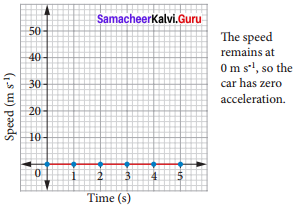
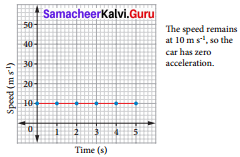
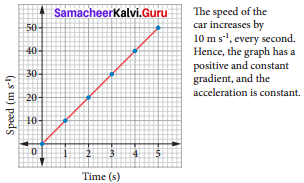
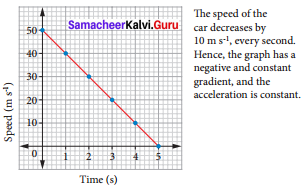
Students can Download Science Chapter 6 Health and Hygiene Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Solutions Term 1 Chapter 6 Health and Hygiene
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Health and Hygiene Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the appropriate answer :
Health And Hygiene 7th Standard Question 1.
Ravi has sound mind and physically fit body. Which refers to
(a) Hygiene
(b) Health
(c) Cleanliness
(d) Wealth
Answer:
(b) Health
Health And Hygiene Class 7 Question 2.
Sleep is not only good for body, but it is also good for
(a) Enjoyment
(b) Relaxation
(c) Mind
(d) Environment
Answer:
(c) Mind
7th Science Health And Hygiene Question 3.
Our living place should be
(a) Open
(b) Closed
(c) Clean
(d) Unclean / Untidy
Answer:
(c) Clean
7th Standard Science Health And Hygiene Question 4.
The tobacco chewing causes
(a) Anamia
(b) Periodontitis
(c) Tuberculosis
(d) Pneumonia
Answer:
(b) Periodontitis
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Science Question 5.
The first aid is to
(a) To save money
(b) To prevent scars
(c) To prevent the medical care
(d) To relieve the pain
Answer:
(d) To relieve the pain
II. Fill in the blanks :
Health And Hygiene Questions And Answers Pdf Question 1.
A group of people living together in a particular area is called ______
Answer:
Community
Samacheer Kalvi Guru Science 7th Question 2.
Iam green colour box with garbage. Who am I ?
Answer:
Bio degradable waste
Health And Hygiene Class 7 Questions And Answers Question 3.
Eyes are considered as to the world.
Answer:
windows
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Standard Science Question 4.
The hair follicles produce which keeps the hair smooth.
Answer:
oil
Health And Hygiene Chapter Question 5.
Tuberculosis is caused by the bacterium .
Answer:
Mycobacterium tuberculae
III. True (or) False, If false give the correct statement.
Health And Hygiene Questions And Answers Question 1.
All food should be covered.
Answer:
True
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Science Guide Question 2.
Chicken pox also known as Leucoderma.
Answer:
(False) Correct statement: Chicken pox is also known as vanicella.
Question 3.
Stomach ulcer is a non-commnicable disease.
Answer:
True.
Question 4.
Rabies is a fatal disease.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
First- degree bums damage the whole skin.
Answer:
False. Correct statement: First -degree bums affects the outer layer (epidermis) of the skin only
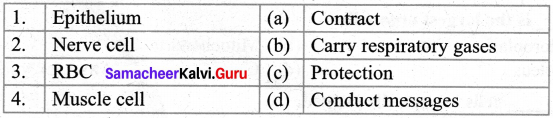
IV. Match the following:
| 1. | Rabie | (a) | Salmonella |
| 2. | Cholera | (b) | Yellow urine |
| 3. | Tuberculosis | (c) | Cramps in legs |
| 4. | Hepatitis | (d) | Hydrophobia |
| 5. | Typhoid | (e) | Mycobacterium |
Answer:
- d
- c
- e
- b
- a
V. Analogy.
Question 1.
First degree bum: epidermis :: second degree bum : _________
Answer:
Dermis.
Question 2.
Typhoid: Bacteria:: Hepatitis: _________
Answer:
Vims.
Question 3.
Tuberculosis : air:: Cholera: _________
Answer:
Water.
VI. Choose the correct alternative from the following:
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Oral hygiene is good.
Reason (R) : Sound teeth and healthy gums with healthy surrounding tissues,
(a) Both A and R are true
(b) Both A and R are false
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Chicken pox is a viral communicable disease.
Reason (R) : Characterized by rashes on the whole body, fever, head ache and tiredness.
(a) Both A and R are true
(b) Both A and R are false
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true
VII. Very short Answer.
Question 1.
What is hygiene?
Answer:
Hygiene refers to the good habits and their practices which is followed to prevent disease, maintain good health, especially through cleanliness, consumption of safe drinking water and proper disposal of sewage. It refers to all those activities that are done for improving and maintaining good health and sound mind.
Question 2.
Write about the right way of protect the eyes?
Answer:
Practices to be followed for eye care.
- Do not rub the eyes
- Do not watch TV / Computer for a long time.
- Use cold water for cleaning the eyes.
- Eat lot of carrots which is rich in vitamin A needed for good vision.
- Eat fruits like oranges, sweet lemon etc., regularly.
Question 3.
How to keep your hair clean and health?
To keep the hair clean and healthy:
Answer:
- The regular hair wash and massage of the scalp will remove the dead skin cells, excess oil and dust.
- Rinsing the hair well with clear water and using good toothed comb for hair dressing is highly essential for their maintenance.
Question 4.
Sobi frequently playing with her mobile, suggest your ideas to protect his eye from irritation?
Answer:
- Stop playing with the mobile for a long time
- Keep the mobile at a distance from the eyes while playing.
- Wash eyes with cold water at intervals.
Question 5.
Give any two communicable disease, which spreads in your locality during monsoon?
Answer:
- Cholera
- Diarrhoea
Question 6.
What first aid will you provide in the case of bruises?
Answer:
- Bruises refer to scratches. It is a surface damage that does not penetrate the lower tissues.
- The affected area should be washed with cold running water and cleaned with an antiseptic cram on the wound.
Question 7.
Ravi said “Ganga had minor burn, so I washed with water” Do you agree with his statement or not? Explain Why?
Answer:
- Yes, In case of minor bums, the affected area should be washed with cold water.
- In case of severe bums, deeper layers of tissues get destroyed and blisters appear.
VIII. Short answer.
Question 1.
Why the first aid is essential?
Answer:
Safety and First Aid
First aid is the immediate treatment given to the victim of trauma or sudden illness before medical help is made available. The first aid is
- To save the life
- To prevent further bleeding and determine the condition of the patient.
- To relive the pain
- To provide a medical care available at the earliest
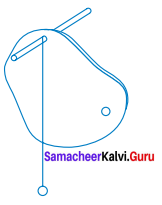
Question 2.
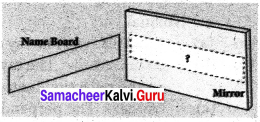
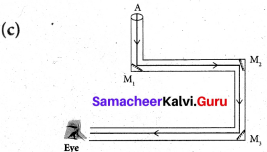
What is this picture? Explain.

Answer:
It says that “Waste should not be thrown there”.
Question 3.
Distinguish between the following pairs Communicable diseases and Non communicable diseases.
Answer:
| S.no | ||
| 1. | These diseases spread from one person to another person. | These diseases do not spread from one person to another person. |
| 2. | They are spread through contaminated air, water, food or vectors, e.g Tuberculosis, Cholera. | They are caused due to wearing out of body parts or malnutrition etc., eg. Goiter, Night blindness. |
Question 4.
What steps you will follow to keep the teeth healthy?
Answer:
- Good oral hygiene implies sound teeth and healthy gums with healthy surrounding tissues.
- When you brush two times a day, it will prevent the formation of tartar and plaque on, your teeth and gums.
- When you floss, it will remove food particles, plaque, and bacteria which build up between your teeth. When you start flossing, your gums may bleed a little bit, but after few days that will be stopped.
- It should be started only with proper medical guidance.
- Eat a well balanced diet and avoid habits like chewing tobacco.
Question 5.
Name the mode of transmission of communicable disease.
Answer:
Communicable diseases spread from one person to another person through various modes as given below.
Mode of Transmission:
- Food and water borne diseases – e.g Cholera, Typhoid
- Air borne diseases – e.g Tuberculosis, cold
- Insect other animals borne diseases – e.g Malaria, Rabies.
- Contaminated food and water, air and Insects are the modes for transmission of communicable disease.
Question 6.
The hair is thin, spares and lost very often. Suggested your ideas to reduce this problem?
Answer:
The condition of the hair reflects the nutritional status and general health of the body. Thin, sparse and lots of hair indicates poor nutritional status.
The following measures will help to maintain hair growth and avoid hair loss.
- The regular hair wash and massage of the scalp will remove the dead skin cells, excess oil and dust.
- Rinsing the hair well with clear water and using good toothed comb for hair dressing is highly essential for their maintenance.
- Eating a balanced diet which provides all nutrients needed for the body will promote hair growth.
- Applying oil to the skin and massaging the scalp will promote hair growth.
- Use of chemicals (dyes, shampoos) must be used to avoid hair loss.
IX. Answer in Details.
Question 1.
Write about any three communicable diseases in details.
Answer:
Communicable diseases are those that spread from one person to another. Diseases spread through contaminated air, water, food or vectors (insects and ohter animals) are palled as communicable diseases.
Tuberculosis:
- Tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculae.
- It spreads from one person to another person through air by spitting and prolonged contact with sharing materials of the patient.
Symptoms:
Fever, weight loss, Chronic cough, blood spitting and difficulty in breathing.
Prevention and treatment:
- Getting BCG vaccination
- Giving special attention to the patient,
- Regular medication like DOT
Cholera:
- Cholera is caused by Vibrio cholera.
- It spreads through the consumption contaminated food or water.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of Cholera is vomiting, severe diarrhoea and cramps in legs.
Hepatitis:
- Hepatitis is one of the most dangerous and fatal diseases caused by Hepatitis Virus A, B, C, D, E.
- Its mode of transmission are contaminated water, sharing of needles and blood transfusion.
Symptoms:
Loss of appetite, (Anorexia), vomiting, eyes and urine in yellow color.
Prevention and treatment:
- Drink boiled water.
- Proper cleaning of hands.
Question 2.
List the situations in which first aid is given. What would you do if a person suffers from skin burns?
Answer:
The tissue damage caused by heat, chemical, electricity, sunlight or nuclear radiation is known as Bums. Mostly bums are caused by scalds, building fires, flammable liquid and gases. According to burning. There are three types of bums.
- First-degree bums affect only the outer layer (called the epidermis) of the skin.
- Second-degree bums damage the epidermis and the layer beneath it called ther dermis.
- Third -degree bums involve damage or complete destruction of the skin to its full depth and damage to underlying tissues also. People who experience such bums often require skin grafting.
First Aid for Burning
In case of minor bums, the affected area should be washed with cold water and an antiseptic cream should be applied. In case of severe bums, where deeper layers of tissues get destroyed and blisters appear, use of water should be avoided. The burnt area should be covered with a clean non-sticking cloth or bandages. Larger bums need immediate medical attention.
It is very important to keep a fire extinguisher readily available.
Question 3.
How the disease are transmitted from one person to the other person?
Answer:
Communicable Diseases are those that spread from one person to another. Diseases spread through contaminated air, water, food or vectors (insects and ohter animals) are called as Communicable diseases.
- The communicable diseases are caused by disease causing microbes such as Bacteria, viruses etc.
- These microbes are found in contaminated food, water, air etc.
- Some of them like the malarial parasite complete their life cycle in the body of a mosquito.
- Thus air food and water, sweat act as modes of transmitting these microbes from an infected person to a healthy person.
- E.g. The cycle given below shows how food and water borne diseases are transmitted.
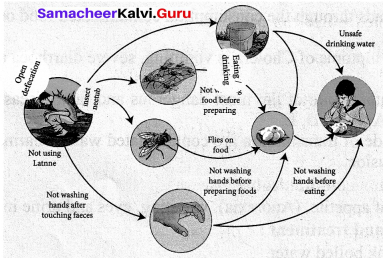
| S.no | Mode of Transmission | Examples |
| 1 | Contaminated food and water | Cholera, Typhoid |
| 2 | Contaminated air | Tuberculosis |
| 3 | Insect / Animal borne diseases | Malaria, Rabies |
X. Higher Order thinking question
Question 1.
A person is sleeping during day time. Why does this happen with some people that they feel sleepy during day time in office or in the classroom. Have you ever come across such situation? Explain.

Answer:
- Many people are tired and do not have the energy to perform day to day activities. They tired and tend to sleep in the classroom or work place. Though sleep can be due to various reasons, the common reason for this condition is Anaemia.
- People who are Anaemic have less number of Red blood cells in their blood.
- The Red blood cells have haemoglobin which caries oxygen to all the cells of the body.
- People who are Anaemic will have less slow oxygen supply to all the cells of the body.
- Energy production in the cells is less and they feel tired and sleepy always. This is due to in the diet. Prevention : Eat food rich in Iron.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Health and Hygiene Additional Questions
I. Choose the appropriate answer.
Question 1.
Anorexia means _______
(a) Excess thirst
(b) Excess sweating
(c) Loss of hair
(d) Loss of appetite
Answer:
(d) Loss of appetite
Question 2.
Drinking boiled water can prevent _______
(a) Tuberculosis
(b) Rabies
(c) Cholera
(d) Chicken pox
Answer:
(c) Cholera
Question 3.
High fever is a symptom of _______
(a) Rabies
(b) Typhoid
(c) Scurvy
(d) Hepatits
Answer:
(b) Typhoid
Question 4.
_______ is a non communicable disease.
(a) small pox
(b) Varicella
(c) Rheumatism
(d) Flu
Answer:
(c) Rheumatism
Question 5.
Intake of _____ can help to prevent Anaemia.
(a) cod liver oil tablet
(b) oranges
(c) whole egg
(d) eggs
Answer:
(a) cod liver oil tablet
II. Fill in the Blanks.
- Dengue causes decrease in number of _______ in blood
- _____ is a non communicable disease caused by loss of pigmentation in the skin.
- The pigment present in our skin is _______
- Extreme fear for water is called _______
- _______ vaccine prevents Tuberculosis.
Answer:
- Platelets
- Leucoderma
- Melanin
- hydrophobia
- BCG
III. True or False – if false give the correct statement.
Question 1.
Rabies can be caused by the bite of monkeys.
True.
Question 2.
We must eat lot of carrots to prevent eye diseases.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
Chronic cough is a symptom of Typhoid.
Answer:
(False) Correct Statement: Chronic cough is a symptom of Tuberculosis.
Question 4.
Raju drank water in a fair and was affected by Dengue. Is this statement True or False.
Answer:
(False) Correct Statement: Dengue is not a water borne disease.
Question 5.
Bum injuries can be fatal.
Answer:
True
Question 6.
Alcoholism is a communicable disease.
Answer:
(False) Correct Statement: Alcoholism is a Non-communicable disease.
IV. Match the following :
Question 1.
| Pellagra | (a) | Water |
| Allergies | (b) | Folic acid |
| Rabies | (c) | Pollen |
| Anaemia | (d) | skin |
Answer:
- d
- c
- a
- b
Question 2.
| Hepatitis | (a) | Citrus fruits |
| Nightblindness | (b) | Vomiting |
| Bleeding gums | (c) | smoking |
| Heart attack | (d) | Poor light |
Answer:
- b
- d
- a
- c
V. Analogy.
Question 1.
Leucoderma: Melanin
Anaemia: ______.
Answer:
Iron.
Question 2.
Tuberculosis : Lungs
Rabies : _____.
Answer:
Nervous system.
VI. Assertion and Reason.
(a) Both A and R are true
(b) Both A and R are false
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : We must offer first aid to a bleeding person.
Reason (R) : We must not use gloves while helping them.
(a) Both A and R are true
(b) Both A and R are false
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : Antibiotics do not help to cure communicable diseases.
Reason (R) : They are caused by microbes.
(a) Both A and R are true
(c) A is due but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
(b) Both A and R are false
Answer:
(d) A is false but R is true
VII. Complete the table.
Question 1.
Tuberculosis _______
________ Virus
Answer:
Bacteria,Hepatitis
Question 2.
Night Blindness ________
_________ Iron
Answer:
Vitamin A, Anaemia
Question 3.
BCG __________
________ Chicken pox
Answer:
Tubeculosis, Varicella Vaccine
Question 4.
Dog ________
________ Dengue
Answer:
Rabies,Mosquito
Question 5.
Tuberculosis ________
__________ Rashes
Answer:
Chronic cough, Chicken pox
VIII. Very short Answers:
Question 1.
Name some diseases which affect the teeth.
Answer:
Bleeding gums, Tooth decay, periodontis.
Question 2.
List two measures to maintain community hygiene.
Answer:
- The surroundings should be kept clean.
- Drains should be covered properly.
Question 3.
Name two disease which can be prevented by vaccination.
Answer:
Polio, Tuberculosis.
Question 4.
Name some diseases caused by lack of trace elements in the body.
Answer:
Anemia, pellagra, night blindness and xerophthalmia, goiter and hypothyroidism.
Question 5.
What is a Vaccine?
Answer:
- A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular disease.
- Vaccine (BCG, Polio, MMR) are given at early childhood to protect from other diseases.
Question 6.
How can we prevent fatality in the case of Rabies?
Answer:
Timely vaccination before the onset of symptoms can prevent fatality in the case of Rabies.
IX. Short Answer.
Question 1.
Write a note on non-communicable diseases.
Answer:
- Communicable diseases do not spread from person to person. They are caused by other factors.
- Antibiotics, or medicines that fight against germs, do not help to cure non- communicable diseases.
- Problems caused by wearing out of body parts:
Rheumatism, heart attack, epileptic seizures, stroke, migraine headaches, Cataract and cancer. - Problems caused by external harmful agents entering the body:
Allergies, asthma, poisons, snakebite, cough from smoking, stomach ulcer, alcoholism. - Problems caused by a lack of trace elements in the body:
Anaemia, pellagra, night blindness and xerophthalmia, goiter and hypothyroidism.
Question 2.
Write a note on Chicken pox.
Answer:
- Causal agent :Chickenpox (chicken pox), also known as varicella, is a highly contagious infection caused by the varicella zoster virus.
- This disease spreads through air and contact with an infected person.
- Symptoms: A appearance of rashes on the whole body, fever, headache and tiredness.
- Prevention and treatment: The chickenpox (Varicella) vaccine is the best way to prevent chickenpox. Special attention should be given to the infected persons.
Question 3.
Write a note an Rabies.
Answer:
- Rabies is a fatal disease, which is transmitted by the bite of the infected dog, rabbit, monkey, cat etc.
- Causal agent: The virus present in the saliva of dog enters the brain via neurons.
- Symptoms: The symptoms of rabies is hydrophobia (extreme fear for water), fever for 2-12 weeks and exaggerations in behavior.
Prevention and treatment
- In early stages rabies is very difficult to detect.
- After an animal is bitten it usually takes two to twelve weeks to shows any symptoms and it may take as long as two years also.
- Fatality can be prevented by timely vaccination before the onset of symptoms.
Question 4.
We should use a handkarchief when we sneeze, Justify.
Answer:
When we are suffering from cold etc, the virus comes out with the droplets and spreads in air. This can infect a healthy individual. Thus we should use a handkerchief while sneezing.
Question 5.
What can we do to maintain personal hygiene?
Answer:
- We must brush our teeth at least twice a day.
- We must have a shower daily.
- We must wash our hair regularly.
- We must wash our face and hands regularly.
- We should keep food covered with a lid.
- We should wear washed and clean clothes.
- We must wear slippers while we go out of the house. Drinking water must be stored in a clean and safe place.
X. Long Answer
Question 1.
List the diseases affecting the eye, their causative agents, impact and Remedial measures.
Answer:
| S. No | Name of the Disease | Causative
Agents |
Impacts / Consequences | Remedial
measures. |
| 1. | Night
Blindness |
Lack of vitamin A, a disorder of the cells in your retina | Makes it hard to see well at night or in poor light. | Eat foods rich in antioxidant, vitamins and minerals. |
| 2. | Conjuncitvitis (Pink eye) | Caused by a virus and bacteria | One or both eyes can be affected. Highly contagious; can be spread by coughing and sneezing | Antibiotic eye drops or
ointments, home remedy |
| 3. | Color
blindness |
genetic condition | 1. Difficulty distinguishing between colors.
2. Inability to see shades or tones of the same color |
There is no known cure for color blindness. Contact lenses and glasses are available with filters to help color deficiencies |
XI. Hots
Question 1.
Richa had a pet dog. She vaccinated him regularly. He suddenly bit a stranger. Do you think that the person could have got Rabies.
Answer:
No, since the dog was vaccinated regularly, there is no chance of the person suffering from Rabies. But still the person should seek medical advise for the treatment.