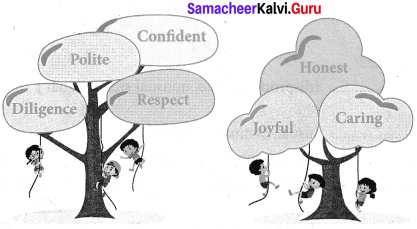
My favourite quality is Good manners. Good manners fetches good name for us. If we develop good manners from childhood it will continue till our adulthood. We shall be role models for others when we display good manners.
Creative Writing
K. Fill in the template given for limerick.
Answer:
There once was a chubby soft Teddy bear (8 syllable)
Whom cute baby had always near (8 syllable)
She played with him (5 syllable)
Even when she swim (5 syllable)
If Teddy’s lost don’t cry baby dear! (8 syllable)
A prayer to the Teacher Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct Synonyms from the options below.
Question 1.
emerge
(a) to appear
(b) come out
(c) reveal
Answer:
(b) come out
Question 2.
engulf
(a) swallow whole
(b) consume
(c) eat
Answer:
(a) swallow whole
Question 3.
nakedness
(a) frank
(b) open
(c) not hiding
Answer:
(a) frank
Question 4.
urban decay
(a) making city rot
(b) deteriorating the city
(c) destroy the city
Answer:
(c) destroy the city
Question 5.
gifted
(a) people with knowledge
(b) people blessed with everything
(c) giving fit
Answer:
(a) people with knowledge
Question 6.
cut throat
(a) highly competitive
(b) competitive
(c) cut the throat
Answer:
(a) highly competitive
Question 7.
value
(a) giving importance
(b) precious
(c) costly
Answer:
(a) giving importance
Question 8.
free
(a) without payment
(b) discount
(c) available without money
Answer:
(a) without payment
II. Pick the Correct Antonyms.
- proportionate × ______ (disproportionate, unusual size, inequal)
- unusual × ______ (usual, common, regular)
- urban × ______ (village, suburban, town)
- accountable × ______ (unaccountable, not responsible, irresponsible)
- imbalance × ______ (balance, not partial, equal)
- animate × ______ (inanimate, not animal, non living)
- tolerance × ______ (intolerance, not tolerate, not adjusting)
- foreigner × ______ (native, inland person, citizen)
- humility × ______ (proud, boasting, dominating)
- indiscriminate × ______ (discriminate, judge carefully, identify)
Answer:
- disproportionate
- usual
- village
- unaccountable
- balance
- inanimate
- intolerance
- native
- proud
- discriminate
III. Choose the Correct Answer (MCQ).
Question 1.
I clean my house and empty the garbage on the road because the road is not ______ in what I feel is my own.
(a) included
(b) indulgence
(c) inclusion
Answer:
(a) included
Question 2.
I take my child to the movie but not my neighbour’s child because that child is beyond my zone of ______
(a) fostering
(b) caring
(c) parenting
Answer:
(c) parenting
Question 3.
Our depends on our power to impress ______
(a) survival
(b) impact
(c) honour
Answer:
(a) survival
Question 4.
We are ______ because we do not ask questions
(a) accountable
(b) learning
(c) enslaved
Answer:
(c) enslaved
Question 5.
The sea does not get ______ from us for the fish it gives us.
(a) tax
(b) royalties
(c) money
Answer:
(b) royalties
Question 6.
Poverty, disease and hunger have no ______
(a) diversity
(b) patriotism
(c) nationality
Answer:
(c) nationality
IV. Short Questions with Answers.
Question 1.
Give an introduction to the lesson ‘A Prayer to the Teacher’.
Answer:
The lesson A Prayer to the Teacher’ is actually the speech given by Subroto Bagchi, the Founder and CEO of Mindtree. The speech was the convocation address given to the teachers graduating from the International Academy for Creative Teaching at Bangalore in 2005.
Question 2.
What was the main theme of Subroto Bagchi’s speech?
Answer:
Subroto emphasizes mainly that the teachers should go beyond the syllabus and teach students the values and skills they need to live a useful and meaningful life.
Question 3.
What is the importance of the ‘power to impress’?
Answer:
Today’s students are forced to impress because their survival depends on their success in the rat race of common entrance tests and competitive exams and competitions.
Question 4.
‘Teach me also to raise my voice’. Is the author asking us to fight?
Answer:
No. The author wants us to speak thoughtfully to protect a life, one who is hurt and for truth. But at the same time when people unnecessarily shout, we should be silent, contemplate and act positively.
V. Paragraph Questions with Answers.
Question 1.
Define ‘inclusion’ and give three examples.
Answer:
Inclusion means valuing all people irrespective of their boundaries like financial and educational status, caste, creed, physical health, designation or nativity.
Examples:
1. Cleaning our house and emptying the garbage on the road because we do not feel the road is also ours.
2. Feeding our child in front of our hungry servant maid, not caring for her with a humanitarian heart that she also is one in our household.
3. Not taking the close neighbour’s child to the movie along with one’s own child, thereby not having a broad parental attitude.
Question 2.
List a few things we need to communicate and convey what we feel.
Answer:
We must be able to communicate with:
- A simple innocent child and nature.
- The disabled and the ones who are hard of hearing and speaking.
- Those who are under privileged and less gifted than us.
- People who are our seniors and elders as well as our juniors and youngsters.
- With all the living as well as the nonliving things around.
By communicating, the speaker means to protect, safe-guard, cherish and to keep them.
Question 3.
‘Teach me to appreciate the interconnected nature of things’. How?
Answer:
The speaker wants the teachers to create an awareness in students about nature when
they teach of nature. Example :
a) It is not just teaching the concept of ‘rising waves’ but also the reasoning what causes the waves to fall.
b) Teaching not only teach the use of fertilizers and pesticides, but even the damage they cause by killing small creatures and felling big trees.
c) We teach the protection and promotion of the interests of consumers but at the same time we must also teach the imbalance it causes in the natural state of things which causes death and destruction on the earth.
d) We must not just teach about birds like crows and sparrows but also teach what makes them to go extinct and how it could be prevented by saving them.
Question 4.
In this increasingly commercial world, the things that truly support life comes freely to us. Justify with suitable evidence.
Answer:
The things that help us to live are mostly got free.
We do not pay the cow for the milk she gives.
The earth does not ask us money for the crops it gives.
The sun that gives light, the air that helps to breathe, the river that gives water and the clouds which give rain do not get paid for their services.
Question 5.
How can we‘develop a world view of things’according to the speaker.
Answer:
The speaker stresses that we must have the ‘one world’ feeling. Poverty, disease and hunger in the world have to be removed. Patriotism in the world should not be intolerance towards religion and race. Enimity and wars in the future must be replaced with love for our fellow human beings. There should be unity in diversity. We should have tolerance towards the differences found in people. No one should be a ‘foreigner’ for us but all people in the world are our brothers and sisters.
VI. Explain the Following Terms.
Question 1.
Narrow domestic walls.
Answer:
Here the speaker Subroto narrates how India had been crushed in ‘narrow domestic walls’ Which means it has been divided by regions or barriers based on class, colour, caste, race, religion, ethnicity, etc. This narrow attitude opposes to a feeling of one united nation or one united human race. These barriers are not favourable for nationalism and internationalism.
Question 2.
‘Illuminated with the power of thousand Suns’
Answer:
As a concluding note of his convocation address, Subroto speaks these words to bless all the new graduates. Anyone, who graduates, dreams to take up the best career, do well in it, achieve and to be elevated. Hence Subroto abundantly blesses the life of the graduates to be lighted and bright, equivalent to the light given by a thousand Suns.
Question 3.
Power of silence.
Answer:
Sometimes silence is more louder than voices. Example if a son makes a mistake and faces his father, expecting that he would scold him and when he does not scold him, the son would feel the silence more painful than his words. Silence gives inner strength.
Question 4.
Engulf me and mine.
Answer:
Here the speaker says that if we continue to fell trees, kill animals, use enormous technology that destroys nature and causes natural imbalance, then one day our own habits and actions would completely damage and destroy us.
A Prayer to the Teacher Grammar Additional
I. Fill in the blanks with prepositional phrases.

Answer:
- into the boat
- in the dustbin
- over the phone
- over the track
- on the road
II. Underline the place prepositional phrases.
Question 1.
Mani was at home when I called.
Answer:
Mani was at home when I called.
Question 2.
The tourists walked along the riverside.
Answer:
The tourists walked along the riverside.
Question 3.
You cannot park your car outside the restaurant.
Answer:
You cannot park your car outside the restaurant.
Question 4.
The flat on the second floor is vacant.
Answer:
The flat on the second floor is vacant.
Question 5.
Nana will put the baby in the cradle.
Answer:
Nana will put the baby in the cradle.
III. Underline the time prepositional phrases.
Question 1.
Chandran will call the doctor by 10.00 a.m.
Answer:
Chandran will call the doctor by 10.00 a.m.
Question 2.
Papa will have his medicine after breakfast.
Answer:
Papa will have his medicine after breakfast.
Question 3.
The buses are crowded during the morning.
Answer:
The buses are crowded during the morning.
Question 4.
I go for a walk in the evening.
Answer:
I go for a walk in the evening.
Question 5.
I have my interview at 11.00 a.m.
Answer:
I have my interview at 11.00 a.m.
IV. Underline the Position Prepositional Phrases.
Question 1.
Arun’s pen was found under the table.
Answer:
Arun’s pen was found under the table.
Question 2.
Ravi’s cap was below the lamppost.
Answer:
Ravi’s cap was below the lamppost.
Question 3.
The Principal sat near the Chief guest.
Answer:
The Principal sat near the Chief guest
Question 4.
The drone was moving above her head.
Answer:
The drone was moving above her head.
Question 5.
He clicked a photo on the Napier bridge.
Answer:
He clicked a photo on the Napier bridge
Warm up
Read the clues gues the professional and fill in the crosswords puzzle
Answer:
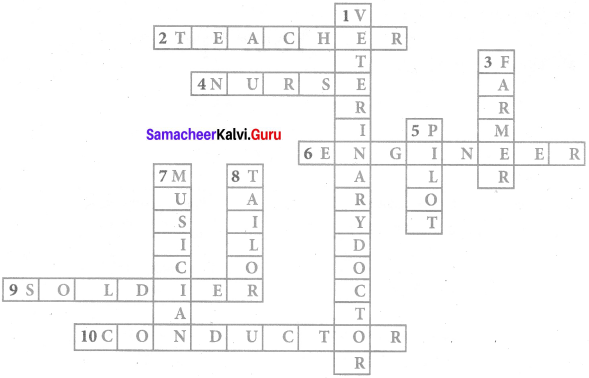
Question 1.
Which is the role of a farmer in society? Discuss and answer.
Farmers are the backbone of our country. They produce the food-crops, the oil-seeds, the commercial crops, and also some raw materials for our industries. Our food and dress materials are obtained from the hard work of farmers. Due to cotton cultivation, several textile mills were established and they gave employment opportunities for the unemployed.
Question 2.
When you grow up, what do you want to become? Why?
Answer:
When I grow up I want to become a Teacher because I can enlighten the children with knowledge.
A Prayer to the Teacher Summary
This lesson is the convocation address given by Subroto Bagchi, Founder and CEO, Mindtree, for the graduating teachers, their faculty and administrators.
The speaker first stresses on inclusion – valuing all people, irrespective of their boundaries like financial and educational status, caste, creed, physical strength, designation or nativity.
He gives three examples: Dumping the garbage on the road which is also ours. Feeding our child in front of our hungry servant maid without a humanitarian heart.
Secondly the speaker says that amidst the cut throat competition, the more we want to impress, the less we communicate. He emphasises to communicate with an innocent child, nature, the dumb and deaf, less gifted, the old and young, the living and non-living things around too. Thirdly he feels that teachers should prepare students for the wide world by teaching them newer and difficult things. Help to learn newer ways to learn that will make learning a joy. Fourthly Subroto emphasises to teach to appreciate the interconnected nature of things. Like creating an awareness about ‘nature’ while the topic ‘Nature’ is taught.
Example:
- Teach not just the concept of ‘rising waves’ but also the reason why the waves fall.
- Not only the use of fertilizers and pesticides but also the damages they cause.
- Teach about birds like crows and sparrows how they go extinct and how to prevent it.
Subroto fifthly wants to inculcate the ability to question. This helps one to get answers, to establish better order of things, to be accountable and in the end it helps us to see the truth emerge.
The speaker sixthly clarifies that in this increasingly commercial world. All things that truly support life comes freely. The cow is not paid for the milk it gives, nor the earth asks money for the crops it gives. The sun gives light, air helps to breathe, the river gives water, clouds give rain, without getting paid for their services.
Seventhly the speaker wants the students to learn the ‘power of silence’. Stress our point without raising our voice and to raise our voice when our silence hurts another life.
Finally the speaker pleads the teachers to develop a world view of things by having a ‘one world’ feeling. By removing poverty, decrease and hunger in the world. Patriotism is not intolerance towards religion and race. Enmity was to be replaced with love for others. There should be unity in diversity. No one is a foreigner. All the people in the world are our siblings.