Students can Download Social Science History Chapter 4 The Delhi Sultanate India Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science History Solutions Term 1 Chapter 4 The Delhi Sultanate
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science The Delhi Sultanate Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answers
The Delhi Sultanate Class 7 In Tamil Question 1.
______ laid the foundation of ‘ Mamluk’ dynasty.
(a) Mohammad Ghori
(b) Jalal-ud-din
(c) Qutb-ud-dinAibak
(d) Iltutmish
Answer:
(c) Qutb-ud-din Aibak
Delhi Sultanate In Samacheer Book Question 2.
Qutb-ud-in shifted his capital to Delhi from .
(a) Lahore
(b) Poona
(c) Daulatabad
(d) Agra
Answer:
(a) Lahore
Delhi Sultanate Questions And Answers Question 3.
completed the construction of the Qutb-Minar.
(a) Razia
(b) Qutb-ud-din -Aibak
(c) Iltutmish
(d) Balban
Answer:
(c) Iltutmish
The Delhi Sultanate Class 7 Question 4.
laid the foundation of the city Tughluqabad near Delhi.
(a) Muhammad-bin -Tughluq
(b) Firoz shah Tughluq
(c) Jalal -ud-din
(d) Ghiyas -ud-din
Answer:
(d) Ghiyas -ud-din
II. Fill in the Blanks
- was the founder, of Tughluq dynasty.
- Muhammad-bin-Tughluq shifted his capital from Delhi to .
- patronized the famous Persian poet Amir Khusru.
- Quwwat-ul-Islam Masjid in Delhi was built by .
- The threat of Mongols under Chengizkhan to India was during the reign of
Answer:
- Ghiyas-ud-din
- Devagiri or Daulatabad
- Balban
- Qutb-ud-din -Aibak
- Iltutmish
III. Match the following
| A | B | |
| Tughril Khan | i. | Governor of Kara |
| Ala-ud-din | ii. | Jalal-ud-din Yakut |
| Bahlol Lodi . | iii. | Governor of Bengal |
| Razia | iv. | Governor of Sirhind |
Answer:
- iii
- iiv
- ii
IV. State True or False :
Question 1.
Qutb-ud-din Aibak died of mysterious fever.
Answer:
(False) Correct statement: Qutb-ud-din Aibak died of mysterious injuries received during an accidental fall from a horse, while playing polo.
Question 2.
Razia was an able and brave fighter.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
The Turkish nobles chose Iltutmish, son of Aibak, as Sultan after the death of Aibak.
Answer:
(False) Correct statement: The Turkish nobles chose Iltutmish, son-in-law of Aibak, as Sultan after the death of Aibak.
Question 4.
FirozShah Tughluq refused to accept an invitation from a Bahmani Prince to intervene in the affairs of the Deccan.
Answer:
True
V. Match the statement with the reason.
Tick (✓) the appropriate answer.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Balban maintained cordial relationship with Mongols
Reason (R): The Mongol ruler, a grandson of Chengiz Khan, assured that Mongols
would not advance beyond Sutlej.
(a) R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A and R are wrong.
(d) A is wrong and R is the correct.
Answer:
(a) R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Find out the correct pair
- Hoysala – Devagiri
- Yadavas – Dwarasamudra
- Kakatias – Warrangal
- Pallavas – Madurai
Answer:
3. Kakatias – Warrangal
(c) Find out the wrong statement /statements
- After Ghori’s death in 1206, his slave Qutbud- din Aibak proclaimed him self the ruler of the Turkish territories in India.
- Razia established the department of spies to gather intelligence about the conspirators and the trouble makers against her rule.
- Balban built forts to guard his empire against the Mongol attack.
- Ibrahim Lodi was defeated by Babur in 1526.
Answer:
2. Razia established the department of spies to gather intelligence about the conspirators and the trouble makers against her rule.
VI. Answer the following in one or two sentences
Question 1.
Name the land granted to army officials in lieu of a regular wage.
Answer:
Iqta is the land granted to army officials in lieu of a regular wage
Question 2.
Who founded the city of Agra?
Answer:
Sikandar Lodi founded the city of Agra.
Question 3.
Name the ruler who established Muslim rule in India in 12th century A.D (CE).
Answer:
Muslim rule in India was established by Muhammad Ghori in 12th century A.D. (CE).
Question 4.
Write a note on chahalgani.
Answer:
In order to counter the possible attack of the Mongols, Iltutmish organised Turkish nobility into a select group of 40 nobles known as chahalgani or The Forty.
Question 5.
How did Ala-ud-din Khalji consolidate the Delhi Sultanate?
Answer:
- The range of Khalji conquests is impressive: in the Punjab (against the Mongols), in Rajasthan and in Gujarat. With his northern frontiers secure, he sent his chief lieutenant Malik Kafur into the southern parts who took even the distant Madurai.
- Thus Ala-ud-din Khalji consolidated the Delhi Sultanate.
Question 6.
List out the contributions of Firoz Shah Tughluq.
Answer:
- Firoz rewarded Sufis and other religious leaders generously and listened to their advice.
- He also created charities to aid poor Muslims
- He built colleges, mosques, and hospitals.
- He banned inhuman punishments and abolished taxes not recognised by Muslim law.
- He promoted agriculture by waiving off the debts of the agriculturalists and constructing many canals for irrigation.
- He built new towns such as Firozabad, Jaunpur, Hissar and Firozpur.
VII. Answer the following :
Question 1.
Write about the invasion of Timur in 1398.
Answer:
- The sacking and massacre by Tamerlane or Timur of Delhi came a decade after Firuz ME Shah Tughluq died.
- Timur had occupied some parts in the north-west of India.
- Taking advantage of India’s weakness, he entered India in December 1398 and plundered Delhi.
- Punjab, besides the Delhi city, was the province that suffered most by Timur’s raid.
- Apart from carrying huge wealth in the form of gold, silver, jewels, also took along Indian artisans like carpenters and masons to work on monuments in Samarkand.
VIII. HOTS :
Question 1.
How would you evaluate Muhammad-bin- Tughluq as Sultan of Delhi?
Answer:
Muhammaad – bin – Tughlug was a learned but cruel man. He was a poor decision maker. There was chaos in the social, economic and political condition of the empire because of his ambiguous decisions. The first and foremost was changing the capital from Delhi to Devagiri or Daulatabad and vice versa which led to loss of money and human lives. He also ordered the revenue to be collected in money instead of grains. This move led to bankruptcy and famine. Though he was wise and learned his hasty decisions led to his downfall.
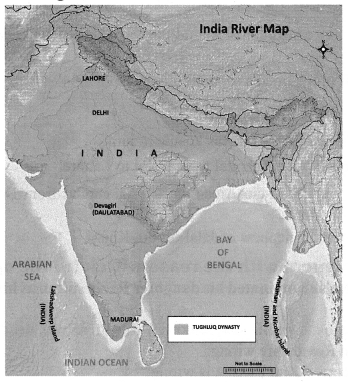
IX. Map Work
On the river map of India draw the extent of Tughluq Dynasty and mark the following places.
- Delhi
- Devagiri
- Lahore
- Madurai.
X. Student Activity :
Question 1.
Match the Father with Son
| A | B | ||
| 1. | Qutb-ud-din Aibak | i. | Rukn-ud-din-Firuz |
| 2. | Iltutmish | ii. | Kaiqubad |
| 3. | Balban | iii. | Ala-ud-din |
| 4. | Ghiyas-ud-din | iv. | Sikandar Lodi |
| 5. | Bahlol Lodi | V. | Aram Shah |
Answer:
- v
- i
- ii
- iii
- iv
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science The Delhi Sultanate Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
___________ is a persian term used for slaves purchased for military service.
(a) Aibak
(b) bandagan
(c) Mamluk
(d) Lodi
Answer:
(b) bandagan
Question 2.
Iltutmish granted ___________ to members of his army.
(a) iqtas
(b) coins
(c) gold
(d) dirams
Answer:
(a) iqtas
Question 3.
___________ was a custom of the Rajputs, in which man would go out and die in the battle field and women would burn themselves on a pyre.
(a) Sati
(b) Devadasi
(c) Janhar
(d) Kaali
Answer:
(c) Janhar
II. Fill in the blanks:
- _____ is an Arabic word meaning slave.
- Iltutmish refused to provide shelter to _____ who had been driven out by chengiz khan.
- One significant military expedition of Ala-ud-din was against, the Deccan Kingdom _____
- _____ was proclaimed a separate sultanate in 1334.
Answer:
- Mamluk
- Kwarezm Shah Jalalud – din
- Devagiri
- Madurai
III. True or False :
Question 1.
Balban abolished ‘The Forty’ as it was hostile to him.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Qutb-ud-din-Aibak shifted his capital from Delhi to Lahore.
Answer:
(False) Correct statement: Qutb-ud-din-Aibak shifted his capital from Delhi to the centre of the kingdom, namely Devagiri.
Question 3.
Ala-ud-din khalfi was the nephew of Jalal-ud-din Khalji.
Answer:
True
IV. Match the statement with the reason. Tick (✓) the appropriate answer:
Question 1.
Statement : Iltutmish nominated his daughter Razia sultan as his successor to the throne of Delhi.
Reason : His most capable son, Rukn-ud-din-Firaz was dead.
(a) Statement and Reason are wrong.
(b) Statement is correct, but Reason is wrong.
(c) Both Statement and Reason are correct.
(d) Statement is wrong but Reason is correct.
Answer:
(c) Both Statement and Reason are correct.
Question 2.
Statement : Ala-ud-din khalji employed spies to report to him directly.
Reason : He wanted to be informed about the movement of the enemy’s army.
(a) Both Statement and Reason are correct.
(b) Statement and Reason are wrong.
(c) Statement is correct and Reason is wrong.
(d) Statement is wrong and Reason is correct.
Answer:
(c) Statement is correct and Reason is wrong.
Question 3.
Find out the wrong statement
(a) Razia made an Ethiopian slave nmed Jalal-ud-din Yakut, her personal attendant.
(b) Hulagu Khan, was the grandson of chengiz khan.
(c) Jalal-ud-din khalji built forts to guard his empire.
(d) Ghiyas-ud-din Tughluq sent his Jauna khan to fight against Warangal.
Answer:
(c) Jalal-ud-din khalji built forts to guard his empire
VI. Answer the following.
Question 1.
Write a short note on the Sack of Chittor.
Answer:
Sack of Chittor :When Ala-ud-din’s army overwhelmed the Rajput army in Chittor and in the context of threat of defeat, the men and women of the fortress, in accordance with their old custom, performed the rite of jauhar.
Question 2.
What is Indo-Saracenic architecture? Name a few structures constructed in this style.
Answer:
- A combination of Persian and Indian architecture is called Indo-Saracenic architecture.
- Mosques and Madrasas were built in this style during the Mughal rule.
- The shape of these buildings were persian while the decoration was Indian.
Eg. QutbMinar, Alai-Darwaza, tombs of Iltutmish.
VII. HOTS :
Question 1.
Alaud – din Khalgi was an able administrator.- Justify.
Answer:
- Ala-ud-din’s political and administrative reforms were as impressive.
- Ala-ud-din undertook a survey of the agrarian resources around his capital and fixed a standard revenue demand.
- He entrusted the task of collecting the revenue to the military officers.
- Ala-ud-din established a system of forced procurement of food grains for Delhi and other garrison centres.
- The procurement prices were fixed and grain collected as tax was stored in state granaries.
- To ensure the enforcement of his new regulations.
- He employed spies who were responsible to report to him directly.